 |

Consumer
Psychology (PSY -
514)
VU
Lecture
42
Post
Purchase Dissonance
Understanding:
Post
Purchase Dissonance
o
Conditions
Leading to Dissonance
o
Dissonance
Reduction
o
Marketing
Implications
Product
Disposition - Alternatives
o
Factors
Influencing Product Disposition
1.
Post Purchase
Dissonance
Consumer
is uncertain of the wisdom of his
decision; he rethinks this decision in the post
purchase stage.
Consumers
may become dissonant (inharmonious)
over a purchase decision as a
result of discrepancy between
a
consumer's
decision and the consumer's
prior evaluation
Dissonance
theory was derived from two
basic principles:
Dissonance
is uncomfortable and drive the
person to reduce it
Individuals
experiencing dissonance will
avoid situations that
produce more
dissonance
Conditions
Leading to Dissonance
Dissonance
is likely to occur under following
conditions:
Minimum
threshold of dissonance is passed.
Consumers may tolerate a certain level of
inconsistency in their
lives
until the point is
reached
The
action is irrevocable. Consumers may not
reverse a decision when they
have purchased a car
Unselected
alternatives have desirable
features
There
are several desirable
alternatives
Available
alternatives are quite
dissimilar in their
qualities
The
buyer is committed to his decision
because it has psychological
significance
There
is no pressure applied to the consumer to
make the decision
Dissonance
Reduction
There
several ways in which
consumer strives to reduce
dissonance. These include:
1.
Change the evaluation of
alternatives
2.
Seek new information to
support his choice
3.
Change his attitudes
1.
Changing Product Evaluations
Consumer
may reevaluate the product
alternatives. This may be accomplished by
consumer's enhancing the
attributes
of the product selected and
decreasing the importance of unselected products'
attributes, that is
consumers
seek to polarize alternatives to reduce
dissonance. Consumers' reevaluating of
the product alternatives
make
them view them as more similar
than was thought at the
purchase stage. Selective
retention may allow
consumer
to forget positive features of the
unselected alternatives and
negative features of the selected
product
2.
Seek new information to
support his
choice
Consumers
may reduce dissonance by
seeking additional information in
order to confirm the wisdom of
their
product
choice. Dissonant individuals actively
avoid information that would
tend to increase their
dissonance.
3.
Change his
attitudes
Consumers
may change their attitude to
make them consonant with his
behavior. Consumers sometimes
purchase
a
product they initially attributed to
negatively through a promotional scheme.
This may produce dissonance
and
to
avoid it they may change
their attitude. Motivation to achieve
consonance will likely take
the form of attitude
change
because that is easier than
renouncing the product.
133

Consumer
Psychology (PSY -
514)
VU
Marketing
Implications
1.
Confirming Expectations
When
the purchase confirms the consumers'
expectations, reinforcement takes place.
When expectations are
not
confirmed
cognitive dissonance takes
place and the consumer will
be likely to reduce the dissonance by
somewhat
negative
evaluation off the brand. Where a product
fails to measure up to the expectations the
result may be no
initial
sale, no repeat sale or unfavorable
word of mouth communication.
The
most important is that
products meet the expectations of the
consumers. Marketers should not build
up
expectations
unrealistically. Today`s advertisements
may seem harmless
exaggeration but it may
build unrealistic
expectations
in the mind of the consumer as a result
unfavorable word of mouth may
spread about the product.
Advertisers
should develop promotions that are
consistent with what can the
products reasonably
deliver
2.
Inducing Attitude
Change
When
attitudes are inconsistent
with purchase behavior they
are likely to change. Marketers
may seek to induce
behavior
changes in consumer through
various means. Promotional
tools including free samples
and saving
coupons
are frequently used.
There
is some evidence that
smaller the incentive greater the
dissonance and greater the
attitude change. The
small
inducements
force the consumer to confront his
purchase behavior with a
ready explanation for that.
Large
inducements
may force the consumer to simply rationalize. A
coupon of Rs 5 will produce
more of the desired
attitude
change than a coupon of Rs.
10.
In
case of free samples the
acceptance of brand may never
take place because the
consumer could fail to
expose
herself
fully to the attitude change
from use of the sample. There
may be an optimum value
range over which
promotional
techniques produce desired attitude
and behavior change. Beyond
that point either too low or
too
high
they may be relatively
ineffective.
3.
Reinforcing the Buyers
Consumers
post purchase information
seeking is usually the result of
dissonance. It is prudent to develop
special
ads
that will reinforce the buyers.
Such an approach pays
handsome dividends when targeting new
buyers. This
approach
is especially good when company is
launching an innovation.
134
Consumer
Psychology (PSY -
514)
VU
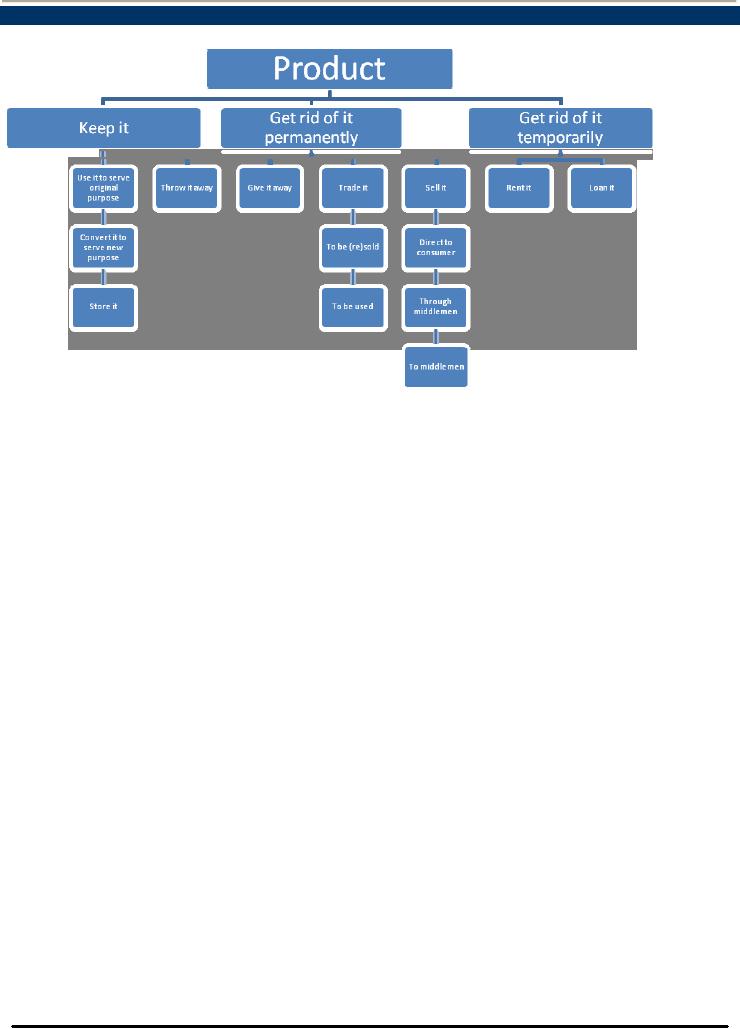
3.
Product Disposition -
Alternatives
Factors
Influencing Product
Disposition
Factors
that influence product disposition
may include:
Psychological
Characteristics of the Decision
Maker
Factors
intrinsic to the Product
Factors
intrinsic to the product (color,
style, etc)
Situational
factors extrinsic to the product
(finances, fashion change,
etc..)
135
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO CONSUMER PSYCHOLOGY:Consumer Behavior
- INTRODUCTION TO CONSUMER PSYCHOLOGY:Consumer research
- INTRODUCTION TO CONSUMER PSYCHOLOGY:Marketing Mix, Product, Price
- INTRODUCTION TO CONSUMER PSYCHOLOGY:Customer Value, Perceived Value
- VALUE AND RETENTION FOCUSED MARKETING AND CONSUMER DECISION MAKING PROCESS
- CONSUMER RESEARCH:Quantitative Research, Qualitative Research
- MAJOR STEPS IN CONSUMER RESEARCH PROCESS:Design of Primary research
- QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH DESIGNS & DATA COLLECTION METHODS
- QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH DATA COLLECTION TECHNIQUES:ATTITUDE SCALES
- QUALITATIVE RESEARCH DESIGNS & DATA COLLECTION METHODS
- CUSTOMER SATISFACTION MEASUREMENT, SAMPLING, AND DATA ANALYSIS AND REPORTING
- MARKET SEGMENTATION AND ITS BASES:Geographical Segmentation
- BASES FOR SEGMENTATION: DEMOGRAPHIC SEGMENTATION PSYCHOGRAPHIC SEGMENTATION
- BASES FOR SEGMENTATION: SOCIOCULTURAL SEGMENTATION USE RELATED SEGMENTATION USAGE SITUATION SEGMENTATION
- BASES FOR SEGMENTATION: BENEFIT SEGMENTATION:Intrinsic Cues
- BASES FOR SEGMENTATION: HYBRID SEGMENTATION STRATEGIES
- MARKET SEGMENTATION IMPLEMENTING SEGMENTATION STRATEGIES ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES CULTURE
- HOW CULTURE IS LEARNT ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Formal Learning
- CULTURE AND ITS MEASUREMENT ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES
- MEASUREMENT OF CULTURE ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Consumer Fieldwork
- SUBCULTURE CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES
- AGE AND GENDER SUBCULTURE CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES
- BASES FOR SEGMENTATION: BENEFIT SEGMENTATION:Market Segmentation
- SOCIAL CLASS CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Occupation
- CONSUMER SOCIAL CLASSES CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Affluent Consumer
- CONSUMER SOCIAL CLASSES CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Membership Group
- CONSUMER SOCIAL CLASSES CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Shopping Groups
- UNDERSTANDING PERSONALITY CHAPTER 5: INDIVIDUAL DETERMINANTS OF CONSUMER BEHAVIOR
- CONSUMER PERSONALITY, TRAIT THEORY AND SELF IMAGES
- CONSUMER MOTIVATION:Needs, Goals, Generic Goals
- UNDERSTANDING LEARNING:Intentional and Incidental Learning, Implications for Marketers
- INSTRUMENTAL CONDITIONING, INFORMATION PROCESSING AND MEMORY
- ATTITUDES:Characteristics of Attitudes, Attitudes have consistency
- ATTITUDE FORMATION AND CHANGE:How attitudes are learned?
- ATTITUDE CHANGE STRATEGIES:Resolving two conflicting attitudes
- INTRODUCTION TO CONSUMER DECISION MAKING:Decision Complexity
- Problem Recognition, Search and Evaluation and Decision and Purchase
- Decision and Purchase:Consumer Decision Rules, Output, Relationship Marketing
- Decisions Related to Post Purchase:Product Set up and Use
- Marketing Implications of Decisions Related to Post Purchase:Understanding
- Post Purchase Evaluation:Determinants of Satisfaction, Consumer Complaint Behavior
- Post Purchase Dissonance:Dissonance Reduction, Marketing Implications
- Consumerism:Roots of Consumerism, The Nature of Consumerism
- Consumerism – Issues and Responses:Environmental Concerns, Consumer Privacy
- Review – Consumer Psychology Course:Consumer Research, Consumerism