30 mg and 60 mg hard prolonged-release capsule
furosemide, respectively
What Lasix Retard is and what it is used for
Lasix Retard is a diuretic, a diuretic, which is used for fluid retention in the body’s tissues ( edema ) and high blood pressure. Lasix Retard inhibits the kidneys’ ability to reabsorb water and salt, leading to increased urinary excretion. Thus, the edema decreases or disappears.
Furosemide contained in Lasix Retard may also be approved for the treatment of other conditions not mentioned in this leaflet. Ask your doctor, pharmacist, or other healthcare professional if you have any further questions, and always follow their instructions.
What you need to know before using Lasix Retard
Do not use Lasix Retard
- if you are allergic to furosemide , related sulfonamides (eg antidiabetic drugs) or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6)
- in severe liver or kidney disease
- you are at risk of dehydration
- you suffer from almost completely eliminated urine excretion
- you suffer from very low potassium and sodium levels in your blood
- you are breastfeeding (the active substance passes into breast milk)
Warnings and cautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Lasix Retard if:
- your kidneys are not working well
- you are taking heart medication that contains digoxin
- you are on a strictly low-salt diet
- you have difficulty emptying your bladder or if you suspect that there may be obstruction to your urine output
- you have low blood pressure
- you get sharp drops in blood pressure
- you have diabetes
- you have gout
- you have low egg white levels in your blood. (If it occurs dose adjustment is required)
- you have systemic lupus erythematosus (disease in which the body’s immune system attacks the body)
- you are older, if you are taking other medicines that can lower your blood pressure , or if you have any other illness that carries a risk of lowering your blood pressure
If you suffer from vomiting, diarrhea, and heavy sweating, there may be an increased risk of disturbing the salt and electrolyte balance in the body. There may then be a need to take an extra blood sample. Contact your doctor if you feel unsure.
Other medicines and Lasix Retard
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines.
The effect of the treatment can be affected if this medicine and certain other medicines are taken at the same time, this also applies to over-the-counter medicines, natural medicines, or other natural products. The treating physician, therefore, needs to be aware of such concomitant medication.
The following drugs should be avoided during concomitant treatment with Lasix Retard:
- gentamicin (used for infections )
- chloral hydrate (a kind of sleeping pill)
- risperidone (used in schizophrenia, among others)
- drugs known to adversely affect hearing such as certain antibiotics ( aminoglycosides ) and diuretics (ethacrynic acid)
The following medicines may be taken with Lasix Retard but may need to be dose-adjusted:
- ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (used for high blood pressure, among other things )
- medicines for high blood pressure
- digitalis glycosides and other drugs that affect the rhythm of the heart
- lithium (used in manic depressive illness)
- NSAID- type anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents such as ibumetin and acetylsalicylic acid
- drugs known to adversely affect the kidneys
- cephalosporins (used for infections )
- sotalol (used for high blood pressure, among other things )
- cisplatin (used in cancer)
- sucralfate (used for stomach ulcers )
- phenytoin (used in epilepsy )
- ciclosporin A (used in organ transplantation)
- methotrexate (used in cancers, among others)
- drugs against diabetes
- adrenaline (used in anesthetics and in hypersensitivity reactions )
- norepinephrine (for low blood pressure )
- curare-like muscle relaxants
- theophylline (used in asthma )
- corticosteroids (used for inflammation , among other things )
- carbenoxolone (used for stomach ulcers )
- large amounts of licorice
- long-term use of laxatives
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Pregnancy
There is a risk that the fetus is affected. Therefore, always consult a doctor before using Lasix Retard during pregnancy.
Breast-feeding
A breastfed baby may be affected. Use therefore not Lasix Retard during lactation except on certain prescriptions from the doctor. Breastfeeding mothers should be aware that the amount of milk may decrease.
Driving and using machines
Due to certain side effects (eg a sharp drop in blood pressure), the degree of alertness and reaction time can change to such an extent that it is not possible to drive motor vehicles or safely handle machines.
You are responsible for assessing whether you are fit to drive a motor vehicle or perform work that requires sharpened vigilance. One of the factors that can affect your ability in these respects is the use of drugs due to their effects and/or side effects. Descriptions of these effects and side effects can be found in other sections. Read all the information in this leaflet for guidance. If you are not sure, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
Lasix Retard contains sucrose
If you have been told by your doctor that you have an intolerance to some sugars, contact your doctor before taking this medicine.
How to use Lasix Retard
Dose one is determined by the doctor who adapts it for you. Always use this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you are unsure.
The recommended dose for adults is 1 capsule of 30 mg or 1 capsule of 60 mg daily, which is usually taken as a single dose in the morning.
The capsules should be swallowed whole and with at least half a glass of liquid.
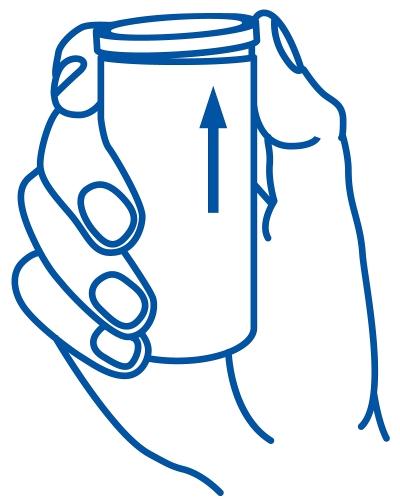
Instructions for use for plastic pipes
The plastic tube opens most easily if you squeeze it in the middle of the tube. Place your thumb under the knurled edge on the side of the lid and move the lid upwards with a gentle movement. If the lid does not come off immediately, move your thumb slightly to the side and try again. (If you grab the lid and pull sharply upwards, the pipe can be difficult to open).
Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Lasix Retard can in very rare cases affect the white blood cells so that the defense against infection deteriorates. If you get an infection with symptoms such as fever with severe general condition or fever with local infection symptoms such as sore throat/pharynx/mouth or urination problems, you should see a doctor as soon as possible so that a blood test can rule out a lack of white blood cells ( agranulocytosis ). It is important that you then have information about your medication.
Very common (more than 1 in 10):
- Disorders of the body’s salt balance or dehydration, especially in the elderly. Detected using blood tests. May cause symptoms such as fatigue, headache and dizziness.
- Decreased blood volume, especially in the elderly, is detected with the help of a blood test.
- Increased blood creatinine levels, which may be a sign of impaired kidney function. Detected using blood tests.
- Increased levels of triglycerides in the blood (blood fats) which may increase the risk of atherosclerosis / increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. Detected using blood tests.
Common (more than 1 in 100):
- Elevated uric acid levels in the blood, which can lead to gout . Gout can be experienced as sore and swollen joints.
- Increased blood cholesterol (blood fats) which can increase the risk of atherosclerosis / increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. Detected using blood tests.
- Increased urine volume.
- Concentration of the blood, ie reduced amount of fluid in the blood, which gives increased concentration of blood components and can increase the risk of blood clots. Detected via blood test. May occur due to excessive diuretic effect.
- Brain effects in users with impaired liver function.
- Gout attacks.
Uncommon (more than 1 in 1000):
- Nausea.
- Hearing loss.
- Decreased platelet count ( platelets ), which can cause bruising and bleeding.
- Skin reactions such as itching , hives , blisters, flaking, redness and inflammation of the skin, slight bleeding in the skin and mucous membranes. Sensitivity to sunlight.
- Impaired glucose tolerance, which manifests itself as elevated blood sugar levels. Risk of developing diabetes .
- Deafness (sometimes persistent).
Rare (less than 1 in 1000):
- Vomiting.
- Diarrhea.
- Inflammation of blood vessels. The symptoms depend on where the vessel / vessels are located.
- Kidney inflammation, which can cause symptoms in the form of fever and pain.
- Earwax.
- Abnormal sensations, such as ant crawling, tingling and a “sugar drinking feeling”.
- Low number of white blood cells , which increases the risk of infection .
- Fever.
Very rare (less than 1 in 10,000):
- Acute inflammation of the pancreas, which can be experienced as pain to varying degrees in the upper abdomen or between the shoulder blades, vomiting and fever.
- High liver enzyme values detected using blood tests.
- Bile duct obstruction, which can cause symptoms such as pain, nausea and vomiting.
- Impact on the blood picture and anemia .
No known frequency (can not be calculated from the available data):
- High pH in the blood, which can cause very serious conditions such as lack of oxygen in the blood.
- Lack of calcium or magnesium , which is detected by blood tests. May increase the risk of osteoporosis.
- Increased level of urea in the blood, which is detected with the help of blood tests.
- Blood clot.
- Increased levels of sodium and chloride in the urine, which is detected with the help of blood tests.
- Difficulty urinating.
- Impaired renal function.
- Skin and mucous membrane changes (sometimes severe).
- Severe widespread skin damage (skin detachment).
- Lichenoid reactions, characterized by small, itchy, reddish-purple, angular rashes on the skin, genitals or in the mouth.
- Pseudo-Bartter syndrome (unusual genetic kidney disease).
- Deterioration or activation of systemic lupus erythematosus (disease in which the body’s immune system attacks the body).
- Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) (sudden drug rash with fever).
- Headache, dizziness, fainting and unconsciousness (caused by low blood pressure or other causes).
- Muscle rupture ( rhabdomyolysis ) is often associated with very low potassium levels in the blood (severe hypokalaemia ).
How to store Lasix Retard
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton after EXP. The expiration date is the last day of the specified month.
Do not store above 30 ° C.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
Contents of the pack and other information
Content declaration
The active substance is furosemide. One capsule contains 30 mg or 60 mg of furosemide.
The other ingredients are sucrose, corn starch, povidone, talc, shellac, stearic acid, alumina hydrate, gelatin, and dyes (yellow iron oxide E172, indigo carmine E132, titanium dioxide E171).
What the medicine looks like and contents of the pack
Appearance: hard capsules, green/yellow.
Depot capsule 30 mg:
Blister 30 pcs, 100×1 (single-dose packaging)
Plastic pipes 100 pcs
Plastic jar 500 pcs (only for dose dispensing).
Depot capsule 60 mg:
Blister 100×1 (single dose pack)
Plastic pipe 100 (2×50) pcs
Plastic jar 500 pcs (only for dose dispensing).
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Sanofi Winthrop Industry
1, rue de la Vierge
Amberès
33565 Carbon -Blanc Cédex
France