 |

Cognitive
Psychology PSY 504
VU
Lesson
43
Language
and thought
Another
important field is Psycholinguistics
that studies the importance
of languages in
Psychology.
Language
Language
is the most impressive of
all cognition. The
difference between human
language and
the
natural communication systems of
other species is enormous.
More than anything
else,
language
is responsible for the
current advanced state of
human civilization. It is principal
means
by
which knowledge is recorded
and transmitted across
generations. Language is far
superior to
animal
communication.
Languages
also provide people with
the principal means of
assessing what another
person
knows.
So, without language human
beings would experience
countless more
misunderstanding
than
they currently do. If there
were no language people will
be bored by technology so,
there will
be
little technology without
language. Therefore without
language much of the joy of
living would
be
lost. Language is very
important in every field
i.e. Religion, Law and
Morality.
Language
is a primary source of cognitive
psychology. Noam Chomsky
made language his
basic
subject
matter and talked about
the importance of language. He
also criticized Behaviorists
that
gave
importance only to the overt
behavior and ignored the
importance of language.
Productivity
& Regularity
Language
is not a random combination of
words. Balanced against the
productivity of language is
its
highly regular character.
The psycholinguist focuses on
two aspects of language:
productivity
and
regularity.
Productivity
refers to the fact that an
infinite number of utterances
are possible in any
language.
Regularity
refers to the fact that
these utterances are
systematic in many
ways.
A
set of rules that accounts
for both productivity and
regularity of natural language is
called
grammar.
What
is Grammar?
A
grammar should be able to
prescribe or generate all
the acceptable sentences of a
language
and
be able to reject all the
unacceptable sentences in the
language.
Some
violations of grammar are
given below;
1.
These are rejecting
syntactic violations
The
girls hits the
boys
The
girl hit a boys
The
boys were hit the
girls
These
are called syntactic
violations. They are fairly
meaningful but contain some
mistakes in
word
combinations or word forms.
The correct sentences
are
�
The
girls hit the
boys.
�
The
girl hits a boy.
�
The
boys hot the
girls.
2.
Reject semantic
violations
Colorless
green ideas sleep
furiously
Sincerity
frightened the cat
129

Cognitive
Psychology PSY 504
VU
These
are correct syntactically
but wrong semantically. In
these sentences words are
correct in
form
and syntactic but their
combination is nonsense.
3.
Reject phonological
violations
Vere
is the wase?
We
produce V and W same
phonologically. These are
mistakes V and W have
different sounds.
This
sentence is correct syntactically
and semantically but be
mispronounced. The
correct
sentence
is where is vase?
To
account for the regularity
of language, linguists need a
grammar. The grammar
includes
Phonology,
Syntax, and Semantics.
Phonology means sound,
syntax means structure,
and
semantics
means meaning.
Linguistic
Intuition
Another
feature that linguists want
a grammar to explain is the
linguistic intuitions of speakers
of
the
language. Linguistic intuitions
are judgments about the
nature of linguistic utterances or
about
the
relationship between linguistic
utterances.
Some
examples of linguistic intuition
are given in Urdu.
For
example,
Larki
nay Larkay ko maara
Larkay
nay larki say maar
khai
Above
two sentences are
paraphrases Ambiguity: Ambiguity
means one word has
more
meanings
that are confusing. For
example, they are cooking
apples. This sentence has
many
meanings.
Some can think it as cooking
as food some can think
cooking means making
salad
etc.
Grammar
can specify well-formed
sentences, ill-formed ones
and why. Explain intuitions
that
have
about such things as
paraphrase and
ambiguity.
Competence
versus performance
Linguistic
competence means a person's
abstract knowledge of the
language. And linguistic
performance
means the actual application
of that knowledge in speaking or
listening. In Chomsky
views
the linguist's task is to
develop a theory of competence
and the psychologist task is
to
develop
a theory of performance.
Our
everyday use of language
does not always correspond
to the prepositions of linguistic
theory.
We
misunderstand the meaning of
sentences. We hear sentences
that are ambiguous but do
not
note
their ambiguity. Another
complication is that linguistic
intuitions are not always
clear.
For
example, a child talks to
his mother and
says
Child:
Look
Mum fis
Mother:
Fis?
Child:
No,
fis.
Mother:
Oh,
fish.
Child:
Yes,
fis.
This
is the fis phenomenon the
child knows but can't
perform.
Syntactic
Formalisms
A
great deal of emphasis in
linguistics has been given
to understanding the syntax of
natural
language.
One central linguistic
concept is phrase
structure.
130
Cognitive
Psychology PSY 504
VU
Phrase
Structure
Phase
structure analysis is not
only significant in linguistics,
but is also very important
to an
understanding
of language processing.
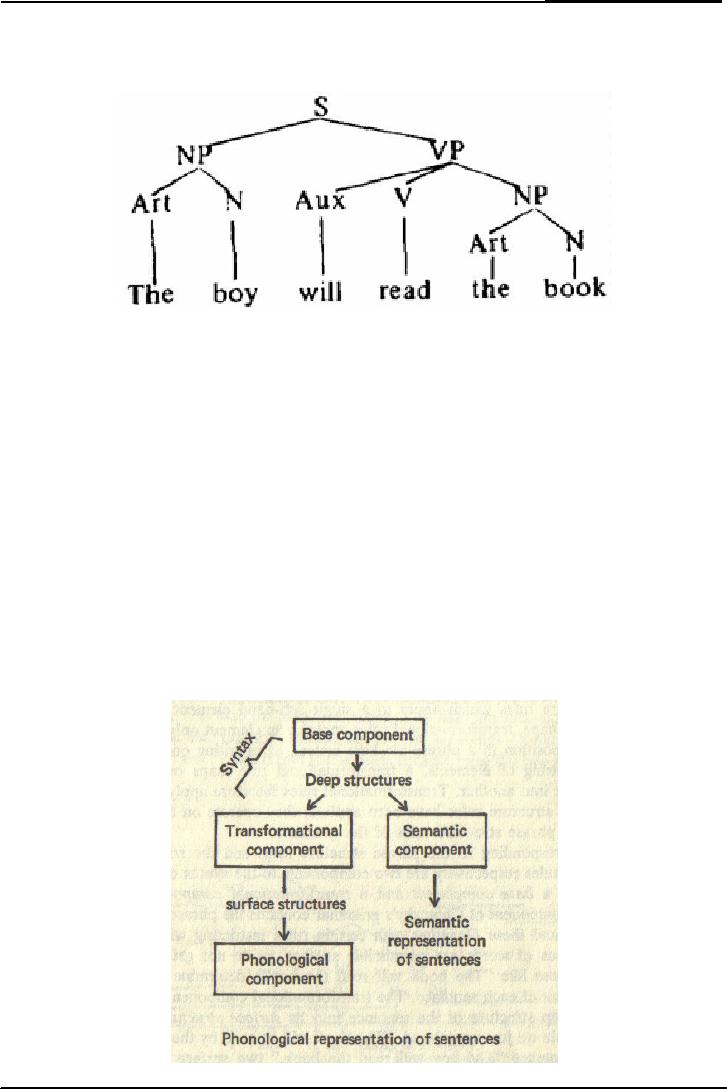
In
the above figure the
structure of phrase is given as an
upside-down tree. In this
phase
structure
tree sentence (s) points to
its subunits nouns phrase
(NP) and verb phrase
(VP), and
each
of these units points to its
subunits.
Chomsky
Noam
Chomsky worked a lot on
language. He made some rules
of grammar. He says
every
sentence
has two structures.
Deep
Structure
Surface
Structure
Then
there is Transformational grammar
that helps in making
sentence.
Deep:
The boy reads the
book
Surface:
The boy +future tense+
read the book. After
the transformation the
sentence become
"The
boy will read the
book".
The
figure, in below, is showing
the Chomsky concept of deep
structure and surface
structure.
How
the sentence start with
the base component then
deep structure then
transformational
component
and semantic component after
these components there is
surface structure and in
the
last
there is phonological
structure.
131

Cognitive
Psychology PSY 504
VU
Language
and Thought
Next
question is that what affect
the structure of language
has on cognition. Language is a
source
of
thinking. A wide variety of
proposals have been put
forth as to the connection
between
language
and thought.
There
are many evidences showed
the relationship between
language and thought;
Aristotle
argued
that thought determined
language 2500 years
ago.
Whorf
argued in the 20th century
Language determines thought. He
claimed that language
determines
or strongly influences the
way a person thinks or
perceives the world. This
proposal
claims
that language and thought
are identical. Arabic has a
large number of words for
Camel.
Eskimos
have a large number of words
for snow. Their language
has any effect on the
Eskimos'
perception
of snow over and above
the effect of experience.
The difference between ice
and
snow
is also clearly understood by
Eskimos than any other
person.
Chomsky
took a modularity position in
this debate of language and
thoughts. He said
language
and
thoughts are separate
systems that have different
process.
One
experiment was compared the
ability of Dani (people of
Indonesia) to learn nonsense
names
of
focal (basic) colors versus
nonfocal colors. English
speakers find it easier to
learn arbitrary
names
for focal colors. Dani
subjects also found it
easier to learn arbitrary
focal colors than
nonfocal
colors even they have no
names for these colors in
their culture.
Natural
order
In
different languages the
sentence order is in these
forms
S=
subject
O=
object
V=
verb
SOV
44
percent of worlds
language
SVO
35
percent of worlds
language
VSO
19
percent of worlds
language
VOS
2
percent of worlds
language
132
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION:Historical Background
- THE INFORMATION PROCESSING APPROACH
- COGNITIVE NEUROPSYCHOLOGY:Brains of Dead People, The Neuron
- COGNITIVE NEUROPSYCHOLOGY (CONTINUED):The Eye, The visual pathway
- COGNITIVE PSYCHOLOGY (CONTINUED):Hubel & Wiesel, Sensory Memory
- VISUAL SENSORY MEMORY EXPERIMENTS (CONTINUED):Psychological Time
- ATTENTION:Single-mindedness, In Shadowing Paradigm, Attention and meaning
- ATTENTION (continued):Implications, Treisman’s Model, Norman’s Model
- ATTENTION (continued):Capacity Models, Arousal, Multimode Theory
- ATTENTION:Subsidiary Task, Capacity Theory, Reaction Time & Accuracy, Implications
- RECAP OF LAST LESSONS:AUTOMATICITY, Automatic Processing
- AUTOMATICITY (continued):Experiment, Implications, Task interference
- AUTOMATICITY (continued):Predicting flight performance, Thought suppression
- PATTERN RECOGNITION:Template Matching Models, Human flexibility
- PATTERN RECOGNITION:Implications, Phonemes, Voicing, Place of articulation
- PATTERN RECOGNITION (continued):Adaptation paradigm
- PATTERN RECOGNITION (continued):Gestalt Theory of Perception
- PATTERN RECOGNITION (continued):Queen Elizabeth’s vase, Palmer (1977)
- OBJECT PERCEPTION (continued):Segmentation, Recognition of object
- ATTENTION & PATTERN RECOGNITION:Word Superiority Effect
- PATTERN RECOGNITION (CONTINUED):Neural Networks, Patterns of connections
- PATTERN RECOGNITION (CONTINUED):Effects of Sentence Context
- MEMORY:Short Term Working Memory, Atkinson & Shiffrin Model
- MEMORY:Rate of forgetting, Size of memory set
- Memory:Activation in a network, Magic number 7, Chunking
- Memory:Chunking, Individual differences in chunking
- MEMORY:THE NATURE OF FORGETTING, Release from PI, Central Executive
- Memory:Atkinson & Shiffrin Model, Long Term Memory, Different kinds of LTM
- Memory:Spread of Activation, Associative Priming, Implications, More Priming
- Memory:Interference, The Critical Assumption, Limited capacity
- Memory:Interference, Historical Memories, Recall versus Recognition
- Memory:Are forgotten memories lost forever?
- Memory:Recognition of lost memories, Representation of knowledge
- Memory:Benefits of Categorization, Levels of Categories
- Memory:Prototype, Rosch and Colleagues, Experiments of Stephen Read
- Memory:Schema Theory, A European Solution, Generalization hierarchies
- Memory:Superset Schemas, Part hierarchy, Slots Have More Schemas
- MEMORY:Representation of knowledge (continued), Memory for stories
- Memory:Representation of knowledge, PQ4R Method, Elaboration
- Memory:Study Methods, Analyze Story Structure, Use Multiple Modalities
- Memory:Mental Imagery, More evidence, Kosslyn yet again, Image Comparison
- Mental Imagery:Eidetic Imagery, Eidetic Psychotherapy, Hot and cold imagery
- Language and thought:Productivity & Regularity, Linguistic Intuition
- Cognitive development:Assimilation, Accommodation, Stage Theory
- Cognitive Development:Gender Identity, Learning Mathematics, Sensory Memory