 |
VU
Lesson
2
FLOW
OF COMMUNICATION
�
An organization is
a group of people associated for
business, political, professional,
religious, social,
or
other purposes. Its activities require
human beings to interact and
react, that is, to
communicate.
They
exchange information, ideas,
plans, order needed supplies
and make decisions,
rules,
proposals,
contracts, and agreements.
All these activities require one
skill, that is communication.
So
we can say that communication is the
"Lifeline" of every organization
�
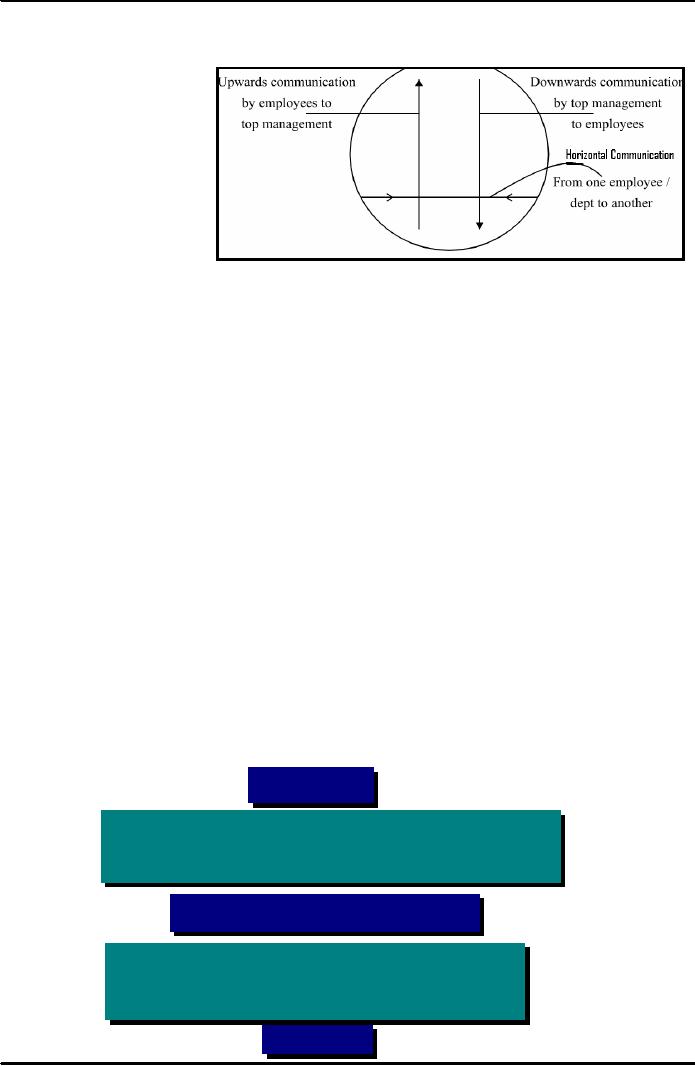
An
exchange of information within an
organization is called internal communication. It
takes place
at
different levels -- downwards,
upwards and
horizontal
�
To
exchange information within
and outside the organization we use a
variety of formal and
informal
forms of communication that carry the
flow of information.
Flow
of Communication
Formal
Planned
communication
Memo,
letter, report, e-mail &
faxes that follow
company's
chain of command
Internal
Communication
Casual
Communication among
employees
e-mail
face to face
conversation
phone
calls, discussions
Informal
Internal
Communication
The
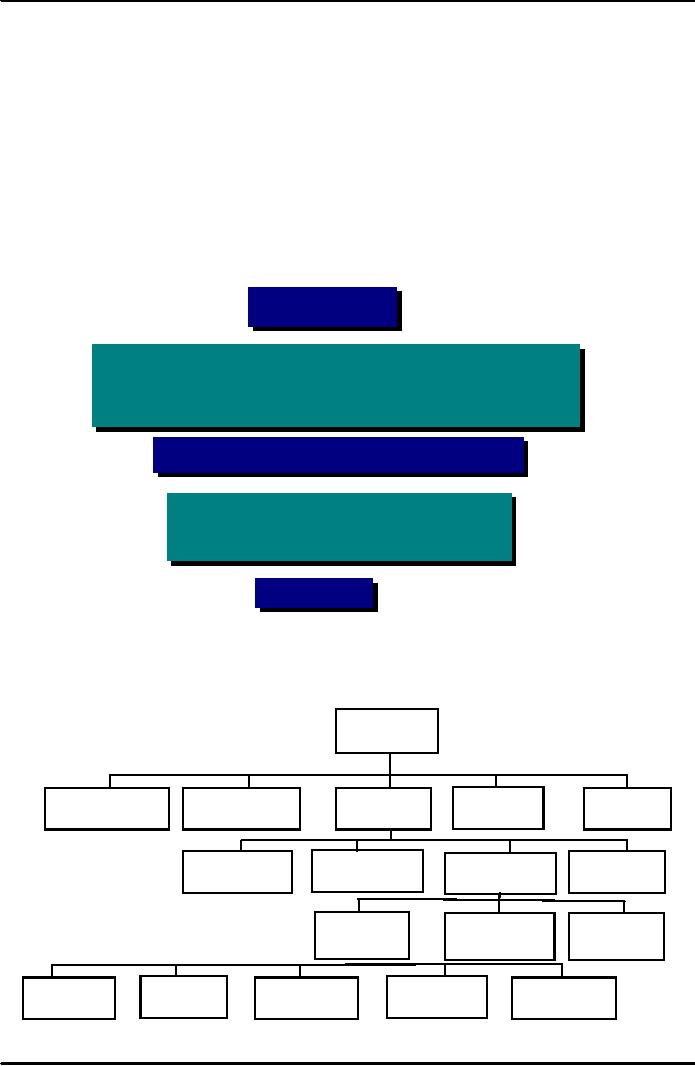
formal Communication Network
�
The
formal flow of information
follows the official chain of
command.
President
VP
VP
VP
VP
VP
Finance
Production
Sales
Human
Marketing
Resources
Sales
Sales
Sales
Sales
Manager
Manager
Manager
Manager
Midwest
East
International
West
District
District
District
1
2
3
Manager
Manager
Manager
Sales
Sales
Sales
Sales
Sales
Rep
Rep
Rep
Rep
Rep
5
VU
Direction
of flow within the
organization
Downward
Flow
�
Organizational
decisions
are made at
top
level and then flow
down
to the people
who
carry them. When
employees
receive
appropriate
downward
communication
from
the
management, they
become
motivated and more
efficient. They need clear
job directions, safety rules,
facts about
organizational
strategy, products, and
viewpoints on important controversial
issues. They are
concerned
about their benefits such as health
care, promotions, pensions,
training, etc.
Upward
Flow
�
To
solve problems and make
intelligent decision manager
need what is going on in the
organization.
Upward internal communication is also
very important. Many executives
want
comments
from employees in addition to the
usual periodic reports.
Successful managers listen
closely
to opinions, complaints, problems,
and suggestions, especially
when these are clearly
put
forward.
They want to know about problem,
emerging trends.
Horizontal
Flow
�
Horizontal
flow takes place between
peers in organizations in order to
solve problems, perform
job
duties,
prepare for meetings, and
cooperate on important projects. So
you can imagine that
people
spend
time on listening to and making requests,
writing notes and memos,
and discussing and
writing
about projects. And they do it through
communication.
Informal
Internal Communication
�
Every
organization has an informal communication
network a grapevine that
supplements
official
channel. It is important source of
information. It is casual conversation of an
organization.
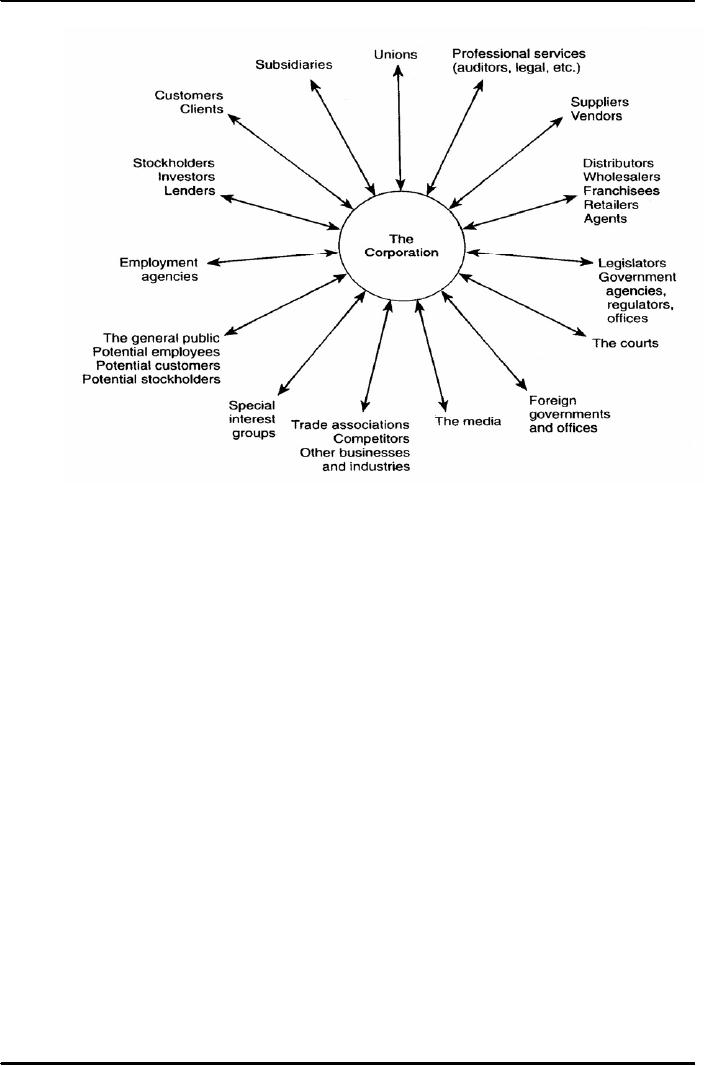
External
Communication
�
Communication
that takes place outside the
organization is called external communication.
The
right
letter, proposal, report, telephone call,
or personal conversation can win
back an angry
customer,
create a desire for a firm's
product or services, encourage
collections, motivate
performance,
and in general, create
goodwill.
Formal
Planned
communication with
outsides
Memo,
letter, report
e-mail,
Fax's
that follow company's
chain of command
External
Communication
Casual
Communication among Customers,
suppliers,
investors, e-mail face to face
conversation
phone
calls, discussions
Informal
6
VU
Various
Aspects of External
Communication
Informal
External Communication
�
Although
external communication is formal, informal
contacts with outsiders are
important for
learning
customer's needs. Plenty of high level
manager recognize the value of keeping in
touch
with
"the real world by creating
opportunities to talk with
and get feedback from
customers and
frontline
companies.
Ways
of External Communication
�
Letters,
pamphlets, annual reports, interviews
with the news media,
etc.
7
Table of Contents:
- COMMUNICATION:Definition of Communication, Communication & Global Market
- FLOW OF COMMUNICATION:Internal Communication, External Communication
- THEORIES OF COMMUNICATION:Electronic Theory, Rhetorical Theory
- THE PROCESS OF COMMUNICATION & MISCOMMUNICATION:Message
- BARRIERS IN EFFECTIVE COMMUNICATION /COMMUNICATION FALLOFF
- NON- VERBAL COMMUNICATION:Analysing Nonverbal Communication
- NON- VERBAL COMMUNICATION:Environmental Factors
- TRAITS OF GOOD COMMUNICATORS:Careful Creation of the Message
- PRINCIPLES OF BUSINESS COMMUNICATION:Clarity
- CORRECTNESS:Conciseness, Conciseness Checklist, Correct words
- CONSIDERATION:Completeness
- INTERCULTURAL COMMUNICATION
- INTERCULTURAL COMMUNICATION:Education, Law and Regulations, Economics
- INDIVIDUAL CULTURAL VARIABLES:Acceptable Dress, Manners
- PROCESS OF PREPARING EFFECTIVE BUSINESS MESSAGES
- Composing the Messages:THE APPEARANCE AND DESIGN OF BUSINESS MESSAGES
- THE APPEARANCE AND DESIGN OF BUSINESS MESSAGES:Punctuation Styles
- COMMUNICATING THROUGH TECHNOLOGY:Email Etiquette, Electronic Media
- BASIC ORGANIZATIONAL PLANS:Writing Goodwill Letters
- LETTER WRITING:Direct Requests, Inquiries and General Requests
- LETTER WRITING:Replies to Inquiries, Model Letters
- LETTER WRITING:Placing Orders, Give the Information in a Clear Format
- LETTER WRITING:Claim and Adjustment Requests, Warm, Courteous Close
- LETTER WRITING:When The Buyer Is At Fault, Writing Credit Letters
- LETTER WRITING:Collection Letters, Collection Letter Series
- LETTER WRITING:Sales Letters, Know your Buyer, Prepare a List of Buyers
- MEMORANDUM & CIRCULAR:Purpose of Memo, Tone of Memorandums
- MINUTES OF THE MEETING:Committee Members’ Roles, Producing the Minutes
- BUSINESS REPORTS:A Model Report, Definition, Purpose of report
- BUSINESS REPORTS:Main Features of the Report, INTRODUCTION
- BUSINESS REPORTS:Prefatory Parts, Place of Title Page Items
- MARKET REPORTS:Classification of Markets, Wholesale Market
- JOB SEARCH AND EMPLOYMENT:Planning Your Career
- RESUME WRITING:The Chronological Resume, The Combination Resume
- RESUME & APPLICATION LETTER:Personal Details, Two Types of Job Letters
- JOB INQUIRY LETTER AND INTERVIEW:Understanding the Interview Process
- PROCESS OF PREPARING THE INTERVIEW:Planning for a Successful Interview
- ORAL PRESENTATION:Planning Oral Presentation, To Motivate
- ORAL PRESENTATION:Overcoming anxiety, Body Language
- LANGUAGE PRACTICE AND NEGOTIATION SKILLS:Psychological barriers
- NEGOTIATION AND LISTENING:Gather information that helps you
- THESIS WRITING AND PRESENTATION:Write down your ideas
- THESIS WRITING AND PRESENTATION:Sections of a Thesis (Format)
- RESEARCH METHODOLOGY:Studies Primarily Qualitative in Nature
- RESEARCH METHODOLOGY:Basic Rules, Basic Form, Basic Format for Books