 |
Elasticity of Market Supply:Producer Surplus for a Market |
| << A Competitive Firm Incurring Losses:Industry Supply in Short Run |
| Elasticity of Market Supply:Long-Run Competitive Equilibrium >> |
Microeconomics
ECO402
VU
Lesson
24
Elasticity of
Market Supply
= ( Δ
Q
/
Q
) /( Δ
P
/
P
)
E
s
�
Perfectly
inelastic short-run supply
arises when the industry's
plant and equipment are
so
fully
utilized that new plants
must be built to achieve
greater output.
�
Perfectly
elastic short-run supply
arises when marginal costs
are constant.
The
World Copper Industry
(1999)
Annual
Production
Marginal
Cost
Country
(thousand
metric tons)
(dollars/pound)
Australia
600
0.65
Canada
710
0.75
Chile
3660
0.50
Indonesia
750
0.55
Peru
450
0.70
Poland
420
0.80
Russia
450
0.50
United
States
1850
0.55
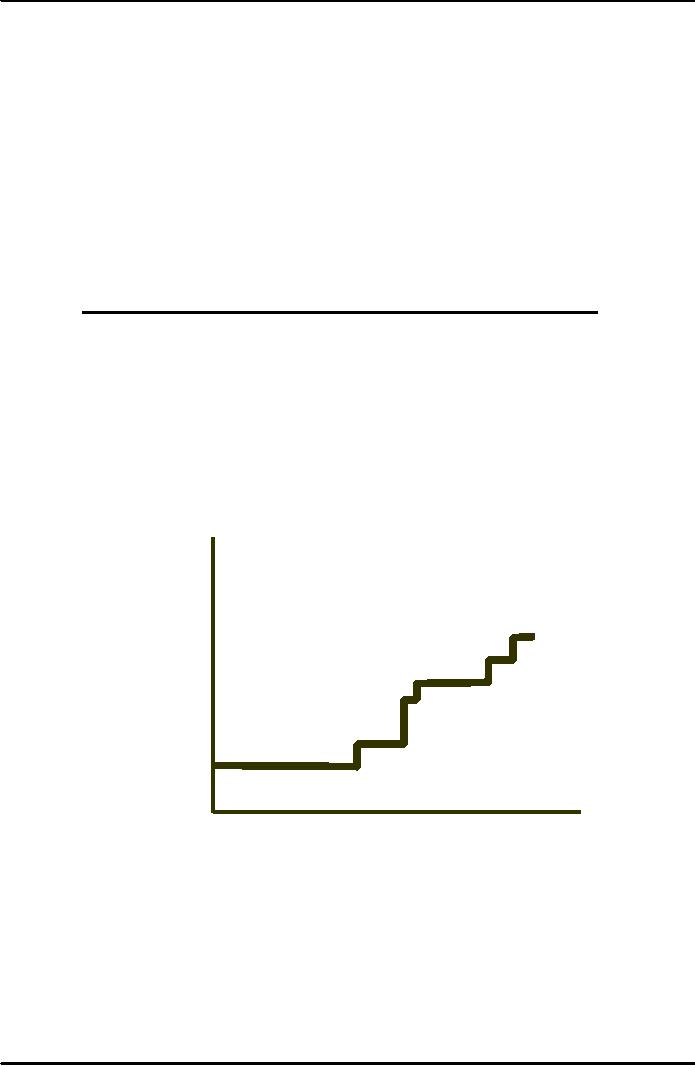
The
Short-Run World Supply of
Copper
Price
($
per pound)
0.90
MCP
0.80
MCC
MCP,MCU
0.70
MC
0.60
MCJ,MC
MCC,MC
0.50
0.40
0
2000
4000
6000
8000
10000
Production
(thousand metric
tons)
Producer
Surplus in the Short
Run
Firms earn a
surplus on all but the
last unit of output.
The
producer
surplus is the
sum over all units
produced of the difference
between the
market
price of the good and
the marginal cost of
production.
121
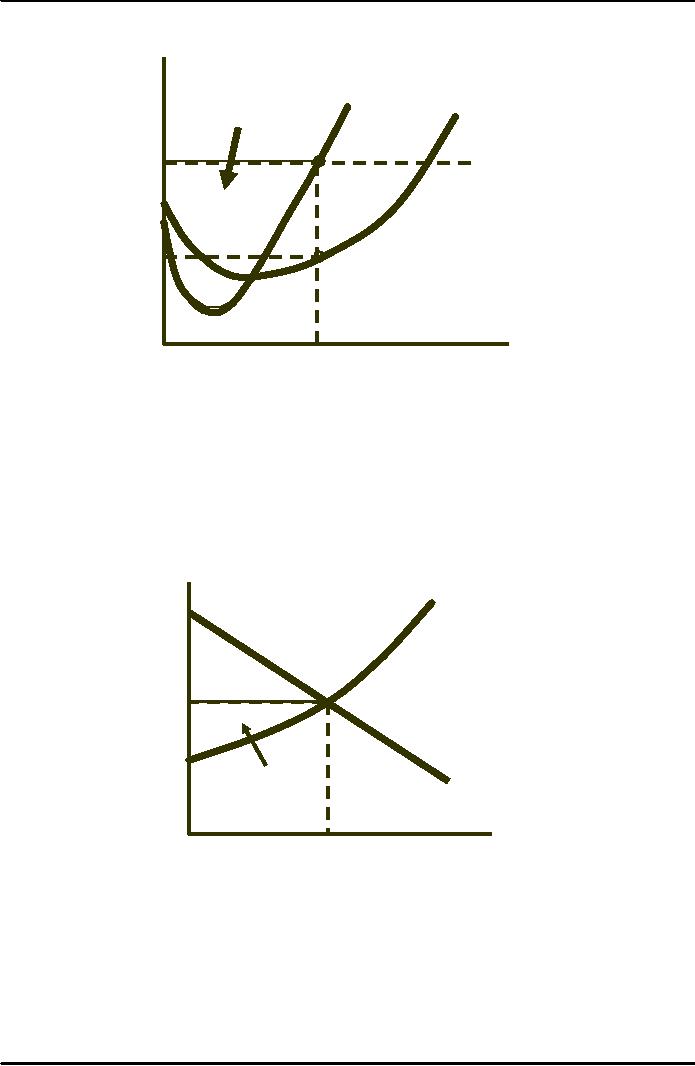
Microeconomics
ECO402
VU
*
At
q MC =
MR.
Between
0 and q
,
MR
> MC for all
units.
Price
($
per
Producer
MC
AVC
unit
of
Surplus
output)
B
A
P
Alternatively,
VC is the
*
sum
of MC or ODCq .
*
*
R
is P x q or OABq .
D
Producer
surplus =
C
R
- VC or ABCD.
q*
0
Output
Producer
Surplus in the
Short-Run
Producer
Surplus =
PS
=
R -
VC
P
ro fit = � - R - V C - F
C
Observation
Short-run with
positive fixed cost
PS
>
�
Producer
Surplus for a
Market
Price
S
($
per
unit
of
output)
Market
producer surplus is
P
the
difference between P*
*
*
and
S from
0 to Q
.
Produce
r
D
Output
Q
*
Choosing
Output in Long
Run
In
the long run, a firm
can alter all its
inputs, including the size
of the plant.
We
assume free entry and
free exit.
122
Microeconomics
ECO402
VU
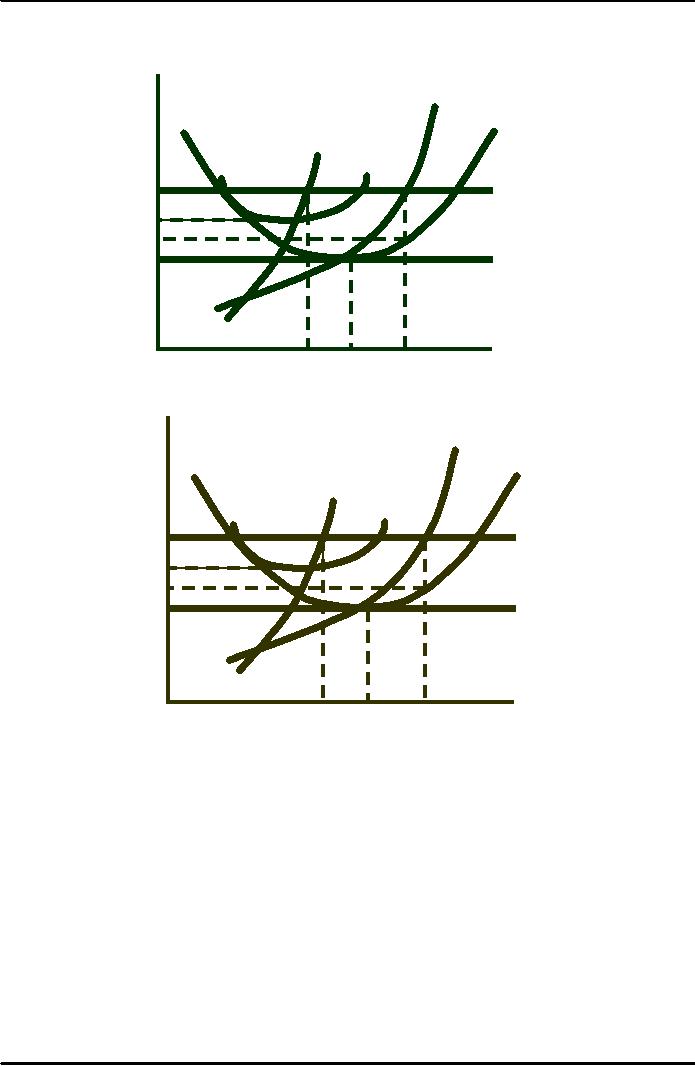
Price
In
the long run, the plant size
will be
increased
and output increased to
q3.
($
per
LMC
Long-run
profit, EFGD
>
short run
unit
of
profit
ABCD.
output)
LAC
SMC
SAC
D
A
E
$40
P
= MR
C
B
G
F
$30
In
the short run, the
firm
is faced with fixed
inputs.
P
= $40
> ATC.
Profit
is equal to ABCD.
q2
q3
q1
Output
Price
Question:
Is the producer
making
($
per
a
profit after increased
output
LMC
unit
of
lowers
the price to $30?
output)
LAC
SMC
SAC
D
A
E
$40
P
= MR
C
B
G
F
$30
q2
q1
q3
Output
Accounting
Profit & Economic
Profit
Accounting
profit (�) = R - wL
Economic
profit (�) = R - wL - rK
�
wL = labor
cost
�
rk = opportunity
cost of capital
Long-Run
Competitive Equilibrium
Zero-Profit
�
If R > wL + rk,
economic profits are
positive
�
If R = wL + rk,
zero economic profits, but
the firms is earning a
normal rate of
return;
indicating
the industry is
competitive
�
If R < wl + rk,
consider going out of
business
Entry and
Exit
123
Table of Contents:
- ECONOMICS:Themes of Microeconomics, Theories and Models
- Economics: Another Perspective, Factors of Production
- REAL VERSUS NOMINAL PRICES:SUPPLY AND DEMAND, The Demand Curve
- Changes in Market Equilibrium:Market for College Education
- Elasticities of supply and demand:The Demand for Gasoline
- Consumer Behavior:Consumer Preferences, Indifference curves
- CONSUMER PREFERENCES:Budget Constraints, Consumer Choice
- Note it is repeated:Consumer Preferences, Revealed Preferences
- MARGINAL UTILITY AND CONSUMER CHOICE:COST-OF-LIVING INDEXES
- Review of Consumer Equilibrium:INDIVIDUAL DEMAND, An Inferior Good
- Income & Substitution Effects:Determining the Market Demand Curve
- The Aggregate Demand For Wheat:NETWORK EXTERNALITIES
- Describing Risk:Unequal Probability Outcomes
- PREFERENCES TOWARD RISK:Risk Premium, Indifference Curve
- PREFERENCES TOWARD RISK:Reducing Risk, The Demand for Risky Assets
- The Technology of Production:Production Function for Food
- Production with Two Variable Inputs:Returns to Scale
- Measuring Cost: Which Costs Matter?:Cost in the Short Run
- A Firm’s Short-Run Costs ($):The Effect of Effluent Fees on Firms’ Input Choices
- Cost in the Long Run:Long-Run Cost with Economies & Diseconomies of Scale
- Production with Two Outputs--Economies of Scope:Cubic Cost Function
- Perfectly Competitive Markets:Choosing Output in Short Run
- A Competitive Firm Incurring Losses:Industry Supply in Short Run
- Elasticity of Market Supply:Producer Surplus for a Market
- Elasticity of Market Supply:Long-Run Competitive Equilibrium
- Elasticity of Market Supply:The Industry’s Long-Run Supply Curve
- Elasticity of Market Supply:Welfare loss if price is held below market-clearing level
- Price Supports:Supply Restrictions, Import Quotas and Tariffs
- The Sugar Quota:The Impact of a Tax or Subsidy, Subsidy
- Perfect Competition:Total, Marginal, and Average Revenue
- Perfect Competition:Effect of Excise Tax on Monopolist
- Monopoly:Elasticity of Demand and Price Markup, Sources of Monopoly Power
- The Social Costs of Monopoly Power:Price Regulation, Monopsony
- Monopsony Power:Pricing With Market Power, Capturing Consumer Surplus
- Monopsony Power:THE ECONOMICS OF COUPONS AND REBATES
- Airline Fares:Elasticities of Demand for Air Travel, The Two-Part Tariff
- Bundling:Consumption Decisions When Products are Bundled
- Bundling:Mixed Versus Pure Bundling, Effects of Advertising
- MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION:Monopolistic Competition in the Market for Colas and Coffee
- OLIGOPOLY:Duopoly Example, Price Competition
- Competition Versus Collusion:The Prisoners’ Dilemma, Implications of the Prisoners
- COMPETITIVE FACTOR MARKETS:Marginal Revenue Product
- Competitive Factor Markets:The Demand for Jet Fuel
- Equilibrium in a Competitive Factor Market:Labor Market Equilibrium
- Factor Markets with Monopoly Power:Monopoly Power of Sellers of Labor