 |

Consumer
Psychology (PSY -
514)
VU
Lesson
16
BASES
FOR SEGMENTATION:
HYBRID
SEGMENTATION STRATEGIES
2.
Hybrid Segmentation
Approaches
Marketers
often segment markets by
combining several segmentation
variables rather than relying on one.
Three
hybrid
segmentations are most
popular in this regard:
Psychographic-Demographic
Profiles Geodemographic Profiles, VALS, and
Yanklovich's mind base
segmentation
1.
Psychographic, Lifestyle and Demographic
Profile
Psychographic
(lifestyles) and demographic
profiles are highly complimentary,
combining the two marketers
are
provided
with powerful information about
their target markets
While
designing the Psychographic, Lifestyle
and Demographic Profile, marketers
must answer the three
important
questions, that include:
1.
Whom should we target?
2.
What should we say?
3.
Where should we say
it?
To
help advertisers answer the
third question many advertising media
vehicles sponsor life-style research on
which
to
base very detailed audience
profiles
Example
A Popular US Magazine
For
a popular US Magazine a professional
audience research firm
conducted a research study to
identify
demographic
and psychographic lifestyle profiles of
the magazine readers. The
collected profiles looked
something
like:
Demographic
Profile
Total
Readers
5,227,000
Gender
Men
66%
Women
34%
Age
18-49
62%
25-54
65%
55+
27%
Average
Age
45
Education
Attended
College or beyond
77%
College
graduate or beyond
55%
Occupation
Professional
Managerial
34%
Top/Middle
Manager
33%
Employed
80%
Income
(Annual)($)
75%
50,000
or more
66%
60,000
0r more
50%
54
Consumer
Psychology (PSY -
514)
VU
75,000
or more
31%
Selected
Lifestyle Profile
(Leisure
Activities)
Attended
movies in the last six
months
73%
Bought
music CD's/tapes in the last 12
months
46%
Attended
live music performance in the
last 12 months
29%
Book
reading
45%
Entertained
friends or relatives in the last 12
months
48%
Household
subscribes to cable
69%
2.
Geo-Demographic Segmentation
Basic
Notion
People
who live close to one
another are likely to have
similar financial means, tastes,
preferences, lifestyles
and
consumption
habits.
Process
Computer
software are used to cluster
the population into lifestyle groupings
based on postal or zip
codes.
Clusters
are created based upon
consumer lifestyles. Specific
cluster includes zip codes
that are composed of
people
with similar lifestyle scattered
throughout the country
Using
Cluster Data
Marketers
use cluster data
for:
Direct
mail campaigns
Select
retail sites
Design
marketing strategies for specific
market segments
3.
Criteria for Effective Targeting of
Market Segments
To
be an effective target market a segment
should be:
Identifiable
Sufficient
(in terms of size)
Stable
or growing
Accessible
in terms of both media and
cost
To
divide the market into
separate segments on the basis of
common
or shared needs
or characteristics that
are
relevant
to the product or service, a marketer
must be able to identify the relevant
characteristics. Variables such as
Geography
(location) and Demography (age, gender,
occupation, race) are easy to
identify. Education, income
and
marital
status can be known through
questionnaires. Other characteristics
such as benefits
sought and
lifestyles
are
more
difficult to identify
Most
marketers prefer to target segments
that are relatively stable in
terms of demographic and
psychological
factors
and are likely to grow
larger over time. Teenagers
are sizable and easily
identifiable market, eager to
buy,
able
to spend and easily
reachable, yet when a marketer
produces merchandise for a
popular teenage fad, interest
in
it
may have waned
55
Consumer
Psychology (PSY -
514)
VU
4.
Implementing Segmentation
Strategies
Once
an organization has identified it most
promising segments it must decide whether
to target one segment
or
several
segments.
Each
targeted segment receives a
specially designed marketing mix
i.e. a specially tailored
product, price,
distribution
network and/or promotional
campaign
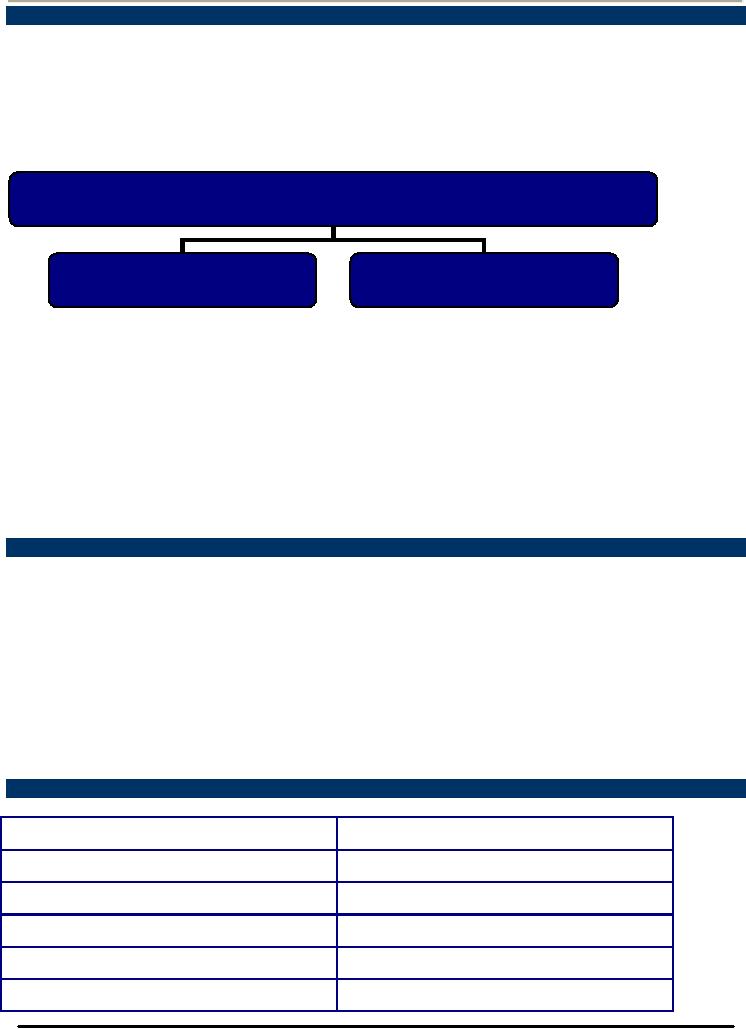
Segmentation
Implementing Strategies
Differentiated
Marketing
Concentrated
Marketing
Targeting
several segments
Targeting
just one segment
Differentiated
Marketing is
highly appropriate for:
�
Financially
strong companies
�
Well
established in a product
category
�
Competitive
with other firms that are
also strong in the category
(soft drinks, automobiles or
detergents)
Concentrated
Marketing is an appropriate
strategy when:
�
A
company is small or new to the
field
�
A
company can survive and
prosper by filling a niche
not occupied by stronger
companies
�
Gum
disease fighting
toothpastes
4.
Countersegmentation
Some
segments concentrate over time to a
point where they don't warrant an
individually designed marketing
program
In
Countersegmentation a company seeks
more generic needs or
consumer characteristics that
would apply to the
members
of two or more segments into
a larger single segment that
could be targeted with individually
tailored
product
or promotional campaign
Example
Some
business schools with wide
course offerings in each department
were forced to use
Countersegmentation
strategy
when they discovered that
students simply did not have
enough available credits to take a
full spectrum of
in
depth courses in their major
areas of studies. They had to
use Countersegmentation, e.g. by
combining
advertising,
publicity, sales promotion
and selling course into a
single course called
promotion
Key
Terms of Chapter 3
AIO's
(activities, interests,
opinions)
Market
Segmentation
Benefit
Segmentation
Positioning
Concentrated
Marketing
Psychographic
Inventory
Countersegmentation
Psychographic
Segmentation
Demographic
Characteristics
Sociocultural
Variables
Demographic
Segmentation
Use
related segmentation
56

Consumer
Psychology (PSY -
514)
VU
Differentiated
Marketing
Usage
situation
Geographic
Segmentation
Hybrid
Segmentation
Mass
Marketing
57
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO CONSUMER PSYCHOLOGY:Consumer Behavior
- INTRODUCTION TO CONSUMER PSYCHOLOGY:Consumer research
- INTRODUCTION TO CONSUMER PSYCHOLOGY:Marketing Mix, Product, Price
- INTRODUCTION TO CONSUMER PSYCHOLOGY:Customer Value, Perceived Value
- VALUE AND RETENTION FOCUSED MARKETING AND CONSUMER DECISION MAKING PROCESS
- CONSUMER RESEARCH:Quantitative Research, Qualitative Research
- MAJOR STEPS IN CONSUMER RESEARCH PROCESS:Design of Primary research
- QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH DESIGNS & DATA COLLECTION METHODS
- QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH DATA COLLECTION TECHNIQUES:ATTITUDE SCALES
- QUALITATIVE RESEARCH DESIGNS & DATA COLLECTION METHODS
- CUSTOMER SATISFACTION MEASUREMENT, SAMPLING, AND DATA ANALYSIS AND REPORTING
- MARKET SEGMENTATION AND ITS BASES:Geographical Segmentation
- BASES FOR SEGMENTATION: DEMOGRAPHIC SEGMENTATION PSYCHOGRAPHIC SEGMENTATION
- BASES FOR SEGMENTATION: SOCIOCULTURAL SEGMENTATION USE RELATED SEGMENTATION USAGE SITUATION SEGMENTATION
- BASES FOR SEGMENTATION: BENEFIT SEGMENTATION:Intrinsic Cues
- BASES FOR SEGMENTATION: HYBRID SEGMENTATION STRATEGIES
- MARKET SEGMENTATION IMPLEMENTING SEGMENTATION STRATEGIES ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES CULTURE
- HOW CULTURE IS LEARNT ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Formal Learning
- CULTURE AND ITS MEASUREMENT ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES
- MEASUREMENT OF CULTURE ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Consumer Fieldwork
- SUBCULTURE CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES
- AGE AND GENDER SUBCULTURE CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES
- BASES FOR SEGMENTATION: BENEFIT SEGMENTATION:Market Segmentation
- SOCIAL CLASS CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Occupation
- CONSUMER SOCIAL CLASSES CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Affluent Consumer
- CONSUMER SOCIAL CLASSES CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Membership Group
- CONSUMER SOCIAL CLASSES CHAPTER 4: ENVIRONMENTAL INFLUENCES:Shopping Groups
- UNDERSTANDING PERSONALITY CHAPTER 5: INDIVIDUAL DETERMINANTS OF CONSUMER BEHAVIOR
- CONSUMER PERSONALITY, TRAIT THEORY AND SELF IMAGES
- CONSUMER MOTIVATION:Needs, Goals, Generic Goals
- UNDERSTANDING LEARNING:Intentional and Incidental Learning, Implications for Marketers
- INSTRUMENTAL CONDITIONING, INFORMATION PROCESSING AND MEMORY
- ATTITUDES:Characteristics of Attitudes, Attitudes have consistency
- ATTITUDE FORMATION AND CHANGE:How attitudes are learned?
- ATTITUDE CHANGE STRATEGIES:Resolving two conflicting attitudes
- INTRODUCTION TO CONSUMER DECISION MAKING:Decision Complexity
- Problem Recognition, Search and Evaluation and Decision and Purchase
- Decision and Purchase:Consumer Decision Rules, Output, Relationship Marketing
- Decisions Related to Post Purchase:Product Set up and Use
- Marketing Implications of Decisions Related to Post Purchase:Understanding
- Post Purchase Evaluation:Determinants of Satisfaction, Consumer Complaint Behavior
- Post Purchase Dissonance:Dissonance Reduction, Marketing Implications
- Consumerism:Roots of Consumerism, The Nature of Consumerism
- Consumerism – Issues and Responses:Environmental Concerns, Consumer Privacy
- Review – Consumer Psychology Course:Consumer Research, Consumerism