| Estradot 25 micrograms / 24 hours transdermal patch |
| Estradot 37.5 microg / 24 hours transdermal patch |
| Estradot 50 micrograms / 24 hours transdermal patch |
| Estradot 75 microg / 24 hours transdermal patch |
| Estradot 100 micrograms / 24 hours transdermal patch |
| estradiol (as hemihydrate) |
1. What Estradot is and what it is used for
Estradot is a preparation used for hormonal substitution therapy ( HormoneReplacement Therapy, HRT ). It contains the female sex hormone estrogen. Estradot is used in women whose period has stopped ( menopause ), at least 12 months after their last natural menstrual period. Estradot is a patch that is applied to the skin.
Estradot is used to:
Relieve symptoms during and after menopause
When menstruation ceases ( menopause ), a woman’s estrogen drops. It can cause problems such as sweating and hot flashes. Estradot relieves these symptoms after menopause. Estradot should only be used if the problems cause problems in daily life.
Prevent osteoporosis (only applies to Estradot 50, 75, and 100 micrograms / 24 hours)
After menopause, some women suffer from osteoporosis. Discuss all possible options with your doctor.
If you have an increased risk of fractures (bone fractures) and other medicines that are not suitable for you, you can use Estradot to prevent osteoporosis after menopause.
What you need to know before using Estradot
Medical background and regular check-ups
The use of HRT involves risks that must be taken into account when deciding to start treatment or continue an ongoing treatment.
Experience is limited for the treatment of women whose menstruation has stopped prematurely (when the ovaries have stopped working or the uterus has been removed). If you belong to that group, the risks of HRT may be different. Talk to your doctor.
Before starting treatment (or resuming treatment), your doctor will ask about your own, and your family’s, medical background. Your doctor may do a general medical and gynecological examination, which also includes an examination of your breasts.
Once you have started treatment, you should go for regular medical check-ups, at least once a year. During these check-ups, you should discuss with your doctor the benefits and risks of continued treatment.
Perform regular breast examinations according to your doctor’s recommendations.
Do not use Estradot
if any of the following apply to you. If you are not sure, talk to your doctor before using Estradot.
Do not use Estradot:
- if you have or have had breast cancer or there is a suspicion that you may have it.
- if you have or have had estrogen-dependent cancer, such as cancer of the lining of the uterus (endometrium), or if there is a suspicion of such cancer.
- if you have unexpected genital bleeding that has not been investigated by a doctor.
- if you have endometrial hyperplasia (severe thickening of the uterine lining) and are not being treated for it.
- if you have or have had a blood clot in a vein (venous thromboembolism ), in your legs (deep vein thrombosis ), or your lungs ( pulmonary embolism ).
- if you have a coagulation disorder, a condition with an increased risk of blood clots (lack of protein C, protein S, or antithrombin).
- if you have or have had a disease caused by blood clots in the arteries are as heart attack, stroke (stroke), or angina.
- if you have or have had any liver disease and still have abnormal liver values.
- if you have porphyria, a rare inherited blood disorder.
- if you are allergic to estradiol or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (see section 6 Contents of the pack and other information).
If any of the above affects you the first time you use Estradot, stop using Estradot and contact your doctor immediately.
Warnings and cautions
Talk to your doctor if you have or have had any of the following problems before starting treatment. They may recur or worsen during treatment with Estradot. Should this occur, have more frequent check-ups with a doctor.
- if you have any disease affecting the lining of the uterus, as well as muscle knots ( fibroids ), endometriosis, or have had endometrial hyperplasia (severe thickening of the uterine lining).
- if you have an increased risk of getting a blood clot (see below “Blood clots in a vein ( thrombosis )”)
- if a close relative has had breast cancer or other estrogen-dependent cancer
- high blood pressure
- liver disease e.g. liver adenoma (benign tumor )
- diabetes
- gallstone disease
- if you get a migraine or severe headache
- if you have systemic lupus erythematosus ( SLE ) – an autoimmune disease that affects many organs in the body
- epilepsy
- asthma
- otosclerosis (ossification of the middle ear leading to a hearing loss)
- hypertriglyceridemia (elevated blood lipids)
- fluid retention due to heart or kidney disease
- Products containing estrogen can cause or worsen the symptoms of hereditary angioedema. Contact a doctor immediately if you experience symptoms of angioedema such as swelling of the face, tongue, and/or throat and/or difficulty swallowing, or hives and difficulty breathing.
You should contact a doctor immediately and discontinue treatment if any of the following occur:
- Some of what is mentioned in the section ‘Do not use Estradot’
- If skin or whites of the eyes turn yellow (jaundice); it may be a symptom of liver disease
- If your blood pressure rises sharply (symptoms may include headache, fatigue, or dizziness)
- If you are experiencing migraine-like headaches for the first time
- If you become pregnant
- If you get symptoms of a blood clot, such as
- painful swelling and redness of the legs
- sudden chest pain
- breathing difficulties further information, see below “Blood clots in a vein ( thrombosis )”
Note: Estradot is not a contraceptive. If it is less than 12 months since your last period, or if you are under 50, you may still need to use contraception to avoid pregnancy. Consult your doctor.
HRT and cancer
Severe thickening of the uterine lining ( endometrial hyperplasia ) and cancer of the uterine lining (endometrial cancer)
The use of HRT with estrogen alone increases the risk of severe thickening of the uterine lining and cancer of the uterine lining.
By taking progestogen as a supplement to estrogen for at least 12 days in each 28-day cycle, you are protected against this extra risk. The doctor will prescribe the progestogen if you have your uterus left. If your uterus has undergone surgery ( hysterectomy ), you should consult your doctor if you can take the medicine without a progestogen.
For women with the uterus left who do not take HRT, an average of 5 out of 1,000 women aged 50-65 will be diagnosed with endometrial cancer.
For women aged 50-65 who have the uterus left and who take HRT with estrogen alone, between 10 and 60 women out of 1,000 users will be diagnosed with endometrial cancer (ie between 5 and 55 extra cases), depending on dose one and how as long as it is taken.
Estradot 75 and 100 micrograms / 24 hours have higher dose estrogen than other HRT-preparat with the only estrogen. The risk of endometrial cancer when used with progestogens is unknown.
Unexpected bleeding
You will have bleeding once a month (so-called dropout bleeding) when you use Estradot in combination with progestogen. But if you get unexpected bleeding or splashing in addition to your monthly bleeding, and these:
- lasts longer than 6 months
- starts after using Estradot for 6 months
- continues after you stop using Estradot
you should see a doctor as soon as possible.
Breast cancer
Data show that hormone replacement therapy ( HRT ) with a combination of estrogen-progestogen or with estrogen alone increases the risk of breast cancer. The increased risk depends on how long you use HRT. The increased risk is seen within 3 years. When treatment is stopped, the increased risk decreases over time, but it can persist for 10 years or more if you have used HRT for more than 5 years.
Comparison
Of 1,000 women aged 50 to 54 who do not take HRT, an average of 13 to 17 will be diagnosed with breast cancer over a 5-year period.
In women who are 50 years old and start taking HRT with estrogen alone for 5 years, 16-17 cases per 1,000 users (ie 0-3 extra cases) will occur.
In women who are 50 years old and start taking HRT with estrogen-progestogen for 5 years, there will be 21 cases per 1,000 users (ie 4-8 extra cases).
Among women aged 50–59 who do not use HRT, an average of 27 out of 1,000 will be diagnosed with breast cancer over a 10-year period.
In women who are 50 years old and start taking HRT with estrogen alone for 10 years, 34 cases per 1,000 users (ie 7 extra cases) will occur.
In women who are 50 years old and start taking HRT with estrogen-progestogen for 10 years, 48 cases per 1,000 users (ie 21 extra cases) will occur.
Check your breasts regularly. Contact a doctor if you notice changes such as:
- indentations or pits
- changes of the nipple
- nodules you can see or feel
It is also recommended that you participate in a mammography examination when you are called to do so. At the mammogram, you must tell the nurse/healthcare professional who performs the examination that you are using HRT, as this medicine may increase the density of the breasts. An increased density in the breasts can make it more difficult to detect lumps on the mammography images.
Ovarian cancer ( ovarian cancer )
Ovarian cancer is rare – much more rare than breast cancer. Use of HRT with estrogen alone or combined estrogen-progestogen has been associated with a slightly increased risk of ovarian cancer.
The risk of ovarian cancer varies with age. The diagnosis of ovarian cancer will, for example, be made on about 2 women out of 2,000 aged 50 to 54 who do not take HRT for a 5-year period. For women who have taken HRT for 5 years, there will be about 3 cases per 2,000 users (ie about 1 extra case).
How HRT affects the heart and blood circulation
Blood clots in a vein ( thrombosis )
The risk of blood clots in the veins is 1.3–3 times higher for women who take HRT than for those who do not, especially during the first year of treatment.
Blood clots can be serious. If a blood clot ends up in the lungs, it can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, collapse or even lead to death.
You are more likely to get a blood clot in a vein if any of the following apply to you. Tell your doctor if any of the following apply to you:
- You have not been able to walk or stand for a long time due to a major operation, injury or illness (see also section 3, “If you need surgery”)
- You are severely overweight ( BMI over 30 kg / m 2 )
- You have a coagulation disorder that requires long-term treatment with drugs that prevent blood clots
- If a close relative has had a blood clot in the bone, lung, or another organ
- You have SLE (systemic lupus erythematosus)
- You have cancer
The symptoms of a blood clot are described in the section “You should contact a doctor immediately and stop the treatment”.
Comparison
For women in their 50s who do not take HRT, over a 5-year period, an average of 4-7 out of 1,000 are expected to get a blood clot in a vein.
For women in their 50s who have taken HRT with estrogen-progestogen for more than 5 years, 9 – 12 out of 1,000 users are expected to get a blood clot in a vein (ie 5 extra cases)
For women in their 50s without a uterus who take estrogen alone for more than 5 years, 5 – 8 out of 1,000 users are expected to get a blood clot in a vein (ie 1 extra case).
Heart disease (heart attack)
There is no evidence that HRT prevents heart attacks.
For women over the age of 60 who take HRT with estrogen-progestin, the risk of developing heart disease is slightly higher than those who do not take HRT.
For women without a uterus who take estrogen alone, there is no increased risk of developing heart disease.
Stroke (apoplexy)
The risk of stroke is about 1.5 times higher for those who take HRT compared to those who do not. The risk of stroke is age-dependent, therefore the number of cases of stroke increases due to the use of HRT with increasing age.
Comparison
For women in their 50s who do not take HRT, an average of 8 out of 1,000 people is expected to have a stroke over a 5-year period.
For women in their 50s who have taken HRT for more than 5 years, 11 out of 1,000 users are expected to have a stroke (ie 3 extra cases)
Other conditions
- Using HRT does not prevent memory loss. The risk of memory loss may be slightly higher in women who start using HRT after the age of 65. Consult your doctor.
Other medicines and Estradot
Some medicines may affect the way Estradot works, which may lead to irregular bleeding. The following applies:
- Medicines for epilepsy (eg phenobarbital, phenytoin, and carbamazepine)
- Medicines for tuberculosis (eg rifampicin, rifabutin)
- Drugs for HIV – infection (for example, nevirapine, efavirenz, ritonavir, and nelfinavir)
- An herbal medicine containing St. John’s wort ( Hypericum perforatum )
- Other anti-infective drugs (eg ketoconazole, erythromycin).
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicines, including medicines obtained without a prescription and herbal remedies.
Results from blood test analyze
If you need to take a blood sample, tell your doctor, or the person taking the blood sample, that you are using Estradot as it may affect the results of some tests.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Estradot is intended for women whose menstruation has stopped. If you become pregnant, stop using Estradot and consult a doctor. You should not use Estradot if you are pregnant or breast-feeding.
Driving and using machines
No known effects on the ability to drive and use machines.
3. How to use Estradot
Always use this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you are unsure. Your doctor will strive to use the lowest dose, which will give you relief of symptoms, and to use Estradot for the shortest possible time. Talk to your doctor if you do not get any relief from the symptoms, or feel that the dose is too high.
How long should Estradot be used?
It is important to use the lowest possible effective dose and only for as long as necessary. Discuss with your doctor from time to time if he/she thinks you are still in need of treatment.
When should treatment be started?
- If you are not already using any other hormone replacement therapy ( patches or tablets) or if you have used continuous combined hormone replacement therapy (where estrogen and progestin are given daily without interruption), you can start Estradot any day.
- If you switch from a cyclic or sequential hormone replacement therapy(where progestogens are added for 12-14 days of the cycle), you can start treatment with Estradot the day after the end of the previous treatment cycle.
When should Estradot be applied?
- The Estradot patch should be replaced twice a week (every three to four days). It is best to always change the patch on the same day of the week each week (eg Monday and Thursday). On the inside of the Estradot packaging, there is space to note down your dosing schedule. Select the two-day schedule that you intend to follow. Always change patches on the two days of the week you have marked.
- The Estradot patch should be on all the time until it is time to replace it with a new patch.
Any remaining adhesive on the skin can be easily rubbed off. Then apply the new Estradot patch elsewhere on the skin.
Women whose uterus has been removed
Estradot is used continuously, without interruption. Additional treatment with progestogen is not required if you do not have a disease that causes the uterine lining to also grow outside the uterus ( endometriosis ). Familiarize yourself with the general risks associated with hormone replacement therapy (Section 2 “Warnings and Precautions”).
Women with an intact uterus
Your doctor should give you another hormone, progestin, in addition to Estradot to reduce the risk of uterine cancer. Estradot is used continuously and without interruption, while the progestogen tablets are taken for a period of at least 12-14 days each month / 28-day cycle. Familiarize yourself with the general risks associated with hormone replacement therapy (Section 2 “Warnings and Precautions”).
You may experience some irregular bleeding or splashing bleeding during the first months of treatment. Tell your doctor if you experience heavy bleeding or continue to have bleeding or splashing bleeding after a few months of treatment so that your treatment can be re-evaluated if necessary (see section 2 “Unexpected bleeding”).
Where should the Estradot be attached?
Attach the patch to the lower abdomen, below the waist. Avoid the waist as clothes can cause the patch to wear away. Never attach the patch to or near your breasts.
When you have to change patches, ie. twice a week according to your schedule, you should attach the new patch to another location. It should take at least a week before the same skin surface is used again.
Before applying Estradot, make sure that your skin is:
- clean, dry, and cool
- free from powder, oil, moisturizer, or skin lotion
- free from damage and/or irritation
How should the Estradot be attached?
Each patch is individually packaged in a protective envelope. Tear up this envelope at the mark (do not use scissors as the patch may be damaged) and remove the patch.
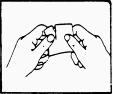
A protective film covers the adhesive side of the patch. The rigid protective film must be removed before the patch is applied to the skin. Apply the patch immediately after opening the envelope and removing the protective film.
Hold the patch with the protective film against you. Remove one-half of the protective film and discard it. Try to avoid your fingers touching the side with glue on.
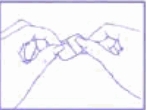
Use the other half of the protective film to hold and apply the adhesive side of the patch to a dry skin surface on the lower abdomen. Press the adhesive side of the patch onto the skin and smooth it out. Fold up the remaining side of the patch.

Grasp the straight edge of the protective film and pull it off the patch.

Apply the rest of the patch to the skin and smooth it out. Press the patch with the palm of your hand for about 10 seconds.

Check that the patch is firmly attached by feeling with a finger around the edges of the patch.

When changing patches, peel off the patch and fold it double with the adhesive side inwards. See section 5, “How to store the Estradot” for instructions on how to dispose of the patch safely. Do not flush it down the toilet.
Other important information
If the patch is firmly attached, it is good to bathe, swim, shower or exercise. If the patch should fall off, e.g. in connection with a bath or shower, shake off the water from the patch. Allow the skin to dry and cool and apply the same patch elsewhere on the lower abdomen (see “Where should the Estradot be attached?”).
If the patch does not adhere properly to the skin, a new patch can be applied. You should continue to follow the same replacement schedule as before, without taking into account the day the new patch was applied.
The patch should be covered when you sunbathe, even in a solarium. When you swim, the patch can be put under the swimsuit.
If you need surgery
If you are going to have surgery, tell your surgeon that you are using Estradot. You may need to stop using Estradot for 4 to 6 weeks before surgery to avoid the risk of blood clots (see section 2, “Blood clots in a vein ( thrombosis )”). Ask your doctor when it is appropriate to start using Estradot again.
If you use more Estradot then you should
Remove the patch if you have used too much Estradot. If you have taken too much medicine or if e.g. If a child has accidentally taken the medicine, contact a doctor, hospital, or the Poison Information Center for risk assessment and advice.
The symptoms of overdose are usually breast tenderness and/or vaginal bleeding. Acute overdose is unlikely due to the route of administration ( patches ). If symptoms persist, consult your doctor.
If you forget to use Estradot
If you forget to change the patch, do so as soon as you remember. Then continue to change patches on the same days as before, without taking into account the day on which the new patch was applied. Never use more than one patch at a time to compensate for forgotten patches.
If you stop using Estradot
When treatment with Estradot is stopped, the risk of breakthrough bleeding or splashing increases. After a long period of discontinuation of treatment, you should consult your doctor before using the patches again.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following diseases are more common in women who take HRT than those who do not:
- Breast cancer
- Severe thickening of the uterine lining ( endometrial hyperplasia ) or cancer of the uterine lining (endometrial cancer)
- Ovarian cancer ( ovarian cancer )
- Blood clots in veins in bones or lungs (venous thromboembolism )
- Heart disease
- Stroke (apoplexy)
- Probable memory loss, if treatment with HRT is started after the age of 65
See section 2 for more information on these side effects.
Some side effects can be serious
The following symptoms require immediate medical attention:
- Sudden chest pain
- Chest pain that radiates to the arm or neck
- Breathing difficulties
- Painful swelling and redness in the legs
- Yellowing of the eyes and face, dark urine, itching (jaundice)
- Unexpected vaginal bleeding or spotting (breakthrough bleeding) when Estradot has been used for some time or after stopping treatment
- Changes in the breasts, such as indentations or pits in the skin of the breasts, changes in the nipples, lumps you can see or feel (breast cancer)
- Painful menstruation
- Unexplained migraine-like headache
Discontinue use of Estradot and consult a doctor immediately if you get any of the above symptoms. Familiarize yourself with the general risks associated with hormone replacement therapy (Section 2 “Warnings and Precautions”).
Other side effects:
The following side effects have also been reported with Estradot. If any of these side effects gets serious, or talk to a doctor or pharmacist.
Very common (may affect more than 1 user in 10):
Headache, skin reactions at the application site (including irritation, burning, rash, dryness, bleeding, bruising, inflammation, swelling, skin pigmentation, hives, and blisters), tension and pain in the breasts, menstrual pain, menstrual disorder.
Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
Depression, nervousness, mood swings, insomnia, nausea, indigestion, diarrhea, abdominal pain, feeling bloated, acne, rash, dry skin, itching, breast enlargement, heavy menstrual bleeding, white or yellowish discharge from the vagina, irregular vaginal bleeding, contractions of the vagina, inflammation of the vagina, abnormal growth of the uterine lining ( endometrial hyperplasia ), pain (eg back pain, arms, legs, wrists, ankles), weakness, fluid accumulation ( edema ) in arms and legs, weight changes.
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
Migraine, dizziness, increase in blood pressure, vomiting, discoloration of the skin, impaired liver function values.
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
Tingling and numbness in hands and feet, blood clots, gallstones, hair loss, muscle weakness, benign growth of smooth muscle in the uterus ( fibroids ), cysts (blisters) near the fallopian tubes, the polyp your cervix, changes in sexual desire, allergic reactions such as rash.
Very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people):
Hives, signs of a severe allergic reaction (including difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, tongue, throat, or skin; dizziness and rash ), decreased tolerance to certain sugars (carbohydrates), involuntary movements that may affect the eyes, head, and neck, contact lens problems, severe skin damage, strong hair growth.
No known frequency(cannot be calculated from the available data):
Breast cancer, abnormal liver function values, allergic skin inflammation, benign lumps in the breast (not cancer).
The following side effects have been reported with other HRTs:
- The disease of the gallbladder
- Various skin diseases:
- dark skin spots, especially on the face and neck, so-called “pregnancy spots” (chloasma)
- painful reddish-purple bumps on the skin (erythema nodosum)
- annular redness or sore rash (erythema multiforme)
- Impaired memory and thought activity (possible dementia)
5. How to store Estradot
- Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
- Store the Estradot in the original package in a cool, dry place. Once the protective envelope has been opened, the patch should be applied to the skin immediately.
- Do not store Estradot in the refrigerator. Do not freeze.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and patch envelope after EXP. The expiration date is the last day of the specified month.
- Do not use this medicine if you notice that the package is damaged or shows signs of being opened earlier.
- After the patch has been removed, it should be folded with the adhesive side inwards and stored safely so that children do not have access to the patch. Return used or unused patches to pharmacies, preferably in the original packaging. Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help to protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
Content declaration
A 25 microgram / 24-hour patch contains 0.39 mg of estradiol (as hemihydrate) and releases approximately 25 micrograms of estradiol per day (24 hours).
A patch of 37.5 micrograms / 24 hours contains 0.585 mg of estradiol (as hemihydrate) and releases approximately 37.5 micrograms of estradiol per day (24 hours).
A 50 microgram / 24 h patch contains 0.78 mg of estradiol (as hemihydrate) and releases approximately 50 micrograms of estradiol per day (24 hours).
A 75 microgram / 24 h patch contains 1.17 mg of estradiol (as hemihydrate) and releases approximately 75 micrograms of estradiol per day (24 hours).
A 100 microgram / 24 h patch contains 1.56 mg of estradiol (as hemihydrate) and releases approximately 100 micrograms of estradiol per day (24 hours).
- The active substance is estradiol (as hemihydrate)
- The other ingredients in the adhesive are acrylic and silicone adhesive, oleyl alcohol, propylene glycol, povidone (E 1201).
- The patch film is an ethylene/vinyl acetate copolymer and vinylidene chloride/methyl acrylate copolymer laminate.
- The protective film (which is removed before application) is a polyester film coated with a fluoropolymer.
What the medicine looks like and the contents of the pack
Estradot 25 micron / 24 hours is a rectangular patch of 2.5 cm 2 with rounded corners. The patch consists of a pressure-sensitive, adhesive layer containing estradiol and is provided with a translucent polymer film on one side and a protective film on the other.
Estradot 37.5 micron / 24 hours is a rectangular patch of 3.75 cm 2 with rounded corners. The patch consists of a pressure-sensitive, adhesive layer containing estradiol and is provided with a translucent polymer film on one side and a protective film on the other.
Estradot 50 micron / 24 hours is a rectangular patch of 5 cm 2 with rounded corners. The patch consists of a pressure-sensitive, adhesive layer containing estradiol and is provided with a translucent polymer film on one side and a protective film on the other.
Estradot 75 micron / 24 hours is a rectangular patch of 7.5 cm 2 with rounded corners. The patch consists of a pressure-sensitive, adhesive layer containing estradiol and is provided with a translucent polymer film on one side and a protective film on the other.
Estradot 100 micron / 24 hours is a rectangular patch of 10 cm 2 with rounded corners. The patch consists of a pressure-sensitive, adhesive layer containing estradiol and is provided with a translucent polymer film on one side and a protective film on the other.
Estradot is available in five different strengths: 25, 37.5, 50, 75 and 100 micrograms / 24 hours. Not all strengths may be marketed.
Estradot is supplied in cartons of 2, 8, 24, and 26 patches. Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorisation Holder
Novartis Sverige AB
Box 1218
164 28 Kista
Manufacturer:
Novartis Pharmacéutica, SA
Ronda de Santa María, 158
08210 Barberá del Vallés (Barcelona)
Spain
Novartis Pharma GmbH
Roonstrasse 25
D-90429 Nuremberg
Germany