 |
Abnormal
Psychology PSY404
VU
LESSON
20
PSYCHOTHERAPY
Psychotherapy
refers
to special and systematic
process for helping people to
overcome their
psychological
difficulties.
Example: Some
psychological difficulties include anxiety,
fear and phobia. All forms
of Psychotherapy
have
three things in common:
1-
Sufferer who seeks help
whom we call patient or
client
2-
A healer who is the therapist
and
3-
A series of contacts between the
client and therapist (number of
sessions between the client
and
the
therapist)
A
system of therapy is a set of principles
and techniques employed in
accordance with a particular theory
of
change.
As many as 400 distinct forms of therapy
are being practiced today.
Two broad categories
are
1.
Global Therapies
Global
therapies help people recognize
and change general features
of their personalities that the
therapist
believe
are the root cause of their
problem. They are
�
Psychodynamic
or psychoanalytic
�
Humanistic
�
Existential
�
Client
centered therapy
�
Gestalt
2.
Problem Focused Therapies
Problem
focused therapies focus on the
symptoms and specific
complaints of the person. They
include
�
Behavioral
therapies
�
Cognitive
therapies
�
Biological
therapies
Therapy
format is
�
Individual
therapy
�
group
therapy
�
family
therapy
�
Couple
therapy
Individual
therapy is in
which the therapist sees the alone
for some period of time
usually weekly.
Group
therapy is in
which the therapist sees the group of
clients such as psychodrama
and self help
groups.
Family
therapy is a
format in which the therapists
meet with all members of
family and point
out
problematic
behavior and interactions and
work on whole family to
change.
In
couple
therapy the therapist works
with two people who share a
long term relationship.
89
Abnormal
Psychology PSY404
VU
Whether
the psychotherapy is beneficial or
not
The
critical question to be asked is about all
these psychotherapies treatments is
whether or not they
actually
help people to cope with and
overcome their psychological
problems.
What
do you say?
What
do you think?
Four
general conclusions have
been reached
1-
People in therapy are better off
than people with similar
problems who receive no
treatment.
2-
Various therapies do appear to
differ in their
effectiveness.
3-
Certain therapies appear to be effective
than others for certain
disorders
4-
A combination of therapy approaches is
more effective than a single approach in
treatment of
certain
disorders.
Important
Concerns of Psychotherapy
�
Psychotherapy
is the use of psychological techniques
and the therapistclient relationship
to
produce
emotional, cognitive, and behavioral
change.
�
Today,
the largest group of mental health
professionals describe themselves as
eclectic, meaning
they
use different treatments for
different disorders.
�
Psychotherapy
outcome research examines whether
and when treatments are
effective, while
psychotherapy
process research searches
for the "active ingredients" in
psychotherapy, that is,
the
therapeutic
activities that promote positive
change.
�
Research
shows that therapy is more effective
when therapists appropriately reveal a
bit about their
own,
similar struggles.
�
Unfortunately,
some therapists do not offer
or even educate their
clients about more and
less
effective
treatments, and there is an
even bigger problem: Most
people who need it do not
get any
psychological
help.
�
Eighty-seven
percent of people with a diagnosable
mental disorder have not
received
treatment in
the
past year, including many
people with common, severe,
and treatable
disturbances.
�
Therapists
working within the biological,
psychodynamic, cognitive behavioral, and
humanistic
paradigms
would approach treatment and
evaluate a mentally ill person in very
different ways.
90
Abnormal
Psychology PSY404
VU
Brief
Historical Perspective
�
We
can trace the roots of the treatment of
psychological disorders to two broad
traditions of
healing:
the spiritual/religious tradition and the
naturalistic/scientific tradition.
�
The
spiritual/religious tradition is an
ancient one that attributes
both physical and mental
ailments
to
supernatural forces.
�
We
see in our culture that people go to
saints, faqirs and peers
for dam and
dua.
�
One
of the earliest examples of this
tradition is the practice of
trephining--chipping
a hole through
the
unfortunate sufferer's skull with a
crude stone tool--presumably, to
allow evil spirits to
escape.
�
The
influence of spiritual beliefs and
rituals should not be ignored since
believing is a powerful
part
of
healing.
�
Naturalistic/scientific
approaches to helping the mentally disturbed
also have ancient
roots.
�
Hippocrates
recommended treatments such as
rest, exercise, and a healthy
diet.
�
In
the 1600s, "insane asylums" were
developed as a new treatment for the mentally
ill.
�
One
rationale for these institutions
was to remove disturbed individuals
from society; another
was
the
hope that rest and isolation
would alleviate their
bizarre behavior.
�
General
paresis is an example not
only of the hope of the biological
approach to etiology
and
treatment
but also of the medical model of
research.
�
First,
a diagnosis is developed and
refined.
�
Second,
clues about causes are put
together like pieces of a puzzle to
form a picture of the specific
etiology
of the disease.
�
Third,
scientists experiment with various
treatments for preventing or curing the
disorder until they
find
an effective treatment.
�
Most
mental disorders appear to be
caused by many
factors.
�
Because
of this, scientists often search
for biological treatments
without knowing a
disorder's
specific
cause.
�
These
treatments focus on symptom
alleviation, reducing
the dysfunctional symptoms of a disorder
but
not eliminating its root
cause.
1-Electroconvulsive
Therapy
�
Electroconvulsive
therapy (ECT) involves deliberately
inducing a seizure by passing
electricity
through
the brain.
�
Approximately
100 volts of electric current is
passed through a patient's brain in
bilateral
ECT,
where
electrodes are placed on the
left and right temples,
and the current passes through
both brain
hemispheres.
�
In
unilateral
ECT,
the electric current is passed through
only one side of the brain, the
non-
dominant
hemisphere.
�
ECT
can be effective in treating severe
depressions that do not
respond to other
treatments,
especially
for a patient at high risk
for suicide.
2-Psychosurgery
�
Psychosurgery
is a controversial biological treatment, as it involves the
surgical destruction of
specific
regions of the brain.
�
Prefrontal
lobotomy is a procedure in which the
frontal lobes of the brain
are surgically and
irrevocably
severed.
�
The
procedure has limited
effectiveness and causes
frequent and severe side
effects, including a
significant
mortality rate, excessive
tranquility, and the absence of
emotional responsiveness.
�
Although
prefrontal lobotomies are no longer performed,
some forms of highly
circumscribed
psychosurgery
are used today to treat severe
disorders.
91
Abnormal
Psychology PSY404
VU
3-Psychopharmacology
�
Psychopharmacology--the
study of the use of medications to treat
psychological disturbances--
has
been the most promising avenue of
biological treatment.
�
In
recent years, scientists
have developed new medications
that have increasingly
specific effects on
emotional
states and mental
disorders.
�
There
is a variety of psychotropic medications, chemical
substances that affect psychological
state.
�
The
success of psychopharmacology is evident
in the expanding development and use
of
psychotropic
medications.
�
Evidence
indicates that medication often is an
effective and safe treatment for
many mental
disorders.
�
Although
psychotropic medications do not cure
underlying causes, symptom
alleviation is
extremely
important.
�
All
medications have side
effects, some of which are
very unpleasant.
�
Partly
as a result of unpleasant side
effects, many patients do
not take their medication
as
prescribed,
and they may experience a
relapse as a result.
�
Many
psychotropic drugs must be taken
for long periods of
time.
�
Despite
the effectiveness of many psychotropic
medications, we share some
concerns that we
sometimes
look to medication to solve problems
that may have psychological
or social roots.
�
4-
Hypnosis
�
An
early influence on the psychodynamic
approach to therapy was Joseph Breuer,
who used
hypnosis
to induce troubled patients to
talk freely about problems in their
lives.
�
Upon
awakening from a hypnotic
trance, many patients reported
relief from their
symptoms.
�
Breuer
attributed their improvement to
catharsis,
the
release of previously unexpressed
feelings,
pent
up emotion that Breuer
assumed was responsible for
his patients' psychological problems.
(
covered
in lecture 21)
92
Table of Contents:
- ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY:PSYCHOSIS, Team approach in psychology
- WHAT IS ABNORMAL BEHAVIOR:Dysfunction, Distress, Danger
- PSYCHOPATHOLOGY IN HISTORICAL CONTEXT:Supernatural Model, Biological Model
- PSYCHOPATHOLOGY IN HISTORICAL CONTEXT:Free association, Dream analysis
- PSYCHOPATHOLOGY IN HISTORICAL CONTEXT:Humanistic Model, Classical Conditioning
- RESEARCH METHODS:To Read Research, To Evaluate Research, To increase marketability
- RESEARCH DESIGNS:Types of Variables, Confounding variables or extraneous
- EXPERIMENTAL REASEARCH DESIGNS:Control Groups, Placebo Control Groups
- GENETICS:Adoption Studies, Twin Studies, Sequential Design, Follow back studies
- RESEARCH ETHICS:Approval for the research project, Risk, Consent
- CAUSES OF ABNORMAL BEHAVIOR:Biological Dimensions
- THE STRUCTURE OF BRAIN:Peripheral Nervous System, Psychoanalytic Model
- CAUSES OF PSYCHOPATHOLOGY:Biomedical Model, Humanistic model
- CAUSES OF ABNORMAL BEHAVIOR ETIOLOGICAL FACTORS OF ABNORMALITY
- CLASSIFICATION AND ASSESSMENT:Reliability, Test retest, Split Half
- DIAGNOSING PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS:The categorical approach, Prototypical approach
- EVALUATING SYSTEMS:Basic Issues in Assessment, Interviews
- ASSESSMENT of PERSONALITY:Advantages of MMPI-2, Intelligence Tests
- ASSESSMENT of PERSONALITY (2):Neuropsychological Tests, Biofeedback
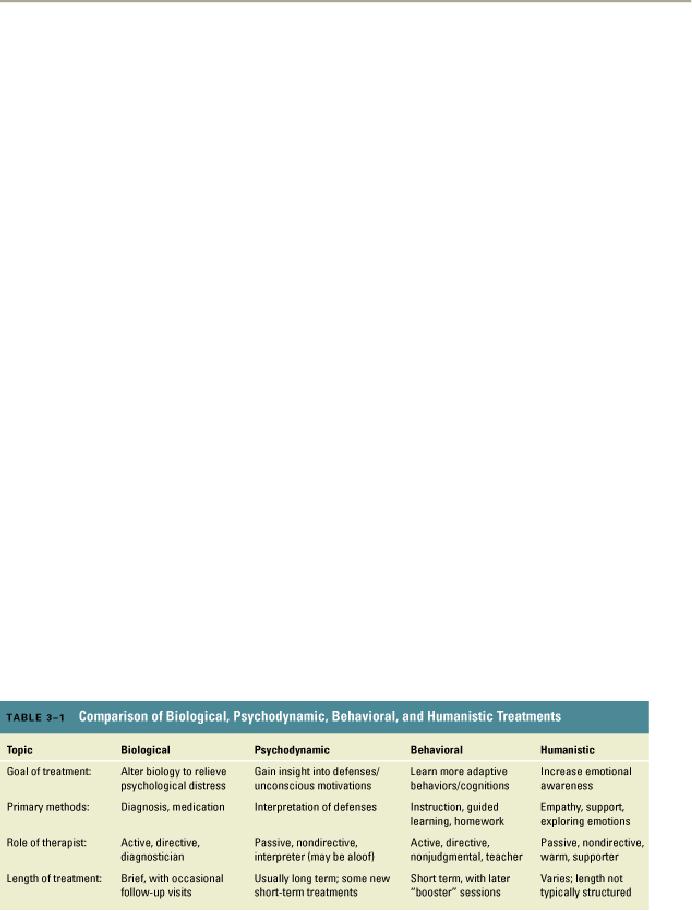
- PSYCHOTHERAPY:Global Therapies, Individual therapy, Brief Historical Perspective
- PSYCHOTHERAPY:Problem based therapies, Gestalt therapy, Behavioral therapies
- PSYCHOTHERAPY:Ego Analysis, Psychodynamic Psychotherapy, Aversion Therapy
- PSYCHOTHERAPY:Humanistic Psychotherapy, Client-Centered Therapy, Gestalt therapy
- ANXIETY DISORDERS:THEORIES ABOUT ANXIETY DISORDERS
- ANXIETY DISORDERS:Social Phobias, Agoraphobia, Treating Phobias
- MOOD DISORDERS:Emotional Symptoms, Cognitive Symptoms, Bipolar Disorders
- MOOD DISORDERS:DIAGNOSIS, Further Descriptions and Subtypes, Social Factors
- SUICIDE:PRECIPITATING FACTORS IN SUICIDE, VIEWS ON SUICIDE
- STRESS:Stress as a Life Event, Coping, Optimism, Health Behavior
- STRESS:Psychophysiological Responses to Stress, Health Behavior
- ACUTE AND POSTTRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDERS
- DISSOCIATIVE AND SOMATOFORM DISORDERS:DISSOCIATIVE DISORDERS
- DISSOCIATIVE and SOMATOFORM DISORDERS:SOMATOFORM DISORDERS
- PERSONALITY DISORDERS:Causes of Personality Disorders, Motive
- PERSONALITY DISORDERS:Paranoid Personality, Schizoid Personality, The Diagnosis
- ALCOHOLISM AND SUBSTANCE RELATED DISORDERS:Poly Drug Use
- ALCOHOLISM AND SUBSTANCE RELATED DISORDERS:Integrated Systems
- SCHIZOPHRENIA:Prodromal Phase, Residual Phase, Negative symptoms
- SCHIZOPHRENIA:Related Psychotic Disorders, Causes of Schizophrenia
- DEMENTIA DELIRIUM AND AMNESTIC DISORDERS:DELIRIUM, Causes of Delirium
- DEMENTIA DELIRIUM AND AMNESTIC DISORDERS:Amnesia
- MENTAL RETARDATION AND DEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS
- MENTAL RETARDATION AND DEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS
- PSYCHOLOGICAL PROBLEMS OF CHILDHOOD:Kinds of Internalizing Disorders
- LIFE CYCLE TRANSITIONS AND ADULT DEVELOPMENT:Aging