 |

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Lesson
14
BIG
FIVE MODEL, MYERS BRIGGS
TYPE INDICATOR
(MBTI)
Continuing
from previous lectures, we are
still at personality part of
individuals. One can ask
question
is
Personality Stable? Behavior is
a function of the situation and the
person in the situation
People's
personalities can be described in a
variety of ways.1). Personality
is
the pattern of relatively
enduring
ways in which a person feels, thinks, and
behaves. 2). Personality is an
important factor in
accounting
for why employees act the
way they do in organizations
and why they have favorable
or
unfavorable
attitudes toward their jobs
and organizations.
Behavioral
and social-cognitive theories: Reciprocal
determinism: the person, the person's
behavior,
and
the environment all influence one
another. Organizational Culture,
Values, beliefs, attitudes
and
assumptions
put into Action
through
behavior. To understand it better, we
need discuss other models
on
this
subject.
The
Big Five Model of Personality:
An
impressive body of research supports
that five basic
dimensions
underlie all other
personality dimensions. The five
basic dimensions are:
Extraversion:
Comfort
level with relationships.
Extroverts tend to be gregarious,
assertive, and
sociable.
Interesting in getting ahead,
Leading through influencing,
Individuals are outgoing;
Likes to
meet
new people and willing to
confront others. Introverts tend to be
reserved, timid, and
quiet.
Agreeableness:
Individual's
propensity to defer to others.
High agreeableness
people--cooperative,
warm,
and trusting. Traits related to
getting along with others.
Characteristics include warm,
easygoing,
compassionate,
friendly, and sociable. Individuals
typically are sociable and have lots of
friends. Low
agreeableness
people--cold, disagreeable, and
antagonistic.
Conscientiousness:
A
measure of reliability. A high
conscientious person is responsible,
organized,
dependable,
and persistent. Includes traits related
to achievement. Traits include high
credibility,
conformity,
and organization. Individuals typically
work hard and put in extra
time and effort to
meet
goals.
Those who score low on
this dimension are easily
distracted, disorganized, and
unreliable.
Emotional
stability: A person's
ability to withstand stress. People
with positive emotional
stability
tend
to be calm, self-confident, and secure.
The fine line between stable
and unstable. Stable is being
calm,
good under pressure,
relaxed, and secure.
Unstable is nervous, poor under
pressure, insecure.
Those
with high negative scores
tend to be nervous, anxious, depressed,
and insecure.
Openness
to experience: The range of
interests and fascination with
novelty. Extremely open
people
are
creative, curious, and artistically
sensitive. Trait related to being
willing to change and try
new
things.
Individuals typically are
willing to take calculated risks.
Those at the other end of the
openness
category
are conventional and find
comfort in the familiar.
What
the MBTI? MBTI is an
inventory of preferences for
behavior and not a diagnostic
psychological
test
for identifying dysfunction or
abilities. It tells you
about your preferences for
orienting yourself in
the
world, and for gathering
information and making decisions.
Katharine
Briggs &
Isabel
Myers, mother-daughter
team
developed Jung's types into the
Myers
Briggs
Type Indicator (MBTI). There
are four categories, each
with two sub-categories are
as follows;
The
4 dimensions: Personality
type dependent on 4 dimensions: It is a 100-question
personality test
that
asks people how they
usually feel or act in
particular situations. Individuals
are classified as:
1.
Extroverted or introverted (E or
I).
2.
Sensing or intuitive (S or
N).
3.
Thinking or feeling (T or
F).
4.
Perceiving or judging (P or J).
44

Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
These
classifications are then
combined into sixteen
personality types. For
example:
INTJs
are
visionaries. They usually have
original minds and great drive for
their own ideas
and
purposes. They are characterized as
skeptical, critical, independent,
determined, and
often
stubborn.
ESTJs
are
organizers. They are realistic,
logical, analytical, decisive,
and have a natural
head
for business or
mechanics.
The
ENTP
type
is a conceptualizer. He or she is
innovative, individualistic, versatile,
and
attracted
to entrepreneurial ideas. This
person tends to be resourceful in
solving challenging
problems
but may neglect routine
assignments.
But
also keep in your mind that
each pair is of preferences
for behavior. They are
not
measures
of
ability.
History:
·
1920's
Carl Jung posits that there
are underlying personality
types
·
1940's
Katharine Briggs and Isabel
Briggs Myers build on Jung's
work and create the
MBTI
test
·
1970's
Serious work to link MBTI types to
careers, love matches,
etc.
·
Today
MBTI widely used in educational,
corporate settings
Jung's
Core Idea in Psychological Types:
When
your mind is active, one of
two mental activities
is
occurring:
Perceiving
-
taking in information
Judging
-
organizing that information &
reaching conclusions
The
MBTI Sub-Categories:
Extraversion
-------------------- Introversion
Sensing
----------------------------
iNtuition
Thinking
----------------------------
Feeling
Judging
---------------------------
Perceiving
Sub-Categories
Defined
·
Focus
Attention:
Extraversion - direct
& receive energy from outer
world
Introversion - direct
& receive energy from inner
world
·
Take in
Data:
Sensing -
data from the five
senses
iNtuition -
data from perception of
meaning; gut-feeling
·
Make
Decisions:
Thinking -
logical, objective, analytical
approach
Feeling -
value-centered, subjective (likes &
dislikes)
·
Orientation to Outer
World:
Judging -
live ordered, structured, planned
lives
Perceiving -
flexible, spontaneous
orientation
45
Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
MBTI
Applications in Organizations:
·
Management/career
development
·
Interpersonal
communications skills
·
Decision
making/problem solving styles
·
Management/leadership
styles
·
Organizational
change
·
Teambuilding
·
Handling
Diversity
·
Conflict
management
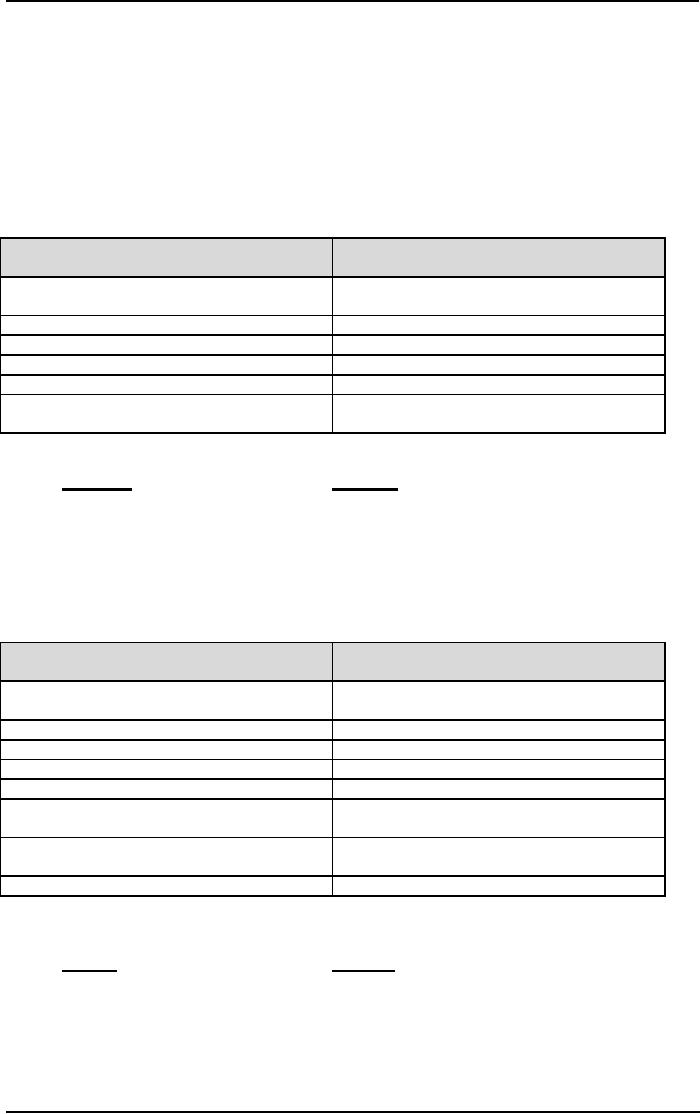
Energy
Extraversion
Introversion
The
Extraverted person directs and
receives
The
Introverted person directs and
receives
energy
from the outside
world.
energy
from the inner world.
prefers
action over
reflection
prefers
reflection over
action
prefers
oral communication
prefers
written communication
shares
thoughts freely
guards
thoughts until they are
(almost) perfect
acts
and responds quickly
reflects
and thinks deeply
enjoys
working in groups
enjoys
working alone or with only
one or two
others
Energy
Source:
Introvert
Extravert
Talkative
Meditative
Open
Reserved
External
Internal
With
a group
Alone
Talks
first
Thinks
first
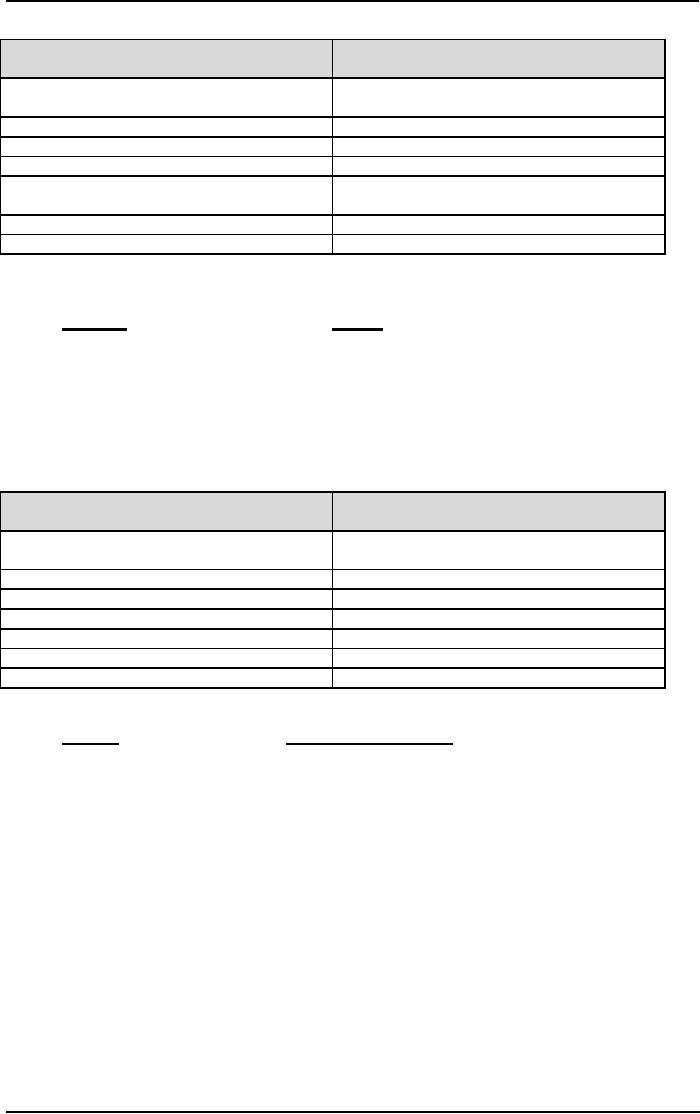
Information
Gathering:
Sensing
iNtuition
The
Sensing
person
prefers to gather
The
iNtuitive
person
prefers to gather
information
in a precise and exact manner.
information
in an inspired or novel manner.
Likes
specific examples
Likes
general concepts
Prefers
following an agenda
Departs
from the agenda if
necessary
Emphasizes
the practical
Emphasizes
the theoretical
Seeks
predictability
Desires
change
Sees
difficulties as problems
Sees
difficulties as opportunities
that
need specific
solutions
for
further exploration
Focuses
on immediate applications of a
Focuses
on future possibilities
situation
of
a situation
Wants
to know what is
Wants
to know what could
be
Information
Gathering
Intuitors
Sensors
Facts
Possibilities
Present
Future
Tangible
Abstract
Practical
Imaginative
5
Senses
"6th
Sense"
46
Leadership
& Team Management MGMT
623
VU
Decision
Making:
Thinking
Feeling
A
Thinking
person
seeks general truths and
A
Feeling
person
seeks individual
and
objectivity
when making decisions.
interpersonal
harmony when making
decisions.
questions
first
accepts
first
knows
when reason is needed
knows
when support is needed
wants
things to be logical
Wants
things to be pleasant
remains
detached when making
decisions
remains
personally involved when
making
decisions
controls
the expression of feelings
expresses
feeling with
enthusiasm
overlooks
people in favor of
tasks
overlooks
tasks in favor of
people
Decision
Making
Feelers
Thinkers
Objective
Subjective
Impersonal
Interpersonal
Justice
Mercy
Why
Who
Head
Heart
Lifestyle:
Judging
Perceiving..
The
Judging
person
likes to come to closure
The
Perceiving person prefers to remain
open
and
act on a decision.
and
adapt to new information.
Likes
things to be settled and ordered
Likes
things to be flexible and open
Finishes
tasks before
the
deadline
Finishes
tasks at
the
deadline
Focuses
on goals, results, and
achievements
Focuses
on processes, options, and
openings
Establishes
deadlines
Dislikes
deadlines
Prefers
no
surprises
Enjoys
surprises
Quickly
commits to plans or decisions
Reserves
the right to change plans or
decisions
Life
Style:
Judgers
Spontaneous
/Perceiver
Decisive
Curious
Definite
Optional
Deadline
Guideline
Closure
Open-ended
Now
Later
The
MBTI Sub-Categories:
Extraversion
-------------------- Introversion
E
I
Sensing
----------------------------
iNtuition
S
N
Thinking
----------------------------
Feeling
T
F
Judging
---------------------------
Perceiving
J
P
There
are no "good" or "bad"
type's only different
types.
Each preference type has a
contribution to
make
to effective teamwork. Each
needs the opportunity to make a
contribution based upon
strengths.
47
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION, ORGANIZATION THE STAGE FOR LEADERSHIP:Challenges, Value creation
- FOCUSING ON PEOPLE: THE KEY TO SUCCESS:People in the Process, Developing and Sustaining A World-class Workforce
- LEADERSHIP:Characteristics of Successful Leader, Why Study Leadership?
- LEADERSHIP (CONTD.):Characteristics of Leaders Who Fail, Why Leaders Fail?
- MANAGERS VS LEADERS:Characteristics, Effective Leadership, Respect for Diversity
- FOLLOWER-SHIP:Importance of Followers, Follower-ship Style
- LEADERSHIP PROCESS:Strategies for Cultivating Exemplary Followers, Important Traits of Leaders
- LEADERSHIP PROCESS (CONTD.):Qualities of Leaders, Self-Confidence, Integrity
- LEADERSHIP THEORIES/ APPROACHES:Personal Characteristics of Leaders, Managerial Grid
- CONTINGENCY THEORIES OF LEADERSHIP:The Fiedler Model, Situational Leadership Theory, Path-Goal Theory
- TRANSACTIONAL, CHARISMATIC AND TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP:Visionary Leadership
- THE LEADER AS AN INDIVIDUAL:Personality, Situation, Heredity, Environment
- ATTITUDE-PERSONALITY:Job Satisfaction, Work Situation, Self - Monitoring
- BIG FIVE MODEL, MYERS BRIGGS TYPE INDICATOR (MBTI):Sub-Categories Defined, Information Gathering
- SITUATIONAL FACTORS:Social and psychological climate, Culture of the organization
- BECOMING A LEADER! WHAT DOES IT MEAN & HOW DO YOU GET IT?:Mission Statement, Leading oneself
- BECOMING A LEADER:Elements of Leadership, CONCEPT OF POWER,
- UNDERSTANDING POWER:Sources of Power, Responses to the Use of Power, Managing Political Behavior
- LEADERSHIP POWER & INFLUENCE:Positional Power, Being an Effective Leader
- LEADERSHIP AND EMPOWERMENT:Power sharing and Empowerment, Share Information
- MOTIVATION:Guidelines for Delegating, Human Resource Approach
- MOTIVATION AT WORK, MOTIVATION AND LEADERSHIP:What Factors Diminish Motivation in the Workplace
- LEADERSHIP COMMUNICATION:Communication & the Four Management Functions
- REVIEW-1:Organizational Performance, That is the Role of Management?, Leaders Vs Managers
- GROUP & TEAM CONCEPT:Groups versus Teams, Deciding When to Use a Team
- TEAM DYNAMICS:Stages of Group Development, Problem-Solving Teams, Benefits of Teams
- BUILDING THE TEAM:Leadership success requires, Strategies for Team Building
- A TEAM-BASED ORGANIZATION:Basic Steps, Span of Control, Categories of Decisions
- DECISION MAKING:Categories of Decisions, The Decision-Making Process
- TEAM DECISION MAKING:Team Problem Solving Techniques, Concept of QC
- EFFECTIVE TEAM COMMUNICATION:Team/Group Communications
- CONFLICT IN TEAM:Sources of Conflict, Scarcity of Resources, Dysfunctional Outcomes
- TRAINING/LEARNING OF TEAM:Training Methods, Phases of Learning Cycles
- LEARNING ORGANIZATION:A Litmus Test, Work Relations
- REWARDING & RECOGNIZING TEAMWORK:Compensating Teams, Individual or Team Rewards?
- MANAGING/LEADING VIRTUAL TEAMS:Communications in Virtual Organizations, Virtual Leadership
- EFFECTIVE TEAM MEETINGS:Better Meetings, Meeting Roles, Meeting Room Facilities
- LEADING TEAM:Team Leadership Structures, Leadership Demands and Duties, Leadership Direction
- REVIEW-II:Types of Teams, Characteristics of High Performance Teams, Sources of Conflict
- STRATEGIC LEADERSHIP:Strategic Management, Determining Strategic Direction, Developing Human Capital:
- LEADING CHANGE:Dynamics of Change, Change Models, Unfreeze
- CREATIVE LEADERSHIP:Awaken Your Senses, How Might These Definitions Be Integrated
- ETHICS IN LEADERSHIP:Character Traits Reflect Ethics, Manifests Honesty
- LOOKING AT THE FUTURE: WHAT COMES NEXT:Benefits of Teams, Ethical Leadership,
- TEAMWORK: LEARNING FROM NATURE:Social Behavior, Termites, Learning from Nature