 |
Monopoly:Elasticity of Demand and Price Markup, Sources of Monopoly Power |
| << Perfect Competition:Effect of Excise Tax on Monopolist |
| The Social Costs of Monopoly Power:Price Regulation, Monopsony >> |
Microeconomics
ECO402
VU
Lesson
32
Monopoly
The
Multiplant Firm
For many
firms, production takes
place in two or more
different plants whose
operating
cost
can differ.
Choosing total
output and the output
for each plant:
�
The
marginal cost in each plant
should be equal.
�
The
marginal cost should equal
the marginal revenue for
each plant.
Algebraically:
Q1 & C1 ⇒
Output
& Cost for Plant 1
Q2 & C2 ⇒
Output
& Cost for Plant 2
Total
Output =
QT =
Q1 +
Q2
Algebraically:
�
= PQ
T -
C
1 ( Q
1 ) -
C
2 ( Q
2 )
Δ�
Δ
(
PQ
T ) Δ
C
1
=0
-
=
Δ
Q1
Δ
Q1
Δ
Q1
Δ
C1
Δ
(
PQ
T )
-
(
MC
)
=0
(
MR
)
Δ
Q1
Δ
Q1
MR
=
MC
1
-
MC
MR
1
=
MC
MR
2
=
MC
=
MC
MR
1
2
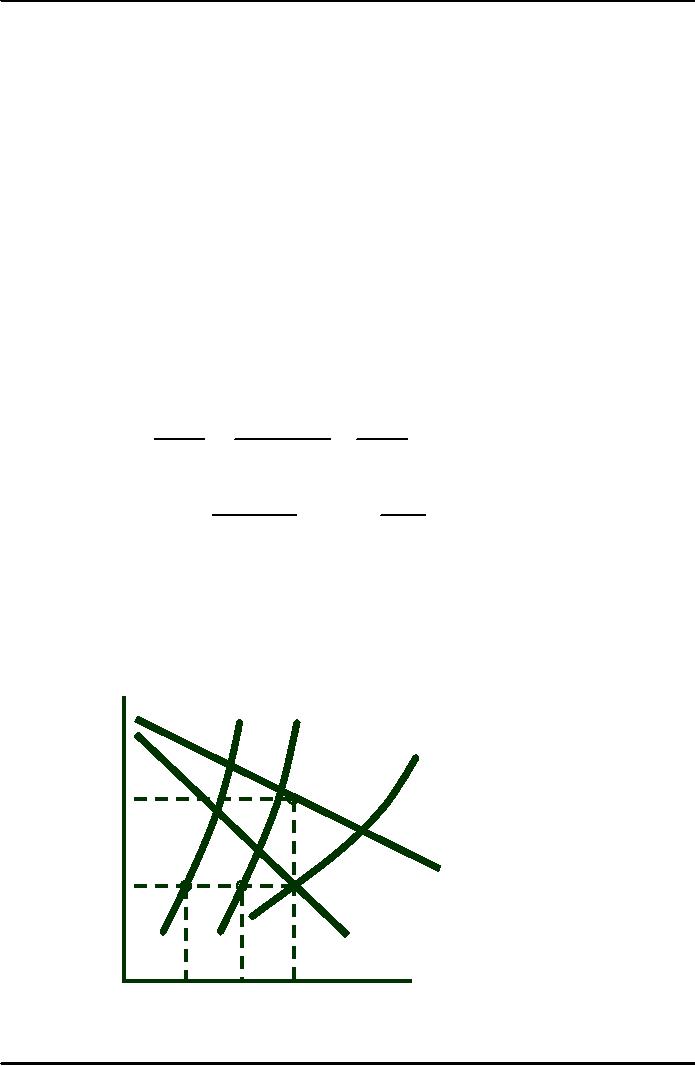
$/Q
MC1
MC2
MCT
P*
D
= AR
MR*
MR
Quantity
Q1
Q
Q
149
Microeconomics
ECO402
VU
Observations:
1)
MCT =
MC1 + MC2
2)
Profit
maximizing
output:
�
$/Q
MCT = MR at
QT and P *
MC1 MC2
�
MCT
MR
= MR*
MR*
= MC1 at
Q1, MR*
�
=
MC2 at
Q2
P*
�
MC1 +
MC2 = MCT,
Q1 +
Q2 =
QT,
and
MR =MC1+MC2
D
= AR
MR*
MR
Q1
Q2
QT
Quantity
Monopoly
Power
Monopoly
is rare.
However,
a market with several firms,
each facing a downward
sloping demand curve
will
produce
so that price exceeds
marginal cost.
Scenario:
Four firms
with equal share (5,000) of
a market for 20,000
toothbrushes at a price of
$1.50.
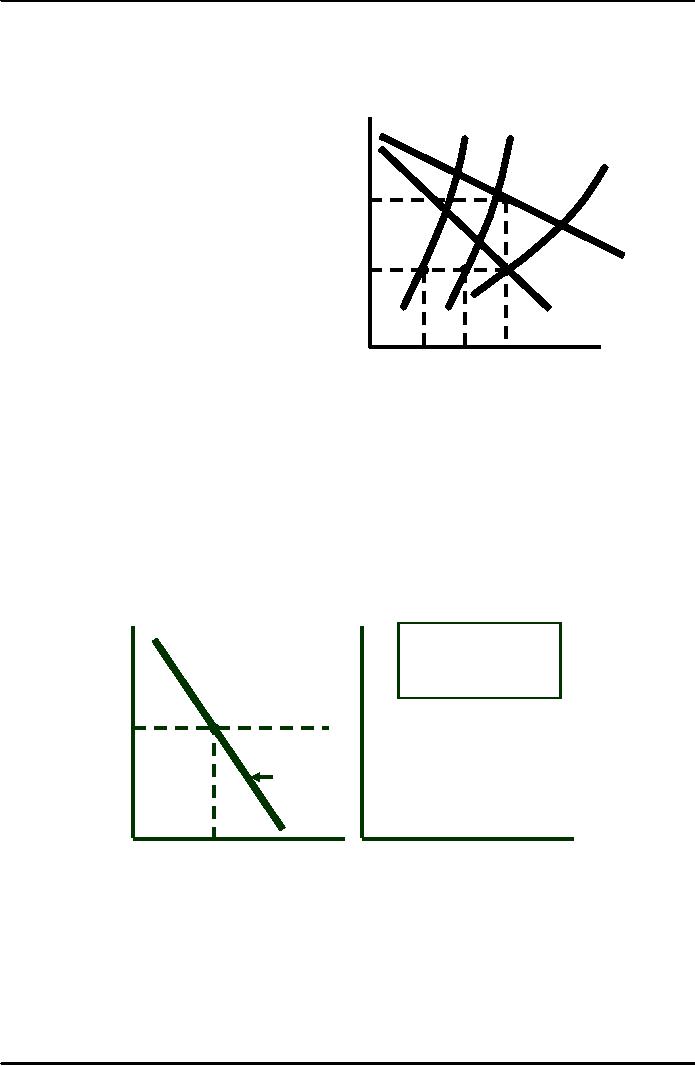
The
Demand for
Toothbrushes
$/Q
$/Q
The
demand curve for
At
a market price
2.00
2.00
Firm
A
of
$1.50, elasticity of
depends
on how much
demand
is -1.5.
their
product differs, and
how
the firms compete.
1.60
1.50
1.50
1.40
Market
Deman
1.00
1.00
QA
30,000
Quantity
10,000
20,000
3,000
5,000
7,000
150
Microeconomics
ECO402
VU
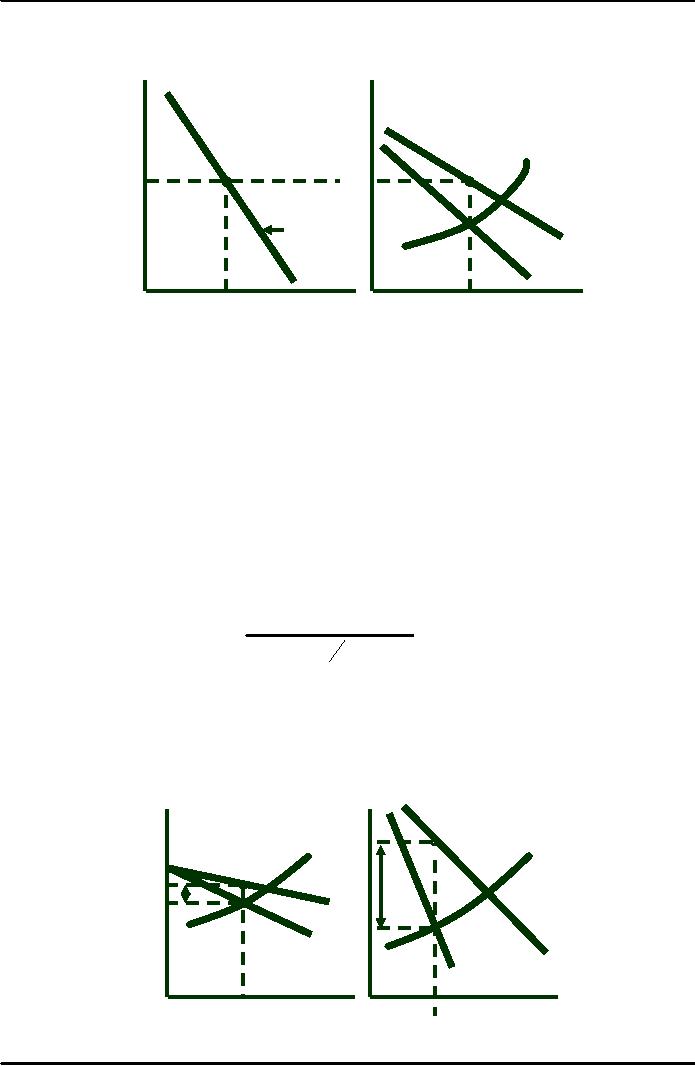
Firm
A sees
a much more
$/Q
$/Q
elastic
demand curve due to
At
a market price
competition--Ed =
-.6.
Still
2.00
2.00
of
$1.50, elasticity of
Firm
A has some monopoly
demand
is -1.5.
power
and charges a price
which
exceeds MC.
1.60
MC
1.50
1.50
1.40
DA
Market
Demand
MR
1.00
1.00
QA
30,000
Quantity
10,000
20,000
3,000
5,000
7,000
Measuring
Monopoly Power
In perfect
competition: P
= MR = MC
Monopoly power:
P
> MC
Lerner's
Index of Monopoly
Power
L = (P -
MC)/P
�
The
larger the value of
L
(between
0 and 1) the greater the
monopoly power.
L
is
expressed in terms of Ed
�
L = (P - MC)/P =
-1/E
d
�
E is elasticity
of demand for a firm, not
the market
d
Monopoly
power does not guarantee
profits.
Profit
depends on average cost
relative to price.
The
Rule of Thumb for
Pricing
MC
=
P
1 +
(
)
E
1
Pricing for
any firm with monopoly
power
d
�
If E
is
large, markup is
small
d
�
If E
is
small, markup is
large
d
Elasticity
of Demand and Price
Markup
$/Q
$/Q
The
more elastic is
demand,
the less the
markup.
P*
M
M
P*
P*-MC
A
M
A
M
Q*
Q*
Quantity
Quantity
151

Microeconomics
ECO402
VU
Markup
Pricing: Supermarkets to Designer
Jeans
Supermarkets
Several
firms
Similar
product
Ed =
-10 for individual
stores
MC
MC
P=
=
=
1.11(MC
)
1
+
(1
-.1)
0.9
Prices
set about 10 11% above
MC.
Convenience
Stores
Higher
prices than
supermarkets
Convenience
differentiates them
Ed =
-5
MC
MC
P=
=
=
1.25(MC
)
1
+
(1
-5)
0.8
Prices
set about 25% above
MC.
Convenience
stores have more monopoly
power.
Question:
�
Do convenience
stores have higher profits
than supermarkets?
Designer
jeans
Ed = -3 to
-4
�
Price 33 -
50% > MC
�
MC
= $12
- $18/pair
�
Wholesale
price = $18 - $27
Sources
of Monopoly Power
Why
do some firm's have
considerable monopoly power,
and others have little or
none?
A
firm's monopoly power is
determined by the firm's
elasticity of demand.
The
firm's elasticity of demand is
determined by:
1)
Elasticity of market
demand
2)
Number of firms
3)
The interaction among
firms
152
Table of Contents:
- ECONOMICS:Themes of Microeconomics, Theories and Models
- Economics: Another Perspective, Factors of Production
- REAL VERSUS NOMINAL PRICES:SUPPLY AND DEMAND, The Demand Curve
- Changes in Market Equilibrium:Market for College Education
- Elasticities of supply and demand:The Demand for Gasoline
- Consumer Behavior:Consumer Preferences, Indifference curves
- CONSUMER PREFERENCES:Budget Constraints, Consumer Choice
- Note it is repeated:Consumer Preferences, Revealed Preferences
- MARGINAL UTILITY AND CONSUMER CHOICE:COST-OF-LIVING INDEXES
- Review of Consumer Equilibrium:INDIVIDUAL DEMAND, An Inferior Good
- Income & Substitution Effects:Determining the Market Demand Curve
- The Aggregate Demand For Wheat:NETWORK EXTERNALITIES
- Describing Risk:Unequal Probability Outcomes
- PREFERENCES TOWARD RISK:Risk Premium, Indifference Curve
- PREFERENCES TOWARD RISK:Reducing Risk, The Demand for Risky Assets
- The Technology of Production:Production Function for Food
- Production with Two Variable Inputs:Returns to Scale
- Measuring Cost: Which Costs Matter?:Cost in the Short Run
- A Firm’s Short-Run Costs ($):The Effect of Effluent Fees on Firms’ Input Choices
- Cost in the Long Run:Long-Run Cost with Economies & Diseconomies of Scale
- Production with Two Outputs--Economies of Scope:Cubic Cost Function
- Perfectly Competitive Markets:Choosing Output in Short Run
- A Competitive Firm Incurring Losses:Industry Supply in Short Run
- Elasticity of Market Supply:Producer Surplus for a Market
- Elasticity of Market Supply:Long-Run Competitive Equilibrium
- Elasticity of Market Supply:The Industry’s Long-Run Supply Curve
- Elasticity of Market Supply:Welfare loss if price is held below market-clearing level
- Price Supports:Supply Restrictions, Import Quotas and Tariffs
- The Sugar Quota:The Impact of a Tax or Subsidy, Subsidy
- Perfect Competition:Total, Marginal, and Average Revenue
- Perfect Competition:Effect of Excise Tax on Monopolist
- Monopoly:Elasticity of Demand and Price Markup, Sources of Monopoly Power
- The Social Costs of Monopoly Power:Price Regulation, Monopsony
- Monopsony Power:Pricing With Market Power, Capturing Consumer Surplus
- Monopsony Power:THE ECONOMICS OF COUPONS AND REBATES
- Airline Fares:Elasticities of Demand for Air Travel, The Two-Part Tariff
- Bundling:Consumption Decisions When Products are Bundled
- Bundling:Mixed Versus Pure Bundling, Effects of Advertising
- MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION:Monopolistic Competition in the Market for Colas and Coffee
- OLIGOPOLY:Duopoly Example, Price Competition
- Competition Versus Collusion:The Prisoners’ Dilemma, Implications of the Prisoners
- COMPETITIVE FACTOR MARKETS:Marginal Revenue Product
- Competitive Factor Markets:The Demand for Jet Fuel
- Equilibrium in a Competitive Factor Market:Labor Market Equilibrium
- Factor Markets with Monopoly Power:Monopoly Power of Sellers of Labor