1 mg / 72 hours transdermal
patch hyoscin (scopolamine)
WHAT SCOPODERM IS AND WHAT IT IS USED FOR
Scopoderm contains the active substance hyoscine (also known as scopolamine), which belongs to a group of medicines called antiemetics.
Scopoderm transdermal patches are used to prevent symptoms of motion sickness, such as nausea, vomiting, and dizziness (balance difficulties) that can occur when traveling by boat, plane, train, or car.
BEFORE YOU USE SCOPODERM
Do not use Scopoderm
Careful oral hygiene is important, as dry mouth is a common side effect when using Scopoderm.
- if you are allergic to the active substance or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- if you have glaucoma.
Warnings and cautions
- if you suffer from excessive satiety, gas and/or pain, constipation, diarrhea, or vomiting, which may be symptoms of bowel obstruction.
- if you suffer from pyloric stenosis (a condition that affects the stomach).
- if you have difficulty urinating (eg due to prostate enlargement).
- if you are elderly, have any metabolic disease, or impaired liver or kidney function.
- if you have or have had pain in your eyes, blurred vision, or see rainbow-colored halos around lights. (Scopoderm should only be used after an eye examination by a doctor).
- if you have or have had epilepsy or epileptic seizures (an increased number of seizures has been reported).
Under these circumstances, Scopoderm may be unsuitable for you.
In rare cases, confusion and/or visual hallucinations may occur. Remove Scopoderm at once and contact your doctor if this should happen.
Caution should be exercised after removing the patch as the side effects may persist for up to 24 hours or longer.
Remove the patch before the X-ray examination.
Children and young people
Scopoderm should not be used in children under 10 years of age, as there is only limited experience with the use of Scopoderm in children.
Older
Scopoderm transdermal patches can be used by the elderly (see recommendations for adults), however, the elderly may be at increased risk of side effects from scopolamine (see section 2, Warnings and Precautions).
Other medicines and Scopoderm
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines.
In particular, tell your doctor if you are taking any of the following medicines, as Scopoderm may interact with them:
- alcohol
- other drugs that affect the brain
- allergy medicines
- antidepressants
- medicines for Parkinson’s disease or virus drugs for irregular heartbeat (antiarrhythmics)
- other medicines for motion sickness
Scopoderm with alcohol
Avoid alcohol consumption when treating with Scopoderm transdermal patches.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Scopoderm may have side effects such as drowsiness, confusion, and dizziness, or may affect your vision. Do not drive, use machines, or perform any activity that requires concentration when you are being treated with Scopoderm.
HOW TO USE SCOPODERM
Always use this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you are unsure.
Adults
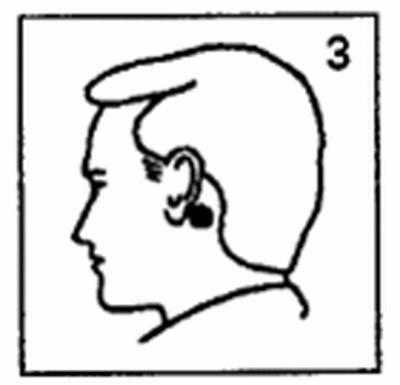
- A patch is applied to a clean, dry, and hair-free skin surface behind the ear the night before or at least 5-6 hours before the start of the trip.
- Open the sachet at the top and remove the beige patch complete with the transparent hexagonal protective film (Fig. 1).
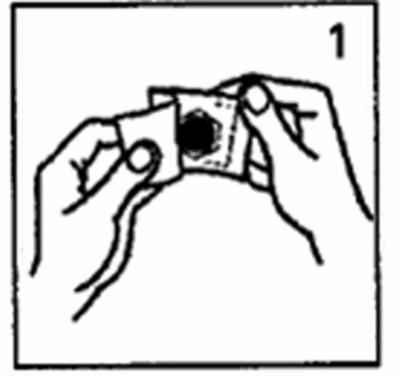
- Hold the edge of the patch and remove the hexagonal transparent protective film without touching the silver-colored adhesive side (Fig. 2).
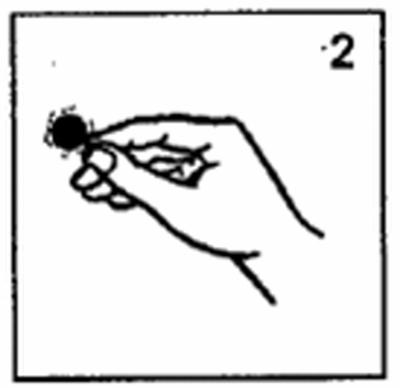
- Press the patch (silver-colored adhesive side down) onto a clean, dry, hair-free skin surface behind the ear (Fig. 3). Check that the patch is firmly attached. Once it is stuck, it must not be moved.
- If Scopoderm, which normally adheres properly to the skin, accidentally falls off, it should be replaced with a new patch.
- After applying the patch, it should not be touched again during use, as the pressure can then cause scopolamine to seep into the edge. If you touch the patch, wash your hands immediately.
- After the patch has been applied or removed, the hands (and after the patch, including the application site) should be washed thoroughly to prevent traces of the active substance from entering the eyes from the fingers as this may lead to temporary misty myopia and enlarged pupils. you (sometimes only in one eye).
- It is enough to put on a Scopoderm transdermal patch to have protection for up to 3 days, but if the trip is shorter, you should remove it earlier. If you need protection for a long time, remove the patch after 3 days and put a new patch behind the other ear. Never use more than one patch at a time.
- If you swim, shower, or wash your hair, this will not affect the adhesion or effect of Scopoderm transdermal patches, provided that the patch does not fall off.
Protection against motion sickness is obtained for at least 72 hours. The patch can be removed earlier if continued protection is not needed. Patches used for less than 72 hours cannot be used again. If protection is needed for longer than 72 hours, an additional patch may be applied, preferably behind the other ear, after the first patch has been removed. Wash the skin where the patch has been applied thoroughly, to avoid any residual patch remaining in effect. The patch must not be split or cut into pieces.
Use for children and adolescents
Scopoderm transdermal patches can be used by children 10 years of age or older (see dosage for adults).
Do not exceed the recommended dose.
If you have any further questions on the use of Scopoderm, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
If you use more Scopoderm than you should
If you accidentally put on too many patches at one time, you may feel restless, agitated, or confused. In case of higher overdose, you may become disoriented, hallucinate or have seizures. In severe cases of overdose, coma and difficulty breathing may occur.
Remove the patch (s) immediately (as some overdose symptoms may persist for up to 24 hours or longer after removal of the patch), talk to your doctor, or contact your nearest emergency department immediately. Take any remaining patches with you.
If you forget to take Scopoderm
Do not use double patches to compensate for forgotten patches.
If you stop using Scopoderm
In isolated cases – usually after several days of use – symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, vomiting, headache, and balance difficulties have been reported after the end of treatment. Contact your doctor if this happens to you.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Some side effects may be serious, but are very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
- Vision changes with increased pressure in the eye (possible signs of glaucoma )If you experience this, remove the patch and contact your doctor immediately.
Very common side effects (may affect more than 1 user in 10)
- dry mouth
- drowsiness, dizziness
- foggy myopia and enlarged pupils (sometimes only in one eye)
- difficulty focusing on objects near or far
Common side effects ( may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- irritation of the eyelids
- skin irritation
Rare side effects ( may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
- difficulty urinating (urinating)
- impaired memory or concentration, restlessness, disorientation, confusion or hallucinations
Very rare side effects ( may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
- general skin rash
Has been reported (occurs in an unknown number of users)
- application site reactions such as itching, reddening of the skin, and burning sensation.
Dry mouth is a very common side effect. Careful oral hygiene is therefore important. Increased risk of epileptics getting cramps and a burning sensation at the site of administration have been reported in a few cases.
Side effects are after discontinuation of Scopoderm transdermal patches
At the end of treatment with Scopoderm, in rare cases – usually after several days of treatment – symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, vomiting, headache, and balance difficulties have been reported.
HOW TO STORE SCOPODERM
- Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children. Used patches are folded and discarded so that children do not have access to them.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and sachet after EXP. dat. The expiration date is the last day of the specified month.
- Do not store above 25 ° C
- Used patches should be folded in half with the adhesive surface inwards before they are discarded.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
FURTHER INFORMATION
Content declaration
- The active substance is hyoscin (scopolamine). Scopoderm contains 1.5 mg of active substance on your transdermal patch .
- The other ingredients are light mineral oil, easy-flowing paraffin, and polyisobutylene.
What the medicine looks like and the contents of the pack
Scopoderm transdermal patch is a flat, round reservoir patch, approximately 1.8 cm in diameter. One side of the patch is beige. The other side is silver-colored and placed on an oversized clear hexagonal protective film.
Scopoderm transdermal patches are available in individual packages in a flat sachet.
Pack sizes: Cartons of 2, 5, and 10 sachets, respectively.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorisation Holder
Baxter Medical AB
Box 63
164 94 Kista
Manufacturer
FAMAR SA
48 th km National Road Athens-Lamia,
19011, Avlonas, Attiki
Greece.