 |
PR AND RESEARCH:Unobtrusive Measures, Questionnaires For Survey |
| << PUBLIC RELATIONS AND RESEARCH:Planning Phase Of Research |
| PROBLEMS SOLVING STRATEGIES:Communicate results >> |
Fundamentals
of Public Relations MCM 401
VU
Lesson
33
PR
AND RESEARCH
Overview
As
explained in the previous lecture research
has a very important place in
drafting or compiling a Public
relations
plan. It is only through research
that PR professionals will be
able to conceive and devise
a
practical
and result oriented strategy
or a plan. In this lecture deeper study
into role of research in
public
relations
plan and strategy will be
studied and explained.
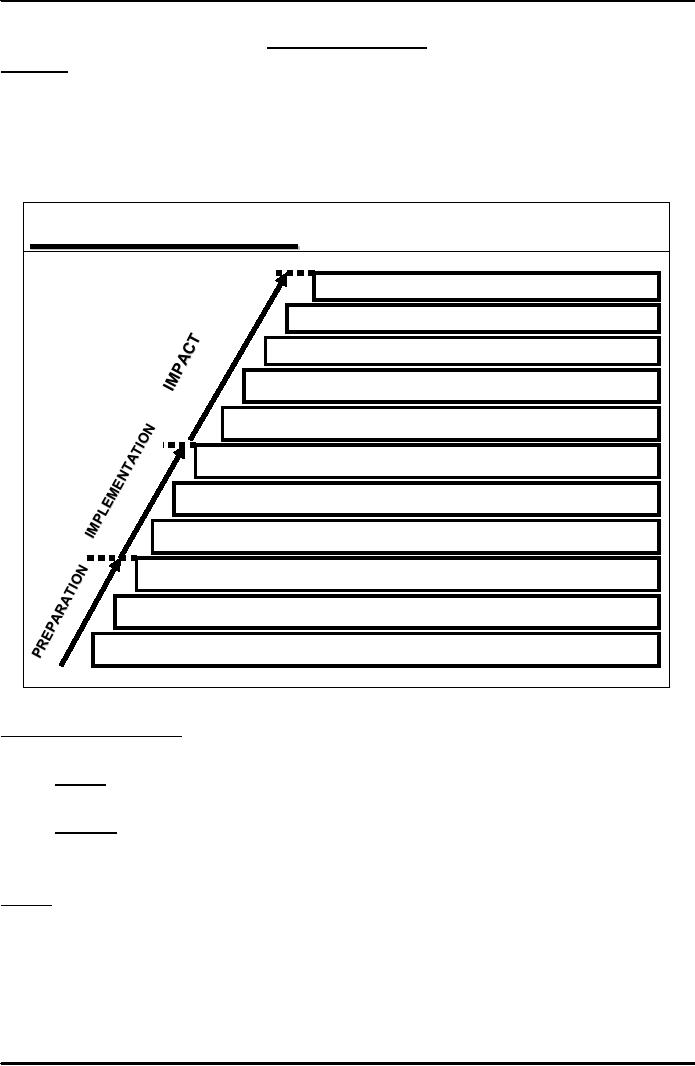
PR
& RESEARCH
Social
& cultural change
No.
who repeat behaviour
No.
who behave as
desired
No.
who change
opinions
No.
who learn message
content
No.
who attend to message &
activities
No.
of messages placed &
implemented
Messages
sent to media & activities
designed
Quality
of messages & activity
presentation
Appropriateness
of message & activity
content
Adequacy
of information for designing
program
Basically
2 Classifications
Basically
there are two main
and practical accepted
methods of research.
1.
Formal
2
types -- qualitative & quantitative,
can be conducted in a laboratory or in
the field.
2.
Informal
This
is conducted without generally
agreed upon rules &
procedures and results of
which can be
used
for description & not for
prediction.
Formal
·
State
the problem.
·
Select
a manageable (& measurable) portion
of the problem.
·
Establish
definitions to be used in the
measurement.
·
Conduct
a search in published literature for
studies similar in subject or
research approach.
80

Fundamentals
of Public Relations MCM 401
VU
·
Develop
a hypothesis.
·
Design
experiments.
·
Obtain
the data.
·
Analyze
the data.
·
Interpret
the data to make inferences
and generalizations.
·
Communicate
the results.
Informal
·
Unobtrusive
Measures.
These
are used to gather
information, permits researchers to
study someone or something
without
interfering
with or interrupting what is going
on.
·
Journalistic
Research.
Journalists
are also trained to gather
Information from the primary (mainly interviews) &
secondary
sources
(public records, media
files, libraries.)
·
Opinion
& Communication Audits.
Audits
could be:
Social,
Economic or Political.
·
Generally,
researchers concentrate on observational
data.
·
Communication
pundits attempt to evaluate various
publics responses to an
organization's
communication
efforts.
·
Publicity
Analysis.
Clippings
from print media and
transcripts from broadcast
publicity can also be used
to determine
the
quantity & quality of
coverage.
Questionnaires
For Survey
How
To Prepare A Questionnaire?
·
Are
the words understandable?
·
Do
they contain abbreviations, jargons or unconventional
phrases?
·
Are
questions technically correct?
·
Are
they too vague?
·
Are
they biased?
·
Are
questions offensive?
·
Do
they require too much effort to
answer?
81
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION & BRIEF HISTORY:Definitions Of Public Relations
- HOW DOES PR WORK?:OVERVIEW, Formulation of policy
- PUBLIC RELATIONS DISTINGUISHED:Size of a PR Department.
- PUBLICS OF PR:Expanded Publics, Few Examples Of Publics
- PLANNING PUBLIC RELATIONS PROGRAMMES:Print Media, Electronic Media
- MEDIAS OF PR:Media for External Publics, Principles of Good Press Relations
- PRESS RELATIONS IN PR:What is News, Secrets Of Good News Release.
- CREATED PRIVATE MEDIA:Private Media, New Forms of House Journals
- SPECIAL USES OF PUBLIC RELATIONS:Crisis Management, Skills Of PR
- BUDGETING IN PR:Labour, Office Overheads, PR & Photographs
- PUBLIC RELATIONS PROBLEMS:Defining PR problems, C’s of PR explained
- METHODS OF COMMUNICATION:Psychology of Public Relations
- PR IN VARIOUS ORGANIZATIONS:Techniques of Trade Association PR
- PR IN LABOUR UNIONS & RELIGIOUS GROUPS:Community Public Relations
- PR IN EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTIONS & IN MEDIA CHANNALS
- USING ADVERTISING FOR P R COMMUNICATION:Role Of PR
- ROLE OF PUBLIC RELATIONS IN MARKETING:How To Educate The Market
- PUBLIC RELATIONS AND CORPORATE STRUCTURE:Corporate Identity Essentials
- E-PR & ITS TOOLS:Immediate Points To Consider, Using Email As PR Tool
- SPONSORSHIP—AN IMPORTANT PR TOOL:PR & Communication Audit
- HOUSE JOURNALS:Possible Publics Of House Journals, Exhibitions & PR
- CRISIS MANAGEMENT IN PR:Plan Of Action Adopted, Interview at your place
- ADVERTISING IN PR:Broad Objectives Of Advertising, Direct Advertising.
- INTERNATIONAL PUBLIC RELATIONS:Media Used, Within Store Contacts
- PUBLIC RELATIONS CONSULTANCY:Disadvantages, Mass Communication
- PUBLIC RELATION’S ROLE IN MARKET EDUCATION:Kinds Of Markets
- MODERN DAY VALUES OF PR:Ethics Of Public Relations
- CHOICE OF MEDIA FOR PR COMPAIGN:Communication Channels & Media
- PR TECHNIQUES:Tactics & Techniques
- DESIGNING PR COMPAIGNS:Definitive Mission statement, Reputation.
- PUBLIC OPINION:Identifying Priority Publics, If Goal Is Attitude Change
- PUBLIC RELATIONS AND RESEARCH:Planning Phase Of Research
- PR AND RESEARCH:Unobtrusive Measures, Questionnaires For Survey
- PROBLEMS SOLVING STRATEGIES:Communicate results
- PERSUASION & COMMUNICATION THEORIES:Message Orientation
- COMMUNICATION CONCEPTS & THEORIES:Research and Persuasion
- PUBLIC RELATIONS & LAW:How To Stay Out Of Trouble
- PUBLIC RELATIONS & CASE STUDIES:Case Analysis, Images Of Public Relations
- PR AND PRINTING PROCESSES:Fundamentals Of Printing
- PUBLIC SPEAKING -- A PR TOOL:Key Benefits, How To Prepare
- PR -- COPING WITH UNEXPECTED:Some Possible PR Ideas
- DREAMS & REALITIES OF PR:Who Takes Charge Of Identity?
- CHANGING INTO OVERDRIVE:How International Is PR?
- GETTING ON WITH PR:Where does PR fit in the structure?
- FUNDAMENTALS OF A SUCCESSFUL NEWSLETTER:RESEARCH, WRITING