 |

Forensic
Psychology (PSY -
513)
VU
Lesson
28
RISK
ASSESSMENT
Objective
To
understand the use of violence reduction
scale for the assessment
of
recidivism.
To
understand the static and dynamic factors
of VRS
When
people come into contact
with the criminal justice
system, they pass through
several stages of
processing.
At each stage, an individual's
risk of re-offending is assessed by
criminal justice
workers.
Risk
assessments are performed by
justice professionals on a daily basis:
pre-trial, before sentencing,
when
determining security level in
custody, prior to release, and
after breaches or critical
incidents
occur
(Hart, 1995). These
assessments can be either
formal or informal in nature.
Risk
assessment is fundamental to the criminal
justice process because it is a
means for
distinguishing
between
offenders who are likely to
re-offend and those who are
at a lower risk for
recidivism.
Violence
reduction scale
Risk
assessment and prediction have
become an important part of
forensic practice for
many
psychologists
and non-psychologist practitioners. The
VRS (Wong & Gordon,
1999- 2003; Wong
&
Gordon,
2006) is designed to integrate the
assessment of risk, need,
responsivity and treatment change
into
a single tool. It assesses the
client's level of violence
risk, identifies treatment targets
linked to
violence,
and assesses the clients'
readiness for change and
their post-treatment improvements on
the
treatment
targets. Treatment improvement or is
designed based on the risk, need and
responsivity
principles.
It is intended for use by
scientists/practitioners to assess and
predict the risk of violence,
to
measure
changes in risk after treatment,
and to make treatment decisions.
VRS
addresses two types of
factors:
�
Static
Risk Factors
�
Dynamic
Risk Factors
Static
factors refer
towards the things that can
not change like the child
hood history of
criminal.
Dynamic
factors refer
towards the changeable factors like if a person is
taking heroine as a drug,
once
he
decided to quit and quitted the addiction
so risk factor is
eliminated.
PCL-V
receives the criticism that it
only gives the estimation of
severity of the problem and does
not
address
the treatment. VRS eliminate the
criticism by emphasizing the dynamic factors.
So, to work on
changing
aspects and if things got
change, risk factor
minimizes.
The
VRS uses 6 Static and 20
Dynamic variables .The VRS
Static and Dynamic variables
are rated on a
4-point
scale (0, 1, 2 or 3) based on a
careful review of file
information and a semi-structured
interview.
The
VRS static variables can
predict general and violent recidivism,
but remain unchanged
with
treatment.
Higher ratings on the static
variables indicate
worse "track records" of
dysfunctional and
anti-social
behavior.
The
Dynamic
variables,
such as interpersonal aggression and
criminal attitudes, are changeable
risk
predictors;
they can be used as treatment
targets and can measure
changes in risk. Higher
ratings (2 or 3)
of
Dynamic variables indicate
that the variables in question
are closely linked to
violence and, therefore,
are
appropriate targets for
treatment.
The
sum
of the ratings of the
Static and Dynamic variables reflects the
client's level of violence
risk;
the
higher the score, the higher the
risk. In selecting clients for treatment,
those with higher VRS
scores
should
be appropriate candidates for
higher intensity
intervention.
101
Forensic
Psychology (PSY -
513)
VU
Now
let's begin with the
description of static factors of
VRS.
Static
Factors
Few
Static Factors are listed
below:
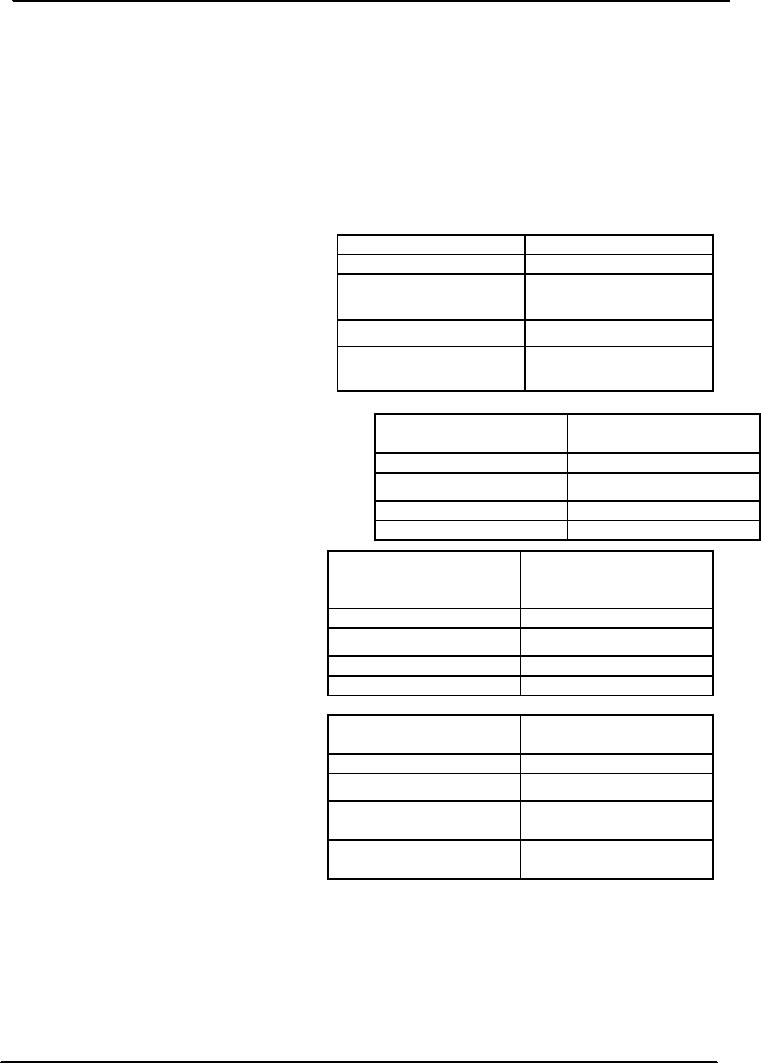
Current
Age
Age
at first violent
conviction
Number
of young offender convictions
Violence
throughout lifespan
Stability
of Family upbringing
How
these factors are scored while
using VRS?
Current
Age
Score
Current
Age
45
or above
0
There
are lesser chances that an
old man
40-44
1
would
commit violence.
So
if the person is 45 years or above 45
score
30-39
2
of
0 is given.
Below
30
3
Age
at first violent
conviction
Age
at first violent
Score
First
case in court that resulted
din some kind of
conviction
conviction
also determine future
violence risks.
30
or above
0
Researches
have shown that if the first offence
was
20-29
1
committed
at the young age there are more
future
risks
of violence. So, high score
is given to the age
15-19
2
below
15.
Below
15
3
Number
of young
Score
Number
of young offender convictions
offender
convictions
In
this category frequency of
convictions at
the
young age are scored to
determine future
No
convictions
0
risks.
1
conviction
1
2
convictions
2
3
or more
3
Violence
throughout lifespan
If
a person is not habitual of
violence and
Violence
throughout
Score
only
committed a single crime there
could be
lifespan
many
reasons and motives for that
particular
Generally
no violence
0
offence,
such individuals are at low
risk for
1
crime
1
further
violence. But if the violence is
the
2
or more crimes but do
2
pattern
of the some one's life then
there are
not
fit in any
pattern
more
chances that he will commit
violence
Violence
is the pattern of
3
after
releasing from prison. So a score of 3
is
life
awarded
to such people.
Prior
Release Failure or Escapes
from jail
102
Forensic
Psychology (PSY -
513)
VU
In
similar way prior release
failures and efforts to
escape from prison are rated
as 0,1,2,3.
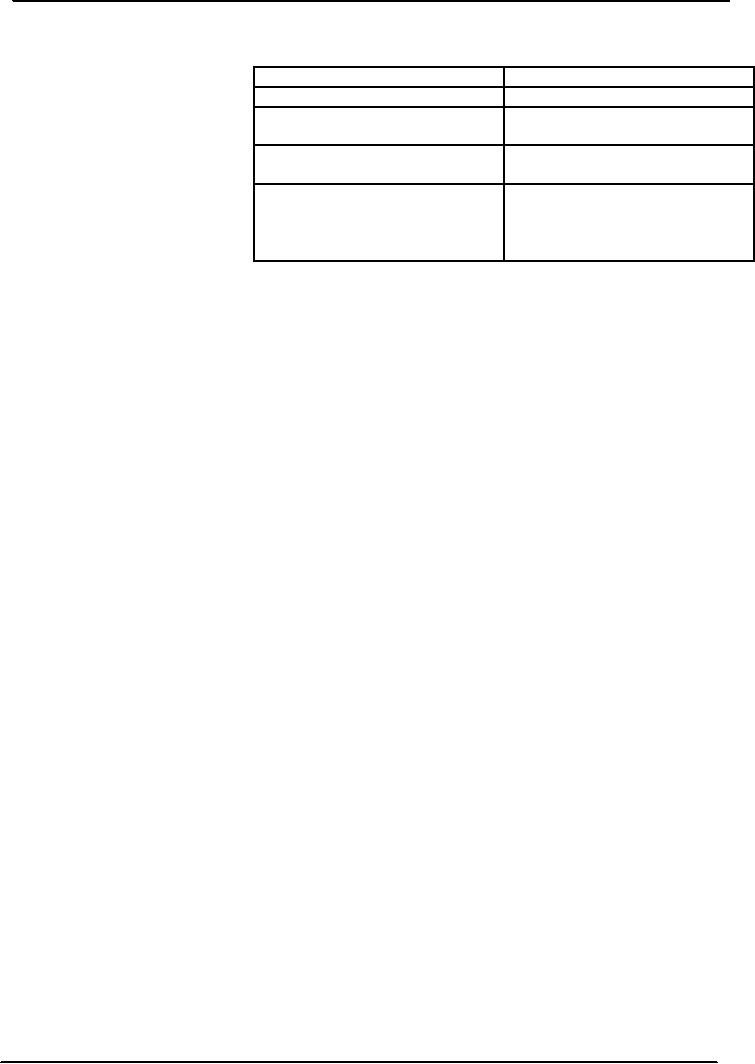
Stability
of Family upbringing
Stability
of Family upbringing
Score
If
person is brought up with
good
Good
upbringing
0
parenting,
0 scores are given.
Quarrels
of parents in childhood
1
but
resolved later in life
Dynamic
Factors
Through
out tension in family,
2
Dynamic
factors have been found
unresolved
and constant
stress
to
predict recidivism as well
as,
Separation
of parents and very
3
or
better than, static factors
and
upsetting
environment (e.g.
are
found more helpful
in
living
with father and
treatment.
These factors are
also
mistreatment
of step mother)
measured
during process
of
therapy.
It is knowledge of dynamic factors that
is necessary in order to assess
changes in an offender's
risk
level. Dynamic factors from
VRS are listed below.
These factors are also
scored in the same
manner
as the static factors are scored.
1.
Violent
Lifestyle (
like having frequent quarrels
with other co prisoners can
also determine
future
risks)
2.
Criminal
Personality ( if
test scores determine that
person has any personality
disorder they
are
more likely to re-offend)
3.
Criminal attitude
4.
Work
Ethic (
this factor is very good
predictor as the individual who
has non serious
attitude
towards
work is more risky then the
person who is seriously and
devotedly accomplishing the
work)
5.
Criminal
Peers ( if
person keeps bad company there is more
risk of future violence and
if the
person
has company of good people
then he is more likely to spend a
non violent life
afterwards)
6.
Interpersonal Aggression
7.
Emotional Control
8.
Violence during
institutionalization
9.
Weapon use
10.
Insight
into violence ( If
one admits that one has
committed some thing wrong
and have insight
of
his crime then less
chances of future
violence)
11.
Mental
Disorder (although
mentally ill people do not
commit crimes but some
time their
severity
of mental disorder can also
predict the future
behaviour)
12.
Substance
Abuse (substance
abusers are at very high
risk of future recidivism.
Because one can
commit
several type of crimes either to get
drugs or under influence of those
drugs)
13.
Stability of relationship with significant
other
14.
Community
Support ( the
degree of support from family,
neighbors and relatives is also
measured
and can predict the risk of
recidivism)
15.
Released to high risk
situation
16.
Violence cycle
17.
Impulsivity
18.
Cognitive Distortion
19.
Compliance with community
supervision
20.
Security Level of anticipated release
institution
103
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO FORENSIC PSYCHOLOGY:Future of Forensic Psychology
- INTRODUCTION TO FORENSIC PSYCHOOGY:Way of police investigation
- FORENSIC PSYCHOLOGY AND POLICE:Violent Criminals
- POLICE PSYCHOLOGY:Use of excessive force, Corruption, Personnel Selection
- POLICE PSYCHOLOGY:Fitness-for-Duty Evaluation (FFDE), False Confessions
- INVESTIGATIVE PSYCHOLOGY:For instance, Empirical and logical approach
- INVESTIGATIVE PSYCHOLOGY:Crime Scene Investigation, Staging
- PSYCHOLOGY OF VIOLENCE:Law of Conservation of Energy, Super ego
- PSYCHOANALYTIC MODEL AND VIOLENCE:Fixation at Oral Stage
- PSYCHOANALYTIC MODEL AND VIOLENCE:Defense Mechanism, Rationalization
- JUNGIAN PSYCHOLOGY AND VIOLENCE:Freudian Methods, JUNGIAN PSYCHOLOGY
- JUNGIAN PSYCHOLOGY AND VIOLENCE:Religion and mental illnesses
- BEHAVIORIST PERSPECTIVE AND VIOLENCE:Shadow’s violence, Child’s violence
- BEHAVIORIST PERSPECTIVE AND VIOLENCE:Operant Conditioning
- BEHAVIORIST PERSPECTIVE AND VIOLENCE:Schedules of Punishment
- SOCIAL LEARNING MODEL AND VIOLENCE:Observational learning, Vicarious punishment
- MORAL DEVELOPMENT AND VIOLENCE:Symbolic functioning, Formal operational stage
- BIO-PSYCHO-SOCIAL MODEL:Mental hospitals are factories of abuse
- ISLAMIC PERSPECTIVE ABOUT VIOLENCE:Morality is essential
- ISLAMIC MODEL:Nafs al-Ammara, Nafs al-Lawwama, Nafs ul Naatiqa
- TREATMENTS FOR THE SOUL:Tawba, Sabr o Shukr, Niyyat o Ikhlaas, Taffakkur
- CRIMINOGENIC PERSONALITY:Personality Disorders, Common Crimes
- CRIMINOGENIC PERSONALITY AND VIOLENCE:Mnemonic, Similarities
- CRIMINOGENIC PERSONALITY AND VIOLENCE:Terrorism and Psychopaths
- LEARNING DISABILITIES/MENTAL RETARDATION AND VIOLENCE
- ASSESSMENT OF PERSONALITY DISORDERS:Reasons for referral, Personality Inventories
- ASSESSMENT OF PERSONALITY DISORDERS:Different cutoff scores
- RISK ASSESSMENT:Violence reduction scale, Stability of Family upbringing
- TREATMENT OF VIOLENT BEHAVIOR / PERSONALITY PSYCHODYNAMIC PSYCHOTHERAPY
- JUNGINA THERAPEUTIC MODEL:Limits of re-parenting, Personality Typologies
- GROUP THERAPY FOR OFFENDERS:Learning in Groups, Humanistic Groups
- PSYCHOTHERAPIES IN FORENSIC SETTINGS:Narrative Therapy
- PSYCHOTHERAPIES IN FORENSIC SETTINGS:Solution Focused Therapy
- PSYCHOTHERAPIES IN FORENSIC SETTINGS:Avoiding reactance, Externalization
- PSYCHOTHERAPY IN FORENSIC SETTINGS AND SPECIAL CHALLENGES
- FORENSIC PSYCHOTHERAPY:Exploring therapeutic alliance, Music Therapy
- VIOLENCE REDUCTION PROGRAM:Target Population, Lack of motivation
- VIOLENCE REDUCTION PROGRAM:Criminal attitude, Interpersonal Aggression
- VICTIM SUPPORT:Main features of PTSD, Emotional Support
- VICTIM SUPPORT:Debriefing, Desensitization, Eidetic Therapy, Narrative Therapy
- SUBSTANCE MISUSE TREATMENT PROGRAM:Marijuana, Unconventional drugs
- SUBSTANCE MISUSE TREATMENT PROGRAM:Stages of Change, Homosexuality
- EXPERT WITNESS:Insanity Pleas, Sexual Offence Risk, Instructions
- COUNTER TERRORISM:Misconceptions, Psychologists & Propaganda war
- SUMMING UP FORENSIC PSYCHOLOGY:Problems with Risk Assessment, Expert Witness