 |
PUBLIC RELATIONS DISTINGUISHED:Size of a PR Department. |
| << HOW DOES PR WORK?:OVERVIEW, Formulation of policy |
| PUBLICS OF PR:Expanded Publics, Few Examples Of Publics >> |
Fundamentals
of Public Relations MCM 401
VU
Lesson
3
PUBLIC
RELATIONS DISTINGUISHED.
Overview
In
this lecture we will try and
distinguish public relations from other
activities in which an organization
indulges
to project its image or for
the conveying of a particular message to the target
public. We will
distinguish
public relations from advertising,
marketing. sales promotion, publicity
and propaganda. This
will
enable the students to precisely
know the difference between these
various applications of public
relations.
Difference
between PR & Advertising
Public
relations and advertising are normally
confused to be same, which is
not at all true or correct.
The
best
way to distinguish it from advertising
will be to first of all try
and define advertising and
public
relations.
This definition will clearly
explain the difference.
Advertising
presents the most persuasive
possible selling message to the
right prospects for the
product or
service
at the lowest possible cost.
While public relations role is of
informing,
educating &
creating
understanding
through
knowledge
for the same product. In fact
advertising will be more
successful
when
prior PR activity has
created knowledge and understanding of the
product or service being
promoted
---
also known as Market
Education.
Therefore advertising is merely a tool of
public relations, where
by
market
research PR manager decides type of
advertising and on this basis determines
choice & use of
media.
So to sum up following will explain the
difference between PR and
advertising.
1.
PR
is not a form of advertising, and is in
fact bigger activity than
advertising.
2.
PR
relates to all the communications of the
total organizations, while advertising is
mainly limited
to
marketing functions.
PR
is neither "free advertising"
nor
"unpaid
for advertising". In fact it is time
consuming & time
3.
costs
money.
4.
At
times advertising may not be
used by an organization, but every
organization is involved in PR.
5.
PR
embraces every one & everything,
while advertising is limited to special
selling & buying
tasks
6.
Marketing
is the management process responsible
for identifying, anticipating &
satisfying
customer
requirements profitably.
PR
is about creating & understanding
through knowledge "Market
Education" the
basis of effective
7.
marketing
policy as it has to be applied to every
part of marketing
mix.
Difference
between PR & Sales
Promotion
Sales
promotion consists of short term schemes,
usually at the point of sales,
but also in direct
response
marketing,
to launch products or to revive or
increase sales. At times
sales promotion may have PR
aspects
yet
it is not PR.
PR
is confused with sales
promotion, mainly because Sales
promotion brings the producer closer
to
consumer.
Sales promotion consists of short /
long term specific schemes
while PR takes care of
larger
benefits
through broad based plans
based on knowledge.
Difference
Between PR & Propaganda
Propaganda
is the means of gaining support for an
opinion, creed or belief. This is another
form of
communication
& by no means PR. Successful PR
must be credible, whereas
propaganda is liable to invite
suspicion
or at least disagreement.
Difference
Between PR & Publicity
A
simple definition would explain
publicity as resulting from information
being made known. So as
6

Fundamentals
of Public Relations MCM 401
VU
Publicity
results from information being
made known by PR plan.
PR
is very much about the behavior of
individuals, organizations,
products
& services.
Publicity
only yields an image,
subject to PR which provides
adequate
knowledge for that
image.
Public
Relations Department
When
a company is engaged in lot of PR
work then it is recommended
that it should be handled through
the
company's internal Public Relations
Department.
The
PR Practitioner is more of an All Rounder. He is at
the same time a communicator, advisor and
a
campaign
planner.
Size
of a PR Department.
PR department
may be large or small depending
upon:
a)
Size of the organization.
b)
Value placed on PR by
management;
c)
Special PR requirements of the
organization.
Taking
(c ) a stage further, a mass
consumer product manufacturer
may spend much more on
advertisement
than
on PR, while a technical or
industrial company may spend
little on advertisement but rely strongly
on
PR.
PR
Department Staff.
The PR department
may consist of no more than
a PR Manager and a secretary
with word processing
capability.
Depending upon the activity &
size of operation the organization may
have Press officer,
photographer
and a presentation specialist. See chart
below for possible staffing of a PR
department in a
large
manufacturing company.
Role
Of PR Manager
PR
manager is the executive who
manages the company's PR.
His / Her responsibilities can
be;
To
set the targets or define
objectives for PR
operations;
To
estimate the working hours
and other resources that
needs to be cost.
To
decide priorities that will
control the choice of publics,
media to reach
Them,
timing of operations, best
use of manpower and
other
Resources
such as equipment etc.
To
decide the feasibility of carrying out
the declared objectives in
the light
of
available funds, existing staff and
equipment etc.
Four
Fold Specialist Task Of PR
Manager
1.
To establish and maintain a correct
image of the organization and its
policies, products,
services
and
personnel.
2.
Monitor outside opinion &
convey this intelligence to
management;
3.
Advise management on communication
problems, solutions &
techniques;
Inform
all publics about policies,
activities, products, services &
personnel so that
maximum
knowledge
& understanding is won.
7
Fundamentals
of Public Relations MCM 401
VU
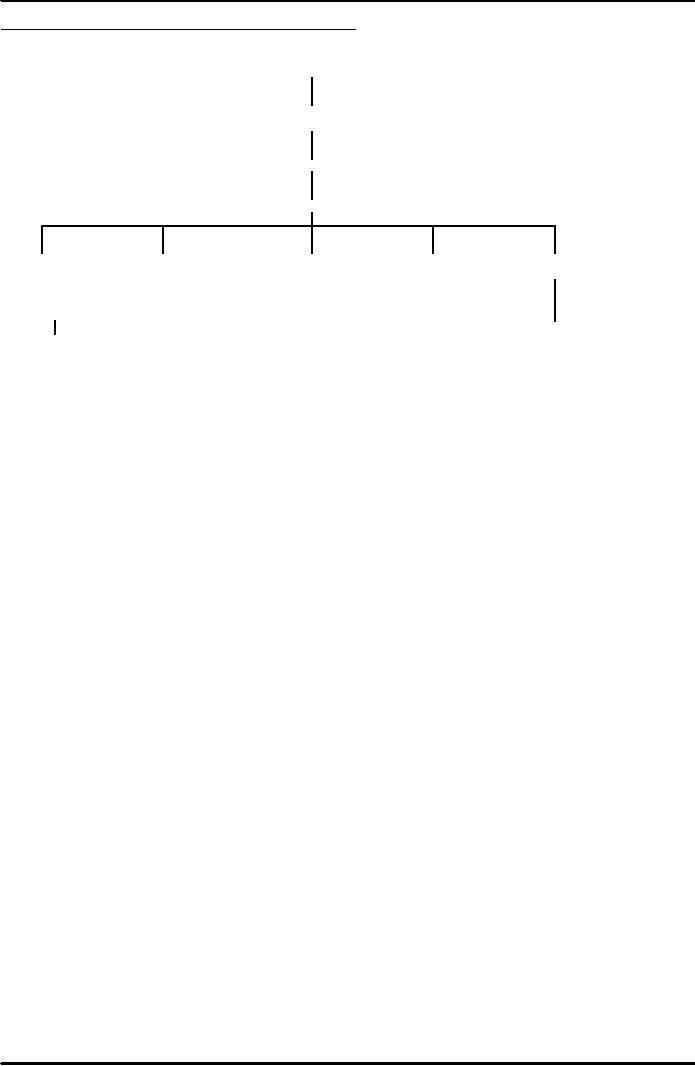
A
Typical Organization Chart of A PR
Department
Public
Relations Manager
Secretary
Assistant
Public Relations
Manager
Secretary
House
Works
Visits
Photographer
Print
and
Press
Officer
Journal
Organizer
Publications
Editor
Officer
Secretary
Secretary
8
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION & BRIEF HISTORY:Definitions Of Public Relations
- HOW DOES PR WORK?:OVERVIEW, Formulation of policy
- PUBLIC RELATIONS DISTINGUISHED:Size of a PR Department.
- PUBLICS OF PR:Expanded Publics, Few Examples Of Publics
- PLANNING PUBLIC RELATIONS PROGRAMMES:Print Media, Electronic Media
- MEDIAS OF PR:Media for External Publics, Principles of Good Press Relations
- PRESS RELATIONS IN PR:What is News, Secrets Of Good News Release.
- CREATED PRIVATE MEDIA:Private Media, New Forms of House Journals
- SPECIAL USES OF PUBLIC RELATIONS:Crisis Management, Skills Of PR
- BUDGETING IN PR:Labour, Office Overheads, PR & Photographs
- PUBLIC RELATIONS PROBLEMS:Defining PR problems, C’s of PR explained
- METHODS OF COMMUNICATION:Psychology of Public Relations
- PR IN VARIOUS ORGANIZATIONS:Techniques of Trade Association PR
- PR IN LABOUR UNIONS & RELIGIOUS GROUPS:Community Public Relations
- PR IN EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTIONS & IN MEDIA CHANNALS
- USING ADVERTISING FOR P R COMMUNICATION:Role Of PR
- ROLE OF PUBLIC RELATIONS IN MARKETING:How To Educate The Market
- PUBLIC RELATIONS AND CORPORATE STRUCTURE:Corporate Identity Essentials
- E-PR & ITS TOOLS:Immediate Points To Consider, Using Email As PR Tool
- SPONSORSHIP—AN IMPORTANT PR TOOL:PR & Communication Audit
- HOUSE JOURNALS:Possible Publics Of House Journals, Exhibitions & PR
- CRISIS MANAGEMENT IN PR:Plan Of Action Adopted, Interview at your place
- ADVERTISING IN PR:Broad Objectives Of Advertising, Direct Advertising.
- INTERNATIONAL PUBLIC RELATIONS:Media Used, Within Store Contacts
- PUBLIC RELATIONS CONSULTANCY:Disadvantages, Mass Communication
- PUBLIC RELATION’S ROLE IN MARKET EDUCATION:Kinds Of Markets
- MODERN DAY VALUES OF PR:Ethics Of Public Relations
- CHOICE OF MEDIA FOR PR COMPAIGN:Communication Channels & Media
- PR TECHNIQUES:Tactics & Techniques
- DESIGNING PR COMPAIGNS:Definitive Mission statement, Reputation.
- PUBLIC OPINION:Identifying Priority Publics, If Goal Is Attitude Change
- PUBLIC RELATIONS AND RESEARCH:Planning Phase Of Research
- PR AND RESEARCH:Unobtrusive Measures, Questionnaires For Survey
- PROBLEMS SOLVING STRATEGIES:Communicate results
- PERSUASION & COMMUNICATION THEORIES:Message Orientation
- COMMUNICATION CONCEPTS & THEORIES:Research and Persuasion
- PUBLIC RELATIONS & LAW:How To Stay Out Of Trouble
- PUBLIC RELATIONS & CASE STUDIES:Case Analysis, Images Of Public Relations
- PR AND PRINTING PROCESSES:Fundamentals Of Printing
- PUBLIC SPEAKING -- A PR TOOL:Key Benefits, How To Prepare
- PR -- COPING WITH UNEXPECTED:Some Possible PR Ideas
- DREAMS & REALITIES OF PR:Who Takes Charge Of Identity?
- CHANGING INTO OVERDRIVE:How International Is PR?
- GETTING ON WITH PR:Where does PR fit in the structure?
- FUNDAMENTALS OF A SUCCESSFUL NEWSLETTER:RESEARCH, WRITING