 |
MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION:Monopolistic Competition in the Market for Colas and Coffee |
| << Bundling:Mixed Versus Pure Bundling, Effects of Advertising |
| OLIGOPOLY:Duopoly Example, Price Competition >> |
Microeconomics
ECO402
VU
Lesson
39
MONOPOLISTIC
COMPETITION
Characteristics
1)
Many firms
2)
Free entry and
exit
3)
Differentiated product
The
amount of monopoly power
depends on the degree of
differentiation.
Examples
of this very common market
structure include:
Toothpaste
Soap
Cold
remedies
Toothpaste
Brand J and
monopoly power
�
Suppose an MNC is
the sole producer of Brand
J
�
Consumers
can have a preference for
Brand J---taste, reputation,
decay preventing
efficacy
�
The
greater the preference
(differentiation) the higher
the price.
The
Makings of Monopolistic
Competition
Two important
characteristics
�
Differentiated
but highly substitutable
products
�
Free
entry and exit
A
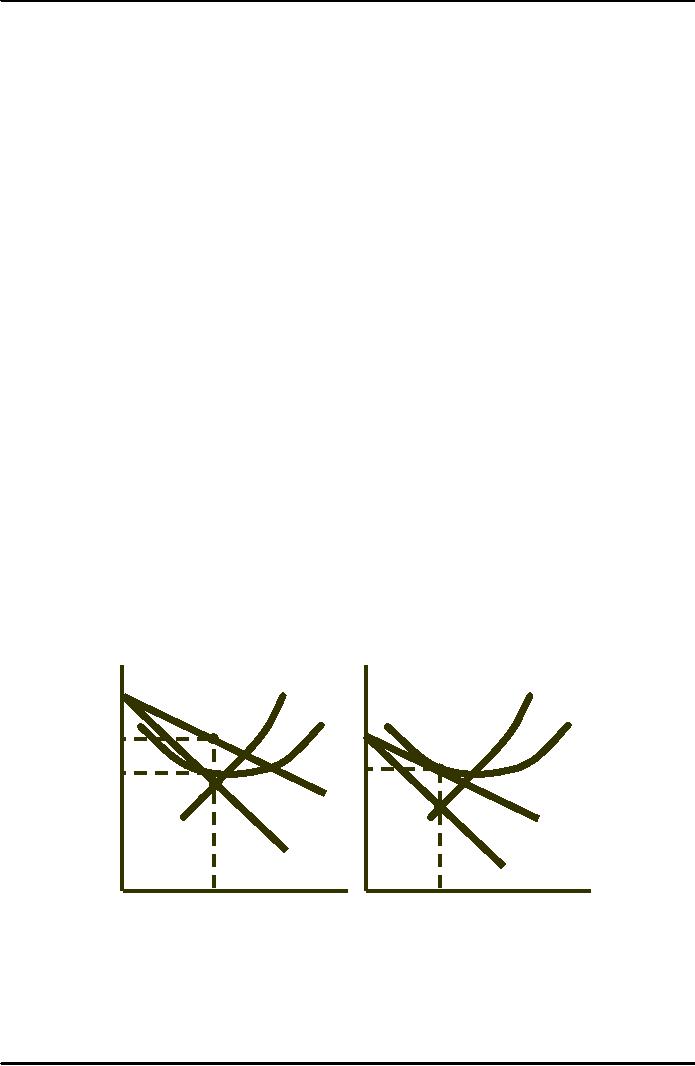
Monopolistically Competitive Firm in
the Short and Long
Run
$/Q
$/Q
Long
Run
Short
Run
MC
MC
AC
AC
PSR
PLR
DSR
DLR
MRSR
MRLR
Quantity
QSR
QLR
Quantity
Observations
(short-run)
Downward
sloping demand--differentiated
product
Demand is
relatively elastic--good
substitutes
MR
< P
Profits are
maximized when MR
= MC
179
Microeconomics
ECO402
VU
This firm is
making economic
profits
Observations
(long-run)
Profits will
attract new firms to the
industry (no barriers to
entry)
The old
firm's demand will decrease
to DLR
Firm's output
and price will
fall
Industry output
will rise
No economic
profit (P = AC)
P > MC -- some
monopoly power
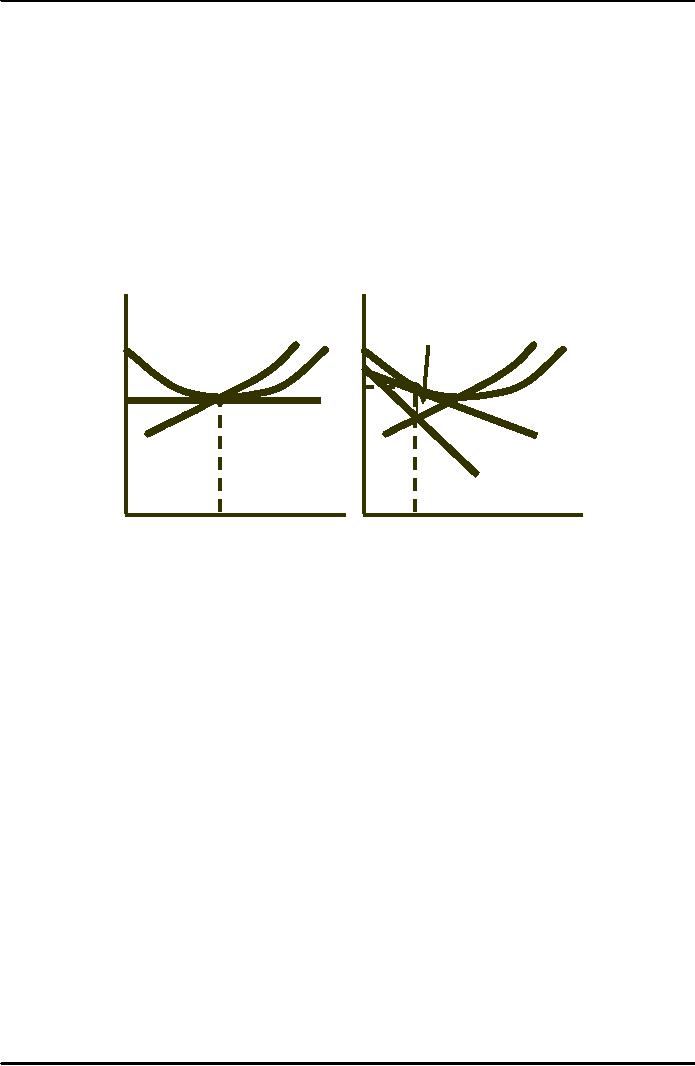
Monopolistically
Competitive vs. Perfectly
Competitive Equilibrium
Monopolistic
Competition
Perfect
Competition
$/Q
$/Q
Deadweight
loss
MC
AC
MC
AC
P
PC
D=
DLR
MRLR
Quantity
Quantity
QC
QMC
Monopolistic
Competition and Economic
Efficiency
The monopoly
power (differentiation) yields a
higher price than perfect
competition. If
price
was lowered to the point
where MC = D, consumer surplus
would increase by the
shaded
triangle.
With no
economic profits in the long
run, the firm is still
not producing at minimum
AC
and
excess capacity
exists.
Questions
1)
If the market became
competitive, what would
happen to output and
price?
2)
Should monopolistic competition be
regulated?
Monopolistic
Competition in the Market
for Colas and
Coffee
The
markets for soft drinks
and coffee illustrate the
characteristics of monopolistic
competition.
180

Microeconomics
ECO402
VU
Elasticities
of Demand for Brands of
Colas and Coffee
Colas:
Brand X -2.4
Brand
Y -
5.2
to -5.7
Ground
Coffee:
Hills
Brothers -7.1
Maxwell
House
-8.9
Chase
and Sanborn -5.6
Questions
1)
Why is the demand for
Brand X more price inelastic
than for Brand Y?
2)
Is there much monopoly power
in these two markets?
3)
Define the relationship
between elasticity and
monopoly power.
181
Table of Contents:
- ECONOMICS:Themes of Microeconomics, Theories and Models
- Economics: Another Perspective, Factors of Production
- REAL VERSUS NOMINAL PRICES:SUPPLY AND DEMAND, The Demand Curve
- Changes in Market Equilibrium:Market for College Education
- Elasticities of supply and demand:The Demand for Gasoline
- Consumer Behavior:Consumer Preferences, Indifference curves
- CONSUMER PREFERENCES:Budget Constraints, Consumer Choice
- Note it is repeated:Consumer Preferences, Revealed Preferences
- MARGINAL UTILITY AND CONSUMER CHOICE:COST-OF-LIVING INDEXES
- Review of Consumer Equilibrium:INDIVIDUAL DEMAND, An Inferior Good
- Income & Substitution Effects:Determining the Market Demand Curve
- The Aggregate Demand For Wheat:NETWORK EXTERNALITIES
- Describing Risk:Unequal Probability Outcomes
- PREFERENCES TOWARD RISK:Risk Premium, Indifference Curve
- PREFERENCES TOWARD RISK:Reducing Risk, The Demand for Risky Assets
- The Technology of Production:Production Function for Food
- Production with Two Variable Inputs:Returns to Scale
- Measuring Cost: Which Costs Matter?:Cost in the Short Run
- A Firm’s Short-Run Costs ($):The Effect of Effluent Fees on Firms’ Input Choices
- Cost in the Long Run:Long-Run Cost with Economies & Diseconomies of Scale
- Production with Two Outputs--Economies of Scope:Cubic Cost Function
- Perfectly Competitive Markets:Choosing Output in Short Run
- A Competitive Firm Incurring Losses:Industry Supply in Short Run
- Elasticity of Market Supply:Producer Surplus for a Market
- Elasticity of Market Supply:Long-Run Competitive Equilibrium
- Elasticity of Market Supply:The Industry’s Long-Run Supply Curve
- Elasticity of Market Supply:Welfare loss if price is held below market-clearing level
- Price Supports:Supply Restrictions, Import Quotas and Tariffs
- The Sugar Quota:The Impact of a Tax or Subsidy, Subsidy
- Perfect Competition:Total, Marginal, and Average Revenue
- Perfect Competition:Effect of Excise Tax on Monopolist
- Monopoly:Elasticity of Demand and Price Markup, Sources of Monopoly Power
- The Social Costs of Monopoly Power:Price Regulation, Monopsony
- Monopsony Power:Pricing With Market Power, Capturing Consumer Surplus
- Monopsony Power:THE ECONOMICS OF COUPONS AND REBATES
- Airline Fares:Elasticities of Demand for Air Travel, The Two-Part Tariff
- Bundling:Consumption Decisions When Products are Bundled
- Bundling:Mixed Versus Pure Bundling, Effects of Advertising
- MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION:Monopolistic Competition in the Market for Colas and Coffee
- OLIGOPOLY:Duopoly Example, Price Competition
- Competition Versus Collusion:The Prisoners’ Dilemma, Implications of the Prisoners
- COMPETITIVE FACTOR MARKETS:Marginal Revenue Product
- Competitive Factor Markets:The Demand for Jet Fuel
- Equilibrium in a Competitive Factor Market:Labor Market Equilibrium
- Factor Markets with Monopoly Power:Monopoly Power of Sellers of Labor