 |

Database
Management System
(CS403)
VU
Lecture No.
02
Reading
Material
"Database
Systems Principles, Design and
Implementation"
written
by Catherine Ricardo, Maxwell
Macmillan.
Overview of
Lecture
o Some
Additional Advantages of Database
Systems
o Costs
involved in Database systems
o Levels of
data
o Database
users
Difference
between Data and
Information
Data is
the collection of raw facts
collected from any specific
environment for a
specific
purpose. Data in
itself does not show
anything about its
environment, so to get
desired
types of
results from the data we
transform it into information by
applying certain
processing on
it. Once we have processed
data using different methods
data is converted
into
meaningful form and that
form of the Data is called
information
Example:
Example:
Fig. 1: Data and
Information
17

Database
Management System
(CS403)
VU
If we
consider the data in the
above figure without the
titles or the labels
associated with
the
data (EmpName, age, salary)
then it is not much useful.
However, after
attaching
these
labels it brings some
meanings to us, this
meaningfulness is further increased
when
we
associate some other labels,
like the company name and
the department name etc.
So
this is a
very simple example of processing
that we can do on the data to make
it
information.
Once we
have clear idea of what
data and information is we proceed
with another term
knows as
"schema" Schema is a repository or
structure to express the
format and other
different
information about data and
database, as we can see from
the database
definition
"Database
is a self describing collection of
interrelated records." The
word self
describing
means that the data
storage and retrieval mechanism and
its format is
described
in the database, Actual place
where these definitions and
descriptions are
performed
is database schema.
o Database
Application:
Database
Application is a program or group of
programs which is used for
performing
certain
operations on the data stored in
the database. These operations
may contain
insertion
of data into a database or
extracting some data from
the database based on
a
certain
condition, updating data in
the database, producing the
data as output on any
device
such as Screen, disk or
printer.
o Database
Management Systems:
Database
management system is software of
collection of small programs to
perform
certain
operation on data and manage
the data.
Two
basic operations performed by
the DBMS are:
�
Management
of Data in the Database
Management
of Users associated with the
database.
�
Management
of the data means to specify
that how data will be stored,
structured and
accessed
in the database.
Management
of database users means to
manage the users in such a
way that they can
perform
any desired operations on
the database. DBMS also
ensures that a user can
not
perform
any operation for which he
is not allowed. And also an
authorized user is not
allowed
to perform any action which
is restricted to that user.
In
General DBMS is a collection of Programs
performing all necessary actions
associated
to a
database.
18

Database
Management System
(CS403)
VU
Further
Advantages of Database Systems:
Database
systems are very much
beneficent to enterprises and businesses,
some of the
advantages
are listed below:
o Data
consistency
o Better
data security
o Faster
development of new
applications
o Economy
of scale
o Better
concurrency control
o Better
backup and recovery procedures
o Data
Consistency:
Data
consistency means that the
changes made to different
occurrence of data should
be
controlled
and managed in such a way
that all the occurrences
have same value for
any
specific
data item. Data inconsistency
leads to a number of problems,
including loss of
information
and incorrect results. In database
approach it is controlled because data
is
shared
and consistency is controlled and
maintained.
o Better
Data Security:
All
application programs access
data through DBMS, So DBMS
can very efficiently
check
that which user is performing
which action and accessing
which part of data , So
A
DBMS is
the most effectively control
and maintain security of Data stored in a
database.
o Faster
Application Development:
The
database environment allows us
faster application development
because of its many
reasons.
As we know that database is
designed with the factor of
future development in
mind
So
whenever we have to build a
new application to meet the
growing needs of the
computerized
environment, it may be easy due to
the following reason:
The
data needed for the
new application already
resides in the database.
�
19

Database
Management System
(CS403)
VU
�
The
data might not already
reside in the database but
it could be derived
from
the data present in the
database
Thus we
can say that, to develop a
new application for an
existing database system
less
effort is
required in terms of the
system and database design.
o Economy
of Scale:
Databases
and database systems are designed to
share data stored in one location
for
many
different purposes, So it needs not be
stored as many number of times in
different
forms as
it is used, for example the
data used by Admission
Department of any
education
institution
can be used to maintain the attendance
record of the students as
well as the
examination
records of the students. So it saves us
lots of efforts and finances
providing
economy
of scale.
o Better
Concurrency Control:
Concurrency
means the access of database
form as number of points
simultaneously.
Concurrency
control means to access the
database in such a way that
all the data
accesses
are
completed correctly and transparently.
One example of controlled
concurrency is the
use of
ATM Machine for withdrawal of
money (cash). All ATM machines of a
bank are
interconnected
to a central database system
worldwide, so that a user can access
its
account
from anywhere in the world
and can get cash from any
ATM terminal. As there
are
thousands of ATM terminal across
the world for a specific
bank so as a result
thousands
of user process and access the
bank's database. All this
process is managed
concurrently
using the database systems and is done in
such an efficient manner
that no
two user
face any delay in the processing of
their requests.
o Better
Backup and Recovery
Facility:
Data is a
very important resource and is very
much valuable for any
organization, loss of
such a
valuable resource can result in a huge
strategic disasters. As Data is stored
on
today's'
storage devices like hard disks
etc., It is necessary to take periodic
backups of
data so
that in case a storage
device looses the data due
to any damage we should be
able
20

Database
Management System
(CS403)
VU
to restore
the data a nearest point,
Database systems offer excellent
facilities for taking
backup of
data and good mechanism of restoring
those backups to get back the
backed-up
data.
It some
time happens that a database
which was in use and very
important transactions
were
made after the last
backup was made, all of a sudden due to
any disastrous situation
the
database crashes (improper
shutdown, invalid disk
access, etc.) Now in such
a
situation
the database management
system should be able to recover
the database to a
consistent
state so that the
transactions made after the
last backup are not
lost.
Cost
Involved:
Enjoying
all these benefits of the
database systems do have some
additional costs on
any
organization
which is going to adopt a database
environment. These charges may also
be
known as
the disadvantages of the
database system. Different
types of costs
(Financial
and
Personnel) which an organization
faces in adopting a database
system are listed
below:
o High
Cost:
Database
Systems have a number of inherent
charges which are to be born
by any
organization
that is going to adopt it.
High Cost is one of these inherent
charges, it
includes
the need for specialized
software which is used to
run database systems,
Additional
and specialized hardware and technically
qualified staff are the
requirements
for
adopting to the database
system, all these
requirements need an organization to
invest
handsome
amount of money to have all
the requirements of the
database systems.
o Conversion
Cost:
Once an
organization has decided to adopt
database system for its
operations, it is not
only
the finance and technical
man-power which is required
for switching on to
database
system,
it further has some
conversion charges needed
for adopting the database
system,
this is
also a very important stage
for making decision about
the way the system will
be
converted
to database system.
21

Database
Management System
(CS403)
VU
o Difficult
Recovery Procedures:
Although
the database systems and database
management systems provide very
efficient
ways of
data recovery in case of any
disaster, still the process of
recovering a crashed
database
is very much technical and
needs good professional skills to
perform a perfect
recovery
of the database.
Importance
of Data
o Data as a
Resource:
A resource is
anything which is valuable
for an organization. There can be a
number of
resources
in any organization, for
example, Buildings, Furniture,
Vehicle, Technical
Staff,
Managers,
supporting staff and Machinery
etc. As all these are
resources for
organizations
and are consumed very much
carefully to get full benefit
out of them, Data
in the
same way is a very important
resources and needs to considered equally
important
as other
resource are considered.
Why we call data as a
resource?
Data is
truly considered a resource because for
an organization to make proper
decisions
at proper
time it is only the data
which can provide correct
information and in-turn
cause
good
utilization of other organizational
resources. Organizations can not make good
and
effective
decisions if the required data is
not available in time or in
the correct and
desired
format, such bad and
miscalculated decisions ultimately lead to
the failure of
organizations
or business.
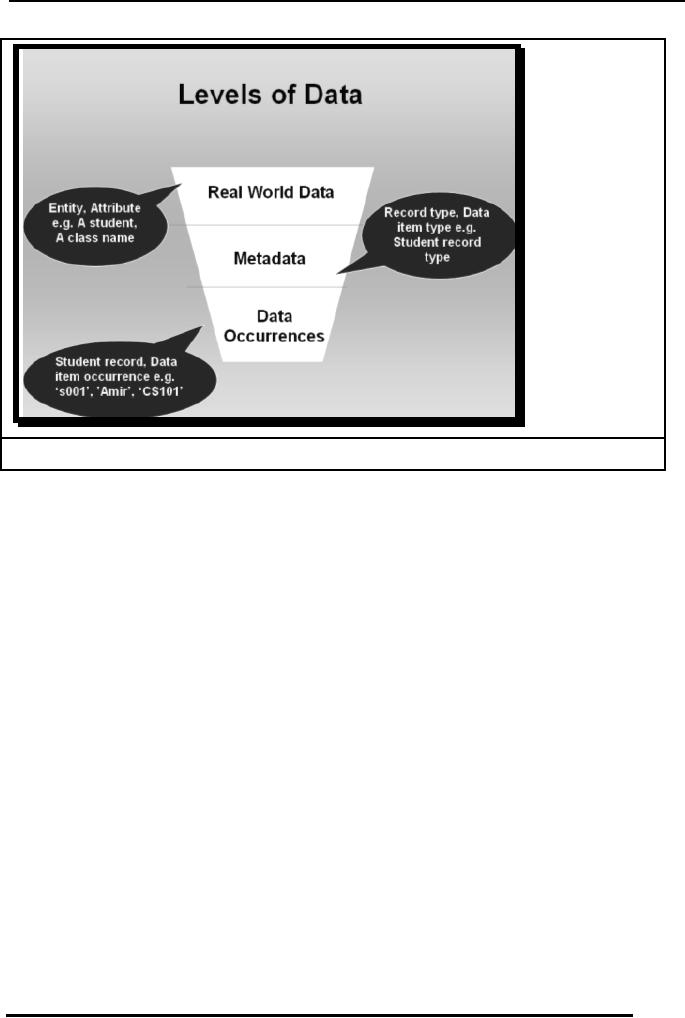
Levels of
Data
o Real
World Data
The
real world level of data
means that level of data at
which entities or objects
exist in
reality,
it means that any object
existing in reality have a name and
other identifiable
attributes
through which we can identify
that specific object or
entity.
Example:
Any
Student
22

Database
Management System
(CS403)
VU
o Meta
Data:
For
storage of the data related
to any entity or object
existing at real world level
we
define
the way the data will be
stored in the database. This is
called Meta data. Meta
data
is also
known as schema for the
real world data. It tells
that what type of data will
be
stored in
the database what will be size of a
certain attribute of the
real world data,
how
many and
what attributes will be used to store
the data about the
entity in the
database.
Example:
Name ,
Character Type, 25 character size
field,
Age,
Date
type,
8 bytes
size
Class,
Alpha
Numeric,
8 byte
size field
o Existence
of Data:
Existence
of the data level shows
the actual data regarding
the entities as real world
level
according
to the rules define at the
Meta Data level.
Example:
According
to the definition given in
the Meta data level
the Actual data or
Data
occurance
for the entity at real
world level is shown
below:
Name
Age
Class
Ali
20/8/1979
MCS-I
Amir
22/3/1978
MCS-II
etc...
23
Database
Management System
(CS403)
VU
Fig. 2:
Levels of Data
Users of
Database Systems:
o Application
Programmers
o End Users
Na�ve
�
Sophisticated
�
o Application
programmers:
This
category of database users
contains those people who create
different types of
database
application programs that we
have seen earlier.
Application programmers design
the
application according to the
needs of the other users of
the database in a
certain
environment.
Application programmers are
skilled people who have
clear idea of the
structure
of the database and know
clearly about the needs of
the organizations.
o End
Users:
24

Database
Management System
(CS403)
VU
Second
category of the Database
users are the end users,
this group of users contains
the
people
who use the database
application programs developed by
the Application
programmers.
This category further
contains two types of
users
Na�ve
Users
�
Sophisticated
Users
�
Na�ve
Users
�
This
category of users is that
category who simply use
the application database
programs
created
by the programmers. This
groups has no interaction
with other parts of
there
database
and only use the programs
meant for them. They
have not to worry about
the
further
working of the
database.
Sophisticated
Users:
�
This
type of users has some
additional rights over the
Na�ve users, which means
that they
can
access the data stored in
the database any of their
desired way. They can access
data
using
the application programs as
well as other ways of
accessing data. Although
this
type of
users has more rights to
access data, but these
users have to take
more
responsibility
and they need to be aware of the
database structure. Moreover
such users
should be
skilled enough to be able to get
data from database with
making and damage or
loss to
the data in database.
o Database
Administrators (DBA):
This
class of database users is
the most technical class of
db users. They need to have
the
knowledge
of how to design and manage the
database use as well as to
manage the data
in the
database. DBA is a very responsible
position in an organization. He is
responsible
for
proper working of the
database and DBMS, has the
responsibility of making
proper
database
backups and make necessary actions for
recovering the database in
case of a
database
crash. To fulfill the requirements of a
DBA position a DBA needs
vast
experience and
very elegant technical
skills.
25

Database
Management System
(CS403)
VU
� Duties
of the DBA
A
Database administrator has
some very precisely defined
duties which need be
performed
by the DBA very religiously.
A short account of these
jobs is listed below:
o Schema
definition
o Granting
data access
o Routine
Maintenance
�
Backups
�
Monitoring
disk space
�
Monitoring
jobs running
o Schema
Design
DBA in
some organization is responsible for
designing the database schema,
which
means
that DBA is the person who
create all the meta Data
information for the
organization
on which the database is
based. However in some very
large scale
organizations
this job is performed by the
Database designer, which is hired
for the
purpose of
database Design and once the
database system, is installed and
working it is
handed
over to the DBA for
further operation.
o Granting
Access to Users:
DBA is
also responsible for grant of
access rights to the
database users. Along
with
granting
and revoking (taking back)
the rights the DBA
continuously monitors and ensure
the
legal use of these
rights.
o Monitoring
Disk Space :
When a
new database is created it
takes a limited space but as
a result of daily activity
the
database
acquires more data and grows in size
very rapidly. The DBA
has to monitor the
disk
space usage and statistics to ensure
that no data over flow
occurs at any stage.
o Monitoring
Running Jobs:
To ensure
the secure and proper
functioning of the database
system a DBA
continuously
monitors
some associated activities also and
ensure that all users are
using their
26
Database
Management System
(CS403)
VU
authorities
legally and different devices attached to
the database system are
functioning
properly.
Typical Components of a
Database Environment:
Different
typical components of a database
environment are shown in the
figures below;
they
describe graphically the
role of different types of
users.
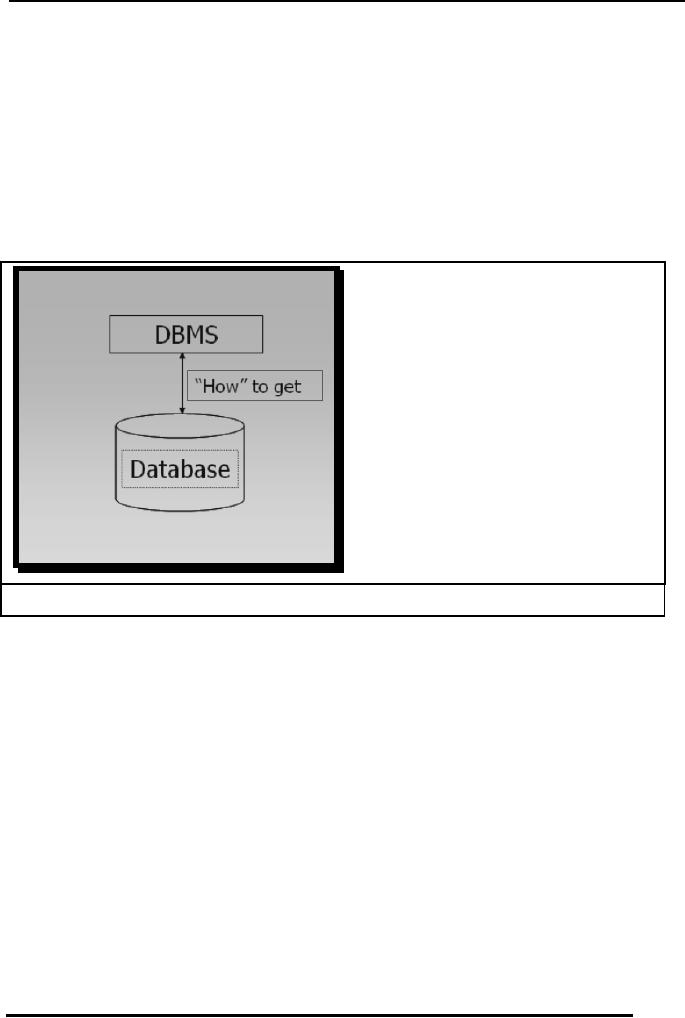
Fig. 3:
DBMS and Database
Database
is used to store data and DBMS
uses mechanisms to get data
from the database
27
Database
Management System
(CS403)
VU
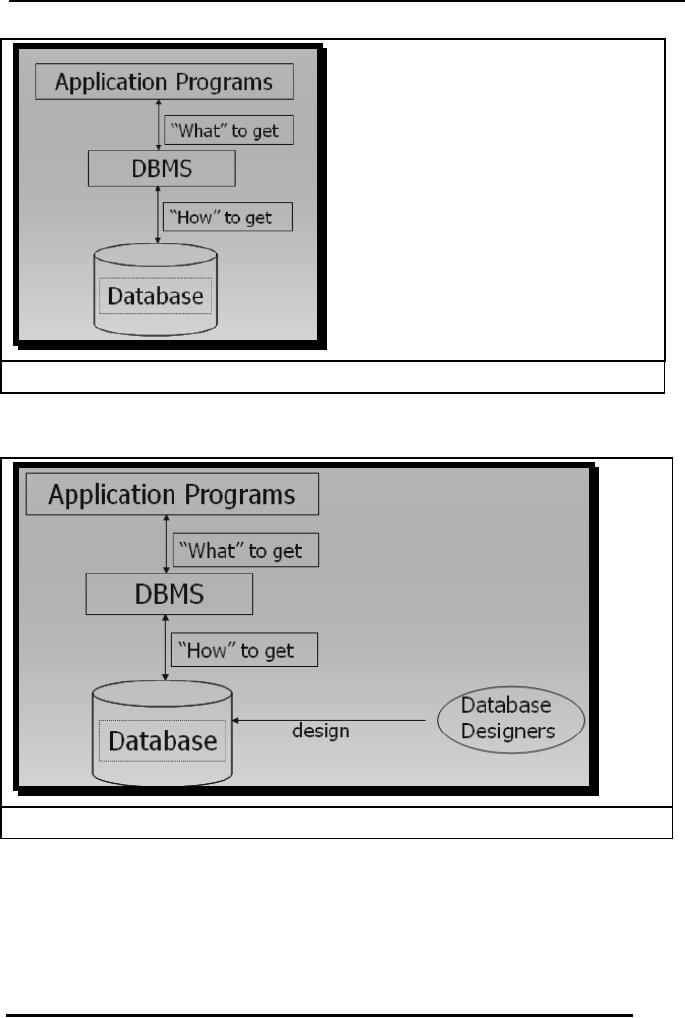
Fig. 4:
Application Programs
Application
programs talk to DBMS and
ask for the data
required
Fig. 5:
Database Designers
Database
designers design (for large
organizations) the database and
install the DBMS
for
use by the users of the
database in any specific
organization.
28
Database
Management System
(CS403)
VU
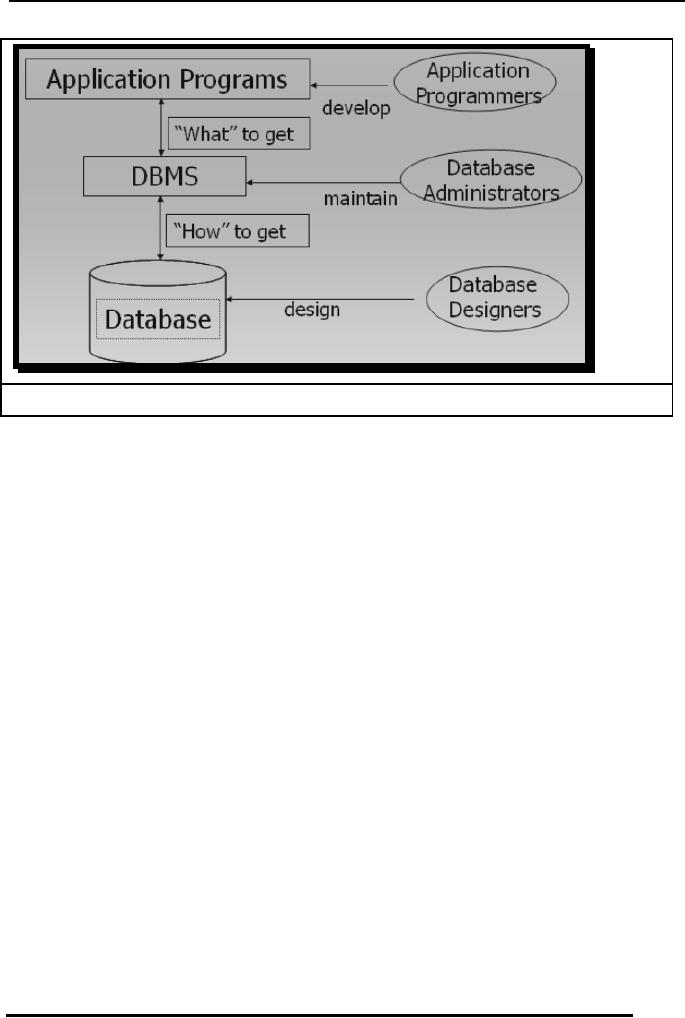
Fig. 6:
Database Administrator
Once
Database has been installed
and is functioning properly in a
production
environment
of an organization the Database
Administrator takes over the
charge and
performs
specific DBA related
activities including:
o Database
maintenance.
o Database
Backup.
o Grant of
rights to database
users.
o Monitoring
of Running Jobs
o Managing
Print jobs
o Ensuring
quality of Service to all
users.
29
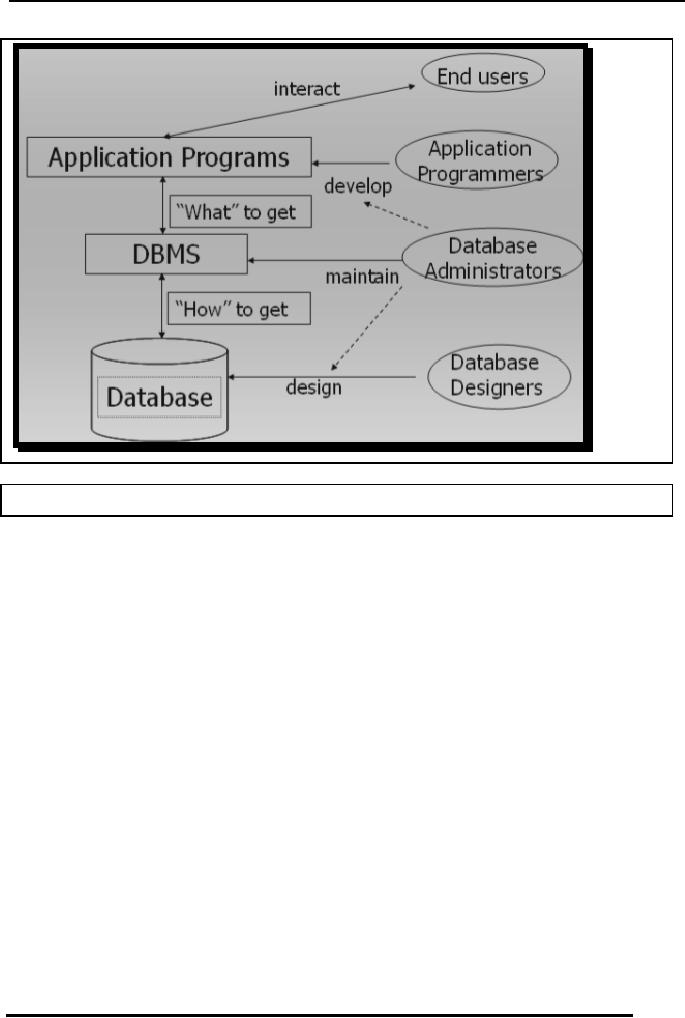
Database
Management System
(CS403)
VU
Fig. 7:
Database Administration's interaction
with other users
o Database
administrator can interact with
the database designer during
database
design
phase so that he has a clear
idea of the database
structure for easy
reference
in future.
o This
helps DBA perform different
tasks related to the
database structure.
o DBA also
interacts with the
application programmers during
the application
development
process and provides his services
for better design of
applications.
o End
users also interact with the
system using application
programs and other
tools
as specified in
the description above.
This
concludes lecture number 2, in
case of any queries, please
feel free to contact.
30
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Databases and Traditional File Processing Systems
- Advantages, Cost, Importance, Levels, Users of Database Systems
- Database Architecture: Level, Schema, Model, Conceptual or Logical View:
- Internal or Physical View of Schema, Data Independence, Funct ions of DBMS
- Database Development Process, Tools, Data Flow Diagrams, Types of DFD
- Data Flow Diagram, Data Dictionary, Database Design, Data Model
- Entity-Relationship Data Model, Classification of entity types, Attributes
- Attributes, The Keys
- Relationships:Types of Relationships in databases
- Dependencies, Enhancements in E-R Data Model. Super-type and Subtypes
- Inheritance Is, Super types and Subtypes, Constraints, Completeness Constraint, Disjointness Constraint, Subtype Discriminator
- Steps in the Study of system
- Conceptual, Logical Database Design, Relationships and Cardinalities in between Entities
- Relational Data Model, Mathematical Relations, Database Relations
- Database and Math Relations, Degree of a Relation
- Mapping Relationships, Binary, Unary Relationship, Data Manipulation Languages, Relational Algebra
- The Project Operator
- Types of Joins: Theta Join, Equi–Join, Natural Join, Outer Join, Semi Join
- Functional Dependency, Inference Rules, Normal Forms
- Second, Third Normal Form, Boyce - Codd Normal Form, Higher Normal Forms
- Normalization Summary, Example, Physical Database Design
- Physical Database Design: DESIGNING FIELDS, CODING AND COMPRESSION TECHNIQUES
- Physical Record and De-normalization, Partitioning
- Vertical Partitioning, Replication, MS SQL Server
- Rules of SQL Format, Data Types in SQL Server
- Categories of SQL Commands,
- Alter Table Statement
- Select Statement, Attribute Allias
- Data Manipulation Language
- ORDER BY Clause, Functions in SQL, GROUP BY Clause, HAVING Clause, Cartesian Product
- Inner Join, Outer Join, Semi Join, Self Join, Subquery,
- Application Programs, User Interface, Forms, Tips for User Friendly Interface
- Designing Input Form, Arranging Form, Adding Command Buttons
- Data Storage Concepts, Physical Storage Media, Memory Hierarchy
- File Organizations: Hashing Algorithm, Collision Handling
- Hashing, Hash Functions, Hashed Access Characteristics, Mapping functions, Open addressing
- Index Classification
- Ordered, Dense, Sparse, Multi-Level Indices, Clustered, Non-clustered Indexes
- Views, Data Independence, Security, Vertical and Horizontal Subset of a Table
- Materialized View, Simple Views, Complex View, Dynamic Views
- Updating Multiple Tables, Transaction Management
- Transactions and Schedules, Concurrent Execution, Serializability, Lock-Based Concurrency Control, Deadlocks
- Incremental Log with Deferred, Immediate Updates, Concurrency Control
- Serial Execution, Serializability, Locking, Inconsistent Analysis
- Locking Idea, DeadLock Handling, Deadlock Resolution, Timestamping rules