 |
Cognitive
Psychology PSY 504
VU
Lesson
28
Memory
Atkinson &
Shiffrin Model
Before
studying long term memory,
the overview of Atkinson and
Shiffrin model is
very
important.
It gives us overview and
makes us see where long
term memory belongs.
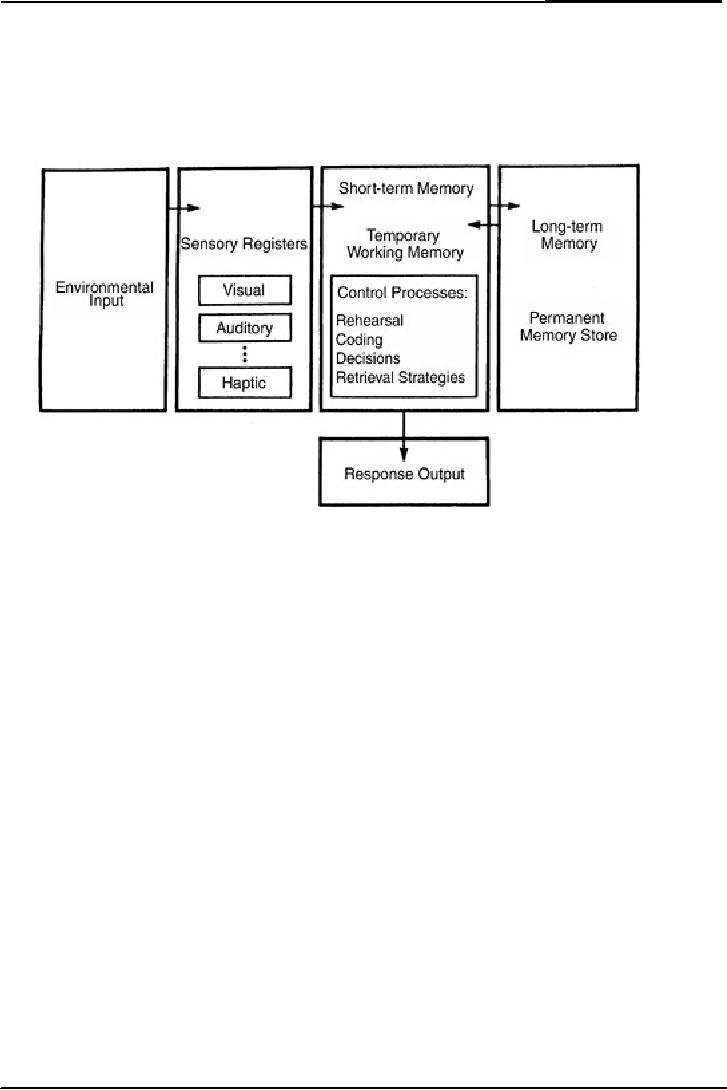
In
first box there is
environmental input. First of
all the input comes in
sensory register from
environment.
This information may be
visual or auditory etc. then
this input goes to short
term
memory.
Arrows are showing this
process.
Sometimes
we listen a word that we
have listened ago. It has
been stored in our long
term
memory.
Short term memory pull
out information from long
term memory and match
this
information
with environmental input or
information and then
response out put.
In
short term memory there
are control processes. These
processes happened in short
term
memory.
These are rehearsal, coding,
decisions and retrieval
strategies.
Like
when someone tells us
telephone number we want to
store it in our mobile.
Until we
do
not store this number we
rehearse the number in our
mind. If we want to remember
the
information,
for long term, we code
the information in someway. We
make decisions about
information
at our short term memory
stage. Or short term memory
makes decisions. The
strategies
of revision are also present
in our short term memory.
For example if we are
shopping
the
things in market we make
decisions to buy the
things.
Our
current information goes
into long term memory
and stored information in
long term memory
comes
in short term memory. For
example a depressive patient
remind all his or her
past life
events
that make him or her
more depressive. So therapists
help patient to forget old
things.
These
old things are stored in
long term memory. Long
term memory is permanent
memory. LTM
provides
information according to context
and scenario. Long term
memory already creates set
or
pattern
in short term memory. The
concept of LTM is closely related to
the STM. Long
term
memory
constantly interacts with
short term memory. Every
experience, sensory
experience,
every
thing is survived or stored in
our long term
memory.
Long
Term Memory
A
memory that lasts more
than 20 seconds is Long term
memory.
So
if you can recall something
after 20 seconds it is in your
LTM.
83

Cognitive
Psychology PSY 504
VU
What
is it?
Through
repetition the information is
stored in our long term
memory.
Different
things to different
people
Memory
has different meanings for
different people.
Memory
for students is about
studies.
Memory
for older people is about
finding keys.
Memory
for young children is about
remembering how to tie their
shoe laces.
Memory
for scholars is about
remembering what the book
was all about.
So,
there are different
questions we have about
memory.
Different
kinds of LTM
There
are different kinds of Long
term memory.
1.
Episodic versus
Procedural
Amnesia
patients forget their names
but don't forget how to
brush their teeth.
Like
in films or movies, hero or
heroine is injured and his
or her memory is lost. They
forget about
themselves
but they know how to
wear dress or how to make
shave.
So
in amnesia episodic memory
become upset.
2.
Semantic versus
Sensory
In
semantic memory we remember
meanings of things. Like
what is home? What is
book?
What
is rose?
Sensory
memory means we remember
analog representations of things.
Sensory
representation
is analog representation .It
represents original
things.
Like
recall a perfume, imagine
the taste of chocolate. What
is a smell of rose?
3.
Implicit versus
Explicit
Things
you learned on purpose as
opposed to things you
learned anyway, like
teacher
shouting
What
do we study?
Transfer
from STM into LTM
Retrieval
from LTM back into
STM
Recall
versus Recognition
Applications
Studying
and testing
Role
of rote learning
Eyewitness
testimony
84
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION:Historical Background
- THE INFORMATION PROCESSING APPROACH
- COGNITIVE NEUROPSYCHOLOGY:Brains of Dead People, The Neuron
- COGNITIVE NEUROPSYCHOLOGY (CONTINUED):The Eye, The visual pathway
- COGNITIVE PSYCHOLOGY (CONTINUED):Hubel & Wiesel, Sensory Memory
- VISUAL SENSORY MEMORY EXPERIMENTS (CONTINUED):Psychological Time
- ATTENTION:Single-mindedness, In Shadowing Paradigm, Attention and meaning
- ATTENTION (continued):Implications, Treisman’s Model, Norman’s Model
- ATTENTION (continued):Capacity Models, Arousal, Multimode Theory
- ATTENTION:Subsidiary Task, Capacity Theory, Reaction Time & Accuracy, Implications
- RECAP OF LAST LESSONS:AUTOMATICITY, Automatic Processing
- AUTOMATICITY (continued):Experiment, Implications, Task interference
- AUTOMATICITY (continued):Predicting flight performance, Thought suppression
- PATTERN RECOGNITION:Template Matching Models, Human flexibility
- PATTERN RECOGNITION:Implications, Phonemes, Voicing, Place of articulation
- PATTERN RECOGNITION (continued):Adaptation paradigm
- PATTERN RECOGNITION (continued):Gestalt Theory of Perception
- PATTERN RECOGNITION (continued):Queen Elizabeth’s vase, Palmer (1977)
- OBJECT PERCEPTION (continued):Segmentation, Recognition of object
- ATTENTION & PATTERN RECOGNITION:Word Superiority Effect
- PATTERN RECOGNITION (CONTINUED):Neural Networks, Patterns of connections
- PATTERN RECOGNITION (CONTINUED):Effects of Sentence Context
- MEMORY:Short Term Working Memory, Atkinson & Shiffrin Model
- MEMORY:Rate of forgetting, Size of memory set
- Memory:Activation in a network, Magic number 7, Chunking
- Memory:Chunking, Individual differences in chunking
- MEMORY:THE NATURE OF FORGETTING, Release from PI, Central Executive
- Memory:Atkinson & Shiffrin Model, Long Term Memory, Different kinds of LTM
- Memory:Spread of Activation, Associative Priming, Implications, More Priming
- Memory:Interference, The Critical Assumption, Limited capacity
- Memory:Interference, Historical Memories, Recall versus Recognition
- Memory:Are forgotten memories lost forever?
- Memory:Recognition of lost memories, Representation of knowledge
- Memory:Benefits of Categorization, Levels of Categories
- Memory:Prototype, Rosch and Colleagues, Experiments of Stephen Read
- Memory:Schema Theory, A European Solution, Generalization hierarchies
- Memory:Superset Schemas, Part hierarchy, Slots Have More Schemas
- MEMORY:Representation of knowledge (continued), Memory for stories
- Memory:Representation of knowledge, PQ4R Method, Elaboration
- Memory:Study Methods, Analyze Story Structure, Use Multiple Modalities
- Memory:Mental Imagery, More evidence, Kosslyn yet again, Image Comparison
- Mental Imagery:Eidetic Imagery, Eidetic Psychotherapy, Hot and cold imagery
- Language and thought:Productivity & Regularity, Linguistic Intuition
- Cognitive development:Assimilation, Accommodation, Stage Theory
- Cognitive Development:Gender Identity, Learning Mathematics, Sensory Memory