 |
BUSINESS REPORTS:A Model Report, Definition, Purpose of report |
| << MINUTES OF THE MEETING:Committee Members’ Roles, Producing the Minutes |
| BUSINESS REPORTS:Main Features of the Report, INTRODUCTION >> |

VU
Lesson
29
BUSINESS
REPORTS
Model
Business Reports
A
Model Report
October
10, 2003
The
General Manager,
Fit
Garment Industries,
Multan
Road Lahore.
Dear
Sir,
Subject:
Report on the
strike of the workers in the
factory.
Following
your instructions, I have probed
into the matter regarding the strike of
all the workers in
the
factory. Here are my
findings.
On
Monday morning, in the production
unit 2, two workers started
a fight on a money matter.
Ahmad
had lent some money to
Kareem, who made several
promises but did not
return a single
penny.
On
Monday morning Ahmad
demanded an immediate return of
his amount but instead of an
apologetic
behaviour
Kareem abused Ahmad. Hot
remarks were exchanged.
Kareem picked up a hammer and
hit it
hard
on Ahmad's head. It started
bleeding.
He
was rushed to the hospital by the
workers. Members of the labour
union reached and all
the
workers
took out a procession. The
President of the union gave a
call for strike. They
raised slogans
against
the
culprit. While addressing the mob,
union leaders demanded a
prompt termination of the culprit.
They
wanted
to continue the strike till the acceptance of
their demand.
However,
on the assurance of the Production Manager, they
agreed to call off their
strike.
Everything
was done amicably.
On
Monday morning Ahmad
demanded an immediate return of
his amount but instead of an
apologetic
behaviour
Kareem abused Ahmad. Hot
remarks were exchanged.
Kareem picked up a hammer and
hit it
hard
on Ahmad's head. It started
bleeding.
He
was rushed to the hospital by the
workers. Members of the labour
union reached and all
the
workers
took out a procession. The
President of the union gave a
call for strike. They
raised slogans
against
the
culprit. While addressing the mob,
union leaders demanded a
prompt termination of the culprit.
They
wanted
to continue the strike till the acceptance of
their demand.
However,
on the assurance of the Production Manager, they
agreed to call off their
strike. Everything
was
done
amicably.
Sir,
You
have asked for my
suggestions, so I recommend Mr.
Kareem's termination. I do feel that
a
case
of fraud and assault should be
registered in the police station. Mr.
Ahmad should be treated at the
expenses
of the company and should be granted paid
leave for one
month.
Yours
truly,
A.
Sheikh
Regional
Manager
122
VU
Definition
A
Business Report is an impartial, objective, planned presentation of
facts to one or more persons
for a
specific
business purpose. An orderly, objective
message used to convey
information from one
organizational
area to another or from one
institution to another to assist in
decision making or problem
solving."
Reports
have been classified in
numerous ways by management
and by report-preparation
authorities.
We
classify reports on the
bases of their forms, uses,
contents, etc.
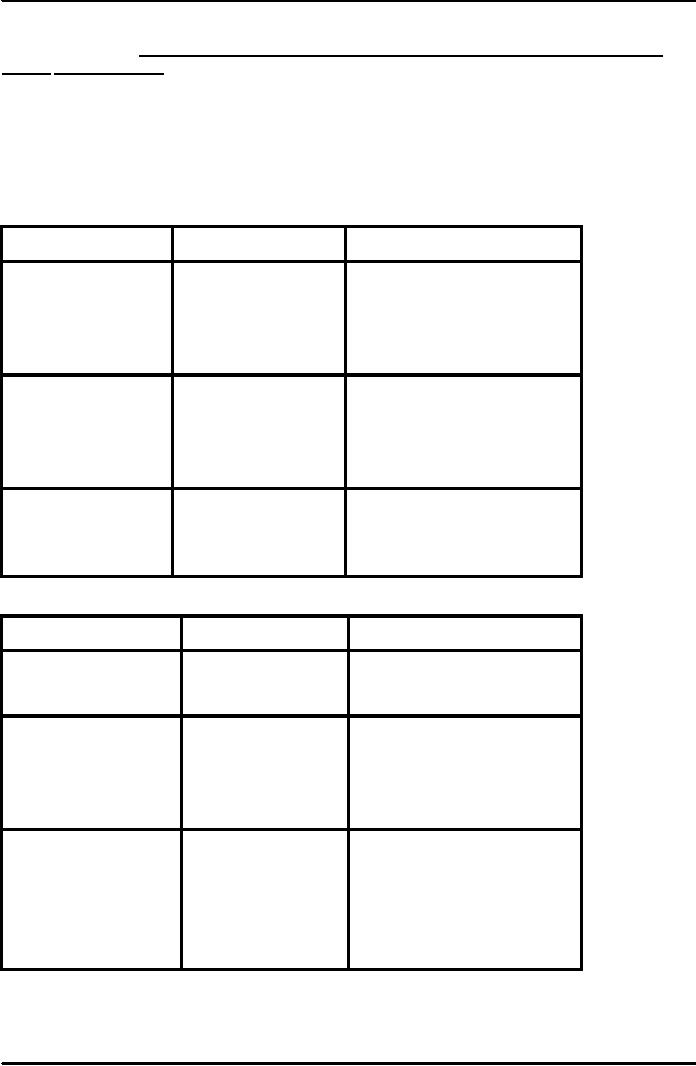
Purpose
of report
Purpose
of Report
Common
Examples
Reparation
& Distribution
To
monitor and control
Plans,
operating reports,
Internal
reports move upward on
operations
personal
activity reports
recurring
basis; external reports go
to
selected audiences.
To
implement policies
Lasting
guideline, position Internal reports move
downward or
and
procedures
papers
on
a non-recurring basis
To
comply with
Reports
IRS, SEC,
External
reports are sent on a
regulatory
requirements
EEOC,
Human Rights
recurring
basis
Commission
Definition
Purpose
of Report
Common
Examples
Reparation
& Distribution
To
obtain new business or Sales
proposals
External
reports are sent on
non-
findings
recurring
basis
To
document client work
Interim
progress reports, External reports
are sent on a non-
final
reports
recurring
basis
To
guide decisions
Research
reports,
Internal
reports move upward on a
justification
reports,
non-recurring
basis
trouble
shooting reports
(Classifications)
123

VU
Classification
of Report
Formal
or Informal
Formal
reports are
carefully structured; they stress
objectivity and organization, contain,
much
detail,
and are written in a style
that tends to eliminate such
elements as personal pronouns.
Informal
reports are
usually short messages with natural,
casual use of language. The
internal
memorandum
generally can be described as an
informal report.
Short
or Long Reports?
"Short-or-long"
can be a confusing classification for
reports. A
one-page memorandum is
obviously
short, and a
term paper of twenty pages
is obviously long. What
about in-between lengths?
One
important distinction generally holds
true: as a report becomes longer, it
takes on more
characteristics
of
formal reports. Thus, the
formal-informal and short-long
classifications are closely
related.
What
Makes A Good Business
Report
Business
reports are like bridges
spanning time and space. Organizations
use them to provide a
formal,
verifiable
link among people, places,
and times. Some reports are
needed for internal communication:
others
are
vehicles for corresponding with
outsiders. Some are required as a
permanent record; others are
needed
to
solve an immediate problem or to
answer a passing question. Many
move upward through the chain
of
command
to help managers monitor the
various units in the organization; some move downward
to explain
management
decisions to lower-level employees
responsible for day-to-day
operations.
The
purpose of a business
report
is
to
convey essential information in an
organized, useful format.
And
despite
technological advances, the ability to
accumulate data, organize
facts, and compose a
readable text
remains
a highly marketable
skill.
A
well-prepared business report will
provide COMPLETE, ACCURATE
information about an
aspect
of a company's operations. The
subject of a report may vary
from expenses to profits,
production to
sales,
marketing trends to customer relations.
The information provided by a
report is often meant
to
influence
decisions, to determine changes,
improvements, or solutions to problems. Therefore, the
report
must
also be CLEAR, CONCISE, and
READABLE.
The
format
of a
business report may vary,
from a brief informal
report intended
for in-house use to a
voluminous
formal
report intended
for a national public
distribution. Some reports consist
entirely of prose
while
others consist of statistics;
and still other reports may
employ a combination of prose, tables,
charts,
and
graphs.
The
style
of a
report depends upon the
audience. An informal report to be
read only by close
associates
may be worded personally; in such a
report "I" or "we" is acceptable. A
formal report, on the
other
hand, must be impersonal and
expressed entirely in the third
person. Note the difference
Style
Informal:
I
recommend that the spring campaign
concentrate on newspaper and television
advertising.
Formal:
It
is recommended that the spring
campaign concentrate on newspaper
and television advertising.
Informal:
After
discussing the matter with
our department managers, we came up
with the following
information.
Formal:
The
following report is based
upon information provided by the
managers of the Accounting,
Marketing,
Personnel, and Advertising
Departments.
Deciding
on Format and Length
Preprinted
form. Basically
for "fill in the blank"
reports. Most are relatively short
(five or fewer pages)
and
deal
with routine information,
often mainly numerical. Use this
format when it's requested by the
person
authorizing
the report.
Letter.
Common
for reports of five or fewer pages
that are directed to
outsiders. These reports
include
all the normal parts of a letter,
but they may also have
headings, footnotes, tables,
and figures.
124

VU
Memo.
Common
for short (fewer than ten
pages) informal reports distributed
within an
organization.
Memos have headings at the top:
To,
From, Date, and
Subject.
In
addition, like longer
reports,
they
often have internal headings
and sometimes have visual.(organizational
plan)
Deciding
on Approach
Audience
attitude is the basis for
decisions about organization. When the
audience is considered either
receptive
or open minded, use the direct
approach.
Lead
off with a summary of your
key findings, conclusions,
and recommendations. This
"up-front"
approach
is by far the most popular
and
convenient
order
for business reports because
it
saves time and
makes
the best of the report
easy to follow. For
those who have questions or
want more information,
later
parts of the report provide
complete findings and supporting details.
In
addition to being more
convenient
for readers, the direct approach
also produces a more
forceful report. You
are sure of
yourself
when
you state your conclusions confidently at
the outset.
Types
of Reports
A
memo report is a cross
between interoffice memo and
a formal report
Memo
reports can be used
to:
�
Answer a
request for
information
�
Report
progress
�
Make
recommendations
�
State
facts
�
Communicates
ideas
�
Send
statistical data
�
Explain
trend within an organization
Two
types of Memo Reports
1.
Informational Memorandum
Reports
2.
Analytical memo
Reports
Informational
Memorandum Reports
The
central purpose of informational reports
is to inform and to summarize
information, similar to
the
speech to inform. Obviously,
these reports vary widely in content, depending on
type of business,
purpose,
topics discussed, and
readers' needs. The
following reports are often
used in organizations:
Information
Memo reports will
�
Inform
�
To
summarize some information
requested
�
Organize
information objectively
�
Make
recommendation
Conference
Reports
Topics
for conference reports range
from summaries of personal
sales called conferences to
write-
ups
of meetings attended by hundreds of
persons. For example, A credit or
collection manager or
account
executive
may make similar reports after
conferences with clients.
The
text of such reports is usually
organized by
topics
discussed or presented simply in a
chronological order. Some
firms have standardized headings
for the often-
written
reports to ensure that the same
information or main topics
are recorded in all of
them.
Progress
Reports
Progress
reports show, "progress," accomplishments, or
activity over time or at a given stage of
a
major
assignment. The organizational plan is
usually inductive, including
topics similar to
these.
1.
Introduction (purpose, nature of
project)
2.
Description of accomplishments during the
reporting period.
125

VU
3.
Unanticipated problems (if
any)
4.
Plans for the next reporting
period.
5.
Summary (overall appraisal of progress to
date)
6.
(Periodic report)
Periodic
Reports
They
are routine reports prepared at
regular time interval-daily, weekly,
monthly quarterly or
annually.
Examples
of such reports are:
1.
Sales
Reports
2.
Financial
Reports
They
reports are prepared on pre-printed
form.
Analytical
Memorandum Reports
This
analytical memorandum report,
seeks to analyze a situation or problem;
it may end with or without
a
specific
recommendation.
Such
reports:
�
On the
causes of decline in Sales
Volume
�
On the
evaluation of a person before recruitment
�
On
individual being considered for
promotion
�
On the
analysis of a particular book
Recommendation-Justification
Reports
Many
analytical reports will have a
special purpose: to recommend a
change or remain with
the
status
quo (policy), support the idea
that something is desirable or
undesirable (value), or defend the
accuracy
of information (fact). Your
report may be in response to a
specific request, or it may be
voluntary.
�
Organizing
memo reports
�
Itemize
the information
�
Present
the fact with absolute
fairness and accuracy
�
Be
careful not to mix you
opinion with the facts you
report
�
Reserve
your comments for your
conclusions and recommendations(letter
report)
126
Table of Contents:
- COMMUNICATION:Definition of Communication, Communication & Global Market
- FLOW OF COMMUNICATION:Internal Communication, External Communication
- THEORIES OF COMMUNICATION:Electronic Theory, Rhetorical Theory
- THE PROCESS OF COMMUNICATION & MISCOMMUNICATION:Message
- BARRIERS IN EFFECTIVE COMMUNICATION /COMMUNICATION FALLOFF
- NON- VERBAL COMMUNICATION:Analysing Nonverbal Communication
- NON- VERBAL COMMUNICATION:Environmental Factors
- TRAITS OF GOOD COMMUNICATORS:Careful Creation of the Message
- PRINCIPLES OF BUSINESS COMMUNICATION:Clarity
- CORRECTNESS:Conciseness, Conciseness Checklist, Correct words
- CONSIDERATION:Completeness
- INTERCULTURAL COMMUNICATION
- INTERCULTURAL COMMUNICATION:Education, Law and Regulations, Economics
- INDIVIDUAL CULTURAL VARIABLES:Acceptable Dress, Manners
- PROCESS OF PREPARING EFFECTIVE BUSINESS MESSAGES
- Composing the Messages:THE APPEARANCE AND DESIGN OF BUSINESS MESSAGES
- THE APPEARANCE AND DESIGN OF BUSINESS MESSAGES:Punctuation Styles
- COMMUNICATING THROUGH TECHNOLOGY:Email Etiquette, Electronic Media
- BASIC ORGANIZATIONAL PLANS:Writing Goodwill Letters
- LETTER WRITING:Direct Requests, Inquiries and General Requests
- LETTER WRITING:Replies to Inquiries, Model Letters
- LETTER WRITING:Placing Orders, Give the Information in a Clear Format
- LETTER WRITING:Claim and Adjustment Requests, Warm, Courteous Close
- LETTER WRITING:When The Buyer Is At Fault, Writing Credit Letters
- LETTER WRITING:Collection Letters, Collection Letter Series
- LETTER WRITING:Sales Letters, Know your Buyer, Prepare a List of Buyers
- MEMORANDUM & CIRCULAR:Purpose of Memo, Tone of Memorandums
- MINUTES OF THE MEETING:Committee Members’ Roles, Producing the Minutes
- BUSINESS REPORTS:A Model Report, Definition, Purpose of report
- BUSINESS REPORTS:Main Features of the Report, INTRODUCTION
- BUSINESS REPORTS:Prefatory Parts, Place of Title Page Items
- MARKET REPORTS:Classification of Markets, Wholesale Market
- JOB SEARCH AND EMPLOYMENT:Planning Your Career
- RESUME WRITING:The Chronological Resume, The Combination Resume
- RESUME & APPLICATION LETTER:Personal Details, Two Types of Job Letters
- JOB INQUIRY LETTER AND INTERVIEW:Understanding the Interview Process
- PROCESS OF PREPARING THE INTERVIEW:Planning for a Successful Interview
- ORAL PRESENTATION:Planning Oral Presentation, To Motivate
- ORAL PRESENTATION:Overcoming anxiety, Body Language
- LANGUAGE PRACTICE AND NEGOTIATION SKILLS:Psychological barriers
- NEGOTIATION AND LISTENING:Gather information that helps you
- THESIS WRITING AND PRESENTATION:Write down your ideas
- THESIS WRITING AND PRESENTATION:Sections of a Thesis (Format)
- RESEARCH METHODOLOGY:Studies Primarily Qualitative in Nature
- RESEARCH METHODOLOGY:Basic Rules, Basic Form, Basic Format for Books