 |
SUBCULTURE CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES |
| << MEASUREMENT OF CULTURE ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Consumer Fieldwork |
| AGE AND GENDER SUBCULTURE CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES >> |
Consumer
Psychology (PSY -
514)
VU
LESSON21
SUBCULTURE
CHAPTER
4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES
Understanding:
�
Sub
cultural Analysis
�
Nationality
Structure
Subculture
The
members of a specific subculture
possess beliefs, values and
customs that set them apart
from other members
of
the same society. In addition they
adhere to most of the dominant cultural
values, and behavioral patterns of
the
larger
society.
Subculture
is defined as a distinct cultural group
that exists as an identifiable
segment within a larger,
more
complex
society
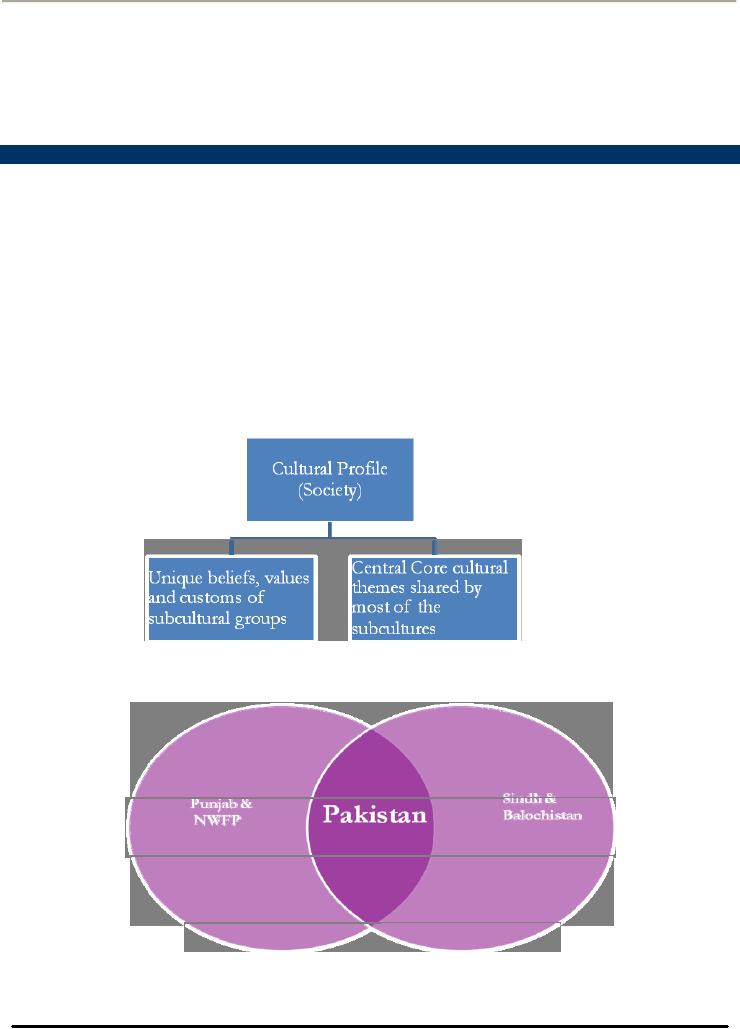
Cultural
Profile of a Society
Cultural
Profile of a society or nation is
composite of two distinct
elements:
1.
Unique beliefs, values and
customs subscribed by members of
specific of sub cultural
groups
2.
Central Core cultural themes shared by
most of the population regardless of
specific sub cultural
memberships
Thus
the cultural profile of the Pakistani
Society may be denoted by the
sub-cultures of the country's four
provinces
as denoted by the figure below
In
this way a young girl of Pakistan
may simultaneously
be:
�
Student
of Engineering
�
Muslim
Middleclass (Buying Power)
70

Consumer
Psychology (PSY -
514)
VU
�
Lahori
Sub
cultural Analysis
Sub
cultural Analysis enables marketers to
focus on sizable and natural
market segments. Marketers
must
determine
whether the beliefs, values and
customs shared by the members of a
specific subgroup make them
desirable
candidate for special marketing
effort.
Subcultures
therefore are relevant units of analysis
for market research and
these subcultures are
dynamic for
example
different ethnic groups of the Pakistani
population have been
changing and will continue
to change in
size
and economic strength in the coming
years.
Examples
of major sub cultural categories may be
as following:
Examples
Categories
Nationality
Pakistani,
Afghani, Irani
Religion
Hindu,
Muslim, Christian, etc.
Geographic
Region
Punjab,
NWFP, Sindh,
Balochistan
Age
Teenager,
Elderly
Gender
Female,
Male
Occupation
Govt.
Servant, Private Job
Social
Class
Lower,
middle, Upper
Nationality
and ethnic subcultures develop in order
to serve their members in
three ways:
To
provide a source of psychological
group identification
To
offer a patterned network of groups
and institutions supportive of the
subculture
To
serve as a frame of reference
through which to evaluate the
dominant culture.
71
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO CONSUMER PSYCHOLOGY:Consumer Behavior
- INTRODUCTION TO CONSUMER PSYCHOLOGY:Consumer research
- INTRODUCTION TO CONSUMER PSYCHOLOGY:Marketing Mix, Product, Price
- INTRODUCTION TO CONSUMER PSYCHOLOGY:Customer Value, Perceived Value
- VALUE AND RETENTION FOCUSED MARKETING AND CONSUMER DECISION MAKING PROCESS
- CONSUMER RESEARCH:Quantitative Research, Qualitative Research
- MAJOR STEPS IN CONSUMER RESEARCH PROCESS:Design of Primary research
- QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH DESIGNS & DATA COLLECTION METHODS
- QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH DATA COLLECTION TECHNIQUES:ATTITUDE SCALES
- QUALITATIVE RESEARCH DESIGNS & DATA COLLECTION METHODS
- CUSTOMER SATISFACTION MEASUREMENT, SAMPLING, AND DATA ANALYSIS AND REPORTING
- MARKET SEGMENTATION AND ITS BASES:Geographical Segmentation
- BASES FOR SEGMENTATION: DEMOGRAPHIC SEGMENTATION PSYCHOGRAPHIC SEGMENTATION
- BASES FOR SEGMENTATION: SOCIOCULTURAL SEGMENTATION USE RELATED SEGMENTATION USAGE SITUATION SEGMENTATION
- BASES FOR SEGMENTATION: BENEFIT SEGMENTATION:Intrinsic Cues
- BASES FOR SEGMENTATION: HYBRID SEGMENTATION STRATEGIES
- MARKET SEGMENTATION IMPLEMENTING SEGMENTATION STRATEGIES ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES CULTURE
- HOW CULTURE IS LEARNT ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Formal Learning
- CULTURE AND ITS MEASUREMENT ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES
- MEASUREMENT OF CULTURE ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Consumer Fieldwork
- SUBCULTURE CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES
- AGE AND GENDER SUBCULTURE CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES
- BASES FOR SEGMENTATION: BENEFIT SEGMENTATION:Market Segmentation
- SOCIAL CLASS CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Occupation
- CONSUMER SOCIAL CLASSES CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Affluent Consumer
- CONSUMER SOCIAL CLASSES CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Membership Group
- CONSUMER SOCIAL CLASSES CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Shopping Groups
- UNDERSTANDING PERSONALITY CHAPTER 5: INDIVIDUAL DETERMINANTS OF CONSUMER BEHAVIOR
- CONSUMER PERSONALITY, TRAIT THEORY AND SELF IMAGES
- CONSUMER MOTIVATION:Needs, Goals, Generic Goals
- UNDERSTANDING LEARNING:Intentional and Incidental Learning, Implications for Marketers
- INSTRUMENTAL CONDITIONING, INFORMATION PROCESSING AND MEMORY
- ATTITUDES:Characteristics of Attitudes, Attitudes have consistency
- ATTITUDE FORMATION AND CHANGE:How attitudes are learned?
- ATTITUDE CHANGE STRATEGIES:Resolving two conflicting attitudes
- INTRODUCTION TO CONSUMER DECISION MAKING:Decision Complexity
- Problem Recognition, Search and Evaluation and Decision and Purchase
- Decision and Purchase:Consumer Decision Rules, Output, Relationship Marketing
- Decisions Related to Post Purchase:Product Set up and Use
- Marketing Implications of Decisions Related to Post Purchase:Understanding
- Post Purchase Evaluation:Determinants of Satisfaction, Consumer Complaint Behavior
- Post Purchase Dissonance:Dissonance Reduction, Marketing Implications
- Consumerism:Roots of Consumerism, The Nature of Consumerism
- Consumerism – Issues and Responses:Environmental Concerns, Consumer Privacy
- Review – Consumer Psychology Course:Consumer Research, Consumerism