 |

Abnormal
Psychology PSY404
VU
LESSON
04
PSYCHOPATHOLOGY
IN HISTORICAL CONTEXT
1.
Psychological Model
It
is a long leap from
a.
Witch craft and Demonological
concepts
b.
From notorious biological
methods (Insulin shock therapy,
Lobotomy, Electroconvulsive therapy)
of
1920's and 1930's.
Plato
listed two causes of mental
disorders (a). Social and
cultural influence's in one's life. (b).
learning that
took
place in the environment.
Moral
therapy a treatment approach of the 18th century, the term Moral really meant
emotional or
psychological
rather than code of conduct. Moral
therapy proposed humane treatment and
responsible care
of
institutionalized psychologically disturbed
individuals.
Moral
therapy also advocated providing
opportunities for appropriate social
and interpersonal contact.
Mental
Hygiene Movement with heroic
efforts of Dorthea Dix
improved and reformed the asylums
and
inspired
the construction of new institutions in America
and in other countries as
well.
The
Psychological tradition was
dormant/dead for some time
but in 20th century is reemerged in form
of
several
schools of thought.
a.
Freudian
psychoanalytic model
b.
Jungian
analytical psychology model
c.
Adlerian
Individual psychology model
d.
Humanistic
model
e.
Behavioral
model
f.
Cognitive
model
Psychoanalytic
or Psychoanalysis or psychodynamic
approach pioneered by Sigmund Freud
(1856-1939)
emphasized
on internal mental processes
and childhood experiences.
The core elements of this
approach
include.
i.
Analysis
of mental structures in
conflict.
ii.
Levels
of consciousness
iii.
Defense
mechanisms
iv.
Psychosexual
stages of development.
Id→ Pleasure
Principle
Mental
Structures
Ego
→Reality
Principle
Super
Ego →
Moral
Principle
The
human psyche consists of
id,
ego and
super
ego, the thoughts
attitudes and behaviors of
three are in
state
of conflict called intra-psychic
conflict.
Id
is the
unorganized reservoir of wishes or
passions related to our
sexual and aggressive
drives, it strives
for
immediate gratification that
bypasses demands of reality,
order logic and reason. The
Id is like a child
when
it wants something it wants it
there and then without
regard for consequences, so Id
operates on
pleasure
principle.
17
Abnormal
Psychology PSY404
VU
This
refers to Greek concept of
hedonism meaning pleasure.
The energy within the Id is
labeled as the
libido.
The Id has its own
characteristic way of processing
information, cognitive style referred as
primary
process.
The thinking patterns of Id
are illogical, irrational,
emotional immature and
purely selfish.
Ego
the selfish and dangerous
drives
of id do not go unchecked ego
ensures that we must find
ways to
meet
our basic needs with
out offending everyone around
us. The ego operates
according to the reality
principle
and the cognitive operations of the ego
are characterized by logic, reason
and are referred as the
secondary
process.
The
ego is the master control, it
tries to resolve conflicts between the
demands of Id with in the
permitted
boundaries
of super ego.
The
ego has the role to mediate
conflict between the Id and
super ego according to
realities of the world. If
it
mediates successfully, we see an
intelligent, creative individual
who is well adjusted while
if ego is
unsuccessful
either Id or super ego will be
strong.
If
Id is strong, we see an antisocial criminal
and if super ego is strong we see a
pure, rigid,
nonflexible
individual.
Super ego is the storehouse of moral
and ethical standards taught by
parents, teachers and
culture
(it also refers to the
conscience of the psyche). It operates
according to the moral Principle when
we
do
something wrong, when ethical, moral
standards are violated than
super ego generates
guilt.
Example
You
go to a garden where you see
red roses you face
intra-psychic conflict
Id→
Ego↔
Super
Ego
I
want red rose and I want I
can afford to buy red
roses Stealing is bad. The
sign says
it
now.
from
flower shop
don't
pluck flowers.
Example
You
go to a store you see a lovely
jacket but the price is high
but no one is looking you
face intra-psychic
conflict:
Example
Id→
Ego↔
Super
Ego
I
want the jacket and I want I have to be
realistic I Stealing is
bad.
it
now.
cannot
afford the jacket.
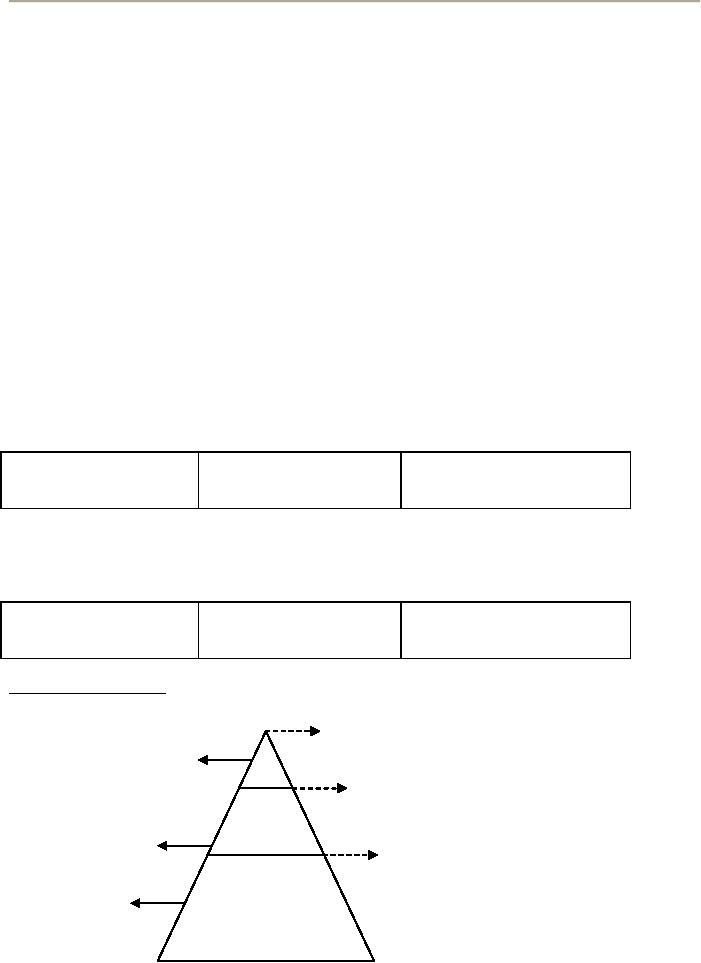
Levels
of Consciousness:
Consciousness
Preconscious/
Sub
conscious
Unconscious
18
Abnormal
Psychology PSY404
VU
According
to this triangle, the top smallest part
is the conscious experience the middle
small layer is
subconscious
and the largest portion is
unconscious.
According
to Freud that part of the mind about
which we are aware is
consciousness but it is a small
part of
mental
life. You are listening to me it is
your conscious mental
activity. The preconscious
comprises of
thoughts
or activities that are
easily made conscious by an
effort to remember or say,
you have the present
lecture's
handout in front of you and
you are conscious that
you are writing on it.
The largest segment is
the
unconscious
not easily reachable yet it
gives rise on to important
needs and influences our
behavior.
Example
All
your nightmares, phobias,
fears influence you and you
can not get rid of them
because they lie in
unconscious.
Freud suggested techniques of reaching
the unconscious
Free
Association
Dream
Analysis
Means
of Tapping
Transference
Unconscious
Analysis
of humor
Analysis
of Freudian Slips
Example
You
stand near a river, the top
water is the conscious part, fill
out some muddy water in container, it is
the
sub-conscious
and when you dug the river
bed and find something
buried in it well that is the
unconscious
part.
Defense
Mechanism
The
ego fights a battle to stay on
top of id and super ego.
The conflicts between id and
super ego produce
anxiety
that is a threat to ego. The threat or
anxiety experienced by ego is a signal
that alerts the ego to
use
unconscious
protective processes that
keep primitive emotions associated
with conflicts in check.
These
protective
processes are defense
mechanisms or coping styles.
Id
↓
Coping
styles
Ego
↑
Super
ego
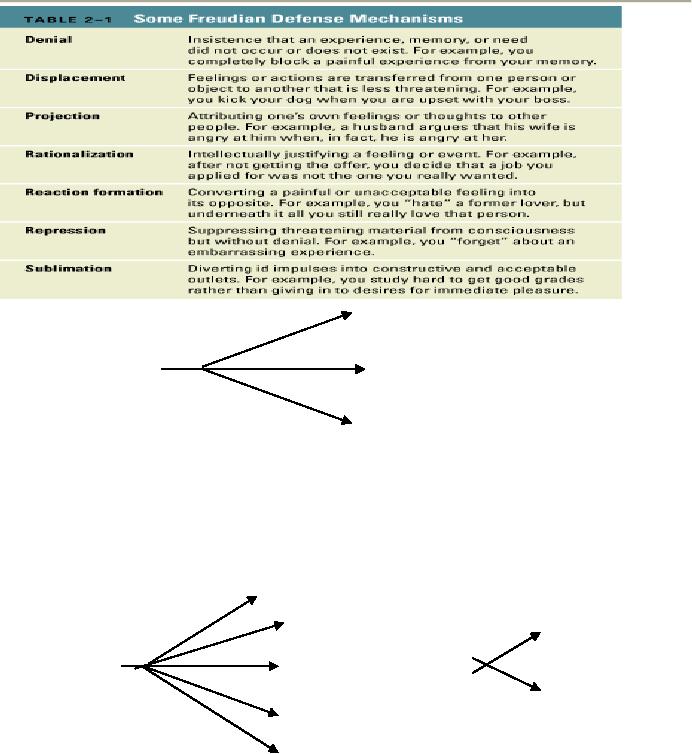
Defense
Mechanisms
a.
Denial
b.
Displacement
c.
Projection
d.
Rationalization
e.
Reaction
formation
f.
Repression,
sublimation
19
Abnormal
Psychology PSY404
VU
Protect
ego
Defense
Mechanism
Distort
Reality
Operate
at unconscious level
Humour
and sublimation are defense
mechanisms that correlate
with psychological health
Who
uses these defense
mechanisms?
Normal
and abnormal?
Both?
Psychosexual
stages of development
Freud
theorized that during childhood we
pass through a number of psycho
sexual stages of development.
Oral
Birth to 2 years
Anal
2
to 3 years
Oedipal
Complex
Psychosexual
stages of
Phallic
3
to 5 years
development
Latency
5
to 12 years
Electra
Complex
Genital
12
years (Puberty)
Each
stage of development represent a specific
period of development where our
basic needs arise and
an
under
or over gratification of the needs at
any stage leaves a strong
impression on the individual in form
of
a
fixation or psychopathology reflected
throughout his adult
life.
In
the oral stage the major source of
pleasure is the mouth where the
infant sucks, bites, through
mouth,
any
fixation at this stage appears in
form of nail biting ,
chewing pencils, paper etc.
smoking cigarettes. In
the
Anal stage, which extends
from one to three years
toilet training begins. Any
conflict or fixation at this
stage
appears in form of a person
who is very neat, clean and
strict in following rules/norms.
Phallic
stage begins at the three
years and goes up to five
years, boys have oedipal complex a
wish to have
sexual
attachment with their mother
while girls shift away
from mother and get
closer to father an
experience
labeled as Electra
complex.
20
Abnormal
Psychology PSY404
VU
Latency
stage is where interest in
sexual drive is less but it
is the Genital stage where
interest in opposite
gender
develops tendency to impress the opposite
gender is more. One is more
preoccupied to make a
good
impression on opposite gender through
one's looks, dress and
conversation. Often you see a
young
growing
up standing in front of the mirror
and either trying to focus
how to look even better etc.
Each
stage
of development is important for moral healthy
adjustment any fixation at
any stage may result in
form
psychopathology
or an immediate behavior.
Neo-Freudians
Carl
Jung (1875-1961)
Alfred
Adler (1870-1937)
Karen
Horney (1885-1952)
Carl
Jung and Alfred Adler
were followers of Freud but they
drifted away from him
and disagreed on the
concept
of sexuality. Jung conceived humans as
having a collective unconscious or archetypes
i.e. a
collection
(store) of primitive ideas,
images that are inherited
and shared across the human
race. So
collective
unconscious is wisdom accumulated by
society and culture and
passed down from generation
to
generation.
Alder advocated that humans
are social beings motivated
by social needs than by
sexual needs.
Karen
Horney believed that environmental
factors and childhood relationships
are the most
important
factor
in secure psychological
adjustment.
Techniques
of Psychoanalysis
Psychoanalysis
is a therapeutic process which reveals
unconscious mental process
and conflicts through
catharsis
and insight.
Free
association the
patient is asked to lie on a
couch and the therapist sits
behind the client, then the
patient
is asked to give a running account of
his thought pattern uninterrupted
without social censoring
it.
This
technique brings to the conscious level
emotionally loaded material
that at times can be
painful,
threatening
to be discussed at conscious
level.
Dream
analysis refers
to the process in which the contents of
the dream usually the id impulses
(wishes)
related
to the unconscious conflicts. The therapist interprets
the contents of dreams and
relates them to
various
unconscious wishes.
Example
Suppose
you go to the bazaar and you
want to buy a very expensive pair of
shoes, costing a fortune.
Your
mother
refuses to buy and says
that you are out of
your mind. So at night, you
dream that you are owner
of
that
shoe shop so your id desire
has been fulfilled in a
dream.
The
relationship between the patient and the
therapist /clinician/psychoanalyst/counselor is
very
important.
Patient
→
therapist
Relationship
The
patient may relate with
therapist positively as with an important
person in his life like
parents, teachers,
and
friends. We label it as positive
transference phenomenon.
The
patient may relate negatively
with the therapist with anger
resentment or dislike. We say
negative
transference
has occurred. The patient
may at times like the therapist
while at times resent him so
an
ambivalent
transference takes place.
The therapist (is human) he
also at times project his
feelings, emotion
usually
positive ones towards the
patient this is counter transference. This should
not happen.
Therapist
←
Client
Ambivalent
positive negative
Therapist
→
Client
Counter
transference
21
Abnormal
Psychology PSY404
VU
Freudian
slips means
you wanted to say something
but you said something
wrong or embarrassing
say
Freud
went to USA to deliver lectures on
psychoanalysis and a professor
introduced him as Dr.
Fraud,
though
he apologized but that is a Freudian
slip.
Humor
is an
essential part of psyche.
What sort of humor do you
read and enjoy? For Freud
humor is
mostly
related to death and sex
two unknown areas of your
life about which you
are not sure
22
Table of Contents:
- ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY:PSYCHOSIS, Team approach in psychology
- WHAT IS ABNORMAL BEHAVIOR:Dysfunction, Distress, Danger
- PSYCHOPATHOLOGY IN HISTORICAL CONTEXT:Supernatural Model, Biological Model
- PSYCHOPATHOLOGY IN HISTORICAL CONTEXT:Free association, Dream analysis
- PSYCHOPATHOLOGY IN HISTORICAL CONTEXT:Humanistic Model, Classical Conditioning
- RESEARCH METHODS:To Read Research, To Evaluate Research, To increase marketability
- RESEARCH DESIGNS:Types of Variables, Confounding variables or extraneous
- EXPERIMENTAL REASEARCH DESIGNS:Control Groups, Placebo Control Groups
- GENETICS:Adoption Studies, Twin Studies, Sequential Design, Follow back studies
- RESEARCH ETHICS:Approval for the research project, Risk, Consent
- CAUSES OF ABNORMAL BEHAVIOR:Biological Dimensions
- THE STRUCTURE OF BRAIN:Peripheral Nervous System, Psychoanalytic Model
- CAUSES OF PSYCHOPATHOLOGY:Biomedical Model, Humanistic model
- CAUSES OF ABNORMAL BEHAVIOR ETIOLOGICAL FACTORS OF ABNORMALITY
- CLASSIFICATION AND ASSESSMENT:Reliability, Test retest, Split Half
- DIAGNOSING PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS:The categorical approach, Prototypical approach
- EVALUATING SYSTEMS:Basic Issues in Assessment, Interviews
- ASSESSMENT of PERSONALITY:Advantages of MMPI-2, Intelligence Tests
- ASSESSMENT of PERSONALITY (2):Neuropsychological Tests, Biofeedback
- PSYCHOTHERAPY:Global Therapies, Individual therapy, Brief Historical Perspective
- PSYCHOTHERAPY:Problem based therapies, Gestalt therapy, Behavioral therapies
- PSYCHOTHERAPY:Ego Analysis, Psychodynamic Psychotherapy, Aversion Therapy
- PSYCHOTHERAPY:Humanistic Psychotherapy, Client-Centered Therapy, Gestalt therapy
- ANXIETY DISORDERS:THEORIES ABOUT ANXIETY DISORDERS
- ANXIETY DISORDERS:Social Phobias, Agoraphobia, Treating Phobias
- MOOD DISORDERS:Emotional Symptoms, Cognitive Symptoms, Bipolar Disorders
- MOOD DISORDERS:DIAGNOSIS, Further Descriptions and Subtypes, Social Factors
- SUICIDE:PRECIPITATING FACTORS IN SUICIDE, VIEWS ON SUICIDE
- STRESS:Stress as a Life Event, Coping, Optimism, Health Behavior
- STRESS:Psychophysiological Responses to Stress, Health Behavior
- ACUTE AND POSTTRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDERS
- DISSOCIATIVE AND SOMATOFORM DISORDERS:DISSOCIATIVE DISORDERS
- DISSOCIATIVE and SOMATOFORM DISORDERS:SOMATOFORM DISORDERS
- PERSONALITY DISORDERS:Causes of Personality Disorders, Motive
- PERSONALITY DISORDERS:Paranoid Personality, Schizoid Personality, The Diagnosis
- ALCOHOLISM AND SUBSTANCE RELATED DISORDERS:Poly Drug Use
- ALCOHOLISM AND SUBSTANCE RELATED DISORDERS:Integrated Systems
- SCHIZOPHRENIA:Prodromal Phase, Residual Phase, Negative symptoms
- SCHIZOPHRENIA:Related Psychotic Disorders, Causes of Schizophrenia
- DEMENTIA DELIRIUM AND AMNESTIC DISORDERS:DELIRIUM, Causes of Delirium
- DEMENTIA DELIRIUM AND AMNESTIC DISORDERS:Amnesia
- MENTAL RETARDATION AND DEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS
- MENTAL RETARDATION AND DEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS
- PSYCHOLOGICAL PROBLEMS OF CHILDHOOD:Kinds of Internalizing Disorders
- LIFE CYCLE TRANSITIONS AND ADULT DEVELOPMENT:Aging