 |

Personality
Psychology PSY 405
VU
Lesson
8
THE
PSYCHOLOGICAL TYPES
Even
those people, who have not
read Jung, are familiar with
his famous psychological types.
Which are
discussed
in his famous book, the
psychological types, published in 1921,
his main focus is on two
types,
introverts,
extroverts. Types refer to
orientation or the way an individual
interacts with other
people.
Introverts:
The
introverts are quiet,
imaginative, more interested in staying at
home alone, reading
or
enjoying
one's own company. The
introverts are usually
labeled as self-centered or book worms
and
preferring
indoor activities.
Extroverts:
Extroverts
tend to be sociable, outgoing, an interested in
parties, picnics, people and
group
activities.
They are the ones who
loved to be socialized and visit other's
rather than staying alone.
Along
with
these two orientations there
are some four functions of
our thinking process as
well, such as
sensing,
thinking,
feeling, intuiting. So we get eight types
of people, such as thinking
extrovert, feeling
extrovert,
sensing
extrovert, intuiting extrovert,
thinking introvert, feeling
introvert, sensing introvert,
intuiting
introvert.
Stages
of Development
Childhood:
From
birth to adolescence: During
this period the psychic energy is
used in learning to walk, to
talk and
other
skills of survival, than this
energy is spend in learning to
educate.
Young
Adulthood:
From
Adolescence to forty years:
During
this stage, one selects
one's profession, gets married,
raise
children,
and relate to the community. At this
level, the person is usually
is energetic, outgoing, passionate
and
loving.
Middle
Ages:
From
about forty to later years:
This
is the most important stage,
because almost all biological
and
physical
needs are satisfied and
now individual strives to find
meaning in life. So, after
material
development,
spiritual development begins to take
shape.
Life
after Retirement:
After
active work, one finds
refuge in the need to help others, so the
task of finding a new
meaning
provides
energy to continue living
further.
Life
Goal:
The
goal of life is the harmony of the
psyche that is combining
various parts of the personality in to
one.
This
is also called the transcendent
function or the self.
Individuation:
On
the other hand, individuation is the exact
opposite of the life goal.
Individuation is becoming aware
of
each
and every part of the psyche
such as the anima, animus, shadow, and
self.
Causality:
According
to Jung, adult personality should be
understood in terms of past experiences
which guide us,
and
provide
solution to our problems but
our behavior is also guided
by teleology that is human behavior
is
always
guided by past as well as by
future. So past experiences
push us forward and future goals
pull us
ahead.
Synchronicity:
When
you dream of a person and
shortly in the near future, the
person appears in front of
you, when you
dream
of a place and you visit it in future,
when you dream of an event
and the event takes place, this
is
called
meaningful coincidence. The example
Abraham Lincoln, who needed
Blackstone's commentaries.
32
Personality
Psychology PSY 405
VU
Research
Techniques:
1.
Word
Association Test: He redesigned Wundt's
word association test and used it
extensively
with
his patient's.
2.
Dream
Analysis: For Jung a dream is
just what it appears to be.
It provides individual with
an
awareness
and understanding of his problem and
solution to the problem as
well.
3.
For
Jung, personal unconscious, collective
unconscious and archetypes are
very important. The
unity
of all these into self is
the goal of life.
4.
Jung's
personality theory has a
background of history, religion and
anthropology (culture and
civilization).
5.
There
is emphasis on personality development
following a stage of development
where
spiritual
development is emphasized.
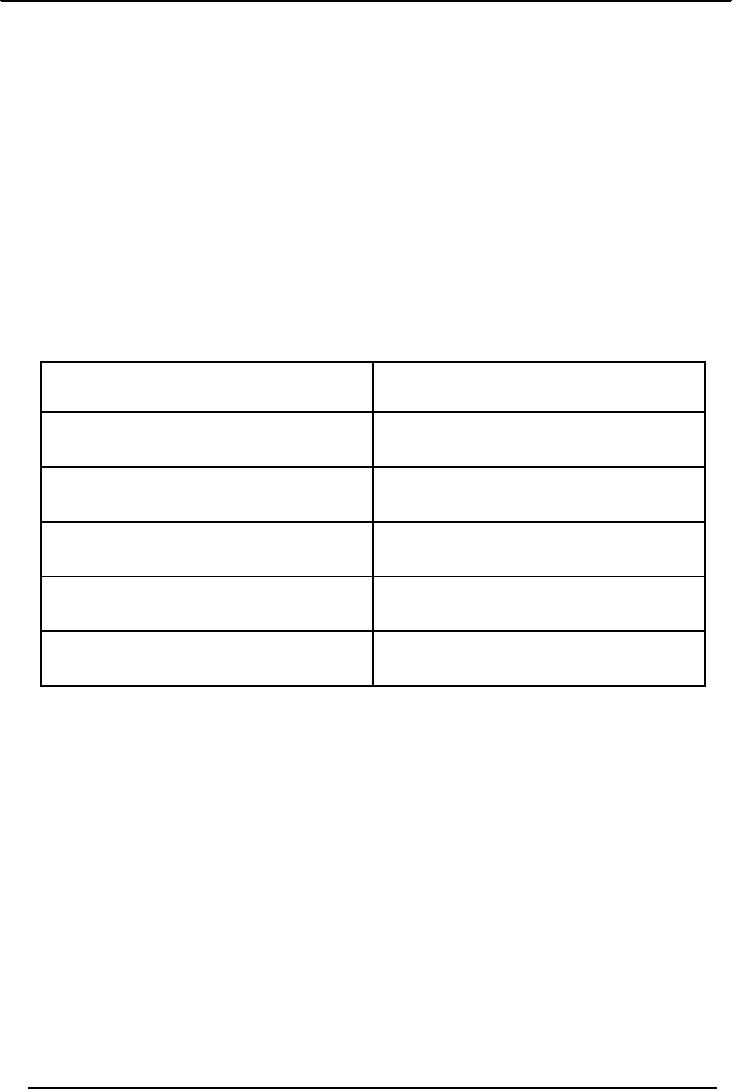
Comparison
with Freud:
JUNG
FREUD
His
theory is psychological and
social in
Freud's
theory is biological in nature
emphasis
Emphasis
on unification
of
different
Emphasis
on sex and aggression
component
of the psyche
Dreams
have manifest and latent
meaning
Dreams
are what in individual sees
them
Stages
of development are five,
beginning from Stages of
development are four,
focuses from
birth
up till adolescence
birth
till retirement
Psychological
types are provided,
introverts
Psychological
types are not
provided
and
extroverts
33
Table of Contents:
- THE NATURE OF PERSONALITY THEORY:Objectives of Personality Psychology
- PERSONALITY MEASUREMENT:Observational Procedures, Rating Scales
- MAIN PERSPECTIVES:Psychometrics, observation, Behavioral Coding Systems
- SIGMUND FREUD: A PSYCHOANALYTIC THEORY OF PERSONALITY
- INSTINCT: WHAT MOTIVATES HUMAN BEHAVIOR?, The Oral Stage
- PSYCHOANALYTIC THEORY OF SIGMUND FREUD:The Ego, Free association
- THEORY OF CARL JUNG:Biographical Sketch, Principles of Opposites, The Persona
- THE PSYCHOLOGICAL TYPES:Childhood, Young Adulthood, Middle Ages
- ALFRED ADLER:Biographical Sketch, Individual Psychology, Feeling of Inferiority
- INDIVIDUAL PSYCHOLOGY:Fictional Finalism, Social Interest, Mistaken Styles of Life
- KAREN HORNEY:Adjustment to Basic Anxiety, Adjustment Techniques
- ADJUSTMENT TO BASIC ANXIETY:Moving Towards People, Moving Against People
- ERIK ERIKSON:Anatomy and Destiny, Ego Psychology, Goal of Psychotherapy
- ERIK ERIKSON:Human Development, Goal of Psychotherapy
- SULLIVAN’S INTERPERSONAL THEORY:Core Concepts, The Self-System
- SULLIVAN’S INTERPERSONAL THEORY:Cognitive Process, Tension
- CONSTITUTIONAL PSYCHOLOGY:The Structure of Physique, Evaluation
- SHELDON’S SOMATOTYPE THEORY:The Structure of Physique
- MASLOW’S THEORY:Self-Actualizers Aren't Angels, Biographical Sketch
- MASLOW’S THEORY:Basic Concepts of Humanistic Psychology, Problem Centering
- ROGERS PERSON CENTERED APPROACH:Humanistic, Actualizing tendency
- ROGERS PERSON CENTERED APPROACH:Fully functioning person
- ROGERS PERSON CENTERED APPROACH:Client Centered Therapy,
- KELLY’S COGNITIVE THEORY OF PERSONALITY THEORY:Biographical Sketch
- CORE CONCEPTS OF GEORGE KELLY’S COGNITIVE THEORY OF PERSONALITY
- GORDON ALLPORT: A TRAIT THEORY OF PERSONALITY:Personality as a
- GORDON ALLPORT: A TRAIT THEORY OF PERSONALITY:Secondary Traits
- FACTOR ANALYTIC TRAIT THEORY:Factor Analysis, The Nature of Personality
- FACTOR ANALYTIC TRAIT THEORY:The Specification Equation, Research Methods
- HENRY MURRAY’S PERSONOLOGY:Need, Levels of Analysis, Thema
- HENRY MURRAY’S PERSONOLOGY (CONTINUED)
- ALBERT BANDURA’S SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY:BIOGRAPHICAL SKETCH
- ALBERT BANDURA’S SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY:Reciprocal Determinism
- THE STIMULUS RESPONSE THEORY OF DOLLARD AND MILLER:Core Concepts
- THE STIMULUS RESPONSE THEORY OF DOLLARD AND MILLER:Innate Equipment
- SKINNER’S THEORY OF PERSONALITY:Biographical Sketch, Books
- SKINNER’S THEORY OF PERSONALITY:Positive Reinforcement, Generalization
- ALBERT ELLIS THEORY OF PERSONALITY:Biographical Sketch, Social Factors
- THE GRAND PERFECT THEORY OF PERSONALITY:Genes and Biology
- PERSPECTIVES OR DOMAINS OF PERSONALITY PSYCHOLOGY:Dispositional
- PERSPECTIVES OR DOMAINS OF PERSONALITY PSYCHOLOGY
- PERSPECTIVES OR DOMAINS OF PERSONALITY PSYCHOLOGY:Need
- THE GRAND THEORY OF PERSONALITY:Psychosexual Stages of Development
- PERSONALITY APPRAISAL:Issues in Personality Assessment
- PERSONALITY PSYCHOLOGY: NEW DIRECTIONS IN THE DISCIPLINE