 |
Microeconomics
ECO402
VU
Lesson
28
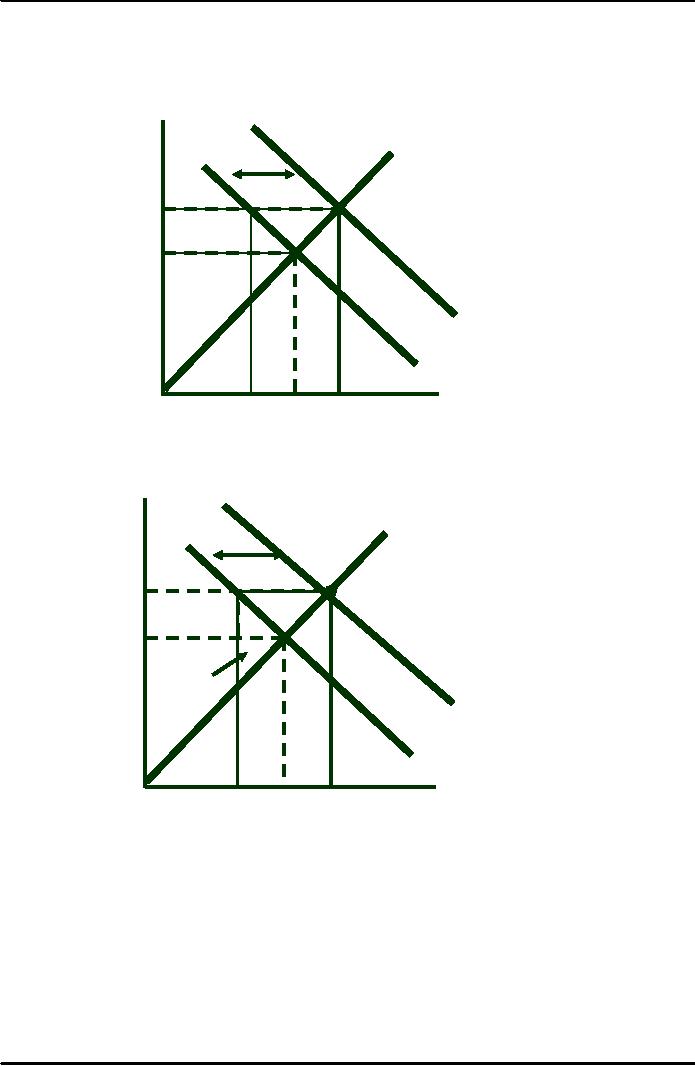
Price
Supports
Price
S
Q
To
maintain a price Ps
the
government buys
quantity
Qg .
The
change in
P
consumer
surplus = -A
- B,
D
A
and
the change in
producer
B
surplus
is A
+ B + D
P
D+
D
Quantity
Q
Q
Q
The
cost to the
government
is the
speckled
rectangle
Price
Ps(Q2-Q1)
S
Q
Total
welfare loss
Ps
A
D
D-(Q2-Q1)ps
B
P0
Total
Welfare
Loss
D+
D
Quantity
Q0
Q2
Q1
Question:
Is there a
more efficient way to
increase farmer's income by
A
+ B + D?
Price
Supports and Production
Quotas
Production
Quotas
The government
can also cause the
price of a good to rise by
reducing supply.
What
is the impact of controlling
entry into the taxicab
market?
134
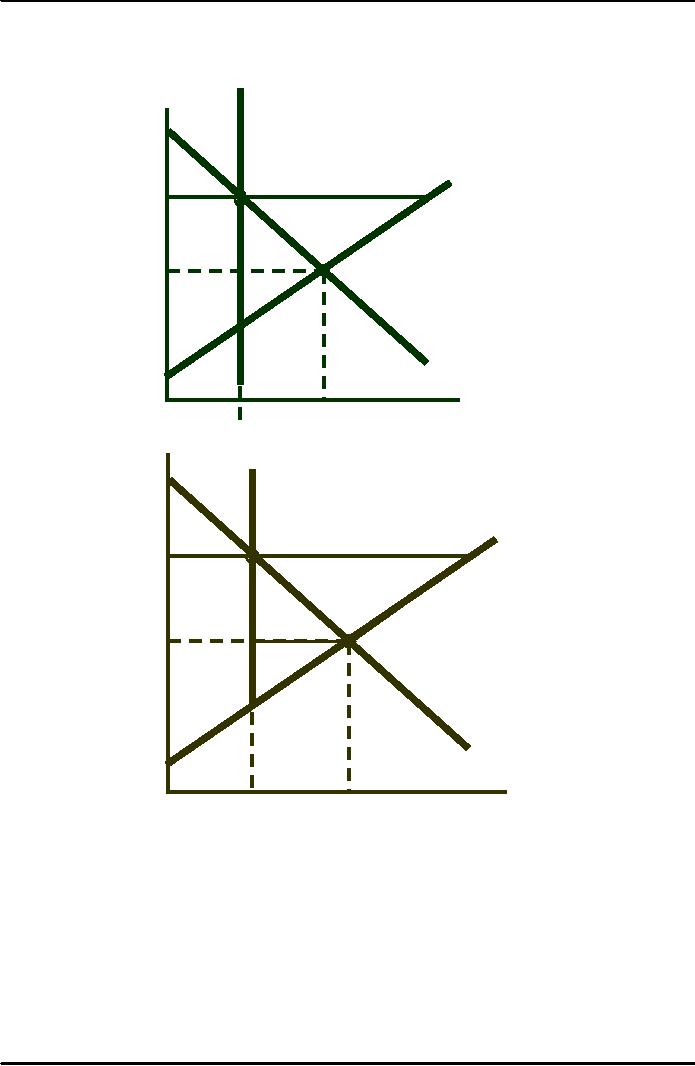
Microeconomics
ECO402
VU
Supply
Restrictions
S
Supply
restricted to
·
Price
Q1
'
·
Supply
shifts to S'
@
Q1
S
P
S
D
P
·CS
reduced by A
+ B
C
·Change
in PS = A
- C
D
Q
Q
Quantity
·P
S
Price
is
maintained with
s
and
incentive
S
·Cost
to government = B
+ C + D
P
A
D
B
P
C
D
Q
Q
Quantity
ĆPS =A - C + B + C +
D
=A
+ B + D.
The
change in consumer and
producer surplus is the same
as with price
supports.
Ćwelfare = -A - B
+ A + B + D - B - C - D = -B - C.
Questions:
How could
the government reduce the
cost and still subsidize
the farmer?
Which is more
costly: supports or acreage
limitations?
135
Microeconomics
ECO402
VU
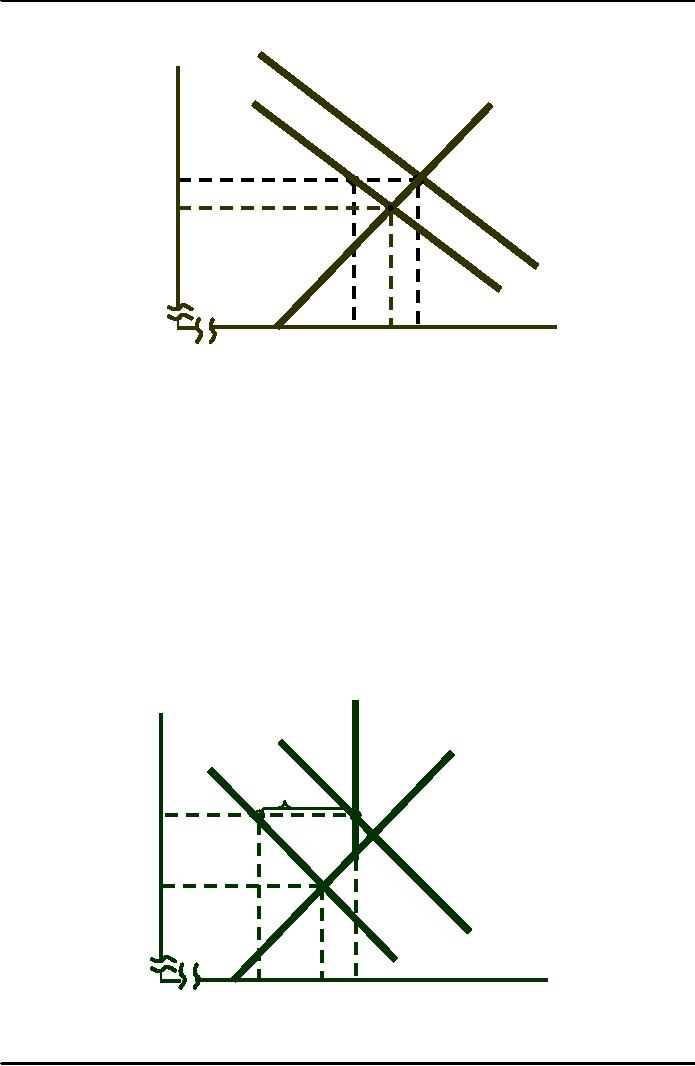
The
Wheat Market in
1981
·AB consumer loss
Pric
e
S
·ABC producer
gain
By
buying 122
million
bushels
Q
the
government
P0 =
$3.70
increased
the
C
A
market-clearing
B
P0 =
$3.46
price.
D
+ Qg
D
1,800
2,56
2,6302,68
Quantity
Supporting
the Price of
Wheat
1981
Change in
consumer surplus=(-A
-B)
A
= (3.70 - 3.46)(2,566) = $616
million
B
= (1/2)(3.70 - 3.46)(2,630 -
2,566)
=
$8 million
·
Change in
consumer surplus: -$624
million.
Cost to the
government:
$3.70
x 122 million bushels = $452
million
Total
cost = $624 + 452 = $1,076
million
Total
gain = A
+ B + C = $638
million
Government
also paid 30 cents/bushel =
$806 million
The
Wheat Market in
1985
S
Price
S
Q
To
increase the
price
to $3.20, the
government
bought
P0 =
466
million bushels
$3.20
and
imposed
a
production quota
of
2,425 bushels.
P0 =
$1.80
D+
D
1,80
1,95
2,23
2,42
Quantity
136
Microeconomics
ECO402
VU
1985
Government
Purchase:
·
Government cost
= $3.20 x 466 =
$1,491million
·
80 cent
subsidy = .80 x 2,425 =
$1,940 million
·
Total
cost = $3.5 billion
Import
Quotas and
Tariffs
Many
countries use import quotas
and tariffs to keep the
domestic price of a product
above
world
levels
Import
Tariff or Quota That
Eliminates Imports
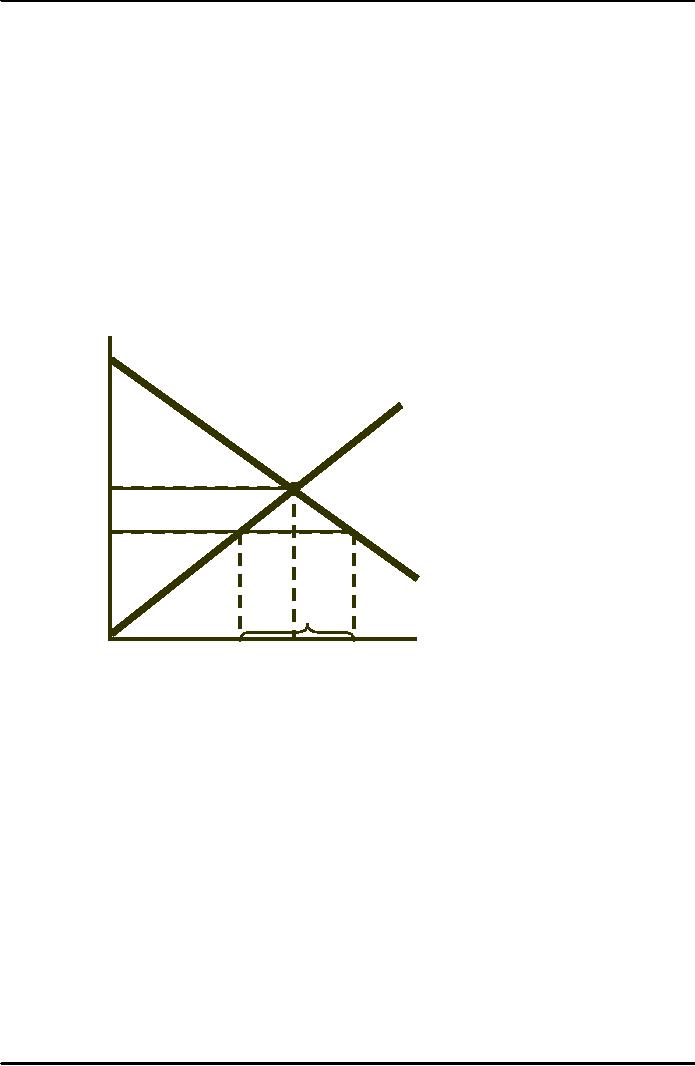
In
a free market, the
Price
domestic
price equals the
world
price PW.
S
By
eliminating imports,
the
price is increased to
PO. The
gain is area A.
The
loss
to consumers A
+ B + C,
P0
so
the deadweight loss
is
B +
C.
A
B
C
PW
How
high would
D
a
tariff have
to
be to get the
Import
same
result?
QD
QS
Q0
Quantity
The
increase in price can be
achieved by a quota or a
tariff.
Area
A is again the gain to
domestic producers.
The
loss to consumers is A + B + C +
D.
If
a tariff is used the
government gains D, so the
net domestic product loss is
B + C.
If
a quota is used instead,
rectangle D becomes part of
the profits of foreign
producers, and
the
net domestic loss is B + C +
D.
Question:
Would a
country be better off or
worse off with a quota
instead of a tariff?
137
Table of Contents:
- ECONOMICS:Themes of Microeconomics, Theories and Models
- Economics: Another Perspective, Factors of Production
- REAL VERSUS NOMINAL PRICES:SUPPLY AND DEMAND, The Demand Curve
- Changes in Market Equilibrium:Market for College Education
- Elasticities of supply and demand:The Demand for Gasoline
- Consumer Behavior:Consumer Preferences, Indifference curves
- CONSUMER PREFERENCES:Budget Constraints, Consumer Choice
- Note it is repeated:Consumer Preferences, Revealed Preferences
- MARGINAL UTILITY AND CONSUMER CHOICE:COST-OF-LIVING INDEXES
- Review of Consumer Equilibrium:INDIVIDUAL DEMAND, An Inferior Good
- Income & Substitution Effects:Determining the Market Demand Curve
- The Aggregate Demand For Wheat:NETWORK EXTERNALITIES
- Describing Risk:Unequal Probability Outcomes
- PREFERENCES TOWARD RISK:Risk Premium, Indifference Curve
- PREFERENCES TOWARD RISK:Reducing Risk, The Demand for Risky Assets
- The Technology of Production:Production Function for Food
- Production with Two Variable Inputs:Returns to Scale
- Measuring Cost: Which Costs Matter?:Cost in the Short Run
- A Firm’s Short-Run Costs ($):The Effect of Effluent Fees on Firms’ Input Choices
- Cost in the Long Run:Long-Run Cost with Economies & Diseconomies of Scale
- Production with Two Outputs--Economies of Scope:Cubic Cost Function
- Perfectly Competitive Markets:Choosing Output in Short Run
- A Competitive Firm Incurring Losses:Industry Supply in Short Run
- Elasticity of Market Supply:Producer Surplus for a Market
- Elasticity of Market Supply:Long-Run Competitive Equilibrium
- Elasticity of Market Supply:The Industry’s Long-Run Supply Curve
- Elasticity of Market Supply:Welfare loss if price is held below market-clearing level
- Price Supports:Supply Restrictions, Import Quotas and Tariffs
- The Sugar Quota:The Impact of a Tax or Subsidy, Subsidy
- Perfect Competition:Total, Marginal, and Average Revenue
- Perfect Competition:Effect of Excise Tax on Monopolist
- Monopoly:Elasticity of Demand and Price Markup, Sources of Monopoly Power
- The Social Costs of Monopoly Power:Price Regulation, Monopsony
- Monopsony Power:Pricing With Market Power, Capturing Consumer Surplus
- Monopsony Power:THE ECONOMICS OF COUPONS AND REBATES
- Airline Fares:Elasticities of Demand for Air Travel, The Two-Part Tariff
- Bundling:Consumption Decisions When Products are Bundled
- Bundling:Mixed Versus Pure Bundling, Effects of Advertising
- MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION:Monopolistic Competition in the Market for Colas and Coffee
- OLIGOPOLY:Duopoly Example, Price Competition
- Competition Versus Collusion:The Prisoners’ Dilemma, Implications of the Prisoners
- COMPETITIVE FACTOR MARKETS:Marginal Revenue Product
- Competitive Factor Markets:The Demand for Jet Fuel
- Equilibrium in a Competitive Factor Market:Labor Market Equilibrium
- Factor Markets with Monopoly Power:Monopoly Power of Sellers of Labor