Prionelle 150 micrograms / 30 micrograms Levonorgestrel / Ethinyl Estradiol Coated Tablets
What Prionelle Is And What Prionelle Is And Used For
Prionelle is used as a contraceptive.
Prionelle is a combination pill that contains low amounts of two different female sex hormones. Each tablet contains both Ethinyl estradiol (an estrogen ) and levonorgestrel (a progestogen ). Due to the low levels of hormones, Prionelle is one of the low-dose birth control pills. All tablets in the pack contain the same hormone at a constant dose, the contraceptive pill is therefore called monophasic.
The preventive effect of combined contraceptive pills is based on the interplay between different factors. The most important is considered to be that ovulation is inhibited and the changes in the uterine lining and by the secretions in the cervix.
Menstruation is affected so that the bleeding becomes more regular, menstruation often becomes less painful and the amount decreases.
Levonorgestrel and Ethinylestradiol contained in Prionelle may also be approved for the treatment of other conditions not mentioned in this product information. Ask your doctor, pharmacist, or another healthcare professional if you have any further questions, and always follow their instructions.
What You Need To Know Before You Use Prionelle
Generally
Before you start using Prionelle, read the information about blood clots in section 2. You must read the symptoms of blood clots – see section 2, “Blood clots”.
This leaflet describes several situations in which you should stop taking Prionelle, or when the protective effect of the contraceptive pill may be reduced. In these situations, you should not have intercourse, or you should take extra measures in the form of non-hormonal methods, e.g. condoms or any other barrier method. Do not use “safe periods” based on the menstrual cycle or temperature changes. These methods can be unreliable as Prionelle disrupts the normal changes in body temperature and the lining of the cervix during the menstrual cycle.
Like other birth control pills, Prionelle does not protect against HIV infection ( AIDS ) or other sexually transmitted diseases.
Do not use Prionelle:
Do not use Prionelle if you have any of the conditions listed below. If you have any of these conditions, you need to tell your doctor. The doctor will discuss what other type of contraception may be more appropriate.
- If you have (or have had) a blood clot in a blood vessel in your legs (deep vein thrombosis, DVT), in your lungs ( pulmonary embolism ), or any other organ
- If you know you have a disease that affects blood coagulation – e.g. protein C ‑ deficiency, protein S ‑ deficiency, antithrombin ‑ III ‑ deficiency, Factor V Leiden or antiphospholipid antibodies
- If you need to have an operation or if you stay in bed for a longer period (see section “Blood clots”)
- If you have (or have had) a heart attack or stroke (stroke)
- If you have (or have had) angina (a condition that causes severe chest pain and maybe the first sign of a heart attack) or transient ischemic attack ( TIA – transient stroke symptoms)
- If you have any of the following conditions that may increase the risk of a blood clot in your arteries:
- Severe diabetes with damaged blood vessels
- Very high blood pressure
- A very high level of fat in the blood ( cholesterol or triglycerides )
- A condition called hyperhomocysteinemia
- If you have (or have had) a type of migraine called “migraine with aura”
- If you have jaundice or severe liver disease
- If you have hepatitis C and are being treated with medicines containing
- Ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir
- Dasabuvir
- Glekaprevir / pibrentasvir
- Sofosbuvir / velpatasvir / voxilaprevi (see also section “Other medicines and Prionelle”)
- If you have or have had cancer that is affected by sex hormones (eg breast cancer or genital cancer)
- If you have or have had a benign or malignant liver tumor
- If you have unexplained bleeding from the abdomen
- If you are pregnant or think you may be pregnant
- If you are allergic to Ethinyl estradiol or levonorgestrel or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
If any of the above occur for the first time while you are taking the pill, stop using the tablets immediately and consult a doctor.
Warnings And Cautions
| When should you contact a doctor? Seek medical attention immediatelyif you notice any possible signs of a blood clot that may indicate a blood clot in your leg (ie deep vein thrombosis ), a blood clot in your lung (ie pulmonary embolism ), a heart attack, or a stroke (see section “Blood clots” below). For a description of the symptoms of these serious side effects, go to “How to recognize a blood clot”. |
Tell your doctor if any of the following conditions apply to you.
If the condition occurs or worsens when you use Prionelle, you should also consult a doctor.
- If you smoke
- If you have diabetes
- If you are overweight
- If you have high blood pressure
- If you have heart valve disease or a heart rhythm disorder
- If you have Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis ( chronic inflammatory bowel disease)
- If you have a systemic lupus erythematosus ( SLE – a disease that affects your natural immune ystem)
- if you have hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS – a disorder of blood coagulation that leads to kidney failure )
- If you have sickle cell anemia (a hereditary disease of the red blood cells )
- If you have increased blood fats ( hypertriglyceridemia ) or a hereditary condition. Hypertriglyceridemia has been associated with an increased risk of developing pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas)
- If you need to have an operation or stay in bed for a longer period (see section 2 “Blood clots”)
- If you have just given birth, you are at increased risk of getting blood clots. Ask your doctor how soon after giving birth you can start using Prionelle
- If you have an inflammation of the veins under the skin (superficial thrombophlebitis )
- If you have varicose veins
- If a close relative has had a blood clot, heart attack, or stroke
- If you suffer from migraines
- If a close relative has had breast cancer
- If you have liver or biliary tract disease
- If you have a condition that first appeared or worsened during pregnancy or previous use of sex hormones eg
- Hearing loss
- A metabolic disease called porphyria
- A skin disease called herpes gestationis
- A neurological disease called Sydenham’s Korea)
- If you have or have had chloasma (yellow-brown pigment spots, especially on the face); if so, you should avoid exposing yourself to too much sunlight or ultraviolet radiation.
- Contact a doctor immediately if you experience symptoms of angioedema, such as swelling of the face, tongue, and/or throat and/or difficulty swallowing or hives, possibly with difficulty breathing. Products containing estrogen can cause or worsen the symptoms of hereditary or acquired angioedema.
BLOOD CLOTS
Using combined hormonal contraceptives such as Prionelle increases the risk of blood clots compared to not using these drugs. In rare cases, a blood clot can block the blood vessels and cause serious problems.
Blood clots can form
- In veins (called venous thrombosis, venous thromboembolism, or VTE)
- In the artery (called arterial thrombosis, arterial thromboembolism, or ATE).
It is not always possible to fully recover from blood clots. In rare cases, they can have serious lasting effects and, in very rare cases, be fatal.
It is important to remember that the overall risk of a dangerous blood clot due to Prionelle is small.
HOW TO FEEL A BLOOD CLOTH AGAIN
Seek medical attention immediately if you notice any of the following signs or symptoms.
| Do you experience any of these signs? | What can you possibly suffer from? |
|---|---|
| swelling of a leg or along a vein in the leg or foot, especially if you also get: pain or tenderness in the leg that is only felt when you stand or walk increased heat in the affected leg discoloration of the skin on the leg, e.g. pale, red or blue | Deep vein thrombosis |
| sudden unexplained shortness of breath or rapid breathing sudden cough for no apparent reason that could cause you to cough up blood severe chest pain that may increase with deep breathing severe instability or dizziness fast or irregular heartbeat severe pain in the abdomen you are not sure, talk to a doctor because some of these symptoms, e.g. cough and shortness of breath, can be mistakenly interpreted as a milder condition such as a respiratory infection (such as a common cold). | Pulmonary embolism |
| Symptoms that usually occur in one eye: immediate loss of vision or blurred vision without pain that can lead to vision loss | Retinal venous thrombosis (blood clot in the eye) |
| chest pain, discomfort, pressure, heavinesspressure or feeling of fullness in the chest, arm, or below the sternum feeling full, indigestion or feeling of suffocationdiscomfort in the upper body that radiates to the back, jaw, neck, arm, and abdomensweating, nausea, vomiting or dizziness extreme weakness, anxiety or shortness of breakfast or irregular heartbeat | Myocardial infarction |
| sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arms, or legs, especially on one side of the body sudden confusion, difficulty speaking or understanding sudden vision problems in one or both eyes sudden difficulty walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination Sudden, severe or prolonged headache for no known reason consciousness or fainting with or without seizures sometimes the symptoms of a stroke can be short-lived with almost immediate or complete recovery, but you should still seek medical attention immediately because you are at risk of having a new stroke. | Stroke |
| swelling and slight blue discoloration of an arm or leg severe pain in the abdomen ( acute abdomen) | Blood clots that block other blood vessels |
BLOOD CLOTS IN A FRIEND
What can happen if a blood clot forms in a vein?
- The use of combined hormonal contraceptives has been associated with an increased risk of blood clots in the vein (venous thrombosis ). However, these side effects are rare. They usually occur during the first year of using a combined hormonal contraceptive.
- If a blood clot forms in a vein in the leg or foot, it can lead to deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
- If a blood clot moves from the bone and stays in the lung, it can lead to a pulmonary embolism.
- In very rare cases, a blood clot can form in a vein in another organ such as the eye ( retinal venous thrombosis ).
When is the risk of developing a blood clot in a vein greatest?
The risk of developing a blood clot in a vein is greatest during the first year that you use combined hormonal contraceptives for the first time. The risk can also be higher if you start again with a combined hormonal contraceptive (same product or another product) after a break of 4 weeks or longer.
After the first year, the risk decreases, but it is always slightly higher than if you did not use a combined hormonal contraceptive.
When you stop using Prionelle, the risk of a blood clot returns to normal within a few weeks.
How big is the risk of developing a blood clot?
The risk depends on your natural risk of VTE and the type of combined hormonal contraceptive you are taking.
The total risk of a blood clot in the leg or lungs with Prionelle is small.
- Of 10,000 women who use a combined hormonal contraceptive that contains levonorgestrel such as Prionelle, about 5‑7 develop a blood clot in one year.
| Risk of developing a blood clot during a year | |
|---|---|
| Women who do not use combined pills and who are not pregnant | About 2 out of 10,000 women |
| Women who use a combined hormonal contraceptive that contains levonorgestrel such as Prionelle | About 5-7 out of 10,000 women |
Factors that may increase the risk of a blood clot in a vein
The risk of a blood clot with Prionelle is small but some conditions increase the risk. The risk is higher:
- If you are overweight (body mass index or BMI over 30 kg / m 2 )
- If someone in your family has had a blood clot in their bones, lungs, or another organ at a young age (eg for about 50 years). In this case, you may have a hereditary blood clotting disease
- If you need to undergo surgery stay in bed for an extended period due to injury or illness, or if your leg is plastered. The use of Prionelle may need to be stopped for several weeks before an operation or while you are less mobile. If you have to stop taking Prionelle, ask your doctor when you can start taking it again
- With increasing age (especially if you are over about 35 years old)
- If you gave birth a few weeks ago
The more conditions you have, the greater the risk of developing a blood clot.
Air travel (over 4 hours) can temporarily increase the risk of a blood clot, especially if you have any of the other factors listed here.
You must tell your doctor if any of these conditions apply to you, even if you are unsure. Your doctor may decide that you need to stop taking Prionelle.
If any of the above conditions change when you use Prionelle, e.g. a close relative suffers from a blood clot with an unknown cause, or you gain a lot of weight, talk to your doctor.
BLOOD CLOTS IN AN ART
What can happen if a blood clot forms in an artery?
In the same way as a blood clot in a vein, a clot in an artery can lead to serious problems. It can e.g. cause a heart attack or stroke.
Factors that may increase the risk of a blood clot in an artery
It is important to know that the risk of a heart attack or stroke due to the use of Prionelle is very small but may increase:
- With increasing age (after about 35 years of age)
- If you smoke. When using combined hormonal contraceptives such as Prionelle, you should stop smoking. If you can not stop smoking and are over 35 years old, your doctor may advise you to use another type of contraceptive
- If you are overweight
- If you have high blood pressure that is not controlled with treatment
- If a close relative has had a heart attack or stroke at a young age (younger than 50 years). In this case, you may also be at greater risk for a heart attack or stroke
- If you or a close relative have high blood fats ( cholesterol or triglycerides )
- If you get migraines, especially migraines with an aura
- If you have heart problems (valve disease, a heart rhythm disorder called atrial fibrillation )
- If you have diabetes
If you have more than one of these conditions or if any of them are particularly serious, the risk of developing a blood clot can be even greater.
If any of the above conditions change when you use Prionelle, e.g. If you start smoking, a close relative suffers from thrombosis of unknown cause, or if you gain a lot of weight, talk to your doctor.
Birth control pills and cancer
Breast cancer is diagnosed slightly more often in women who use birth control pills than in women of the same age who do not use birth control pills. The small increase in the number of breast cancer diagnoses gradually decreases during the first ten years after discontinuation of use. It is not known whether this difference is due to the contraceptive pill. It may be that women who use birth control pills are examined more often and thus any cancer is detected earlier.
In rare cases, benign liver tumors and, even more uncommonly, malignant liver tumors have been reported in birth control pill users. These tumors can cause internal bleeding. Contact a doctor immediately if you have severe pain in the abdominal region.
The most important risk factor for cervical cancer is human papillomavirus infection ( condyloma ). Some studies have shown that long-term use of birth control pills can contribute to an increased risk of condyloma. However, it is not clear to what extent this is due to other factors such as sexual habits (including reduced condom use) or increased detection as a result of more regular cervical smears in women using birth control pills.
Mental disorders
Some women who use hormonal contraceptives, including Prionelle, have reported depression or depression. Depression can be severe and can sometimes lead to suicidal thoughts. If you experience mood swings and symptoms of depression, you should contact a doctor as soon as possible for advice.
Other Medicines And Prionelle
Some medicines can affect the levels of birth control pills in the blood and thus prevent birth control pills from working properly. This applies, among other things, to medicines for the treatment of:
- Epilepsy eg
- Primidone
- Phenytoin
- Barbiturate
- Carbamazepine
- Oxcarbazepine
- Topiramate
- Felbamate
- Tuberculosis eg
- Rifampicin
- Rifabutin
- HIV and hepatitis C virus infections;
- Fungal infections
- Griseofulvin
- Azole antifungals such as I
- Traconazole
- Voriconazole
- Fluconazole
- Bacterial infections (
- Macrolide antibiotics, eg
- Clarithromycin
- Erythromycin
- Macrolide antibiotics, eg
- Certain heart diseases
- High blood pressure (calcium channel blockers, eg verapamil, diltiazem );
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatism
- Etoricoxib
- Herbal medicines containing St. John’s wort (used mainly to treat depression).
Birth control pills can also affect the effectiveness of other medicines, for example:
- Cyclosporine, a drug that inhibits the immune system
- Omeprazole, a drug for gastrointestinal ulcers and acid reflux
- Lamotrigine, an antiepileptic drug
- Melatonin, a sleeping pill
- Midazolam, a hypnotic drug for use in anesthesia
- Tizanidine, a muscle relaxant
- Selegiline, a drug used to treat Parkinson’s disease
Do not use Prionelle if you have hepatitis C and are taking medicines containing
- Ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir,
- Dasabuvir
- Glecaprevir / pibrentasvir
- Sofosbuvir / velpatasvir / voxilaprevir as treatment with these products may lead to elevated liver levels (elevation of the liver enzyme ALAT ).
Your doctor will prescribe another contraceptive before starting treatment with this combination of medicines. Prionelle can be started again about 2 weeks after the end of treatment. See section “Do not use Prionelle”.
Tell your doctor/midwife or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines. Also, tell other doctors or dentists who prescribe other medicines to you that you are using Prionelle. They can tell you if you need to use additional contraceptive methods and if so, for how long. You can also get advice at the pharmacy.
Prionelle With Food And Drink
You should not drink grapefruit juice while using Prionelle as it could increase the risk of side effects.
Pregnancy And Breastfeeding
Pregnancy
Prionelle should not be used by pregnant women or women who think they may be pregnant. If you suspect that you are pregnant and you are already using Prionelle, you should contact your doctor/midwife as soon as possible.
Breast-feeding
Prionelle is not recommended during breastfeeding. If you want to use birth control pills while you are breastfeeding, you should consult your doctor/midwife.
Driving And Using Machines
Prionelle has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
You are responsible for assessing whether you are fit to drive a motor vehicle or perform work that requires sharpened attention. One of the factors that can affect your ability in these respects is the use of drugs due to their effects and/or side effects. Descriptions of these effects and side effects can be found in other sections. Read all the information in this leaflet for guidance. If you are not sure, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
Prionelle Contains Lactose Monohydrate And Sucrose
Prionelle contains lactose monohydrate and sucrose. If you have been told by your doctor that you have an intolerance to some sugars, contact your doctor before taking this medicine.
How To Use Prionelle
Always use Prionelle exactly as your doctor/midwife has told you. Always follow the doctor’s / midwife’s prescription and the instructions on the pharmacy label. If you are not sure, talk to your doctor/midwife or pharmacist.
When and how to take the tablets
The Prionelle pack contains three or thirteen tablet tablets with 21 tablets each. On each tablet map, weekdays are marked. The tablet should be taken at about the same time each day, along with some liquid. Follow the direction of the arrows until all 21 tablets have been taken. Do not take any tablets for the next seven days. During these seven days, you usually get menstrual-like bleeding (loss of bleeding). This usually starts two to three days after you take the last Prionella tablet. Start the next tablet chart on day eight, even if you are still bleeding. This means that you always start a new tablet chart on the same day of the week and that you will have your dropout bleeding on approximately the same days each month.
How to start with your first Prionelle tablet card
- When no hormonal contraceptive method has been used in the last month started taking Prionelle on the first day of the menstrual cycle, ie the first day of bleeding. Take a tablet that is marked with the current day of the week (eg if the bleeding starts on a Friday, you should take a tablet that is marked “Friday”). Then take the tablets in turn in the direction of the arrows. Prionelle works from day one, so no additional method of contraception is necessary. You can also start taking Prionelle on days two to five of the menstrual cycle, but then you will need to use an extra method of contraception ( barrier method, such as a condom) as a supplement during the first seven days of tablet treatment in the first menstrual cycle.
- When changing from another combination contraceptive ( contraceptive pill, vaginal ring, or patch )You can start taking Prionelle the day after the last tablet of the previous pill (this means that there should be no tablet interruption). If you already use a contraceptive pill where there are some inactive tablets per map (ie delivered with 28 tablets per map), you can start with Prionelle after the last active tablet (if you are unsure which tablet it is, you can ask your doctor/midwife, or ask at the pharmacy). You can also start later, but never later than the day after the tablet-free interval (or the day after the last inactive tablet) for your previous pill. If you have used a vaginal ring or a patch you should preferably start using Prionelle on the same day as the ring or patch is removed and at the latest when treatment with the next ring or patch should have started. If you follow these instructions, no additional method of contraception is needed.
- When changing from mini-pills ( birth control pills that only contain progestogens )You can stop taking the mini-pills any day and start taking Prionelle at the same time the next day. Note that you should use an additional method of contraception (a barrier method ) if you have intercourse during any of the first seven days of treatment.
- When changing from the contraceptive methods contraceptive syringe, contraceptive rod, or IUDStart taking Prionelle on the day you should have a new syringe or the day the contraceptive pill or IUD is removed. Note that you should use another method of contraception (a barrier method; eg condoms or diapers ) if you have intercourse during any of the first seven days of treatment.
- After childbirth, you have just given birth, and a doctor/midwife may ask you to wait with Prionelle until you have had your first normal period. Sometimes you can start earlier, and ask your doctor/midwife for advice. If you are breastfeeding and want to use Prionelle, you should discuss this with your doctor/midwife before you start.
- After abortion or miscarriage your doctor for advice.
If You Take More Prionelle Than You Should
If you have ingested too much medicine or if a child has accidentally ingested the medicine: contact a doctor or hospital for risk assessment and advice.
No serious adverse effects have been reported after taking too many Prionelle tablets at the same time. If you have taken several tablets at the same time, you may experience nausea, vomiting, or bleeding from the vagina. Even girls who have not had their first period but have accidentally used this medicine may experience this type of bleeding.
If You Want To Quit Prionelle
You can stop taking Prionelle at any time. If you stop because you want to get pregnant, it is recommended that you wait until you have had your first natural menstrual bleeding before trying to get pregnant. This facilitates the calculation of when the birth is to take place. Ask your doctor/midwife about other methods of contraception if you do not want to get pregnant.
If You Forget To Take Prionelle
If less than 12 hours have passed since you should have taken your tablet, you are still protected against pregnancy. Take the tablet as soon as you remember and take the next tablet at the usual time.
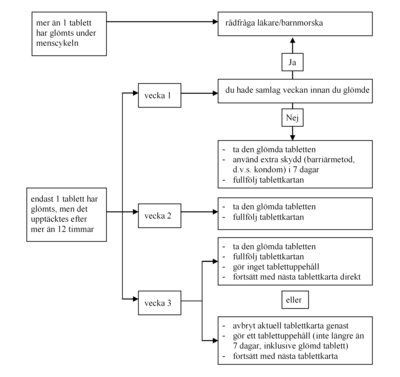
If more than 12 hours have elapsed, the effect of the contraceptive pill may be reduced. The more tablets in a row that you have missed, the higher the risk that the preventive effect has decreased. The risk of getting pregnant is especially high if you forget tablets at the beginning or end of the tablet chart. Therefore, always follow the instructions given below (see also the diagram):
- More than 1 tablet in the tablet map has been forgotten: Contact your doctor/midwife for advice.
- 1 tablet forgotten during week 1:Take the skipped tablet as soon as you remember, even if it means taking two tablets at the same time. Take the following tablets at the usual time, but do not forget to use extra contraceptive protection ( barrier method, eg condom) for the next seven days. If you have had intercourse during the week before the forgotten tablet, there is a risk that you will become pregnant. Inform your doctor/midwife immediately.
- 1 tablet was forgotten during week 2:Take the skipped tablet as soon as you remember, even if it means taking two tablets at the same time. Take the following tablets at the usual time. The contraceptive pill still has the desired effect and you do not need to use extra preventive protection. If more than 1 tablet is forgotten, supplementary contraceptive protection should be used for 7 days.
- 1 tablet is forgotten during week 3:You can choose between one of the following two options and you do not need to use extra preventive protection:
- Take the skipped tablet as soon as you remember, even if it means taking two tablets at the same time. Take the following tablets at the usual time. When the tablet map is finished, start the next tablet map immediately, without tablet interruption. You will probably not get any proper bleeding until the end of the second tablet chart. However, you may experience spotting and breakthrough bleeding during the days you take tablets.
- You can discontinue the intake from the current tablet map and continue with a new tablet map after a tablet pause of up to seven days ( including the day you forgot to take the tablet ).
If you have forgotten to take tablets in a tablet chart and you do not get your period during the first normal tablet-free break, you may be pregnant. Consult a doctor/midwife before starting the next tablet chart.
If you suffer from gastrointestinal problems (eg vomiting or severe diarrhea)
If you vomit or have severe diarrhea, the active ingredients in the Prionella tablet may not be fully absorbed. If you vomit within 3-4 hours after taking the tablet, it gives the same situation as if you have not taken the tablet. Therefore, follow the instructions for the forgotten tablet above. Contact a doctor if you have severe diarrhea.
If you want to postpone a period
You can postpone your period if you start the next Prionelle tablet card immediately after the previous card is used up. You can continue to take tablets from the new map for as long as you wish until the entire map is used up. If you want your period to start earlier than that, just stop taking the tablets from the other map. Take a tablet break for a maximum of seven days (during which you get your period) and then start a new pack. During the second tablet chart, you may experience breakthrough bleeding or splashing bleeding even on the days when you take tablets. Start the next tablet chart after the usual seven-day tablet break.
If you want to change the start date for your period
If you take your tablets according to the instructions, you will experience a loss of bleeding about the same day of the week every four weeks. If you want to change this to another day, you can shorten (but never extend) the tablet break next time.
For example. If you usually start bleeding on a Friday and in the future want the bleeding to start on a Tuesday (three days earlier), you can start on the next tablet chart three days earlier than usual. If the tablet break becomes very short (eg 3 days or less), there may be no bleeding. You may instead experience breakthrough bleeding or spotting while using the next tablet chart.
If you experience unexpected bleeding
When using all birth control pills, during the first months there may be irregular bleeding (breakthrough bleeding and splashing bleeding) between your regular dropout bleeding. You may need to use menstrual pads, but continue to take the tablets as usual. The irregular bleeding usually stops as soon as the body has adapted to the contraceptive pill (normally after about three rounds of treatment). If they persist after this, become stronger or return, you should inform the doctor/midwife.
If menstruation is absent
If you have taken all the tablets at the right time, have not vomited or had severe diarrhea, or used other medicines, it is very unlikely that you would be pregnant. Continue to take Prionelle as usual.
If there is no bleeding twice in a row, you may be pregnant. Inform doctor/midwife immediately. Do not start on the next tablet card until your doctor/midwife has verified that you are not pregnant.
Possible Side Effects Of Prionelle
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. If you get any side effects, especially if they are serious or persistent, or if your health changes and you think it may be due to Prionelle, talk to your doctor.
An increased risk of blood clots in the veins (venous thromboembolism, VTE) or blood clots in the arteries ( arterial thrombosis, ATE) is present for all women taking hormonal combined contraceptives. For more information on the different risks of using combined hormonal contraceptives, see section 2 “What you need to know before using Prionelle”.
Contact a doctor immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms of angioedema:
- Swelling of the face, tongue, and/or throat and/or difficulty swallowing
- Hives
- Possibly difficulty breathing (see also section “Warnings and precautions”).
During the first rounds of treatment, you can be expected to get some side effects, e.g.
- Chest tightness
- Nausea
- Spotting
These initial side effects usually disappear within 2 to 4 months of treatment.
Other side effects that have been reported in birth control pill users are:
Common side effects of prionelle (may affect up to 1 in 10 people ):
- Weight gain
- Headache
- Depression
- Mood swings
- Nausea
- Abdominal pain
- Breast tenderness
- Chest pain
- Chest tightness
- Bleeding
Uncommon side effects of prionelle ( may affect up to 1 in 100 people ):
- Fluid retention (accumulation of fluid in the body)
- Migraine
- Decreased sexual desire
- A moderate increase in blood pressure
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Skin rash
- Hives
- Missed menstrual bleeding
- Breast enlargement
Rare side effects of prionelle ( may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people ):
- Hypersensitivity reaction
- Decreased glucose tolerance
- Increased blood sugar
- Increased insulin requirements
- Weight loss
- Increased sexual desire
- Decreased tear flow
- Difficulty wearing contact lenses
- Hepatic effects
- Pruritus
- Jaundice
- Gallstones and cholera in the face
- Skin reactions
- Fluid secretion from the breasts and altered discharge from the vagina
- Dangerous blood clots in a vein or artery which includes heart attack
- Stroke
- Blood clot in a leg, foot or in the lungs
How To Store Prionelle
- Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
- No special storage instructions.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton after EXP. day. The expiration date is the last day of the specified month.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
Contents Of The Pack And Other Information
Content Declaration
- The active substances are levonorgestrel 150 micrograms and Ethinyl estradiol 30 micrograms.
- The other ingredients are
- Lactose monohydrate
- Maize starch
- Povidone
- Sucrose
- Talc
- Calcium carbonate
- Glycerol
- Macrogol
- Titanium dioxide (E 17and 1)
- Magnesium stearate
- Carnauba wax
What The Medicine Looks Like And The Contents Of The Pack
- The tablets are white, biconvex, and round.
- Each tablet blister contains 21 tablets.
- Pack sizes ( calendar pack) of 21, 3×21 and 13×21 tablets.
- Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder And Manufacturer
CampusPharma AB
Karl Gustavsgatan 1A
411 25 Gothenburg