1 mg / g vaginal cream
estriol
What Ovesterin Is And What Ovesterin Used For
Ovesterine belongs to a group of medicines called Hormone Replacement Therapy ( HRT ) and is for vaginal use. Ovesterine contains the female sex hormone estriol, a so-called estrogen.
Ovesterine is used for topical treatment of ailments such as dryness or irritation of the vagina in women after the last regular period ( menopause ). The medical term for this is “vaginal atrophy.” Declining estrogen levels in the body cause it after menopause.
Östriol helps to keep the genital mucosa elastic and resistant to both mechanical influences and infection.
Ovesterine works by replacing the estrogen that is normally produced in a woman’s ovaries. Ovesterin is inserted into the vagina to release the hormone where it is needed. This can relieve the feeling of discomfort in the vagina.
A doctor must first diagnose estrogen deficiency to ensure the correct diagnosis.
What You Need To Know Before Using Ovesterin
Do Not Use Ovesterin
Medical background and regular check-ups
The use of HRT involves risks that must be considered when deciding to start or continue an ongoing treatment. Consult a physician before starting a treatment or to discuss whether to continue treatment
Experience is limited for treating women whose menstruation has stopped prematurely (when the ovaries have stopped working or due to surgery). If your period has stopped prematurely, HRT’s risks may differ. Talk to your doctor.
Before starting treatment (or resuming treatment), your doctor will ask about your and your family’s medical background. Your doctor may do a general medical and gynecological examination, including an examination of your breasts.
Once you have started treatment, you should go for regular medical check-ups at least once a year. During these check-ups, you should discuss with your doctor the benefits and risks of continued treatment.
Perform regular examinations of the breasts according to the doctor’s recommendations.
Do not use Ovesterin
if any of the following apply to you. If you are not sure, talk to your doctor before taking Ovesterin.
- If you are allergic to estriol or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- If you have or have had breast cancer or there is a suspicion that you may have it
- If you have or have had estrogen-dependent cancer, such as cancer of the uterine lining (endometrium), or if there is a suspicion of such cancer.
- If you have unexpected genital bleeding that a doctor has not investigated.
- If you have endometrial hyperplasia (severe thickening of the uterine lining) and are not being treated for it.
- If you have or have had a blood clot in a vein (venous thromboembolism ), in your legs (deep vein thrombosis ), or in your lungs ( pulmonary embolism ).
- If you have a coagulation disorder, a condition with an increased risk of blood clots (lack of protein C, protein S, or antithrombin).
- If you have or have recently had a disease caused by a blood clot in the arteries, such as a heart attack, stroke, or angina.
- If you have or have had any liver disease and still have abnormal liver values.
- If you have porphyria, a rare inherited blood disorder.
If any of the above affects you the first time you use Ovesterin, stop using Ovesterin and contact your doctor immediately.
Warnings and cautions
Ovesterin vaginal cream should not be combined with estrogen preparations with systemic effects, such as tablets, as the estrogen concentrations achieved have not been studied in terms of safety and risks.
Talk to your doctor if you have had any of the following problems before starting treatment, as these may come back or worsen during treatment with Ovesterin. Should this occur, have more frequent check-ups with a doctor.
- Muscle knots ( fibroids ) in the uterus
- Uterine lining tissue that grows outside the uterus ( endometriosis ) or has previously had severe thickening of the uterine lining ( endometrial hyperplasia ).
- Increased risk of getting a blood clot (see below “Blood clots in a vein ( thrombosis )”)
- Increased risk of getting estrogen-dependent cancer (such as if a close relative has had breast cancer or other estrogen-dependent cancer)
- High blood pressure
- Liver disease, e.g., benign tumor
- Diabetes
- Gallstone disease
- Migraine or severe headache
- An autoimmune disease that affects many organs in the body (systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE )
- Epilepsy
- Asthma
- Ossification of the middle ear leading to hearing loss (otosclerosis)
- Fluid retention due to heart or kidney disease.
Tell your doctor if you have hepatitis C and are following a combination regimen of the medicines ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir. Using a combination of these drugs with certain estrogen-containing products may cause elevated liver function tests (increase in liver enzyme ALT); The risk of this happening with Ovesterin is currently unknown.
You should contact a doctor immediately and discontinue treatment if any of the following occur:
- Any of the things mentioned in the section ‘Do not use Ovesterin’
- If the skin or whites of the eyes turn yellow (jaundice); it may be a symptom of liver disease
- If your blood pressure rises sharply (symptoms may include headache, fatigue, or dizziness)
- If you are experiencing migraine-like headaches for the first time
- If you become pregnant
- If you get symptoms of a blood clot, such as
- Painful swelling and redness of the legs
- Sudden chest pain
- For breathing difficulties and more information, see below “Blood clots in a vein ( thrombosis ).”
Note: Ovesterin is not a contraceptive. If it is less than 12 months since your last period, or if you are under 50, you may still need to use contraception to avoid pregnancy. Consult your doctor.
Hormone therapy and cancer
Severe thickening of the uterine lining ( endometrial hyperplasia ) and cancer of the uterine lining (endometrial cancer)
Using HRT tablets with estrogen alone for a long time may increase the risk of developing cancer of the uterine lining (endometrium).
It is unclear if there is a similar risk with Ovesterin when used for repeated treatment or for a long time (over a year). However, the uptake of Ovesterin into the blood is very low, so adding progestogens is unnecessary.
If you experience breakthrough bleeding or splashing bleeding, there is usually nothing to worry about, but you should make an appointment with your doctor. It may be a sign that your uterine lining has become thicker.
To prevent overstimulation of the uterine lining, the maximum dose should not exceed 1 application (0.5 mg), and the maximum dose should not be used for more than a few weeks (maximum 4 weeks).
The following risks apply to hormone replacement therapy ( HRT ) circulating in the blood. Ovesterin 1 mg / g vaginal cream, on the other hand, is used topically in the vagina, and the uptake into the blood is very low. The conditions described below are unlikely to worsen or recur during treatment with Ovesterin 1 mg / g vaginal cream, but you should consult a doctor if you are concerned.
Breast cancer
There are indications that the use of Ovesterin 1 mg / g vaginal cream does not increase the risk of breast cancer in women who have not had breast cancer before. It is unknown whether Ovesterin 1 mg / g vaginal cream can be used safely in women with breast cancer.
Check your breasts regularly. Contact a doctor if you notice changes such as:
- Indentations or pits
- Changes in the nipple
- Nodules you can see or feel.
You are also recommended to participate in a mammogram when you are called.
Ovarian cancer ( ovarian cancer )
Ovarian cancer is rare – much rare than breast cancer. Estrogen-only use of HRT has been associated with a slightly increased risk of ovarian cancer.
The risk of ovarian cancer varies with age. For example, about 2 women out of 2,000 aged 50 to 54 who do not receive HRT will be diagnosed with ovarian cancer over 5 years. For women who have had HRT for 5 years, there will be about 3 cases per 2,000 users (i.e., about 1 extra case).
How HRT affects the heart and blood circulation
Blood clots in a vein ( thrombosis )
The risk of blood clots in the veins is 1.3-3 times higher for women who take HRT than for those who do not. It is unknown whether Ovesterin presents the same risk.
Blood clots can be serious. If a blood clot ends up in the lungs, it can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, collapse or even lead to death.
You are more likely to get a blood clot in a vein if the following apply to you. Talk to your doctor if any of the following apply to you:
- You have not been able to walk or stand for a long time due to a major operation, injury or illness (see also section 3, “If you need surgery”)
- You are severely overweight ( BMI over 30 kg / m 2 )
- You have a coagulation disorder that requires long-term treatment with drugs that prevent blood clots.
- If a close relative has had a blood clot in the bone, lung, or another organ
- You have SLE (systemic lupus erythematosus)
- You have cancer.
The symptoms of a blood clot are described in the section “You should contact a doctor immediately and discontinue treatment if any of the following occur” above.
Compare
For women in their 50s who do not use HRT, the number of cases of blood clots in a vein over five years is expected to be 4-7 per 1,000.
For women in their 50s who use HRT with estrogen alone for more than 5 years, 5-8 cases per 1,000 users are diagnosed (in other words, a different case).
Heart disease (heart attack)
For women who take estrogen alone, there is no increased risk of developing heart disease.
Stroke _
The risk of stroke is about 1.5 times higher for those who take HRT than those who do not. The risk of stroke is age-dependent. Therefore, the number of cases of stroke increases due to the use of HRT with increasing age.
Comparison
For women in their 50s who do not take HRT, an average of 8 out of 1,000 people are expected to have a stroke over 5 years. For women in their 50s who have taken HRT for more than 5 years, 11 out of 1,000 users are expected to have a stroke (i.e., 3 different cases).
Other conditions
Using HRT does not prevent memory loss. The risk of memory loss may be slightly higher in women who start using HRT after age 65. Consult your doctor.
Other Medicines And Ovesterin
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines, including medicines obtained without a prescription, herbal medicines, or other natural products.
The estriol dose ( estrogen ) in Ovesterin vaginal cream is low, and the treatment is local. Therefore, Ovesterin is not expected to affect or be affected by the concomitant use of other medicines. If you are not sure, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
Tell your doctor if you have hepatitis C and are following a combination regimen of the medicines ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir. Using a combination of these drugs with certain estrogen-containing products may cause elevated liver function tests (increase in liver enzyme ALT); The risk of this happening with Ovesterin is currently unknown.
Pregnancy And Breastfeeding
Ovesterin is intended for women whose menstruation has stopped. If you become pregnant, stop taking Ovesterin and consult a doctor.
Driving And Using Machines
No effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been observed.
Ovesterin Vaginal Cream Contains Cetyl Alcohol And Stearyl Alcohol
It may cause local skin reactions (e.g., contact dermatitis).
How To Use Ovesterin
- Always use this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you are unsure.
- The first 2-3 weeks (maximum 4 weeks ): One dose per day, preferably at bedtime. Insert a pre-filled syringe deep into the vagina.
- After that: After 2-3 weeks of treatment, the symptoms should have subsided, and then the dose is reduced to one dose twice a week.
- Other doses according to doctor’s prescription.
How should a cream be used?
Use the dosing syringe to insert cream into the vagina.
1. Remove the cap on the cream tube and use the tip of the cap to open the tube.
2. Screw the nozzle of the dosing syringe onto the tube.
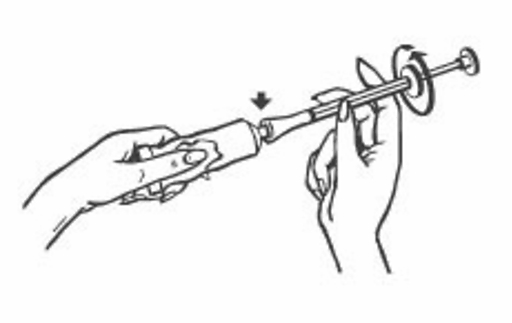
3. Squeeze as much cream into the dosing syringe to fill to the mark (to stop the flask, see the arrows in the figure).
4. Unscrew the dosing syringe and screw the cap onto the tube.
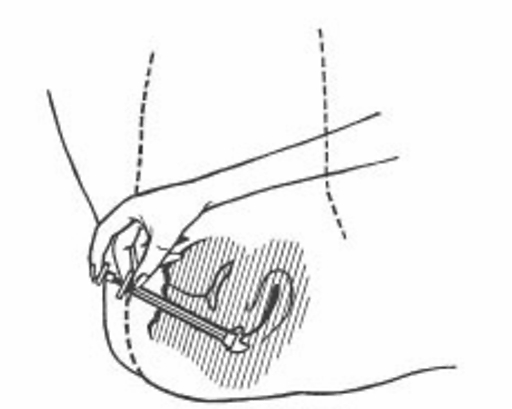
5. Lie on your back when using the cream. Insert the dosing syringe deep into the vagina and slowly push in the plunger.
After use, the dosing syringe should be cleaned in warm soapy water. When disassembling the dosing syringe, you must take a little closer to loosen the plunger. After cleaning, push the plunger back. Rinse thoroughly afterward. Detergents must not be used nor boiling water.
Seek medical attention if symptoms worsen or do not improve within 3-4 weeks.
You should use panty liners after applying Ovesterin vaginal cream as some excess may leak out.
If You Use More Ovesterin Than You Should
The estriol dose ( estrogen ) in Ovesterin vaginal cream is low, and the treatment is local; therefore, no overdose is expected.
If you have ingested too much medicine or if, for example, a child has accidentally ingested the medicine, contact a doctor or hospital for risk assessment and advice.
If You Forget To Use Ovesterin
Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose. If you forget to apply a dose one day, apply a dose as soon as you remember.
If You Need Surgery
If you are going to have surgery, tell your doctor that you are taking Ovesterin. You may need to stop taking Ovesterin for 4 to 6 weeks before surgery to avoid the risk of blood clots (see section 2, “Blood clots in a vein ( thrombosis )”). Ask your doctor when it is appropriate to start taking Ovesterin again.
If you have any further questions about the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Possible Ovesterin Side Effects
This medicine can cause side effects like all medicines, although not everybody gets them.
The side effects wofOvesterin are usually mild and transient. They may also be due to a too-high dose.
Contact your doctor if you experience bleeding from the abdomen. See also “Do not use Ovesterin.”
The following diseases are reported more often in women who use hormone replacement therapy circulating in the blood than in non-users. These risks apply to a lesser extent to vaginally use estrogen treatments:
- Ovarian cancer ( ovarian cancer )
- Blood clots in veins in bones or lungs (venous thromboembolism )
- Stroke
- Probable memory loss, if treatment with HRT is started after the age of 65
See section 2 for more information on these side effects
The following Ovesterin side effects have been reported with Ovesterin (affects unknown users):
- A feeling of tension and tenderness in the breasts
- Bleeding from the genitals
- Nausea
- Fluid accumulation in the body, such as swollen ankles or feet
- Local irritation of the abdomen.
- Flu-like symptoms
The following side effects have been reported with other HRTs:
- Diseases of the gallbladder
- Various skin diseases:
- Dark skin spots, especially on the face and neck, so-called “pregnancy spots” (chloasma)
- Painful reddish-purple bumps on the skin (erythema nodosum)
- Annular redness or sore rash (erythema multiforme).
How To Store Ovesterin
- Keep this medicine out of sight and reach of children.
- Do not store above 25 ° C. Do not freeze.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the carton after EXP. The expiration date is the last day of the specified month.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
Contents Of The Package And Other Information
Content Declaration
- The active substance is estriol 1 mg / g, corresponding to 0.5 mg per dose.
- The other ingredients are octyl dodecanol, cetyl palmitate, glycerol, cetyl alcohol, stearyl alcohol, polysorbate 60, sorbitan stearate, lactic acid, chlorhexidine dihydrochloride, sodium hydroxide, water.
What The Medicine Looks Like And The Contents Of The Pack
Vaginal cream is provided in an aluminum tube of 15 g. The tube is packed in an outer carton together with an applicator
Marketing Authorization Holder And Manufacturer
Marketing Authorisation Holder
Aspen Pharma Trading Limited, 3016 Lake Drive, Citywest Business Campus, Dublin 24, Ireland
Tel: +46 856 642 572
Manufacturer
Aspen Bad Oldesloe GmbH, Industriestrasse 32-36, D-23843 Bad Oldesloe, Germany