 |
Perfect Competition:Total, Marginal, and Average Revenue |
| << The Sugar Quota:The Impact of a Tax or Subsidy, Subsidy |
| Perfect Competition:Effect of Excise Tax on Monopolist >> |
Microeconomics
ECO402
VU
Lesson
30
Perfect
Competition
Review of
Perfect Competition
P = LMC =
LRAC
Normal profits
or zero economic profits in
the long run
Large number of
buyers and sellers
Homogenous
product
Perfect
information
Firm is a price
taker
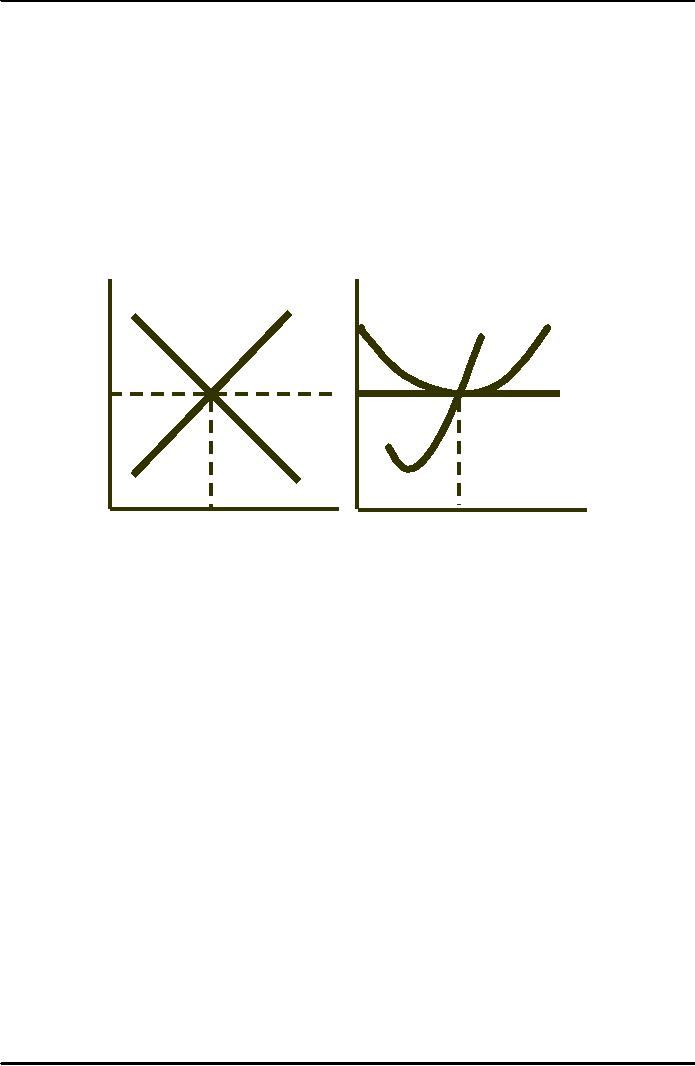
P
Market
P
Individual
Firm
D
S
LMC
LRAC
P0
P0
D
= MR = P
q0
Q0
Q
Q
Monopoly
Monopoly
1)
One seller - many
buyers
2)
One product (no good
substitutes)
3)
Barriers to entry
The
monopolist is the supply-side of
the market and has
complete control over the
amount
offered
for sale.
Profits
will be maximized at the
level of output where
marginal revenue equals
marginal
cost.
Finding
Marginal Revenue
As the sole
producer, the monopolist
works with the market
demand to determine
output
and
price.
Assume a firm
with demand:
�P=6-Q
142
Microeconomics
ECO402
VU
Total,
Marginal, and Average
Revenue
Total
Marginal
Average
Price
Quantity
Revenue
Revenue
Revenue
P
Q
R
MR
AR
$6
0
$0
---
---
5
1
5
$5
$5
4
2
8
3
4
3
3
9
1
3
2
4
8
-1
2
1
5
5
-3
1
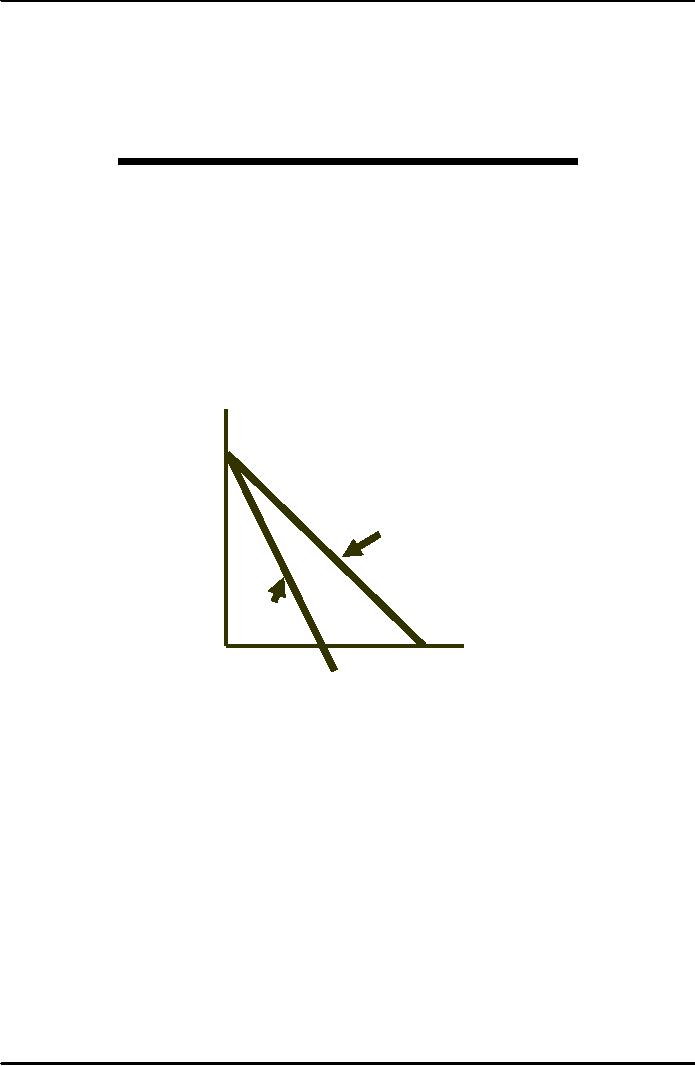
$
per 7
unit
of
output
6
5
Average
Revenue (Demand)
4
3
2
Marginal
1
Revenue
7
Output
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
Observations
1)
To increase sales the price
must fall
2)
MR < P
3)
Compared to perfect
competition
�
No change in
price to change sales
�
MR = P
Monopolist's
Output Decision
1)
Profits maximized at the
output level where MR =
MC
2)
Cost functions are the
same
�
(Q
) =
R
(Q
) -
C
(Q
)
Δ
� /
Δ
Q
= Δ
R
/ Δ
Q
- Δ
C
/ Δ
Q
= 0 =
MC
-
MR
or
MC =
MR
143
Microeconomics
ECO402
VU
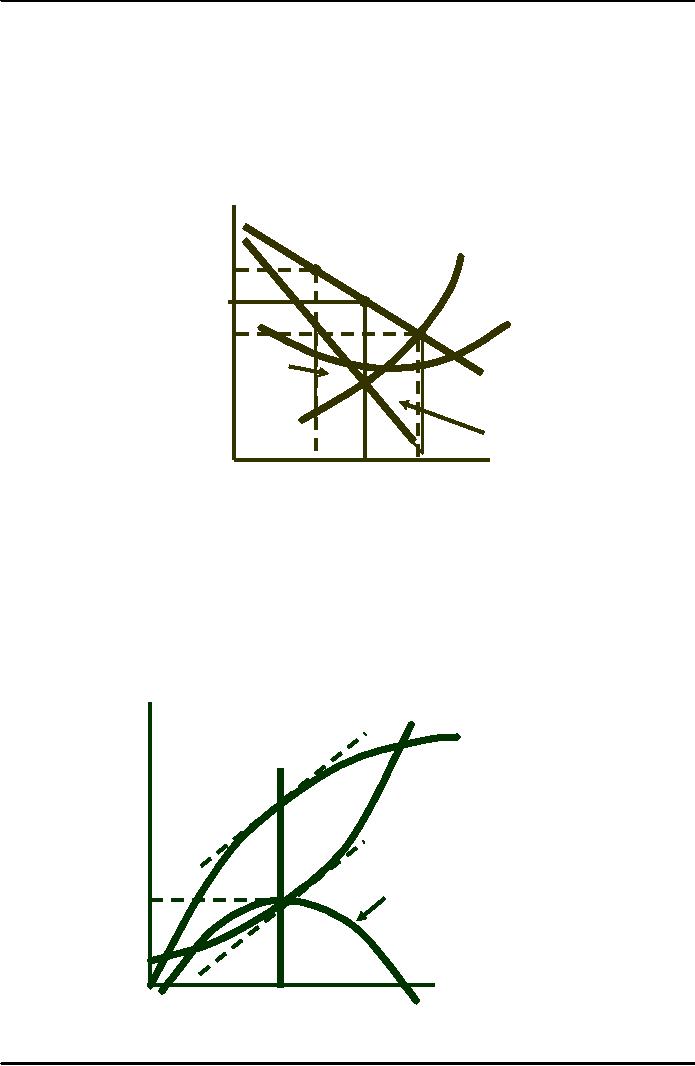
Maximizing
Profit When Marginal Revenue
Equals Marginal
Cost
The
Monopolist's Output
Decision
At output
levels below MR = MC the
decrease in revenue is greater
than the decrease in
cost
(MR > MC).
At output
levels above MR = MC the
increase in cost is greater
than the decrease in
revenue
(MR < MC)
$
per
unit
of
MC
output
P1
P*
A
P2
Lost
profit
D
= AR
Lost
M
profit
Q
Q
Q
Quantity
Monopoly
The
Monopolist's Output
Decision
An
Example
�
By setting
marginal revenue equal to
marginal cost, it can be
verified that profit
is
maximized
at P
= $30
and Q
=
10.
�
This can
be seen graphically:
Example
of Profit Maximization
$
C
t
R
400
300
c
200
t
Profits
150
100
50
c
Quantity
0
5
10
15
20
144
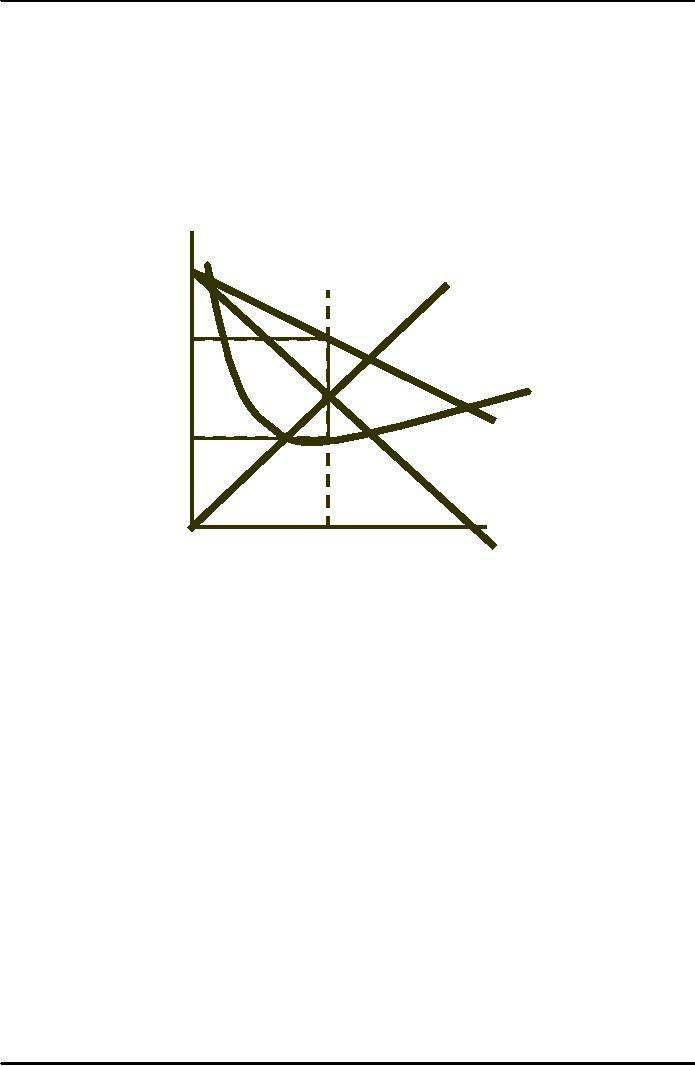
Microeconomics
ECO402
VU
Observations
Slope
of rr'
=
slope cc'
and
they are parallel at 10
units
Profits
are maximized at 10
units
P
= $30, Q = 10,
TR
= P x Q= $300
AC
= $15, Q = 10,
TC
= AC x Q = 150
Profit
= TR - TC
�
$150 =
$300 - $150
$/Q
40
MC
30
AC
Profit
20
AR
15
10
MR
0
5
10
15
20
Quantity
Observations
AC
= $15, Q = 10,
TC
= AC x Q =150
Profit
= TR = TC = $300 - $150= $150
or
Profit
= (P-AC) x Q = ($30 -$15)(10) =
$150
145
Table of Contents:
- ECONOMICS:Themes of Microeconomics, Theories and Models
- Economics: Another Perspective, Factors of Production
- REAL VERSUS NOMINAL PRICES:SUPPLY AND DEMAND, The Demand Curve
- Changes in Market Equilibrium:Market for College Education
- Elasticities of supply and demand:The Demand for Gasoline
- Consumer Behavior:Consumer Preferences, Indifference curves
- CONSUMER PREFERENCES:Budget Constraints, Consumer Choice
- Note it is repeated:Consumer Preferences, Revealed Preferences
- MARGINAL UTILITY AND CONSUMER CHOICE:COST-OF-LIVING INDEXES
- Review of Consumer Equilibrium:INDIVIDUAL DEMAND, An Inferior Good
- Income & Substitution Effects:Determining the Market Demand Curve
- The Aggregate Demand For Wheat:NETWORK EXTERNALITIES
- Describing Risk:Unequal Probability Outcomes
- PREFERENCES TOWARD RISK:Risk Premium, Indifference Curve
- PREFERENCES TOWARD RISK:Reducing Risk, The Demand for Risky Assets
- The Technology of Production:Production Function for Food
- Production with Two Variable Inputs:Returns to Scale
- Measuring Cost: Which Costs Matter?:Cost in the Short Run
- A Firm’s Short-Run Costs ($):The Effect of Effluent Fees on Firms’ Input Choices
- Cost in the Long Run:Long-Run Cost with Economies & Diseconomies of Scale
- Production with Two Outputs--Economies of Scope:Cubic Cost Function
- Perfectly Competitive Markets:Choosing Output in Short Run
- A Competitive Firm Incurring Losses:Industry Supply in Short Run
- Elasticity of Market Supply:Producer Surplus for a Market
- Elasticity of Market Supply:Long-Run Competitive Equilibrium
- Elasticity of Market Supply:The Industry’s Long-Run Supply Curve
- Elasticity of Market Supply:Welfare loss if price is held below market-clearing level
- Price Supports:Supply Restrictions, Import Quotas and Tariffs
- The Sugar Quota:The Impact of a Tax or Subsidy, Subsidy
- Perfect Competition:Total, Marginal, and Average Revenue
- Perfect Competition:Effect of Excise Tax on Monopolist
- Monopoly:Elasticity of Demand and Price Markup, Sources of Monopoly Power
- The Social Costs of Monopoly Power:Price Regulation, Monopsony
- Monopsony Power:Pricing With Market Power, Capturing Consumer Surplus
- Monopsony Power:THE ECONOMICS OF COUPONS AND REBATES
- Airline Fares:Elasticities of Demand for Air Travel, The Two-Part Tariff
- Bundling:Consumption Decisions When Products are Bundled
- Bundling:Mixed Versus Pure Bundling, Effects of Advertising
- MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION:Monopolistic Competition in the Market for Colas and Coffee
- OLIGOPOLY:Duopoly Example, Price Competition
- Competition Versus Collusion:The Prisoners’ Dilemma, Implications of the Prisoners
- COMPETITIVE FACTOR MARKETS:Marginal Revenue Product
- Competitive Factor Markets:The Demand for Jet Fuel
- Equilibrium in a Competitive Factor Market:Labor Market Equilibrium
- Factor Markets with Monopoly Power:Monopoly Power of Sellers of Labor