 |
Abnormal
Psychology PSY404
VU
Lesson
36
ALCOHOLISM
AND SUBSTANCE RELATED
DISORDERS
Recap
of Previous Lecture
Personality
refers to enduring patterns of
thinking and behavior that
define the person and distinguish
him
or her from other people.
These enduring patterns are
ways of expressing emotion as
well as
patterns
of thinking about ourselves and
other people. When enduring
patterns of behavior
and
emotion
bring the person into
repeated conflict with
others, and when they
prevent the person
from
maintaining
close relationships with others, an
individual's personality may be
considered disordered.
The
authors of DSM-IV-TR have
organized ten specific forms of personality disorder
into three
clusters
on the basis of broadly defined
characteristics.
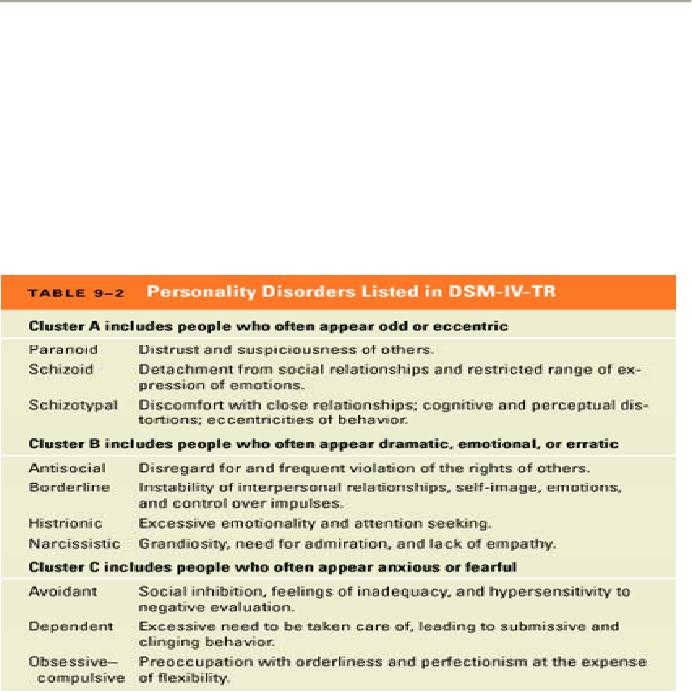
Classification
of Personality Disorders
1-Paranoid
personality disorder
2-Schizoid
personality disorder
3-Schizotypal
personality disorder
4-Antisocial
personality disorder
5-Borderline
personality disorder
6-Histrionic
personality disorder
7-Narcissistic
personality disorder
8-Avoidant
personality disorder
9-dependent
personality disorder
10-Obsessivecompulsive
personality disorder
176
Abnormal
Psychology PSY404
VU
ALCOHOLISM
AND SUBSTANCE RELATED
DISORDERS
Examples
·
We
take aspirin to reduce
headache.
·
We
take an antibiotic to fight an
infection.
·
We
take tranquilizer to calm us after
facing a trauma.
·
We
drink coffee or tea to get going in the
morning.
·
Smoke
a cigarette to relax our
nerves.
·
We
take valium to go to
sleep.
There
are many substances that
are capable of harming the body or
adversely affecting the behavior
and
mood.
The misuse of drugs has
become one of the most disabling
problems of the society.
Examples
·
Sherlock
Holmes fictional character who
took drugs stimulants to alert
him.
·
Sportsmen
take drugs to enhance their
performance but in the long
run their body develops
drug
dependence.
The
term drug applies to any substance
other than food that
changes our bodily and
mental functioning.
Drug
misuse may lead to a temporary
mental syndrome such as
intoxication but chronic excessive
use of
drugs
can lead to a substance use
disorder.
Substance
use disorder can take
two forms
1-
Substance abuse
2-
Substance dependence
1-
Substance Abuse
A
pattern in which people rely heavily on a drug and
they structure their lives around the
drug.
2-
Substance Dependence
In
which people show all
symptoms of substance abuse
plus physical dependence on the
drug.
Drug
Addiction
·
Drug
addiction is in which people show
all symptoms of substance
abuse plus physical
dependence
on
the drug.
·
But
now we use the term substance
dependence and not
addiction.
Drug
Tolerance
·
People
who need increased doses of
drug in order to get its
effect.
·
Withdrawal
symptoms emerge
when individual suddenly
stops taking drugs or
reduces their
dosage.
·
These
symptoms include muscle aches,
pains and cramps, vomiting,
nausea.
·
It
is believed that approximately 7 % of all
adults in United States currently
display some form of
substance
use disorder.
Poly
Drug Use
When
an individual uses two or
more drugs at the same time we
label it as poly drug
use.
Cross
Tolerance
·
When
people take more than one
drug at a time and the drugs interact
with each other. Some
time
the
two drugs display cross
tolerance
177
Abnormal
Psychology PSY404
VU
·
Cross
tolerance is that the drugs
act similarly on the brain and
taking one drug will affect
person's
tolerance
for the other.
Synergistic
Effect
When
different drugs enhance each
other's effect, they have a combined impact
known as a synergistic
effect.
The
drugs that we will focus in
this chapter fall into three
categories
1-
Depressants are
substances which slow the
activity of central nervous
system they include.
The
important depressants
are
·
Alcohol
·
Sedative-Hypnotic
drugs
·
Opioids
2-
Stimulants are
substances that increase the
activity of the central nervous
system, resulting in the
increased
blood pressure, heart rate,
intensified activity, thought
processes and
alertness.
The
important stimulants
are
·
Cocaine
·
Amphetamines
·
Nicotine
·
Caffeine
3-
Hallucinogens are
substances that cause
changes primarily in sensory perception.
They include
·
LSD
·
Cannabis
drugs
The
explanation for drug abuse can be done by
using four
perspectives
1-
Biological
2-
Psychodynamic
3-
Behavioral
4-
Socio-cultural
The
biological view or perspective
suggests that people inherit a
predisposition to drug addiction based
on
their
research of twin and adoptee
studies.
The
psycho dynamic perspective
view that people who turn to
drugs have an inordinate
dependency needs
and
they turn to drugs.
Behavioral
perspective suggests that drug
use is reinforced because it reduces
tension and raises
spirits.
Socio-cultural
perspective suggests that the people
most likely to develop a pattern of drug
abuse are those
where
societies create stress and
their families tolerate drug
abuse.
Treatment
for Substance Abuse
Disorders
Treatment
for substance abuse
disorders include
1-
Insight therapy
2-
Aversive therapy
3-
Behavioral self control
training
4-
Relapse prevention
training
5-
Self help groups
6-
Therapeutic communities
178
Abnormal
Psychology PSY404
VU
The
goals of treatment for substance
use disorders are a matter
of controversy. Some clinicians
believe
that
the only acceptable goal is
total absence from drinking
or drug use. Others have
argued that, for
some
people, a more reasonable
goal is the moderate use of
legal drugs.
Detoxification
·
Alcoholism
and related forms of drug abuse
are chronic conditions.
·
Treatment
is typically accomplished in a sequence
of stages, beginning with a
brief period of
detoxification--the
removal of a drug on which a person has
become dependent--for 3 to 6
weeks.
Medications
·
Following
the process of detoxification, treatment
efforts are aimed at helping
the person maintain
a
state of remission.
·
Several
forms of medication are used to help the
person refrain from
drinking.
Self-Help
Groups: Alcoholics Anonymous
·
Alcoholics
Anonymous (AA) is maintained by alcohol
abusers for the sole purpose
of helping other
people
who abuse alcohol become and
remain sober.
·
AA is
not officially associated
with any other form of
treatment or professional organization.
·
The
viewpoint espoused by AA is fundamentally
spiritual in nature.
·
DSM-IV-TR
uses two terms to describe
substance use disorders, and
these terms reflect
different
levels
of severity.
Substance
Dependence, the
more severe of the two forms,
refers to a pattern of repeated
self-
administration
that often results in
tolerance, the need for
increased amounts of the drug to
achieve
intoxication;
withdrawal, unpleasant physical and
psychological effects that the
person experiences
when
he or she tries to stop
taking the drug; and compulsive
drug-taking behavior.
Substance
Abuse describes
a more broadly conceived,
less severe pattern of drug
use that is defined
in
terms
of interference with the person's ability
to fulfill major role obligations at work
or at home, the
recurrent
use of a drug in dangerous situations,
and repeated legal
difficulties associated with drug
use.
Addiction
is
another, older term that is
often used to describe
problems such as
alcoholism.
The
term has been replaced in
official terminology by the term
substance dependence, with
which it is
synonymous,
but it is still used
informally by many lay
people.
A
drug
of abuse, sometimes
called a psychoactive substance, is a
chemical substance that
alters a
person's
mood, level of perception, or brain
functioning.
People
with a substance use disorder
frequently abuse several
types of drugs; this condition is
known as
poly-substance
abuse.
Alcohol
·
Alcohol
affects virtually every
organ and system in the
body.
·
After
alcohol has been ingested, it is
absorbed through membranes in the
stomach, small intestine,
and
colon.
·
The
rate at which it is absorbed is
influenced by many variables, including
the concentration of
alcohol
in the beverage, the volume and rate of
consumption, and the presence of food in
the
digestive
system.
·
After
it is absorbed, alcohol is distributed to
all the body's organ
systems.
·
Almost
all the alcohol that a person
consumes is eventually broken down or
metabolized in the
liver.
·
If the
person's consumption rate exceeds this
metabolic limit, then blood alcohol
levels will rise.
·
Blood
alcohol levels are measured in
terms of the amount of alcohol per unit
of blood.
179
Abnormal
Psychology PSY404
VU
·
According
to DSM-IV-TR, the symptoms of alcohol
intoxication include slurred speech,
lack of
coordination,
an unsteady gait, nystagmus
(involuntary to-and-fro movement of the
eyeballs
induced
when the person looks upward or to the
side), impaired attention or memory, and
stupor
or
coma.
·
The
prolonged use and abuse of
alcohol can have a devastating
impact on many areas of a
person's
life.
·
1-The
disruption of relationships with family
and friends can be especially
painful.
·
2-Regular
heavy use of alcohol is also
likely to interfere with job
performance.
·
3-Many
heavy drinkers encounter problems with
legal authorities.
·
On
a biological level, prolonged exposure to
high levels of alcohol can
disrupt the functions of
several
important organ systems,
especially the liver, pancreas,
gastrointestinal system,
cardiovascular
system, and endocrine
system.
·
In
fact, over an extended
period of time, alcohol dependence has
more negative health
consequences
than abuse of any other
drug, with the exception of nicotine. The
misuse of alcohol
leads
to an enormous number of severe injuries
and premature deaths in
every region of the world.
180
Table of Contents:
- ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY:PSYCHOSIS, Team approach in psychology
- WHAT IS ABNORMAL BEHAVIOR:Dysfunction, Distress, Danger
- PSYCHOPATHOLOGY IN HISTORICAL CONTEXT:Supernatural Model, Biological Model
- PSYCHOPATHOLOGY IN HISTORICAL CONTEXT:Free association, Dream analysis
- PSYCHOPATHOLOGY IN HISTORICAL CONTEXT:Humanistic Model, Classical Conditioning
- RESEARCH METHODS:To Read Research, To Evaluate Research, To increase marketability
- RESEARCH DESIGNS:Types of Variables, Confounding variables or extraneous
- EXPERIMENTAL REASEARCH DESIGNS:Control Groups, Placebo Control Groups
- GENETICS:Adoption Studies, Twin Studies, Sequential Design, Follow back studies
- RESEARCH ETHICS:Approval for the research project, Risk, Consent
- CAUSES OF ABNORMAL BEHAVIOR:Biological Dimensions
- THE STRUCTURE OF BRAIN:Peripheral Nervous System, Psychoanalytic Model
- CAUSES OF PSYCHOPATHOLOGY:Biomedical Model, Humanistic model
- CAUSES OF ABNORMAL BEHAVIOR ETIOLOGICAL FACTORS OF ABNORMALITY
- CLASSIFICATION AND ASSESSMENT:Reliability, Test retest, Split Half
- DIAGNOSING PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS:The categorical approach, Prototypical approach
- EVALUATING SYSTEMS:Basic Issues in Assessment, Interviews
- ASSESSMENT of PERSONALITY:Advantages of MMPI-2, Intelligence Tests
- ASSESSMENT of PERSONALITY (2):Neuropsychological Tests, Biofeedback
- PSYCHOTHERAPY:Global Therapies, Individual therapy, Brief Historical Perspective
- PSYCHOTHERAPY:Problem based therapies, Gestalt therapy, Behavioral therapies
- PSYCHOTHERAPY:Ego Analysis, Psychodynamic Psychotherapy, Aversion Therapy
- PSYCHOTHERAPY:Humanistic Psychotherapy, Client-Centered Therapy, Gestalt therapy
- ANXIETY DISORDERS:THEORIES ABOUT ANXIETY DISORDERS
- ANXIETY DISORDERS:Social Phobias, Agoraphobia, Treating Phobias
- MOOD DISORDERS:Emotional Symptoms, Cognitive Symptoms, Bipolar Disorders
- MOOD DISORDERS:DIAGNOSIS, Further Descriptions and Subtypes, Social Factors
- SUICIDE:PRECIPITATING FACTORS IN SUICIDE, VIEWS ON SUICIDE
- STRESS:Stress as a Life Event, Coping, Optimism, Health Behavior
- STRESS:Psychophysiological Responses to Stress, Health Behavior
- ACUTE AND POSTTRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDERS
- DISSOCIATIVE AND SOMATOFORM DISORDERS:DISSOCIATIVE DISORDERS
- DISSOCIATIVE and SOMATOFORM DISORDERS:SOMATOFORM DISORDERS
- PERSONALITY DISORDERS:Causes of Personality Disorders, Motive
- PERSONALITY DISORDERS:Paranoid Personality, Schizoid Personality, The Diagnosis
- ALCOHOLISM AND SUBSTANCE RELATED DISORDERS:Poly Drug Use
- ALCOHOLISM AND SUBSTANCE RELATED DISORDERS:Integrated Systems
- SCHIZOPHRENIA:Prodromal Phase, Residual Phase, Negative symptoms
- SCHIZOPHRENIA:Related Psychotic Disorders, Causes of Schizophrenia
- DEMENTIA DELIRIUM AND AMNESTIC DISORDERS:DELIRIUM, Causes of Delirium
- DEMENTIA DELIRIUM AND AMNESTIC DISORDERS:Amnesia
- MENTAL RETARDATION AND DEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS
- MENTAL RETARDATION AND DEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS
- PSYCHOLOGICAL PROBLEMS OF CHILDHOOD:Kinds of Internalizing Disorders
- LIFE CYCLE TRANSITIONS AND ADULT DEVELOPMENT:Aging