 |

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Lesson
24
REVIEW-1
Lecture 24
is mainly to review what
ever we covered so far during
our 23 lectures. The idea
was to give
you
opportunities to review and refresh the topics we
covered so far.
Title
of our course/subject MGT 623 is
"Leadership
and Team
Management"
We
can divide this topic
into two components, the
Leadership and team dynamics to understand
each
component
separately and ultimately understanding
the subject Leadership & team
management and
applying
these concepts at
workplace.
Today's
effective leaders must have the
capability and confidence to build
and develop focused
and
motivated
teams that deliver
outstanding operational performance in
line with the strategic goals of
the
organization.
This course highlights the
processes and techniques leaders have at
their disposal to
develop
their effectiveness and maintain top
team performance.
The
course derives its roots from the
basics of organizational management. In
order to build a strong
footing
for learning of the concepts of
leadership and team management, we need
to understand the
concepts
of organization.
I
tried to give basic
information about organization. An
Organization
is
a deliberate arrangement of
people
to accomplish some specific purpose or
goals.
As
we are discussing the leadership and team
management the main focus reference to an
organization
are
the people. Focusing
on People: the Key to
Success.
Organizational
Performance:
The
organizational performance is judge by
their profit, effectiveness and
efficiency.
Productivity
An
overall measure of the quantity
and quality of work performance
with
resource
utilization taken into
account.
Performance
effectiveness
An
output measure of task or
goal accomplishment.
Performance
efficiency
An
input measure of the resource
costs associated with goal
accomplishment.
That
is the Role of Management?
Management
is more concern about building
working relationship with others,
help the team members
to
develop the skills for
better performance, providing help to
develop team work among them
and
providing
them with a conducive/quality environment
for performance and satisfaction. In
this
connection,
management should know that
each individual is a value-added
worker and if they
are
satisfied
and motivated, organization can achieve
their goals efficiently and
effectively.
What
is Leadership?
Concept
of Leadership is very important in
organizations because leaders
are the ones who make
things
happen.
Without leaders, an organization
would find it difficult to get
things done. Leaders mostly
help
others
to learn just as a coach
would help players play
instead of playing himself. This
lecture
introduces
students to the concept of leadership and
leadership effectiveness by providing
working
definitions
and by emphasizing the cultural
limitations of the concepts. It presents
several cultural
models
that are used throughout the
text to explain cross-cultural difference
in leadership. There is no
90

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
universally
agreeable definition of leadership. Just
go and type "leadership" on Google
and you can
find
more than 186,000,000 different
pages of reference on web. It involves
influencing attitudes,
behaviors,
beliefs and feelings of people and
believes to be an important
topic.
Peter
Drucker the guru of Management
defines Leadership as "The
only definition of a leader is
someone
who has followers." While
John C Maxwell defines "leadership is
influence - nothing more,
nothing
less." According to John W. Gardner
Leadership is "the process of
persuasion and example by
which
an individual (or leadership team)
induces a group to take
action that is in accord
with the
leader's
purpose, or the shared purposes of
all."
Leaders
are
those persons who are
able to influence others and
who possess managerial
authority.
Leadership,
then, is the ability to influence a
group toward the achievement of goals.
Trust
is
the
foundation
of leadership. Leaders develop an
environment of trust where the organizational
members
tend
to establish a follower-ship with the
leader.
Successful
leaders.....
·
Communicate
·
Motivate
·
Build Teams
·
Solve Problems
·
Resolve Conflicts
·
Manage Change
·
Promote Creativity
·
Communicate
·
Motivate
·
Build Teams
·
Solve Problems
·
Resolve Conflicts
·
Manage Change
·
Promote Creativity
Successful
leaders-Challenge the process, Inspire a
shared vision, Enable others
to act, Model the
way,
Encourage
the followers, Change agent, Take
followers to the destination
Do
we need leaders?
Consider
how life would be different
without leadership
·
Families
·
Education
·
Businesses
·
Service associations
·
Teams
·
Countries
·
World
Why
Study Leadership?
·
Understanding
leadership helps organizations:
select
the right people for leadership
positions
train
people in leadership positions to
improve
·
Who
benefits?
leaders
followers
organizations
Leaders
are Effective When
o
The
group achieves its
goals
91

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
o
Internal
processes are smooth
o
The
group can adapt to external
forces
Why
Leaders Fail?
·
Insensitive, abrasive, bullying
style
·
Cold, aloof,
arrogant
·
Betrayal of personal trust
·
Overly ambitious
·
Specific performance problems
·
Micro-managing--does not build a
team
·
Unable to select good
subordinates
Leaders
Vs Managers
Leaders
Managers
Innovate
Administer
Develop
Maintain
Inspire
Control
Take the long-term
Have a short-term
view
view
Ask how and when
Ask what and why
Imitate
Originate
Accept the status
quo
Challenge the status
quo.
Do things right
Do the right things
What
"Followers" Expect
·
Traits
desired in a leader:
Integrity
Consistency
Listen and discern
needs
Open-minded
Honest w/themselves; Inspire
trust
Calm
·
Stays
focused while handling a
volatile situation
One who brings out the
best in me
Trust:
The Foundation of Leadership
The
foundations of trust are Integrity,
Competence, Consistency, Loyalty and
Openness.
Importance
of Followers
·
Followers'
actions/attitudes influence their
leader
For better or
worse
·
Qualities
of effective followers are
same ones we want in
leaders
·
Performance
of leaders & followers are
variables that depend upon one
another
92

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Follower
Traits That Influence the
Leadership Process are like
Values Norms,
Cohesiveness,
Expectations,
Personality, Maturity, Competency levels,
Motivation, Number of followers,
Trust and
confidence
etc.
What
Followers Want
·
Leaders
to be Honest, Forward
-Thinking,
Inspiring
and Competent
·
Colleagues
to be Honest,
Cooperative, Dependable and Competent
Trait
Approach: "Leaders
are born, not made."
Leaders possess certain
traits that make them
leaders.
Common
Traits like Intelligence,
Dominance, Self-confidence, High
energy level, Task
relevant
knowledge
etc.
Behavior
Approach: There
are behavioral determinants of leadership
which can be learned.
People
can
be trained to be effective
leaders.
Contingency
Approach/Theory: Effective
leaders don't use a single
style; they use many
different
styles
and make adjustments based
on the situation.
An
important but often
overlooked contingency
variables
is national culture
Leadership
approaches/New theory:
·
Transformational
Leadership: Focus on
influencing attitudes and assumptions of
staff.
Building
commitment to the mission and objective of the
organisation
·
Transactional
Leadership: Focus on
rewards in exchange for
motivation, productivity
and
effective task accomplishment
·
Charismatic
Leadership: Traits of a
Charismatic Leader are Self-confidence,
with A
vision,
Strong conviction in that
vision, Out of the ordinary
behavior, The image of a
change
agent
Now
we will shift our focus to leader as an
individual and try to understand the
personality and
person
part
of that individual known as "a
leader". To understand this let's
try to start from basic
personality
part.
Personality:
Personality
is the pattern of relatively enduring
ways in which a person feels, thinks, and
behaves.
Personality
is determined by nature (biological
heritage) and nurture (situational
factors).
Organizational
outcomes that have been shown to be
predicted by personality include
job satisfaction,
work
stress, and leadership effectiveness.
Personality is not a useful
predictor of organizational
outcomes
when there are strong situational
constraints. Because personality tends to
be stable over
time,
managers should not expect to
change personality in the short run.
Leaders should accept
employees'
personalities as they are and
develop effective ways to deal
with people. To understand
leader
we need to understand him/her as
individual. For this
understanding personality indicator is
very
important.
Some
Major Forces Influencing
Personality:
Personality
Determinants: An early
argument centered on whether or not
personality was the result
of
heredity
or of environment. Personality appears to
be a result of both influences.
Today, we recognize a
third
factor--the situation.
Personality
is the function of "The Person" and "The
Environment. In other words it is a
Person-
Situation
Interaction.
93

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Types
of work-related behaviour:
Values:
Values
Represent Basic Convictions
·
A
specific mode of conduct or end-state of
existence is personally or socially
preferable to
an
opposite or converse mode of conduct or
end-state of existence.
·
They
have both content and intensity
attributes.
·
An
individual's set of values ranked in
terms of intensity is considered the person's
value
system.
·
Values
have the tendency to be stable.
·
Many
of our values were established in our
early years from parents,
teachers, friends,
and
others.
Importance
of Values
Values
lay the foundation for the
understanding of attitudes and
motivation.
Values
generally influence attitudes and
behaviors. We can predict
reaction based on
understanding
values.
Attitudes:
Attitudes
are evaluative statements
that are either favorable or
unfavorable concerning
objects,
people, or events. Attitudes
are not the same as values,
but the two are
interrelated.
Main
Components of Attitudes: There
are three components of an
attitude
·
Cognitive
component
The
employee thought he deserved the
promotion (cognitive)
·
Affective
component
The
employee strongly dislikes
his supervisor (affective)
·
Behavioral
component
The
employee is looking for another
job (behavioral). In organizations,
attitudes are
important
because of the behavioral
component
Continuing
from previous discussion, to understand
individual knowing the basis of
behavior of
individuals
is very important.
Why
is it important to know an individual's
values? Although Values strongly
influence a person's
perception,
attitudes and ultimately the behavior.
Knowledge of an individual's value
system can
provide
insight into his/her
attitudes.
Leaders
should be interested in their employees'
attitudes because attitudes give
warnings of potential
problems
and because they influence
behavior. Satisfied and committed
employees, for instance, have
lower
rates of turnover and
absenteeism.
Individual
Behavior-Perception: Perception is the
process by which individuals
select, organize, and
interpret
the input from their senses
(vision, hearing, touch,
smell, and taste) to give
meaning and order
to
the world around them. Interpretation of
a situation is known as perception.
Through perception,
people
try to make sense of their
environment and the objects, events, and
other people in it. Play
major
role
on the behaviors of the people.
·
Perception
has three components:
The
perceiver is the
person trying to interpret
some observation that he or
she has just
o
made,
or the input from his or her
senses.
The
target of
perception is whatever the perceiver is
trying to make sense of.
In
o
organizational
behavior, we are often
concerned with person
perception, or another person
as
the target of perception.
94

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
o
The
situation is the
context in which perception
takes place.
Characteristics
of all three components influence
what is actually
perceived
Type
A and Type B Personalities: Individuals
who are Type
A have
an intense desire to achieve,
are
extremely
competitive, have a sense of urgency, are
impatient, and can be hostile. Because
these individuals
are
so driven, they can be difficult to
get along with. These
individuals, though they have the
drive to
accomplish,
do not do well in situations
that require a lot of interaction with
others. These individuals
are
more
likely to have more conflicts..
Type
B individuals
are more relaxed and
easygoing. Type B
characterized
as easy-going, relaxed, and
able to listen carefully and
communicate more precisely than
Type-A
individual.
Positive
Affect - an
individual's tendency to highlight the
positive
aspects
of oneself, other people,
and
the
world in general
Negative
Affect - an
individual's tendency to highlight the
negative
aspects
of oneself, other
people,
and
the world in general
The
Big Five Model of Personality:
An
impressive body of research supports
that five basic
dimensions
underlie all other
personality dimensions. The five
basic dimensions are:
Extraversion.
Comfort
level with relationships.
Extroverts tend to be gregarious,
assertive, and
sociable.
Interesting in getting ahead,
Leading through influencing,
Individuals are outgoing;
Likes to
meet
new people and willing to
confront others. Introverts tend to be
reserved, timid, and
quiet.
Agreeableness:
Individual's
propensity to defer to others.
High agreeableness
people--cooperative,
warm,
and trusting. Traits related to
getting along with others.
Characteristics include warm,
easygoing,
compassionate,
friendly, and sociable. Individuals
typically are sociable and have lots of
friends. Low
agreeableness
people--cold, disagreeable, and
antagonistic.
Conscientiousness:
A
measure of reliability. A high
conscientious person is responsible,
organized,
dependable,
and persistent. Includes traits related
to achievement. Traits include high
credibility,
conformity,
and organization. Individuals typically
work hard and put in extra
time and effort to
meet
goals.
Those who score low on
this dimension are easily
distracted, disorganized, and
unreliable.
Emotional
stability: A person's
ability to withstand stress. People
with positive emotional
stability
tend
to be calm, self-confident, and secure.
The fine line between stable
and unstable. Stable is being
calm,
good under pressure,
relaxed, and secure.
Unstable is nervous, poor under
pressure, insecure.
Those
with high negative scores
tend to be nervous, anxious, depressed,
and insecure.
Openness
to experience: The range of
interests and fascination with
novelty. Extremely open
people
are
creative, curious, and artistically
sensitive. Trait related to being
willing to change and try
new
things.
Individuals typically are
willing to take calculated risks.
Those at the other end of the
openness
category
are conventional and find
comfort in the familiar.
What
the MBTI? MBTI is an
inventory of preferences for
behavior and not a diagnostic
psychological
test
for identifying dysfunction or
abilities. It tells you
about your preferences for
orienting yourself in
the
world, and for gathering
information and making decisions.
Katharine
Briggs &
Isabel
Myers, mother-daughter
team
developed Jung's types into the
Myers
Briggs
Type Indicator (MBTI). There
are four categories, each
with two sub-categories are
as follows;
The
4 dimensions: Personality
type dependent on 4 dimensions: It is a 100-question
personality test
that
asks people how they
usually feel or act in
particular situations. Individuals
are classified as:
1.
Extroverted or introverted (E or
I).
2.
Sensing or intuitive (S or
N).
3.
Thinking or feeling (T or
F).
95

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
4.
Perceiving or judging (P or J).
These
classifications are then
combined into sixteen
personality types. For
example:
INTJs
are
visionaries. They usually have
original minds and great drive for
their own ideas
and
purposes. They are characterized as
skeptical, critical, independent,
determined, and
often
stubborn.
ESTJs
are
organizers. They are realistic,
logical, analytical, decisive,
and have a natural
head
for business or
mechanics.
The
ENTP
type
is a conceptualizer. He or she is
innovative, individualistic, versatile,
and
attracted
to entrepreneurial ideas. This
person tends to be resourceful in
solving challenging
problems
but may neglect routine
assignments.
But
also keep in your mind that
each pair is of preferences
for behavior. They are
not
measures
of
ability.
The
MBTI Sub-Categories:
Extraversion
-------------------- Introversion
E
I
Sensing
----------------------------
iNtuition
S
N
Thinking
----------------------------
Feeling
T
F
Judging
---------------------------
Perceiving
J
P
There
are no "good" or "bad"
type's only different
types.
Each preference type has a
contribution to
make
to effective teamwork. Each
needs the opportunity to make a
contribution based upon
strengths.
We
understand that leadership is a process and
not a position. Three
components playing important
role
in
this process are leader,
followers and situation. In
this lecture, we tried to
explain this
important
component/part
of leadership process.
Situation
is the environment or circumstances in
which an individual performs. Following
are the
factors
that can influence the
situation;
Situational
factors influence the leadership
process:
Size
of the organization
Organizational
life cycle stage
Social
and psychological climate
Patterns
of employment
Type,
place, and purpose of work
performed
Culture
of the organization
Over
all environment
Leader-follower
interaction
Leader-follower
compatibility
Compatibilities
within the followers
The
organizational environment is the set of
forces surrounding an organization
that have the potential
to
affect the way it operates
and its access to scarce
resources. Basically organization
environment has
two
dimensions internal and external. This
can also be known as Macro
and Micro factors or even
General
Environment and Task Environment. All
these factors/forces do affect the
leadership process.
Becoming
a Leader:
96

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
The
leaders
of
a group, team or organization
are the individuals who
influence others behavior.
Leader
effectiveness
is the extent to which a leader actually
does help a group, team or
organization to achieve
its
goals. Leaders are either
appointed by someone external to the
group and they are elected by
group
members
themselves. Some people take
up role of leader by using their
influences. With the passage
of
time,
you can see that leadership
will emerge over time.
The group members will
assess with in the
group
that who is leader worthy. In
this situation, communication
style will play a dynamic
role. A
group
member can become a leader if he or
she has following
qualities/skills;
Think
like a leader
Share
your vision
Develop
your judgment
Adapt
your style
Build
leadership traits
Pick
the right
followers
Build
your power base
Organize
tasks properly
Three
competency of a Leader: there are
three competency of leader;
Leading
the Organization:
Leading
the organization and put the organization
on right path through
setting vision, direction
and
strategy.
They also involve in problem
solving and decision making.
They keenly observe
the
prevailing
politics in the organization and
influence other team
members. Leaders always try
to create a
change
culture in the organization. For
this purpose they take the
risks and innovates the new things
in
the
organization by enhancing business skills
and knowledge.
Leading
others:
One
of the leader's competencies is leading
and managing others. In the
organization, a leader manages
the
effective teams and groups for
achievement of organizational objectives by
building and
maintaining
a working relationship between them. They
motivate other and build the trust on
team
members.
One of the major tasks of leader is to
develop other, which is more
important factor. They
set
a
reward system in the organization
and mostly link it with the
performance or achievement of goals.
Leading
oneself:
This
is also very important to
leading one self. It is the
responsibility of the leader to adopt the
changes
prevails
in the environment. They also
increase the self awareness
for himself that what is
going on in
the
surroundings of the organization. They
always try to lean as more as
they can. They also
develop
the
culture of ethics and integrity
with in the organization.
Developing
adaptability, increasing self-awareness,
managing yourself, increasing capacity to
learn,
exhibiting
leadership stature, displaying drive and
purpose, developing ethics and
integrity.
Leaders
always know about their
strengths, weakness, opportunities,
challenges and know who they
are
as
an individual. They also
know that "Positions do not
possess leadership characteristics, only
people
possess
leadership characteristics."
"Leadership
is not a matter of luck. The harder
you work, the luckier you
are."
1.
Power:
is the desire to influence, give
orders, and carry them
out.
2.
Achievement:
is the need to create/ achieve and build
something of value
3.
Affiliation:
is an interest in knowing and helping
others.
Power-Oriented
Leader: they
strive for leadership because of the
formal authority it brings.
They are
the
bold and have a dominance role in the
organization.
Achievement-Oriented
Leader: they
want to discover, create,
and build some thing.
They are the
creative
and innovators and always
try to achieve some thing
new. They are competent,
skillful and
productive.
Affiliation
Leader: they have
high concern for human
welfare and care about
others and has a desire
to
serve.
They are helpful, unselfish
and considerate of the well being of
others.
Points
to Remember:
97

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
An
individual will prefer one or
two social motives over the others.
Preference depends on
cultural
values,
personal traits, and experiences.
Leadership
is exerted to satisfy one or a
combination of the three motives.
Motivated by power,
achievement,
or affiliation
Leaders
and followers are happiest in
situations that allow expression of
personal social motives.
We
will shift now to another
important topic "Power".
Does having power make a
leader? To answer
this
question we need to understand basic
concepts of power and its
relationship with the process
of
leadership.
Power:
is the possession of control, authority,
or influence over others. (Webster's).
Leadership
power
comes from the followers'
willingness to be influenced, induced,
control and guide.
Sources
of Leadership Power:
The
following are the sources of a
leader's power;
1.
A leader's authority most
commonly stems from the
position to which he or she is
appointed
and
the power to reward or punish
individuals.
2.
An authority in his or her field
has expert power, and others
do what is asked of them out
of
respect.
Referent power is based on personal
magnetism and charisma.
3.
Formal leaders get some of
their authority through
their position.
4.
Informal leaders get their
authority through
charisma.
Understanding
Power: before
understanding power we need to
ask some questions by our
self;
1.
What is power?
2.
How do leaders acquire the power
needed for leadership?
3.
What are organizational
politics?
4.
How do organizational politics
affect the Leadership?
CONCEPT
OF POWER:
Power:
is
the ability of one person or
group to cause another person or
group to do something they
otherwise
might not have done is the principal
means of directing and controlling
organizational goals
and
activities.
Influence:
is the process of affecting the thoughts,
behavior, & feelings of another
person.
Authority:
is
the right to influence another person
formally given by the organization. A
legitimate
power
is known as authority.
Principles
of Power:
·
Power is perceived
·
Power is relative
·
Power bases must be
coordinated
·
Power is a double-edged sword (used and
abused)
Historian
Lord Acton once said, "Power
corrupts, and absolute power corrupts
absolutely."
Dependency:
The Key To Power: If you
want to get things done in a group or
organization, it helps to
have
power. As a leader if you want to
maximize your power, you
will need to increase
others'
dependence
on you. You can, for instance,
increase your power in
relation to your boss by
developing
knowledge
or a skill that he/she needs
and for which he/she perceives no
one ready to substitute. You
will
not be alone in attempting to
build your power bases.
Others, particularly employees and
peers,
will
be seeking to make you dependent on them.
The result is a continual
battle. While you seek
to
maximize
others' dependence on you,
you will be seeking to minimize
your dependence on others, and,
of
course, others will be
trying to do the same.
98
Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Forms
of Power:
·
Personal
power
use of personal influence of
events.
not arrogance.
·
Professional
power
use of professional expertise and
competence, embedded within an
organization, to
make
change or make a contribution.
·
Positional
power
granted by the organization.
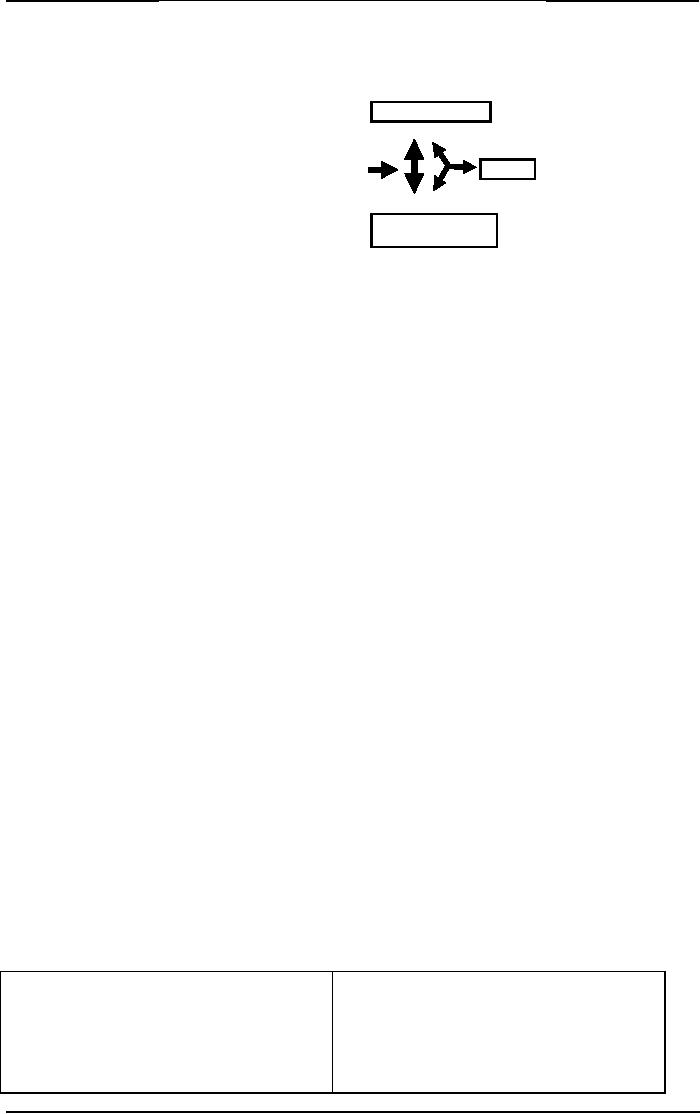
Responses
of the use of power can be
divided into three different
behaviors. If positional power is
used
appropriately
the response of followers will be
compliance. While excessive
power use can
create
resistance
behavior. In case some one is
using personal power the response is
always commitment of
followers.
Same can be understood from the
following figure.
The
more you will move toward
excessive or coercive power the more
you can experience
resistance.
How
do you get power?
·
Key words
Management
People
Motivation
Organization
Team
Culture
Influence
Politics
Organizational
Factors Which Contribute to Political
Behavior
Low
trust
Role
ambiguity
Democratic
decision making
Self-serving
senior managers
High
performance pressures
Unclear
evaluation systems
Scarcity
of resources
Zero-sum
allocations
Managing
Organizational Politics
Reduce
System Uncertainty
Reduce
Competition
Break
Existing Political
Fiefdoms
Managing
Political Behavior:
Maintain
open communication
Clarify
performance expectations
Use
participative management
Encourage
cooperation among work groups
Manage
scarce resources well
Provide
a supportive organizational
climate
What
is Empowerment?
Empowerments
is the process of enabling or authorizing
an individual to think, behave, take
action, and
control
work and decision making in autonomous
ways. It is the state of feeling self-empowered to
take
control
of one's own destiny.
OR
Empowerment
is a social action process
that promotes participation of people,
organizations, and
communities
towards the goals of increase individual and
community control, political
efficacy,
improved
quality of community life and
social justice." (Wallerstein,
1992)
99
Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Why
Important? Powerlessness
·
Living in poverty
Powerlessness
·
Relatively low in
hierarchy
·
Chronic Stress
Disease
·
Lack of Social
Support
Lack
of Control Over
·
Income Inequities
Destiny
·
Racial Discrimination
What
is Empowerment, and How Can
Empower Others?
The
power keys to empowerment: there are
two views about power
keys to empowerment;
1.
Traditional
view: in
traditional view power is
relational in terms of
individuals.
2.
Empowerment
view: In empowerment
view, the emphasis is on the ability to
make
things
happen. Power is relational in terms of problems and
opportunities, not
individuals.
Empowering
Organizations:
"At
the organizational level, OE
[organizational empowerment] refers to
organizational efforts
that
generate
PE [personal empowerment] among members
and organizational effectiveness needed
for goal
achievement"
Provide
opportunities for staff to be
involved in organizational
decision-making, program
development,
and evaluation.
Reduce
organization hierarchies and supervisory structure so
that workers have more control
over
their
work.
Encourage
professional development and
team-building among staff.
Provide
resources that facilitate the
development of political power among
people.
Regard
workers as partners rather than
subordinates.
What
Is the Bottom
line?
Appropriate
employee empowerment is essential to
organizational success.
Everyone
claims to empower employees, but this is
easier said than
done.
A
failed organizational empowerment
initiative is at best a waste of
time.
Power
sharing and Empowerment:
Power
sharing: The
delegation of power or authority to
subordinates in the organization.
What's
wrong
with this concept? Most of
the times, after sharing of power or
authority, people think
that,
employee
misuse it and their influence on
employee will reduce
consequently.
Empowerment:
being
enabled
to
make independent decisions and
take effective
action.
Guidelines
for effective employee
empowerment:
·
·
Select
the right managers.
Share
authority instead of giving it
up.
·
·
Choose
the right employees.
Encourage
dissent.
·
·
Provide
training.
Give
it time.
·
·
Offer
guidance.
Accept
increased turnover.
·
·
Hold
everyone accountable.
Share
information.
·
·
Build
trust.
Realize
that empowerment
has
its
100

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
·
Focus
on relationships.
limitations.
·
Stress
organizational values.
·
Involve
employees in decision-making.
·
Transform
mistakes into
opportunities.
·
Reward
and recognize.
Leadership
and Empowerment: Empowerment
involves sharing or giving power or
influence to
another.
It is the process through which
leaders enable and help others to
gain power and achieve
influence
within the organization. When employees
feel powerful they are more
willing to make
decisions
and take action.
How
Leaders Can Empower
Others:
·
A
leader can involve others in selecting
their work assignments and
tasks
·
He
creates an environment of cooperation,
information sharing, discussions, and
shared ownership
of
goals.
·
He
encourages others to take
initiative, make decisions, and use their
knowledge.
·
He
finds out what others
think and let them help
design solutions.
·
Leader
can give others the freedom
to put their ideas and
solutions into practice.
·
He
recognizes successes and encourages
high performance.
Participative
leadership: some
characteristics of a participative
leader;
·
Begins
with involving people
·
Involvement
leads to understanding, which
leads to commitment
·
Taps
the constructive power of
people
·
Creates
a humanistic and productive
workplace
·
Means
understanding the views and interests of
all affected
Motivation:
There
are over 140 definitions of
the term motivation that have been
used in various
capacities.
Motivation is important because it
explains why employees behave as they
do. Work
Motivation
can
be defined as the psychological forces
within a person that
determine the direction of a
person's
behavior in an organization, a person's
level of effort, and a person's level of
persistence in the
face
of obstacles.
Definition:
Motivation
is the result of the interaction of the
individual and the situation.
Motivation
is the processes that account
for an individual's intensity,
direction,
and
persistence
of
effort toward attaining a
goal.
The
process that initiates, directs,
and sustains behavior to
satisfy physiological or
psychological
needs or wants; the energizing and
directing of behavior, the force
behind our
yearning
for food, our longing
for sexual intimacy, and our
desire to achieve.
Sources
of Motivation: Intrinsic
and Extrinsic Motivation;
Intrinsically
Motivation: is behavior
that is performed for its
own sake; the source of
motivation is
actually
performing the behavior.
a.
Employees who are intrinsically
motivated often remark that
their work gives them a
sense of
accomplishment
and achievement or that they feel
they are doing something
worthwhile.
b.
Motives are intrinsic when
an independent third party cannot
easily verify them.
Extrinsic
Motivation: is behavior
that is performed to acquire material or
social rewards or to
avoid
punishment.
a.
The behavior is not
performed for its own
sake but rather for its
consequences.
b.
This form of motivation may
be linked to operant conditioning.
c.
Motives are extrinsic when
they can easily be verified
by an independent third
party.
101

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Work
motivation explains why employees behave
as they do. Four prominent
theories about work
motivation
need
theory, expectancy
theory, equity
theory, and
organizational
justice theory
provide
complementary approaches to understanding
and managing motivation in
organizations.
Similarly
Abraham
Maslow's hierarchy of needs
also
help us to understand the employees
work
behavior.
Each theory answers
different questions about the
motivational process.
Work
motivation can be
defined as the psychological forces
within a person that
determine the
direction
of a person's behavior in an organization, a person's
level of effort, and a person's level
of
persistence
in the face of obstacles.
Three
Approaches to Motivation:
Individual
Differences Approach: Treats
motivation as a characteristic of the
individual.
Job
& Organization Approach: Emphasizes
the design of jobs and the general
organizational
environment
Managerial
Approach: Focuses on
behaviors of managers, in particular,
their use of goals and
rewards
What
Factors Diminish
Motivation
in the Workplace?
·
Unpredictable change in
·
Meaningless
tasks
direction
·
Red
tape
·
Lack of recognition
·
Lack
of clear goals
·
Absence of humor
·
Failure
to set priorities
·
Micromanagement
·
Distractions
·
Failure to delegate
·
Over-commitment
·
Bureaucratic hurdles
·
Information
overload
·
Interpersonal conflict
·
No
positive feedback
·
Lack of accountability
·
Lack
of autonomy
What
are Some of the Results of
Poor
Motivation in the Workplace?
·
Frustration
·
Laziness
·
Conflict
·
Failure
·
Lack
of meaning
·
Poor
quality
·
Absence
of pride
·
Resistance
·
Resentment
·
Avoidance
·
Turnover
·
Tardiness
·
Detachment
·
Burnout
·
Discouragement
·
Demoralization
·
Negative
organizational
culture
102

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
What
are Some of the Most
Powerful
Motivators
in our Lives?
·
Commitment
·
Sense of
accomplishment
·
Money
·
Cultural norms
·
Meaning
·
Chance to make a
·
Recognition
difference
·
Love
·
Independence
·
Participation
·
Opportunity to serve
·
Emotion
·
Duty
·
Appreciation
·
Habit
·
Collegiality
·
High energy level
·
Competition
·
Perceived need for
·
Hate
change
·
Religious
beliefs
How
Can You Motivate
Yourself?
Stick
with your passions.
Share
your enthusiasm.
Hang
out with high
achievers.
Flavor
tedium with pleasure.
Go
with your strengths.
Make
lists.
Stay
focused on results.
Just
do something.
How
Can You Motivate
Others?
Associate
with highly motivated
people.
Set
a measurable goal.
Make
a compelling case.
Use
emotional temptation.
Set
a fire and keep it going.
Make
it fun.
Explain
how.
Keep
doing something new and
different.
Celebrate
Employee
Motivation:
Good
leadership is key
Create
a culture of trust
Encourage
risk taking
Foster
ownership
Goal-directed
efforts
Applying
Motivational Concepts:
Recognize
individual differences
Match
people to jobs
Set
challenging goals
Encourage
participation
Individualize
rewards
Link
rewards to performance
Check
for equity
Don't
ignore money
Conditions
of Leadership Motivation:
Leadership
generates motivation
when:
o
o
It
increases the number and kinds of
payoffs
103

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
o
Path
to the goal is clear and easily traveled
with coaching and direction
o
Obstacles
and roadblocks are removed
o
The
work itself is personally
satisfying
Money
as a Motivator:
According
to Maslow and Alderfer, pay
should prove especially
motivational to people
who
have
strong lower-level needs.
If
pay has this capacity to
fulfill a variety of needs,
then it should have good
potential as a
motivator.
The
Role of Money:
They
value their services and place
high value on them
They
perceive money as symbol of
their achievement
They
do not remain in low paying
organization
They
are very self
confident
Know
their abilities and
limitations
Communication
is one of the most important
processes that take place in
any organizations.
Effective
communication
allows individuals, groups, teams and
organizations to achieve their goals and
perform
at
a high level, and it affects virtually
every aspect of organizational
behavior.
One
of the defining features of communication
is the sharing of information with
other people.
Another
defining feature is reaching
a common understanding.
In
this case, communication
is
the sharing of information between two or more
individuals or groups
to
reach a common understanding.
Reaching
a common
understanding does
not mean that people have to
agree with each
other.
Communication
is good or effective when
members of organization share
information with each
other
and
all parties involved are
relatively clear about what
information means.
Why
is this important???
Effective
communication is important in
organizations because it affects
practically every aspect
of
organizational
behavior. Good communication prevents
many problems from occurring and
serves as
motivation
in an organization. Why it is important
for leaders?
As
a leader...
You
need people to understand what
you are talking
about.
You
must take into consideration
other people's needs.
You
need to be able to hear
others opinions and
ideas.
You
need to organize and capitalize on the
best ideas.
You
need to delegate.
A
good leader spend 70% of day
on communicating to share vision,
motivate team
members/employees,
pass the information and
build the relationship with
other people.
Communication
and Leadership
·
Effective leaders are
also effective communicators
·
To be effective, the leader must synchronize
verbal and nonverbal
behavior
·
Technology has had a meaningful
impact on leaders' communication and
coordination
·
Effective leaders are
also effective communicators
·
To be effective, the leader must synchronize
verbal and nonverbal
behavior
·
Technology has had a meaningful
impact on leaders' communication and
coordination
104
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION, ORGANIZATION THE STAGE FOR LEADERSHIP:Challenges, Value creation
- FOCUSING ON PEOPLE: THE KEY TO SUCCESS:People in the Process, Developing and Sustaining A World-class Workforce
- LEADERSHIP:Characteristics of Successful Leader, Why Study Leadership?
- LEADERSHIP (CONTD.):Characteristics of Leaders Who Fail, Why Leaders Fail?
- MANAGERS VS LEADERS:Characteristics, Effective Leadership, Respect for Diversity
- FOLLOWER-SHIP:Importance of Followers, Follower-ship Style
- LEADERSHIP PROCESS:Strategies for Cultivating Exemplary Followers, Important Traits of Leaders
- LEADERSHIP PROCESS (CONTD.):Qualities of Leaders, Self-Confidence, Integrity
- LEADERSHIP THEORIES/ APPROACHES:Personal Characteristics of Leaders, Managerial Grid
- CONTINGENCY THEORIES OF LEADERSHIP:The Fiedler Model, Situational Leadership Theory, Path-Goal Theory
- TRANSACTIONAL, CHARISMATIC AND TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP:Visionary Leadership
- THE LEADER AS AN INDIVIDUAL:Personality, Situation, Heredity, Environment
- ATTITUDE-PERSONALITY:Job Satisfaction, Work Situation, Self - Monitoring
- BIG FIVE MODEL, MYERS BRIGGS TYPE INDICATOR (MBTI):Sub-Categories Defined, Information Gathering
- SITUATIONAL FACTORS:Social and psychological climate, Culture of the organization
- BECOMING A LEADER! WHAT DOES IT MEAN & HOW DO YOU GET IT?:Mission Statement, Leading oneself
- BECOMING A LEADER:Elements of Leadership, CONCEPT OF POWER,
- UNDERSTANDING POWER:Sources of Power, Responses to the Use of Power, Managing Political Behavior
- LEADERSHIP POWER & INFLUENCE:Positional Power, Being an Effective Leader
- LEADERSHIP AND EMPOWERMENT:Power sharing and Empowerment, Share Information
- MOTIVATION:Guidelines for Delegating, Human Resource Approach
- MOTIVATION AT WORK, MOTIVATION AND LEADERSHIP:What Factors Diminish Motivation in the Workplace
- LEADERSHIP COMMUNICATION:Communication & the Four Management Functions
- REVIEW-1:Organizational Performance, That is the Role of Management?, Leaders Vs Managers
- GROUP & TEAM CONCEPT:Groups versus Teams, Deciding When to Use a Team
- TEAM DYNAMICS:Stages of Group Development, Problem-Solving Teams, Benefits of Teams
- BUILDING THE TEAM:Leadership success requires, Strategies for Team Building
- A TEAM-BASED ORGANIZATION:Basic Steps, Span of Control, Categories of Decisions
- DECISION MAKING:Categories of Decisions, The Decision-Making Process
- TEAM DECISION MAKING:Team Problem Solving Techniques, Concept of QC
- EFFECTIVE TEAM COMMUNICATION:Team/Group Communications
- CONFLICT IN TEAM:Sources of Conflict, Scarcity of Resources, Dysfunctional Outcomes
- TRAINING/LEARNING OF TEAM:Training Methods, Phases of Learning Cycles
- LEARNING ORGANIZATION:A Litmus Test, Work Relations
- REWARDING & RECOGNIZING TEAMWORK:Compensating Teams, Individual or Team Rewards?
- MANAGING/LEADING VIRTUAL TEAMS:Communications in Virtual Organizations, Virtual Leadership
- EFFECTIVE TEAM MEETINGS:Better Meetings, Meeting Roles, Meeting Room Facilities
- LEADING TEAM:Team Leadership Structures, Leadership Demands and Duties, Leadership Direction
- REVIEW-II:Types of Teams, Characteristics of High Performance Teams, Sources of Conflict
- STRATEGIC LEADERSHIP:Strategic Management, Determining Strategic Direction, Developing Human Capital:
- LEADING CHANGE:Dynamics of Change, Change Models, Unfreeze
- CREATIVE LEADERSHIP:Awaken Your Senses, How Might These Definitions Be Integrated
- ETHICS IN LEADERSHIP:Character Traits Reflect Ethics, Manifests Honesty
- LOOKING AT THE FUTURE: WHAT COMES NEXT:Benefits of Teams, Ethical Leadership,
- TEAMWORK: LEARNING FROM NATURE:Social Behavior, Termites, Learning from Nature