 |
Cognitive
Psychology PSY 504
VU
Lesson
30
Memory
Interference
Various
factors can affect the
amount of activation that is
spread to a knowledge structure.
From
the
previous experiments we can
infer that strength of
encoding has an effect such
that more
strongly
encoded information receives
greater activation. Another
factor is the number
of
alternative
network paths down which
activation can
spread.
Encoding
is a process of transfer the
information from short term
memory to long term
memory
through
codes.
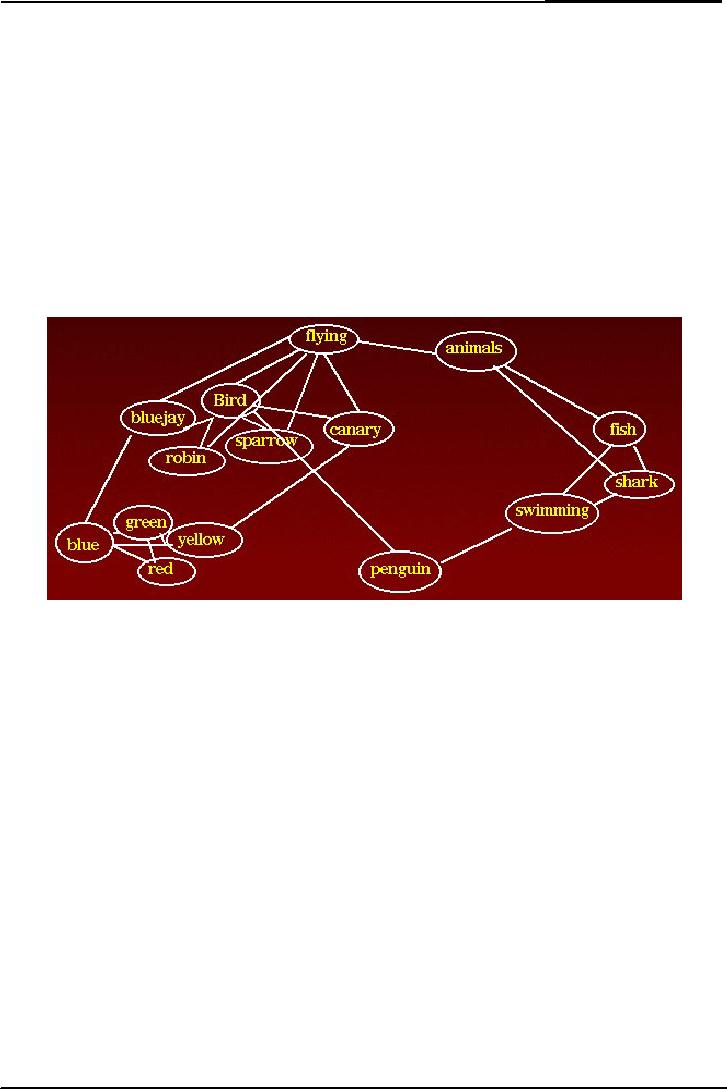
This
following figure is showing
the activation in a network.
The word penguin has
two links, one
is
bird and other is swimming.
Bird and swimming have
their links as well. If we
think about
swimming
the activation model will
become active and we can
recall penguin because of
its
connection
with swimming.
The
Fan Effect
Anderson
(1974) performed an experiment. He
had subjects to memorize 26
facts. In these
statements
some persons were paired
with only one location
and some locations with
only one
person.
Other persons were paired
with two locations and
other locations were paired
with two
persons.
Each statements was followed
by two numbers, reflecting
the number of facts
associated
with the subject and
the location. For instance,
sentence3 is labeled 2-1
because their
subject
occurs in two sentences
(sentences 3 and 4) and its
location occurs in one
sentence
(sentence
3). The sentences
were;
The
doctor is in the bank.
(1-1)
The
fireman is in the park.
(1-2)
The
lawyer is in the church.
(2-1)
The
lawyer is in the park.
(2-2)
Number
of facts associated with
subject and location.
Subjects
were drilled on each
sentence. Before beginning
the reaction time phase,
subjects were
able
to recall all the locations
associated with a particular
type of person (e.g. doctor)
and all the
people
associated with a particular
location (e.g. park). Then
they began a speeded-
recognition
phase
of experiment, during which
they were presented with
sentences and had to judge
whether
they
recognized them from the
study set. Foil sentences
were created by repairing of
people and
locations
from the study
set.
89
Cognitive
Psychology PSY 504
VU
Results
The
recognition time for
sentences as a function of number
facts learned about persons
and
location.
Specific
Location
Specific
Person
1
sentence
2
sentences
1sentence
1.11
1.17
2
sentences
1.17
1.22
Results
are showing recognition time
increases as a function of both
the number of facts
studied
about
the person and the
number of facts studied
about the person and
the number of facts
studied
about the location.
The
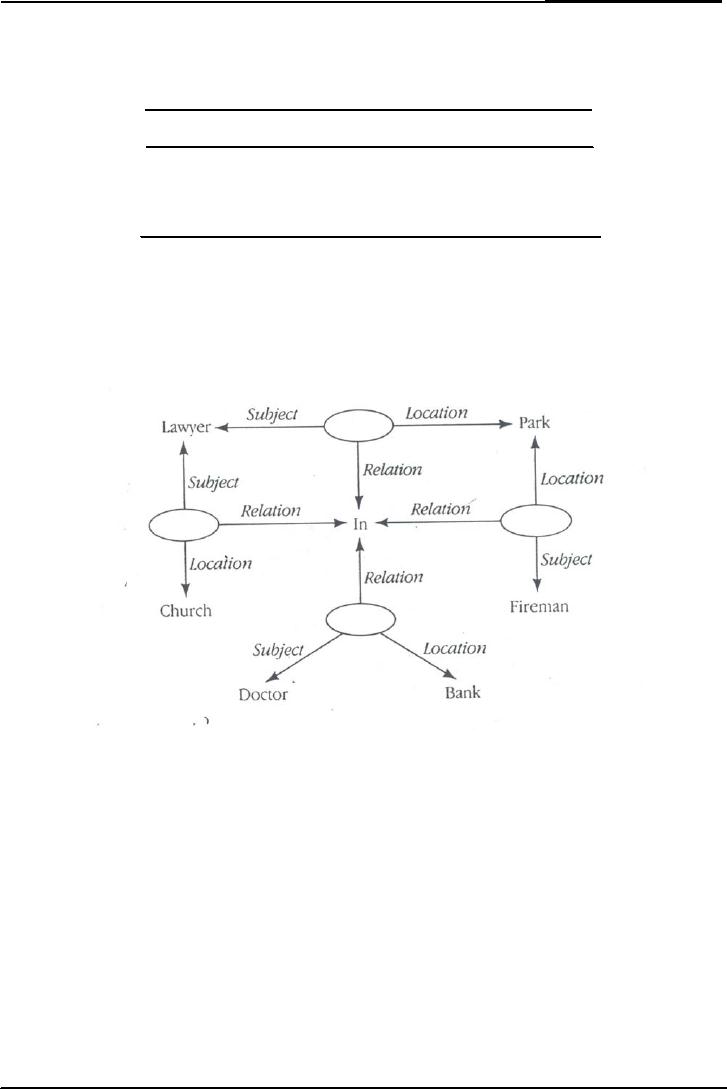
Fan Effect:
Network
The
network representation for
sentences 1 through4 is given
below.
Every
node has three parts
such as relations, subject,
and location. By applying
the activation
concept
to this representation, we can
nicely account for the
increase in reaction time.
Subject
might
recognize such as probe as a
lawyer is in
the park. First
suppose the presentation of
terms
lawyer,
in and park serves to
activate their presentations in
memory. Then activation will
spread
from
these nodes to activate the
target proposition and
enable it to be recognized. Fireman
and
lawyer
interfere with park. But
there is no interference between
doctor and lawyer, so there
is no
fan
effect.
The
Critical Assumption
The
amount of activation reaching
the proposition is inversely
related to the number of
links
leading
from it.
Subjects
should be slower to recognize a
fact involving lawyer and
park than one
connecting
doctor
and bank because more
paths emanate from the
first set of concepts. That
is, in the
lawyer
and park case two
paths point from each of
the concepts to the two
propositions in which
each
was studied, whereas only
one path leads from
each of the doctor and
bank concepts.
90

Cognitive
Psychology PSY 504
VU
Activation:
Limited capacity
This
is one experiment among many
points to a limited-capacity feature of
the spreading-
activation
process. The nodes, such as
lawyer and park, from
which the spread of
activation
starts
can be called source nodes.
One node can has
thousands nodes. This one
node supply
energy
to other nodes the energy of
this node is also transfer
to other but in a very
limited
amount.
Like in an example of experiment of
last lecture the word
dog is also activate other
kind
of
dogs, meats, bones and
other animals.
A
source node has a fixed
capacity for emitting
activation. This capacity is
divided among all
the
paths
emanating from that node.
The more paths that
exist, the less activation
will be assigned to
any
one path and the
slower will be the rate of
activation.
At
one time we can make
many nodes with one
word. Like the word
fish has many links. We
can
remember
many other things, like
other kind of fish, water,
sea, other sea animals
etc.
Another
example of Gambler, we can
make many links with
this word like cards,
the pictures on
cards,
the figures of cards
etc.
Interference
The
fan effect is the name
given to this increase in
reaction time related to an
increase in the
number
of facts associated with a
concept. It is so named because
the increase in reaction
time
is
related to an increase in the
fan of facts emanating from
the network representation of
the
concept.
The term conveys the
fact that additional
information about a concept
interferes with
memory
for a particular piece of
information. Interference affects a
wider range of measures
than
just
recognition time. Fan effect
is reserved for interference
effects as measured by reaction
time.
91
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION:Historical Background
- THE INFORMATION PROCESSING APPROACH
- COGNITIVE NEUROPSYCHOLOGY:Brains of Dead People, The Neuron
- COGNITIVE NEUROPSYCHOLOGY (CONTINUED):The Eye, The visual pathway
- COGNITIVE PSYCHOLOGY (CONTINUED):Hubel & Wiesel, Sensory Memory
- VISUAL SENSORY MEMORY EXPERIMENTS (CONTINUED):Psychological Time
- ATTENTION:Single-mindedness, In Shadowing Paradigm, Attention and meaning
- ATTENTION (continued):Implications, Treisman’s Model, Norman’s Model
- ATTENTION (continued):Capacity Models, Arousal, Multimode Theory
- ATTENTION:Subsidiary Task, Capacity Theory, Reaction Time & Accuracy, Implications
- RECAP OF LAST LESSONS:AUTOMATICITY, Automatic Processing
- AUTOMATICITY (continued):Experiment, Implications, Task interference
- AUTOMATICITY (continued):Predicting flight performance, Thought suppression
- PATTERN RECOGNITION:Template Matching Models, Human flexibility
- PATTERN RECOGNITION:Implications, Phonemes, Voicing, Place of articulation
- PATTERN RECOGNITION (continued):Adaptation paradigm
- PATTERN RECOGNITION (continued):Gestalt Theory of Perception
- PATTERN RECOGNITION (continued):Queen Elizabeth’s vase, Palmer (1977)
- OBJECT PERCEPTION (continued):Segmentation, Recognition of object
- ATTENTION & PATTERN RECOGNITION:Word Superiority Effect
- PATTERN RECOGNITION (CONTINUED):Neural Networks, Patterns of connections
- PATTERN RECOGNITION (CONTINUED):Effects of Sentence Context
- MEMORY:Short Term Working Memory, Atkinson & Shiffrin Model
- MEMORY:Rate of forgetting, Size of memory set
- Memory:Activation in a network, Magic number 7, Chunking
- Memory:Chunking, Individual differences in chunking
- MEMORY:THE NATURE OF FORGETTING, Release from PI, Central Executive
- Memory:Atkinson & Shiffrin Model, Long Term Memory, Different kinds of LTM
- Memory:Spread of Activation, Associative Priming, Implications, More Priming
- Memory:Interference, The Critical Assumption, Limited capacity
- Memory:Interference, Historical Memories, Recall versus Recognition
- Memory:Are forgotten memories lost forever?
- Memory:Recognition of lost memories, Representation of knowledge
- Memory:Benefits of Categorization, Levels of Categories
- Memory:Prototype, Rosch and Colleagues, Experiments of Stephen Read
- Memory:Schema Theory, A European Solution, Generalization hierarchies
- Memory:Superset Schemas, Part hierarchy, Slots Have More Schemas
- MEMORY:Representation of knowledge (continued), Memory for stories
- Memory:Representation of knowledge, PQ4R Method, Elaboration
- Memory:Study Methods, Analyze Story Structure, Use Multiple Modalities
- Memory:Mental Imagery, More evidence, Kosslyn yet again, Image Comparison
- Mental Imagery:Eidetic Imagery, Eidetic Psychotherapy, Hot and cold imagery
- Language and thought:Productivity & Regularity, Linguistic Intuition
- Cognitive development:Assimilation, Accommodation, Stage Theory
- Cognitive Development:Gender Identity, Learning Mathematics, Sensory Memory