 |
QUALITIES OF GOOD WRITERS |
| << QUALITIES OF GOOD WRITERS |
| QUALITIES OF GOOD WRITING:Achieve appropriate readability: >> |
Journalistic
Writing MCM310
VU
LECTURE
3
QUALITIES
OF GOOD WRITERS
1.
Be considerate for your
readers.
For
example, compare the following
two pieces and see which
reflects writers' sense of
consideration.
�
We
do not have enough fuel to
reach Portland. When we land at Sioux
City we hope to take
on
more fuel, which will
take about an hour."
�
We
are encountering 90-mile-an hour
headwinds. This wind and
our full load mean that
we
are
using more fuel than
usual. Consequently, we are
diverting to Sioux City, North
Dakota, to
top
up the fuel tanks as a safety precaution.
Refueling in Sioux City will take
about one hour. I
apologize
for the unavoidable delay. Thank
you."
1.
Investigation:
A
good writer is highly investigative in
his approach. He seeks to
find out at minimum the
answers to the
following
questions: Who, What, Where,
When, Why, How
2.
Dream and reality:
A
good writer knows the communication
reality. He strongly believes that a
message sent is not a
message
received.
A message's success depends
upon the fulfillment of the following
points:
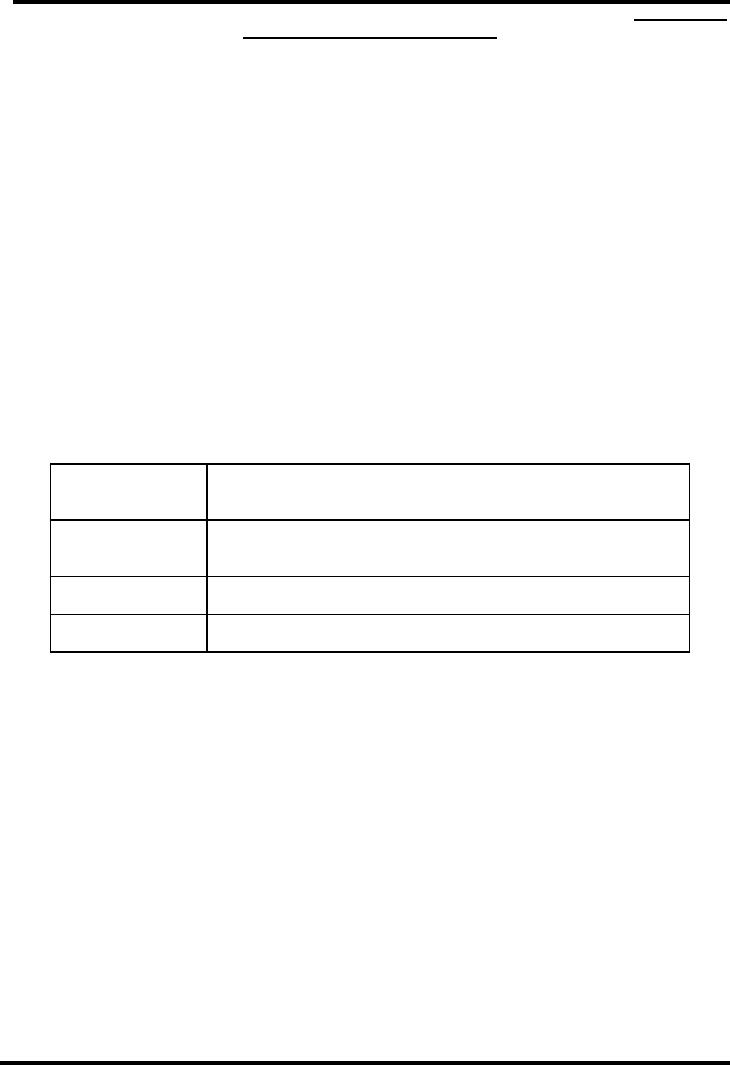
Social
Contact
The
persons who are communicating
have to be in touch with
each
other
Common
Medium
Both
parties must share a common
language or means of
communication.
Transmission
The
message has to be imparted
clearly.
Understanding
The
message has to be received,
properly understood and
interpreted
Probably
the specialist was a dream
writer; that's why, his
message failed.
Plumber
(wrote):
Sir,
Hydrochloric acid is good
for cleaning out clogged
drains.
Specialist
(responded):
The
efficiency of HCL is indisputable, but the
corrosive residue is incompatible
with
metallic permanence.
Plumber
(rewrote):
Thank
you for appreciation.
Specialist
(re-stressed): We cannot
assume responsibility for the production
of toxic and noxious
residue
with
hydrochloric acid, and
suggest you use an alternative
procedure.
Plumber:
Again
Thanked.
Specialist
(in
desperation): Don't
use hydrochloric acid. It
eats hell out of the
pipes.
3.
Know internal biases and
shape perceptions:
They
try to find the resistance of
their readers. For this they collect
all information about their
readers and
then
prepare a game plan.
4.
Persuasive:
Good
writers are strong communicators. They
have the art of strong oral and written
communication
skills.
They use the rhetorical devices to
exhibit standard behavior to influence
their readers. They
know
that
all readers want strong
ethics and morality on the
part of the writer, cooperation,
goodwill, efficiency,
trust
etc. and, they exhibit the
same virtues.
7

Journalistic
Writing MCM310
VU
5.
Knowledge of medium:
Good
writers use their medium:
language in the most effective manner
and according to the reception
level
of
their readers.
8
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO JOURNALISTIC WRITING:Practical, THINGS TO KNOW
- QUALITIES OF GOOD WRITERS
- QUALITIES OF GOOD WRITERS
- QUALITIES OF GOOD WRITING:Achieve appropriate readability:
- QUALITIES OF GOOD WRITING:Be concise, Be creative, Be correct
- THE PROCESS OF WRITING:INVENTION, WHEN YOU START TO WRITE
- THE PROCESS OF WRITING II:ORGANIZING, DRAFTING, REVISING
- ALL ABOUT WORDS:HOW WORDS ARE FORMED?:SUFFIXES
- DICTIONARY-A WRITER’S LANGUAGE TOOL:KINDS OF INFORMATION
- PARTS OF SPEECH:Noun Gender, Noun Plurals, Countable Nouns
- BASIC CLAUSE PATTERNS
- ACTIVE AND PASSSIVE VOICE
- MODIFIERS AND SENTENCE TYPES:COMPOUND SENTENCES
- REPORTED SPEECH:Indirect Questions, Direct commands
- GRAMMATICAL SENTENCE – ISSUES:SUBJECT-VERB AGREEMENT
- GRAMMATICAL SENTENCE – ISSUES II:SENTENCE FRAGMENTS
- EFFECTIVE SENTENCE:PARALLELISM, NEEDED WORDS, SHIFTS
- STYLE: GUIDELINE AND PITFALLS I:COLLOQUIAL VS FORMAL, CIRCUMLOCUTION
- STYLE: GUIDELINE AND PITFALLS II:AMBIGUITY, REDUNDANCY, EUPHEMISM:
- PARAGRAPH WRITING: TYPES AND TECHNIQUES:STRUCTURE
- PARAGRAPH WRITING: TYPES AND TECHNIQUES:Putting on Our Play
- ESSAY WRITING:VARIOUS STRATEGIES FOR ESSAYS, PROMPTS
- SIGNAL WORDS:Non word Emphasis Signals
- EXPOSITORY WRITING:LOGICAL FALLACIES, APPEAL TO EMOTION
- THE WRITING STYLES: REPORT and NARRATIVE WRITING, SHORT REPORTS
- THE WRITING STYLES: DESCRIPTIVE AND PERSUASIVE WRITINGS, Observation
- RESEARCH WRITING AND DOCUMNETING SOURCES:Handling Long Quotations
- Summary and Précis Writing:CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD SUMMARY
- Punctuation:THE PERIOD, THE COMMA, THE SEMICOLON, THE COLON
- MECHANICS:ABBREVIATIONS, NUMBERS, SPELLING, THE HYPHEN
- READING SKILLS FOR WRITERS:EDUCATED READING, STEPS
- PARTS OF A NEWSPAPER:Box-out, By-line, Caption, Exclusive, Feature
- THE LANGUAGE OF THE NEWSPAPERS II:BROADSHEET NEWSPAPER
- News Writing and Style I:WHAT TO LOOK FOR IN A NEWSPAPER
- NEWS WRITING II:Accuracy, Clarity, Style, Qualities of Effective Leads
- EDITORIAL WRITING:WRITING AN EDITORIAL:STRUCTURING AN EDITORIAL
- WRITING FEATURES:GENERATING FEATURE STORY IDEAS
- WRITING COLUMNS:Column and a news report, Purpose, Audience
- WRITING ARTICLES FOR NEWSPAPERS:The Heading, The Lead
- WRITING ANALYSIS:purpose, scope, method, results, recommendations
- LETTERS TO EDITORS:Four important aspects about letters, Organizing letters
- BROADCAST AND WEB NEWS WRITING:WRITE CONCISELY, BROADCAST STYLE
- WRITING PRESS RELEASE, REVIEWS AND OBITUARIES:Summary of Content:
- THE ART OF INTERVIEWINGS
- FINAL THOUGHTS:Practical, Job-Related, Social, Stimulating, Therapeutic