 |
Radio
News, Reporting and Production
MCM515
VU
LESSON
42
THE
MUSIC I
Types
of Music
�
Folk
Music
The
music in the traditional style of a
country or community is called Folk
Music. It is
deep rooted in the
soil
it belongs to and travels
from generation to generation. It
consists of typical tunes and
melodies given
to
folk songs. E.g., maaahia,
tappa, gidda, etc.
�
Classical
Music
It
is a kind of music that
involves high skill of the
singer who possesses a
command on musical notes.
(raga,
raagni,
Thaath, ). Classical Music is purely
based on Ragas.
�
Light
Music
Ghazals,
geet, thhumri etc.
�
Pop
Music
Popular
music fast beat music
rock n roll, jazz
etc.
Note
(sur)
A
single sound of a particular length
and pitch, made by a voice or
musical instrument is called note.
Every
note
represents a frequency of
voice.
Frequency
number of sound waves per
second is called frequency.
Minimum
cycles/second -----------------160
Maximum
cycles/second -----------------1800
Seven
Notes
There
are seven notes in music
which are:
SAA,
RE`, GAA, MAA, PAA, DHAA,
NEE
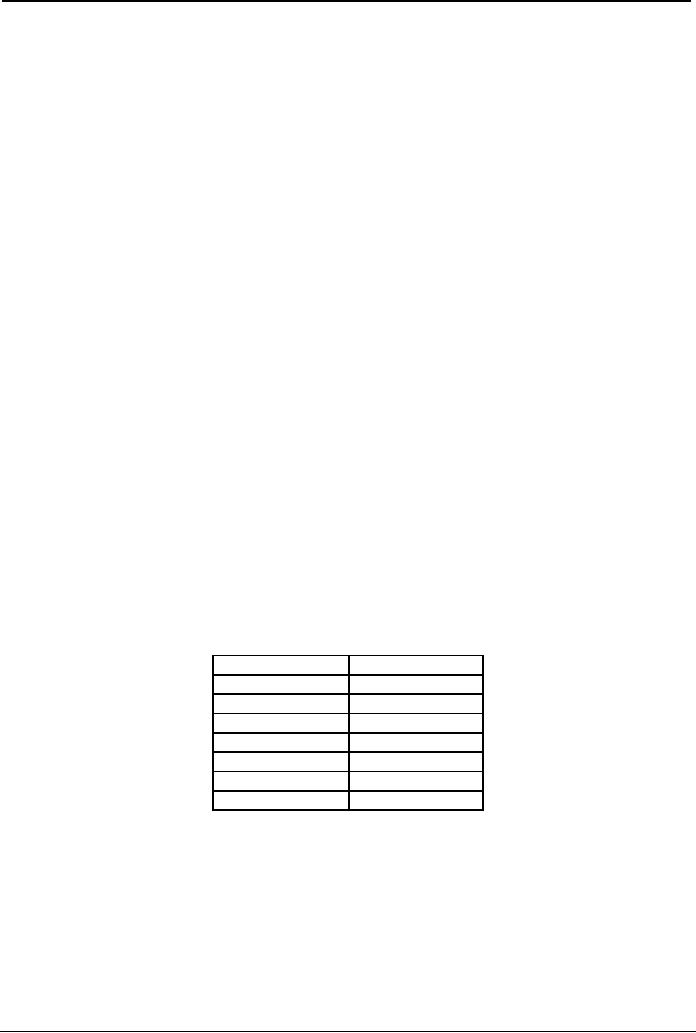
SUR
FREQUENCY
Saa
(kharaj)
9/8
Re`
(rikham)
10/9
Gaa
(gandhaar)
16/15
Maa
(mudham)
9/8
Paa
(puncham)
9/8
Dhaa
(dhevat)
10/9
Nee
(nikhaad)
16/15
Teevar
Sur
The
sharp notes of a raga are
called Teevar
Notes.
Komal
Sur.
The
soft notes of a raga are
called Komal
Notes.
Chord
When
two or more notes are
sounded together they are said to
form a Chord
110

Radio
News, Reporting and Production
MCM515
VU
Concord
When
two or more notes sounded
together produce a pleasant effect on the
ear, the combination is called
a
Concord
or Consonance.
Discord
When
two or more notes sounded
together produce an unpleasant effect on the
ears, the combination of
the
notes is called Discord.
Harmony
When
notes producing concord are
sounded simultaneously, the effect is
called Harmony.
Melody
When
notes producing concord sound
one after the other, the effect is called
Melody.
Unison
When
two notes have the same
frequency, they are said to be in
Unison.
Rhythm
A
strong regular repeated pattern of
sounds or movements is called
rhythm. Equal Distribution of beats
is
called
rhythm.
Thaath
It
is a scale of seven notes
which ragas are derived
from. Thaath is the origin of ragas.
Traditionally there
are
72 thaaths. Pandat Bhaaskar
Raao declared 32 thaaths.
Currently there are 32 valid
thaaths.
Raga
The
arrangement of notes that
sounds pleasant to the ears is
called Raga.
Every
raga depicts a time.
The
minimum notes in a raga are
5.
The
maximum notes in a raga are
7.
111
Table of Contents:
- WHAT RADIO IS:HISTORY OF RADIO, MARCONI –THE INVENTOR
- HISTORY OF RADIO:B.B.C. – 1922, Radio in Sub-Continent, PBC SERVICES
- OBJECTIVES OF BROADCASTING IN PAKISTAN:Information, Islamic ideology
- NEWS VALUES I:CONFLICT, PROGRESS, VICTORY AND DEFEAT
- NEWS VALUES II:TIMELINESS, PROXIMITY, NOVELTY, HUMAN INTEREST
- NEWS VALUES AND ELEMENTS OF NEWS:MISCELLANEOUS NEWS VALUES
- MEASURING THE IMPORTANCE OF NEWS:Intensity of an Event, NEWS STORY TYPES
- TYPES OF NEWS STORIES II:SIMPLE TYPES, ILLNESS, DEATH
- TYPES OF NEWS STORIES III:Conspiracy, Drug Trafficking, Lunar Months
- TYPES OF NEWS STORIES IV:COMPLEX NEWS, Forms of Government, Monarchy
- TYPES OF NEWS STORIES V:Education, Research, Religion
- TYPES OF NEWS STORIES VI:Lifestyles, Receptions, Entertainment
- SOURCES OF NEWS I:Network of Reporters, QUALITIES OF A REPORTER
- SOURCES OF NEWS II:MONITORING, NEWS/ PRESS RELEASE
- SOURCES OF NEWS III:National News Agencies, HARD NEWS, SOFT NEWS
- REPORTING:ORDER OF REPORTING, REPORTER’S QUALITIES, Well informed
- A SUCCESSFUL RADIO REPORTER:Briefing, Reporter’s Ammunition, Meeting Deadline
- INTERPRETATIVE REPORTING I:Growth of Interpretative Reporting
- INTERPRETATIVE REPORTING II:Factual Background, SPEECH STORY
- INTERPRETATIVE REPORTING III:FIRES & ACCIDENTS, CRIME STORIES
- INVESTIGATIVE REPORTING I:Thalidomide Scandal, Watergate Scandal
- INVESTIGATIVE REPORTING II:Identification of the problem, INTERVIEW
- TYPES OF INTERVIEW:Hard News Interview, Informational Interview
- ESSENTIALS OF A GOOD INTERVIEW I:Comments and Opinion, Topic must be specific
- ESSENTIALS OF A GOOD INTERVIEW II:Preparation of the Interview, Language
- RADIO NEWS GLOSSARY:Actuality, Cut, Voicer, Wrap, Hourly, Lead
- FUNDAMENTALS OF NEWS WRITING:Inverted Pyramided Style, Telling the Story
- FUNDAMENTALS OF WRITING NEWS FOR RADIO I:Language
- FUNDAMENTALS OF WRITING NEWS FOR RADIO II:Complex numbers
- ESSENTIALS OF A NEWSCASTER:Authority, Credibility, Language, Pronunciation
- PRODUCTION AND PLANNING:Principals of Planning a Program
- PRODUCER & BUDGETING:Strengths of a Radio Program, Budgeting a Program
- JARGONS OF PRODUCTION (Continued):Frequency spectrum, Dead studio
- TYPES OF TALK:Qualification of a Talker, Essentials of a talk, Vetting a talk
- DISCUSSION:Controlled Discussion, Live Discussion, Current affairs
- DISCUSSION:Selection of the TopicKnowledge of the Topic, Narrowing down the topic
- RADIO FEATURE:Sound Effects, Narration, Dramatic Feature, Religion, Personalities
- RADIO DOCUMENTARY:Commentary, History, Persons, Things, Phenomena
- DRAMA:Solo plays, Series, Serial, Soap, Components of Drama
- SPECIAL AUDIENCE PROGRAM:Children’s Programs, Women’s programs
- SPORTS PROGRAM:Live Programs, Recorded Programs, Preparation of OB
- THE MUSIC I:Folk Music, Classical Music, Light Music, Pop Music
- THE MUSIC II:Classification of Raga In Terms Of Notes, Aado, Khaado
- ETHICS & LIMITATIONS OF MEDIA:Domain of Freedom of Media, Defamation
- RECAP:What Radio Is, Timeliness, Elements of news, Types of Reporting, Production