 |
Perfect Competition:Effect of Excise Tax on Monopolist |
| << Perfect Competition:Total, Marginal, and Average Revenue |
| Monopoly:Elasticity of Demand and Price Markup, Sources of Monopoly Power >> |

Microeconomics
ECO402
VU
Lesson
31
A
Rule of Thumb for
Pricing
We want to
translate the condition that
marginal revenue should
equal marginal cost
into
a
rule of thumb that can be
more easily applied in
practice.
This can be
demonstrated using the
following steps:
ΔR
Δ
(
PQ
)
1
. MR
=
=
ΔQ
ΔQ
⎛
Q
⎞⎛ Δ
P
⎞
ΔP
=
P
+
P
⎜
⎟⎜
⎟
2
. MR
=
P
+
Q
P
⎠⎜ Δ
Q
⎟
ΔQ
⎝
⎝
⎠
=
⎛ P
⎞⎛ Δ
Q
⎞
⎜
Q
⎟⎜
ΔP
⎟
3.
E
d
⎝
⎠⎝
⎠
)(
)
(
1
Q
Δ P
=
4.
Δ Q
P
E
d
⎛
⎞
1
=
P
+P
⎜
5.
M
R
⎟
⎝ E
⎠
d
6
. �
is
maximized
@
MR =
MC
⎡ 1 ⎤
1
P
+
P⎢
=-
⎥
⎣ED ⎦
ED
MC
P =
1
+
(1
E D )
1
7.
-
=
the markup over MC as a
percentage of price
(P-MC)/P
E d
8.
The
markup should equal the
inverse of the elasticity of
demand.
MC
9.
P
=
()
1
1+
Ed
Assume
Ed = -4
MC
= 9
9
9
P=
=
=
$12
(
)
.75
1+ 1
-4
Monopoly
pricing compared to perfect
competition pricing:
Monopoly
P
> MC
Perfect
Competition
P
= MC
Monopoly
pricing compared to perfect
competition pricing:
146
Microeconomics
ECO402
VU
The more
elastic the demand the
closer price is to marginal
cost.
If Ed is a
large negative number, price
is close to marginal cost
and vice versa.
A
Monopolist's Pricing
The
Monopolist's Output
Decision
Price of
Medicine A = $3.50/daily
dose
Price of
Medicine B and Medicine C =
$1.50 - $2.25/daily
dose
MC of Medicine A = 30 - 40
cents/daily dose
♦The
Monopolist's Output Decision
MC
.
35
P =
=
=
1+
[ E
]
1
+
[ -
1
.1]
1
1
D
MC
.
35
=
=
$ 3 .
89
1
+
(-
.
91
)
.
09
♦Price
of $3.50 is consistent with
"the rule of thumb
pricing"
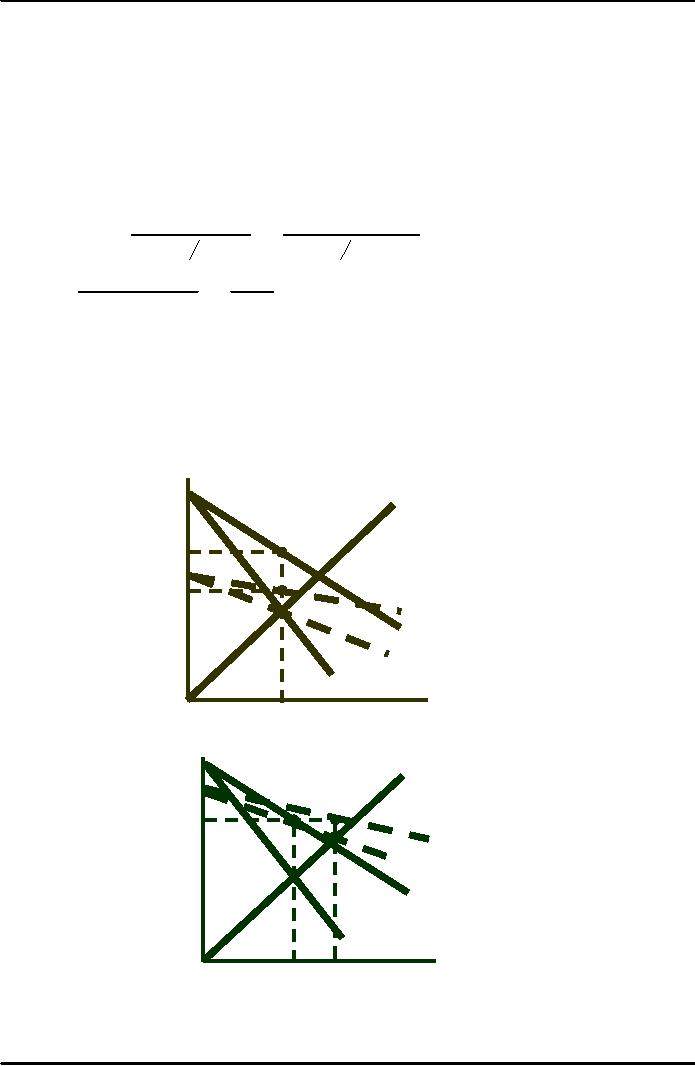
Shifts
in Demand
In perfect
competition, the market
supply curve is determined by
marginal cost.
For a monopoly,
output is determined by marginal
cost and the shape of
the demand
curve.
Shift
in Demand Leads to Change in
Price but Same
Output
MC
$/Q
P1
P2
D2
D1
MR2
MR1
Quantity
Q1=
Q2
MC
$/Q
P1 =
P2
D2
MR2
D
MR1
Q1
Q
Quantity
147
Microeconomics
ECO402
VU
Monopoly
Observations
Shifts in
demand usually cause a
change in both price and
quantity.
A monopolistic
market has no supply
curve.
Monopolist may
supply many different
quantities at the same
price.
Monopolist may
supply the same quantity at
different prices.
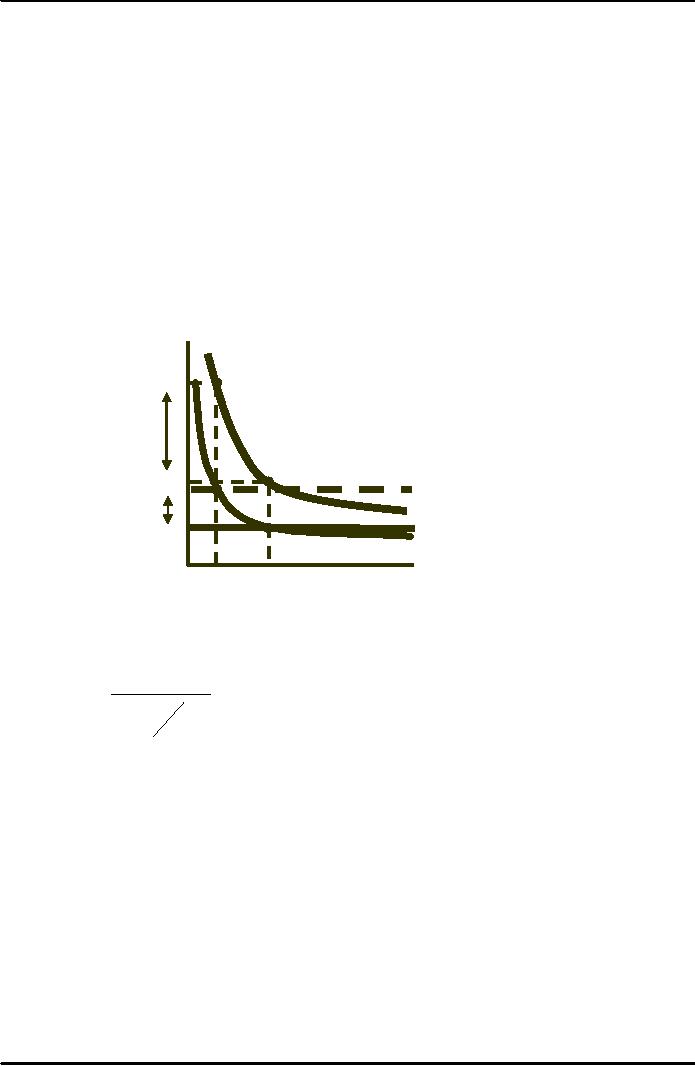
The
Effect of a Tax
Under monopoly
price can sometimes rise by
more
than
the amount of the
tax.
To
determine the impact of a
tax:
t = specific
tax
MC = MC + t
MR = MC + t : optimal
production decision
Effect
of Excise Tax on
Monopolist
$/Q
Increase
in P:
P0 to
P1 >
increase in
tax
P1
ΔP
P0
MC
+ tax
D
= AR
t
MC
MR
Q0
Q1
Quantity
Question
Suppose: Ed =
-2
How much
would the price
change?
Answer
MC
P=
1+ ⎛ 1
⎞
⎜ E
⎟
⎝
⎠
d
If
E
d = - 2 →
P
= 2
MC
If
MC
increases
to MC
+
t
Δ
P
= 2 (
MC
+
t
) = 2
MC
+ 2
t
Price
increases
by
twice
the
tax.
What
would happen to
profits?
148
Table of Contents:
- ECONOMICS:Themes of Microeconomics, Theories and Models
- Economics: Another Perspective, Factors of Production
- REAL VERSUS NOMINAL PRICES:SUPPLY AND DEMAND, The Demand Curve
- Changes in Market Equilibrium:Market for College Education
- Elasticities of supply and demand:The Demand for Gasoline
- Consumer Behavior:Consumer Preferences, Indifference curves
- CONSUMER PREFERENCES:Budget Constraints, Consumer Choice
- Note it is repeated:Consumer Preferences, Revealed Preferences
- MARGINAL UTILITY AND CONSUMER CHOICE:COST-OF-LIVING INDEXES
- Review of Consumer Equilibrium:INDIVIDUAL DEMAND, An Inferior Good
- Income & Substitution Effects:Determining the Market Demand Curve
- The Aggregate Demand For Wheat:NETWORK EXTERNALITIES
- Describing Risk:Unequal Probability Outcomes
- PREFERENCES TOWARD RISK:Risk Premium, Indifference Curve
- PREFERENCES TOWARD RISK:Reducing Risk, The Demand for Risky Assets
- The Technology of Production:Production Function for Food
- Production with Two Variable Inputs:Returns to Scale
- Measuring Cost: Which Costs Matter?:Cost in the Short Run
- A Firm’s Short-Run Costs ($):The Effect of Effluent Fees on Firms’ Input Choices
- Cost in the Long Run:Long-Run Cost with Economies & Diseconomies of Scale
- Production with Two Outputs--Economies of Scope:Cubic Cost Function
- Perfectly Competitive Markets:Choosing Output in Short Run
- A Competitive Firm Incurring Losses:Industry Supply in Short Run
- Elasticity of Market Supply:Producer Surplus for a Market
- Elasticity of Market Supply:Long-Run Competitive Equilibrium
- Elasticity of Market Supply:The Industry’s Long-Run Supply Curve
- Elasticity of Market Supply:Welfare loss if price is held below market-clearing level
- Price Supports:Supply Restrictions, Import Quotas and Tariffs
- The Sugar Quota:The Impact of a Tax or Subsidy, Subsidy
- Perfect Competition:Total, Marginal, and Average Revenue
- Perfect Competition:Effect of Excise Tax on Monopolist
- Monopoly:Elasticity of Demand and Price Markup, Sources of Monopoly Power
- The Social Costs of Monopoly Power:Price Regulation, Monopsony
- Monopsony Power:Pricing With Market Power, Capturing Consumer Surplus
- Monopsony Power:THE ECONOMICS OF COUPONS AND REBATES
- Airline Fares:Elasticities of Demand for Air Travel, The Two-Part Tariff
- Bundling:Consumption Decisions When Products are Bundled
- Bundling:Mixed Versus Pure Bundling, Effects of Advertising
- MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION:Monopolistic Competition in the Market for Colas and Coffee
- OLIGOPOLY:Duopoly Example, Price Competition
- Competition Versus Collusion:The Prisoners’ Dilemma, Implications of the Prisoners
- COMPETITIVE FACTOR MARKETS:Marginal Revenue Product
- Competitive Factor Markets:The Demand for Jet Fuel
- Equilibrium in a Competitive Factor Market:Labor Market Equilibrium
- Factor Markets with Monopoly Power:Monopoly Power of Sellers of Labor