Immunate 500 IU, 250 IU, 1000 IU powder and solvent for solution for injection or infusion
Coagulation factor VIII
1. What Immunate Is And What It Is Used For
Immunate contains coagulation factor VIII, absent in people with haemophilia type A (congenital factor VIII deficiency), also called haemophilia . Factor VIII is important for the blood to coagulate. Hemophilia type A is an inherited blood disease characterized by bleeding that occurs spontaneously or due to a minor injury.
Immunate injection is used in the treatment of and to prevent bleeding in people with haemophilia type A.
Immunate can also be used to treat acquired (non-congenital) factor VIII deficiency.
2. What You Need To Know Before Using Immunate
Do Not Use Immunate
- If you are hypersensitive (allergic) to the active substance or any of the other ingredients of Immunate.
Warnings And Cautions
If you get allergic reactions or other hypersensitivity reactions, e.g.
- Skin rash ( hives )
- Pressure over the chest
- Difficulty breathing
- Dizziness or fainting should be discontinued immediately. Contact your doctor immediately. See also the section on “Side effects”.
The development of inhibitors ( antibodies ) is a known complication that may occur during treatment with any factor VIII drug. The inhibitors, especially at high levels, prevent the treatment from working properly. You or your child will be closely monitored for the development of such inhibitors. If you or your child suffers from bleeding that cannot be controlled with Immunate, tell your doctor immediately.
Virus alert
When medicines are made from human blood or plasma, special measures are taken to prevent the transmission of infection to patients. This includes carefully selecting blood and plasma donors to ensure that those at risk of carrying an infection are excluded and that each donation and plasma pool is tested for signs of virus/infection. The manufacturers of these products also include steps in managing blood and plasma that can inactivate or secrete viruses. Nevertheless, the risk of transmission of infection can not be completely ruled out when drugs made from human blood or plasma are given. This also applies to new, hitherto unknown viruses and other types of infection.
The measures taken are considered effective against enveloped viruses such as HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C, and for the non-enveloped hepatitis A virus. The measures may be of limited value against non-enveloped viruses such as parvovirus B19.
Your doctor may suggest vaccination against hepatitis A and B if you are regularly / repeatedly treated with Immunate.
Immunate contains blood group isoagglutinin (aggregates against blood groups A and B found naturally in people with blood group A, B, or AB). In patients with blood groups A, B, or AB, the red blood cells may rupture ( hemolysis ) when the drug is given several times at short intervals or in very high doses.
You should note the name and batch number of Immunate at each treatment session. This is important so that you can easily check which product kit you used. The batch number label is on the vial and can be removed and pasted into the medical record document or equivalent treatment document.
Other Drugs And Immunate
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines.
Pregnancy And Breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
As haemophilia type A is very rare in women, there is no experience with using Immunate during pregnancy and lactation. It is, therefore, not known whether Immunate can cause birth defects. Follow the instructions given to you by your doctor during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Driving And Using Machines
There is no evidence that Immunate vial affects the ability to drive or use machines.
Immunate Contains Sodium
250 IU and 500 IU: This medicine contains 9.8 mg sodium (the main ingredient in table salt/table salt) per vial. This corresponds to 0.5% of adults recommended daily sodium intake.
1000 IU: This medicine contains 19.6 mg sodium (the main ingredient in table salt/table salt) per vial. This corresponds to 1% of adults recommended daily sodium intake.
3. How To Use Immunate
Immunate uses
- Dosage and treatment time is individual. Follow the dosing instructions given to you by your doctor.
- If you have the impression that the effect of Immunate is insufficient, consult your doctor.
- Immunate should be given intravenously after reconstitution with the diluent provided (water for injections). Immunate should be injected slowly, and you should not exceed a rate of 2 ml/min.
Preparation Of Solution:
Use aseptic technique
- Heat the unopened bottle containing diluent (aqua ad iniect.) To room or body temperature (max. 37 ° C).
- Remove the protective caps from the powder and water bottles (Fig. A) and disinfect both rubber stoppers.
- Take the transfer needle and press its wavy edge on the water bottle (fig. B).
- Remove the protective cover from the other end of the transfer needle without touching the free needle.
- Turn the water bottle, transfer the needle upside down over the powder bottle, and insert the free needle through the centre of the rubber stopper, as far as possible, onto the powder bottle (Fig. C). The water is sucked into the bottle with powder by vacuum.
- After about one minute, separate the two bottles by removing the transfer needle connected to the water bottle from the powder bottle (Fig. D). As the preparation dissolves easily, roll the bottle carefully a few turns so that the powder dissolves completely. NOTE! Do not shake the bottle.
- The solution should be clear or slightly opalescent. Do not use solutions that are cloudy, discoloured or precipitate.
Administration:
Use an aseptic technique.
Injection:
- To prevent particles from the rubber stopper from being transferred with the medicine, use the supplied filter needle. Attach the filter needle to the supplied disposable syringe and insert it through the rubber stopper (Fig. E).
- Any foam disappears if the syringe is removed from the filter needle for a moment.
- Withdraw the solution into the syringe via the filter needle (fig. F).
- Remove the filter needle from the syringe and slowly inject the solution intravenously (maximum injection rate: 2 ml per minute) with the supplied “butterfly” needle (or with the disposable needle).
Infusion:
A single-use infusion set with a suitable filter should be used if the solution is given as an infusion.
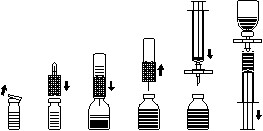
| Fig. A | Fig. B | Fig. C | Fig. D | Fig. E | Fig. F |
If You Take More Immunate Than You Should
- No symptoms of overdose are known.
- Thromboembolic events may occur.
- Hemolysis (abnormally rapid degradation of red blood cells ) may occur in patients with blood types A, B, or AB.
- If you have ingested too much medicine or if, e.g. If a child has ingested the medicine by mistake, contact a doctor, hospital, or the Poison Information Center for risk assessment and advice.
If You Forget To Take IMMUNATE
Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose. Take the next dose as soon as possible and follow the regular dosing schedule. Contact your doctor.
4. Possible Side Effects
Like all medicines, Immunate can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Allergic reactions or other hypersensitivity reactions may occur during treatment with Immunate (uncommon, may affect up to 1 in 100 people). In some cases, severe allergic reactions (so-called anaphylaxis ) and shock conditions have occurred. Signs of such reactions may include
- Swelling of, e.g. face, eyelids, tongue or throat
- Hives
- Itching
- Difficulty breathing
- Shortness of breath (due to narrowing of the trachea)
- Difficulty swallowing
- Burning and stinging sensation at the injection site
- Chills
- Skin redness
- Headache
- Rash
- Low blood pressure (with symptoms such as
- Dizziness
- Numbness
- Fainting
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Restlessness
- Palpitations
- Chest tightness
- Chest pain
- Tingling
- Vomiting
If such symptoms occur, stop treatment immediately and contact your doctor immediately.
In children who have not been previously treated with factor VIII drugs, inhibitory antibodies are very common to develop (see section 2) (occurs in more than 1 in 10 patients). However, for patients who have previously been treated with factor VIII (treatment for more than 150 days), the risk is less, and the complication is less common (it occurs in less than 1 in 100 users). If you or your child develop antibodies, the medicines may stop working properly, and you or your child may experience persistent bleeding. If this happens, consult a doctor immediately.
Other side effects reported after using Immunate (affects an unknown number of users)
- Restlessness
- Irritating or stinging sensation in the skin ( paresthesia )
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Swelling of the eyelid
- Fast heartbeat, palpitations
- Low blood pressure
- Hot flashing
- Pallor
- Shortness of breath ( dyspnoea ), cough
- Vomiting, nausea
- Hives ( urticaria ), rash, itching
- Redness of the skin ( erythema )
- Excessive sweating ( hyperhidrosis )
- Muscle pain ( myalgia )
- Chest pain, chest discomfort
- Edema (fluid retention)
- Fever, chills
- Burning and stinging sensation at the injection site
When the drug is given several times at short intervals or in very high doses, the red blood cells may rupture ( hemolysis ) in patients with blood types A, B, or AB.
Reporting of side effects
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse if you get any side effects. This also applies to any side effects not mentioned in this information. You can also report side effects directly to the Medical Products Agency. By reporting side effects, you can help increase drug safety information.
5. How To Store Immunate
- Keep out of sight and reach of children.
- Store in a refrigerator (2 ° C-8 ° C). Do not freeze. (The bottle of water may burst.)
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the vial after EXP. The expiration date is the last day of the specified month.
Ready-made solution:
- Immunate should be given within 3 hours after dissolution at 15 ° C – 25 ° C.
- Any remaining solution should be discarded.
- Do not use Immunate if you find that the solution is cloudy or has precipitated. The mixed solution should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discolouration before administration. The solution should be clear or slightly opalescent.
The medicine should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
6. Contents Of The Packaging And Other Information
Content Declaration
- The active substance is coagulation factor VIII
- The other ingredients are albumin, glycine, lysine hydrochloride, sodium chloride, trisodium citrate dihydrate, calcium chloride dihydrate and water for injections ( diluent )
What The Medicine Looks Like And The Contents Of The Pack
- Immunate is a sterile, lyophilized concentrate of coagulation factor VIII.
- Each pack contains a vial of powder (concentrate) in strengths of 250, 500, or 1000 IU and a vial of 5 ml, 5 ml, and 10 ml of diluent, respectively. Also included is a kit for preparation and injection containing: a transfer/filter needle, a disposable syringe, a disposable needle, and a butterfly needle.
Marketing Authorization Holder And Manufacturer
Baxalta Innovations GmbH
Industriestrasse 67
1221 Vienna, Austria
Manufacturer
Takeda Manufacturing Austria AG
Industriestrasse 67
1221 Vienna
Austria