 |
TESTING THE PURCHASES SYSTEM |
| << Control Procedures over Purchases and Payables |
| TESTING THE PAYROLL SYSTEM >> |
Fundamentals
of Auditing ACC 311
VU
Lesson
26
TESTING
THE PURCHASES SYSTEM
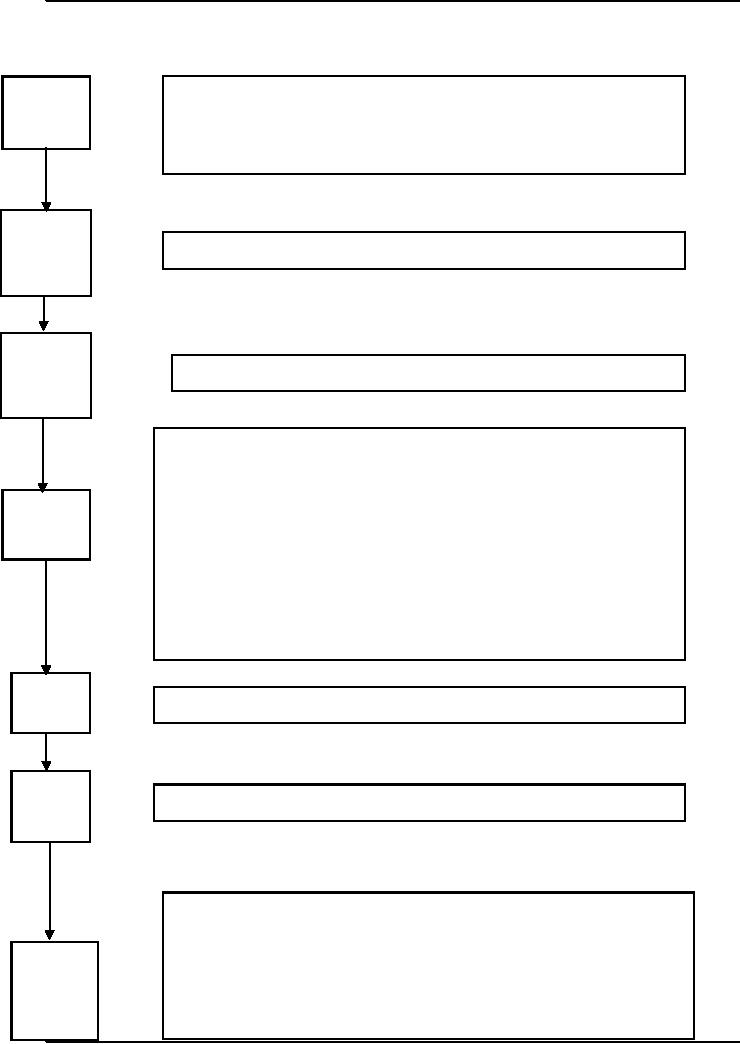
Test
for:
Purchase
(i)
Evidence of a sequence check.
Order
(ii)
Evidence of approval.
(iii)
Adherence to authority
limits
Goods
Test f o r
evidence of a sequence check
Received
Note
Goods
Test f o r
evidence of a sequence check.
Returned
Note
Test
for:
1.
Serial
numbering
2. Evidence of
sequence check
Purchase
3. Evidence of
matching purchase invoices with goods received notes and
purchase
Invoice
orders.
4. Evidence of
checking casts, extensions and tax
treatment
5. Evidence of
account coding.
6.
Initialing of
invoice grid for work
done.
7. Approval
of purchase invoice for further
processing.
Credit
Note
Test
for evidence of matching credit notes to
goods returned notes
Payables
Test
for evidence of authorization of
adjustments to payables ledge
ledger
Text
for:
(i)
Evidence of
review of reconciliation of purchase ledger
listing.
Payables
(ii)
Evidence of
authorization of adjustments to purchase ledger
control account.
Ledger
control
93

Fundamentals
of Auditing ACC 311
VU
CONTROL
OBJECTIVES
The
control objectives in respect of a
wages and salaries system
are as follows:
(a)
Payment of wages and
salaries should be made only
in respect of the client's authorized
employees.
(b)
Payment should be made at
authorized rates of
pay.
(c)
Wages and salaries payments
should be in accordance with
records of work performed,
e.g. time, output,
commissions
on sales.
(d)
Payroll and payroll deductions (tax
and social security) should
be calculated accurately.
(e)
Payment should be made to
the correct
employees.
(f)
Liabilities to the tax authorities
for tax and social
security should be properly
recorded.
94
Table of Contents:
- AN INTRODUCTION
- AUDITORSí REPORT
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Auditing
- OBJECTIVE AND GENERAL PRINCIPLES GOVERNING AN AUDIT OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
- What is Reasonable Assurance
- LEGAL CONSIDERATION REGARDING AUDITING
- Appointment, Duties, Rights and Liabilities of Auditor
- LIABILITIES OF AN AUDITOR
- BOOKS OF ACCOUNT & FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
- Contents of Balance Sheet
- ENTITY AND ITS ENVIRONMENT AND ASSESSING THE RISKS OF MATERIAL MISSTATEMENT
- Business Operations
- Risk Assessment Procedures & Sources of Information
- Measurement and Review of the Entityís Financial Performance
- Definition & Components of Internal Control
- Auditing ASSIGNMENT
- Benefits of Internal Control to the entity
- Flow Charts and Internal Control Questionnaires
- Construction of an ICQ
- Audit evidence through Audit Procedures
- SUBSTANTIVE PROCEDURES
- Concept of Audit Evidence
- SUFFICIENT APPROPRIATE AUDIT EVIDENCE AND TESTING THE SALES SYSTEM
- Control Procedures over Sales and Debtors
- Control Procedures over Purchases and Payables
- TESTING THE PURCHASES SYSTEM
- TESTING THE PAYROLL SYSTEM
- TESTING THE CASH SYSTEM
- Controls over Banking of Receipts
- Control Procedures over Inventory
- TESTING THE NON-CURRENT ASSETS
- VERIFICATION APPROACH OF AUDIT
- VERIFICATION OF ASSETS
- LETTER OF REPRESENTATION VERIFICATION OF LIABILITIES
- VERIFICATION OF EQUITY
- VERIFICATION OF BANK BALANCES
- VERIFICATION OF STOCK-IN-TRADE AND STORE & SPARES
- AUDIT SAMPLING
- STATISTICAL SAMPLING
- CONSIDERING THE WORK OF INTERNAL AUDITING
- AUDIT PLANNING
- PLANNING AN AUDIT OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
- Audits of Small Entities
- AUDITORíS REPORT ON A COMPLETE SET OF GENERAL PURPOSE FINANCIALSTATEMENTS
- MODIFIED AUDITORíS REPORT