500 mg/ml oral solution
sodium oxybate
What Xyrem is and what it is used for
Xyrem contains the active substance sodium oxybate. Xyrem works by strengthening nighttime sleep, but the exact mechanism of action is unknown.
Xyrem is used to treat narcolepsy with cataplexy in adults, adolescents, and children from 7 years of age.
Narcolepsy is a sleep disorder that can include sleep attacks during the normally awake part of the day, as well as cataplexy, sleep paralysis, hallucinations, and poor sleep. Cataplexy is an attack of sudden muscle weakness or paralysis without loss of consciousness, in response to a sudden emotional reaction such as anger, fear, joy, laughter, or surprise.
What you need to know before you take Xyrem
Do not take Xyrem
- if you are allergic to sodium oxybate or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6),
- if you have succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency (a rare metabolic disorder),
- if you suffer from major depression,
- if you are treated with medicines containing opioids or barbiturates.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking Xyrem:
- if you have breathing or lung problems (and especially if you are overweight), as Xyrem can cause breathing difficulties,
- if you have or have previously had a depressive disorder, suicidal thoughts, anxiety, psychosis (a mental disorder that may involve hallucinations, incoherent speech, or disorganized and agitated behavior), or bipolar disorder,
- if you have heart failure, hypertension (high blood pressure ), liver or kidney problems, as your dose may need to be adjusted,
- if you have abused drugs in the past,
- if you have epilepsy as the use of Xyrem is not recommended in this condition,
- if you have porphyria (a rare metabolic disorder).
If any of these apply to you, tell your doctor before taking Xyrem.
While taking Xyrem, tell your doctor right away if you experience bedwetting and incontinence (both urine and stool), feel confused, hallucinate, sleepwalk or have abnormal thoughts. These effects are uncommon, but if they do occur, they are usually mild to moderate in nature.
If you are elderly, your doctor will closely monitor your condition to check whether Xyrem is having the desired effects.
There is a well-known risk of abuse of Xyrem. There are cases of addiction following the illicit use of sodium oxybate.
The doctor will ask if you have abused drugs before you start taking Xyrem and while you are using this medicine.
Children and young people
Xyrem can be taken by adolescents and children from the age of 7 and who weigh more than 15 kg.
Xyrem should not be taken by children under 7 years of age or children weighing less than 15 kg.
If you are a child or teenager, your doctor will monitor your body weight regularly.
While the doctor adjusts the dose, which may take several weeks, the parent/caregiver should carefully monitor the child’s breathing for the first 2 hours after taking sodium oxybate, to assess for abnormalities in breathing, such as short periods of respiratory arrest while the child is asleep, loud breathing and bluish color on the lips and face. If abnormalities in breathing are observed, medical attention should be sought and the physician informed as soon as possible. If an abnormality is observed after the first dose, the second dose should not be given. If no deviation is observed, the second dose can be given. The second dose should not be given earlier than 2.5 hours or later than 4 hours after the first dose one.
If you are or have been upset, especially if you are very depressed or have lost interest in life, you must tell your doctor or care provider.
Other medicines and Xyrem
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines.
In particular, Xyrem should not be taken with sleeping pills or medicines that reduce the activity of the central nervous system (the central nervous system is the part of the body that deals with the brain and spinal cord).
Also, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any of the following types of medicine:
- drugs that increase activity in the central nervous system
- medication for depression
- medicines that can be converted similarly in the body (eg valproate, phenytoin, or ethosuximide used to treat seizures)
- topiramate (used to treat epilepsy )
If you are taking valproate, your daily dose of Xyrem will need to be adjusted (see section 3) as this may lead to an interaction with valproate.
Xyrem with alcohol
You must not drink alcohol while taking Xyrem, as its effects may be increased.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, consult your doctor before using this medicine.
There are very few women who have taken Xyrem at any time during pregnancy and a few of these have miscarried. The risk of taking Xyrem during pregnancy is unknown and therefore the use of Xyrem by pregnant women or women planning to become pregnant is not recommended.
Patients taking Xyrem should not breastfeed as Xyrem is known to pass into breast milk. Changes in sleep patterns have been observed in breastfed infants whose mothers were exposed to sodium oxybate.
Driving ability and use of machinery
Xyrem will affect you if you drive or use tools or machines. Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or perform any activity that is dangerous or requires you to be mentally alert for at least six hours after taking Xyrem. From the time you start taking Xyrem until you know if it makes you sleepy the next day, be extremely careful when driving, operating heavy machinery, or doing anything else that may be dangerous or requires your full mental attention.
For pediatric patients, physicians, parents, and caregivers are advised that the waiting time to perform activities requiring mental alertness or motor coordination that may involve physical risk may need to be longer than 6 hours, depending on individual sensitivity.
Xyrem contains sodium
This medicine contains 182.24 mg of sodium (the main ingredient in common/table salt) per gram. This corresponds to 9.11% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium for adults.
Consult a doctor or pharmacist if your need for sodium oxybate (Xyrem) is 2 g or more daily for an extended period, especially if you have been prescribed a low-salt (low-sodium) diet.
How to take Xyrem
Always take this medicine as directed by your doctor or pharmacist. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you are unsure.
It is important that you only use the syringe included in the package when preparing your dose of Xyrem. The Xyrem syringe has two different measuring scales, one scale may be more helpful to you than the other, depending on the dose your doctor has prescribed. By looking at each scale you will see which one has an exact marking for your dose.
Adults taking Xyrem alone
- For adults, the recommended starting dose is 4.5 g each day, which is given as two separate doses of 2.25 g each.
- Your doctor may gradually increase the dose up to a maximum of 9 g each day, which is given as two separate doses of 4.5 g each.
- Take Xyrem by mouth twice each night:
- Take the first dose at bedtime and the second dose 2.5 to 4 hours later. You may need to set an alarm clock to wake up and take the second dose.
- Food reduces the amount of Xyrem absorbed by the body. It is therefore best if you take Xyrem at fixed times 2 to 3 hours after a meal.
- Prepare both doses before going to bed.
- Take the doses within 24 hours of preparation.
Adolescents and children aged 7 years and older and weighing 15 kg or more taking Xyrem alone
For children who are 7 years of age and older and who weigh 15 kg or more, a doctor will determine the correct dose based on body weight.
Your doctor will determine the right dose for you. Do not exceed the dose prescribed for you.
Adults – Xyrem together with valproate
Your doctor will adjust the dose of Xyrem if you take valproate together with Xyrem.
- For adults, the recommended starting dose of Xyrem in simultaneous treatment with valproate is 3.6 g each day, which is given as two separate doses of 1.8 g each.
- Take the first dose at bedtime and the second dose 2.5 to 4 hours later.
Adolescents and children 7 years of age and older and weighing 15 kg or more taking Xyrem with valproate
If you take valproate together with Xyrem, your doctor will adjust the dose of Xyrem.
Kidney or liver problems
- If you have kidney problems, you should consider reducing your salt intake.
- If you have problems with the liver, the starting dose should be halved.
Instructions for diluting Xyrem
The following instructions explain how to prepare Xyrem. Read the instructions carefully and follow them step by step. Do not allow children to prepare Xyrem.
To help you, the Xyrem box contains 1 bottle of medication, a measuring syringe ( with two different measuring scales ), and two dosing cups with child-proof lids.
Step 1
- Remove the bottle cap by pressing down and turning the cap counterclockwise (to the left).
- After removing the cap, place the bottle upright on a tabletop.
- There is a plastic-covered foil seal at the top of the bottle that must be removed before the bottle is used for the first time.
- Hold the bottle in an upright position and at the same time push the bottle adapter into the neck of the bottle. This only needs to be done the first time the bottle is opened. The adapter can then remain in the bottle for all later use.
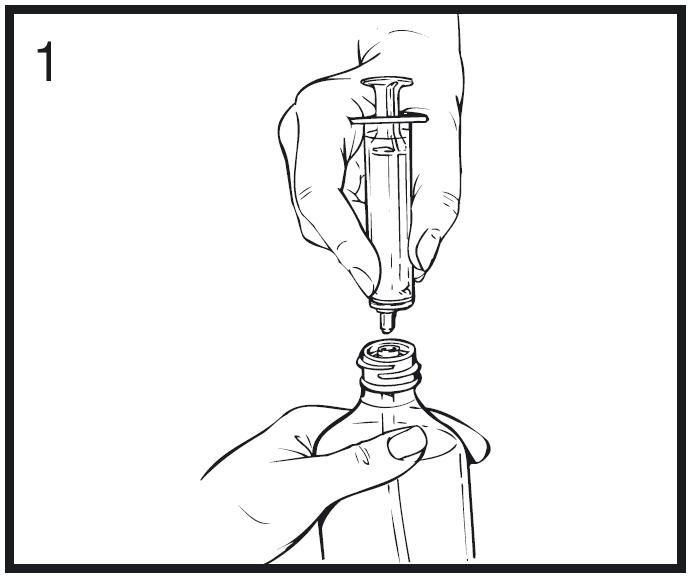
step 2
- Then insert the tip of the measuring syringe into the center opening of the bottle and press firmly downwards.
- While holding the bottle and syringe with one hand, draw up the prescribed dose with the other hand by pulling the plunger. NOTE: Medicine will not flow into the syringe unless the bottle is held upright
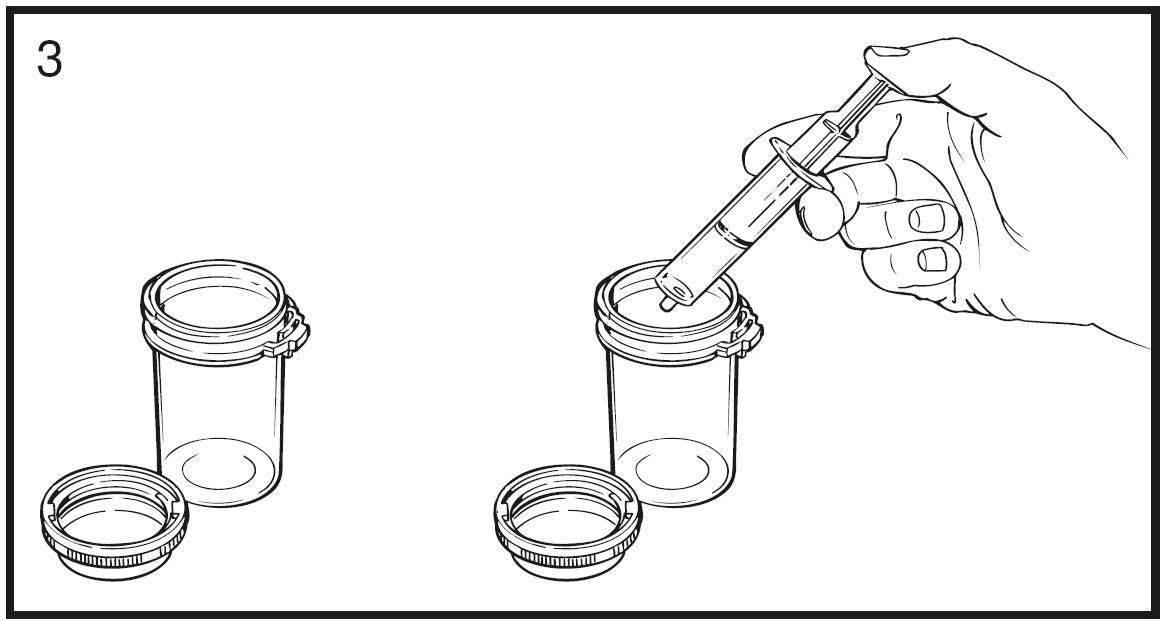
Step 3
- Remove the syringe from the center opening of the bottle.
- Empty the medication from the syringe into one of the dosing cups provided by depressing the plunger. Repeat this step with the other dosing cup.
- Then add about 60 ml of water to each dosing cup (60 ml is about four tablespoons).
Step 4
- Place the supplied lids on the dosing cups and turn each lid clockwise (to the right) until it clicks and locks into the childproof position (note: as the lid of the dosing cup can be turned both clockwise and counter-clockwise, it is only when the click sound is heard that the lid is secure is locked in the childproof mode).
- Rinse out the syringe with water.
- Just before bedtime:
- Adult patients should place the second dose near the bed.
- The parent or caregiver of adolescents and children aged 7 years and older should not leave the second dose near the child’s bed or within reach of the child.
- You may need to set an alarm clock so that you wake up to take the second dose no earlier than 2.5 hours and no later than 4 hours after your first dose.
Then do the following:
- Remove the cap from the first dosing cup by pressing down on the childproof locking tab and turning the cap counterclockwise (to the left).
- Drink the entire first dose while sitting in bed, put the lid back on the cup, and then immediately lie down. For children who sleep longer than 8 hours, but less than 12 hours, the first dose can be given after the child has slept for 1 to 2 hours
- When you wake up or wake the child 2.5 to 4 hours later, remove the cap from the second dosing cup. Drink the entire second dose while sitting in bed and immediately before lying down to continue sleeping. Put the lid back on the other cup.
If you feel that Xyrem has too strong or too weak an effect, contact your doctor or pharmacist.
If you have taken too much Xyrem
Symptoms of Xyrem overdose include agitation, confusion, impaired mobility, impaired breathing, blurred vision, profuse sweating, headache, vomiting, decreased level of consciousness leading to coma and seizures, excessive thirst, muscle cramps, and weakness. If you take or accidentally take more Xyrem than you were told to take, you should immediately seek emergency medical help. You must take the labeled medicine bottle with you, even if it is empty.
If you forget to take Xyrem
If you forget to take the first dose, take it as soon as you remember, then continue as before. If you miss the second dose, skip that dose and do not take Xyrem again until the next night. Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
If you are not sure if you took Xyrem
If you are not sure whether you took a dose, do not take another dose to reduce the risk of overdose.
If you stop taking Xyrem
You should continue to take Xyrem for as long as your doctor tells you. You may find that your cataplexy attacks come back if you stop your medication and you may experience insomnia, headache, anxiety, dizziness, trouble sleeping, sleepiness, hallucination, and abnormal thoughts.
If you forget to take Xyrem for more than 14 consecutive days, you should contact your doctor as you should resume using Xyrem at a reduced dose.
If you have any further questions about this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. These are usually mild to moderate.
Adults – the most common side effects observed in clinical studies (occurring in 10% to 20% of patients):
- dizziness
- nausea
- headache.
If you experience any of these side effects, tell your doctor immediately.
Children and adolescents – most common side effects observed in a clinical study:
- bedwetting (18.3%)
- nausea (12.5%)
- vomiting (8.7%)
- weight loss (8.7%)
- decreased appetite (6.7%)
- headache (5.8%)
- dizziness (5.8%)
- suicidal thoughts (1%)
- feeling mentally unwell (loss of contact with reality) (1%)
If you experience any of these side effects, tell your doctor immediately
Side effects in adults and children are the same. If you experience any of the side effects listed below, tell your doctor immediately:
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 users):
- nausea
- dizziness
- headache
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 users):
- sleep problems including insomnia, abnormal dreams, sleep paralysis, sleepiness, nightmares, sleepwalking, bedwetting, excessive daytime sleepiness, trouble falling asleep in the middle of the night
- feeling drunk, tremors, confusion/disorientation, blurred vision, loss of balance, falling, feeling like everything is spinning ( vertigo )
- palpable heartbeats, increased blood pressure, shortness of breath
- vomiting, stomach ache, diarrhea
- anorexia, decreased appetite, weight loss
- weakness, fatigue, sedation
- sweating
- Depression
- muscle cramps, swelling
- joint pain, back pain
- attention disorder, disturbed sensitivity especially to touch, abnormal sense of touch, abnormal taste
- anxiety, nervousness
- urine leakage (urinary incontinence)
- snoring, stuffy nose
- rash
- sinusitis, inflammation of the nose and throat
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 users):
- psychosis (mental disorder that may involve hallucinations, incoherent speech, or disorganized and agitated behavior)
- the feeling of being haunted ( paranoia ), abnormal thinking, hallucinations, agitation, suicide attempts
- trouble falling asleep, restless legs (a form of numbness and tingling in the legs)
- oblivion
- myoclonus (involuntary muscle contractions)
- involuntary bowel movement
- hypersensitivity
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from available data):
- cramps
- reduced breathing depth or frequency, short pauses in breathing during sleep
- hives
- suicidal thoughts, delusions, thoughts of committing violent acts (including harming others)
- irritability, aggressiveness
- elation ( euphoria )
- panic attack
- mania/bipolar disorder
- dry mouth, dehydration
- swelling of the face ( angioedema )
- bruxism (teeth grinding and jaw clenching)
- pollakiuria/urinary urgency (increased need to urinate)
- tinnitus (noises in the ears such as ringing or buzzing)
- sleep-related eating disorder
- increased appetite
- unconsciousness
- dyskinesia (eg, abnormal, uncontrolled movements of the arms and legs)
- dandruff
- increased sex drive
- nocturia (increased urination at night)
- suffocating feeling
If you experience any of the side effects listed above, tell your doctor immediately.
How to store Xyrem
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Use before the expiry date stated on the bottle after (EXP). The expiration date is the last day of the specified month.
After dilution in the dosing cup, the diluted medicine should be used within 24 hours.
Once you have opened a bottle of Xyrem, any contents that you have not used within 90 days of the opening should be discarded.
Medicines must not be thrown into the drain or among the household waste. Ask the pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer used. These measures will help to protect the environment.
Contents of the packaging and other information
Contents declaration
- The active substance is sodium oxybate. Each ml contains 500 mg sodium oxybate.
- Other ingredients are purified water, malic acid, and sodium hydroxide.
Appearance and package sizes of the medicine
Xyrem is supplied in a 240 ml amber plastic bottle containing 180 ml of oral solution and closed with a child-resistant screw cap. When the bottle is delivered, there is a seal of plastic-covered foil at the top of the bottle under the screw cap. Each package contains one bottle, one bottle adapter, one plastic measuring syringe, and two dosing cups with child-resistant lids.
Xyrem is a clear to the slightly translucent solution.
Marketing Authorisation Holder
UCB Pharma SA, Allée de la Recherche 60, B-1070 Brussels, Belgium
Manufacturer
UCB Pharma SA, Chemin du Foriest, B-1420 Braine l’Alleud, Belgium
Your doctor should have given you an information package about Xyrem, which contains a booklet on how to take the medicine, patient information with frequently asked questions and answers, and a patient card.
Contact the representative of the Marketing Authorization Holder if you would like to know more about this medicine:
UCB Nordic A/S
Tel: + 46 / (0) 40 29 49 00