 |
Macroeconomics
ECO 403
VU
LESSON
10
NATIONAL
INCOME: WHERE IT COMES FROM AND WHERE IT
GOES
(Continued...)
The
Role of Govt.
�
If
the Government:
�
increases
defense
spending:
ΔG
> 0
�
big
tax cuts: ΔT < 0
�
According
to our model, both policies
reduce national
saving:
S
= Y C(Y - T) - G
↑
G
=> ↓
S
↓
T =>
↑ C => ↓
S
The
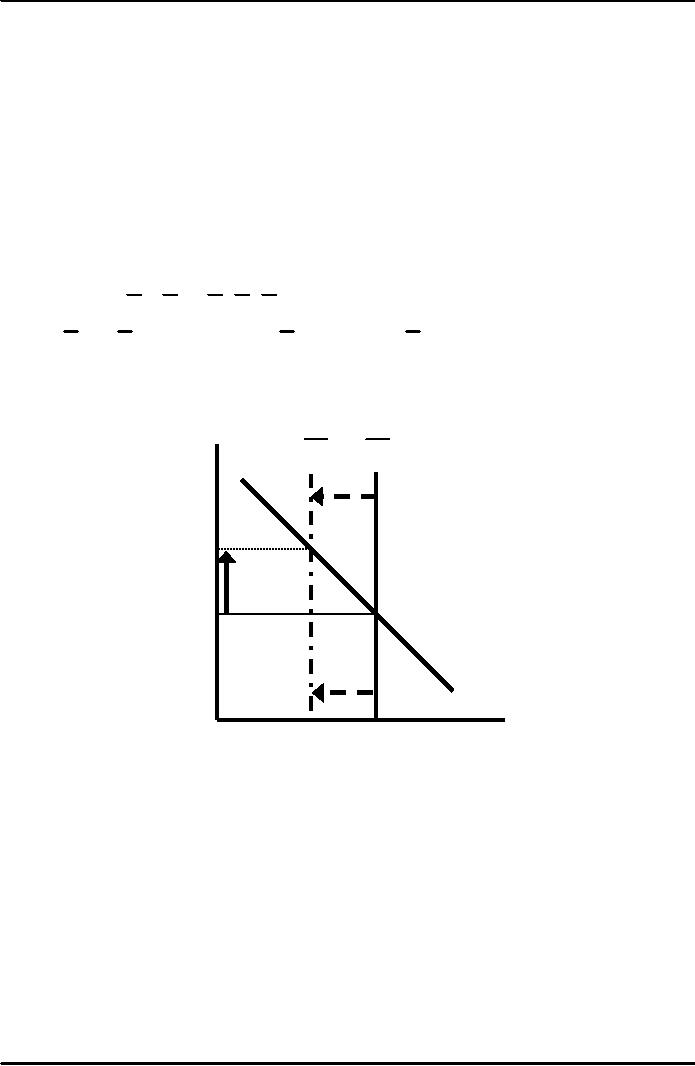
Role of Govt.
r
S2
S1
r2
r1
I
(r )
I2
I1
S,
I
1.
The increase in the deficit
reduces saving...
2.
...this causes the real
interest rate to
rise...
3.
...this reduces the level of
investment.
32
Macroeconomics
ECO 403
VU
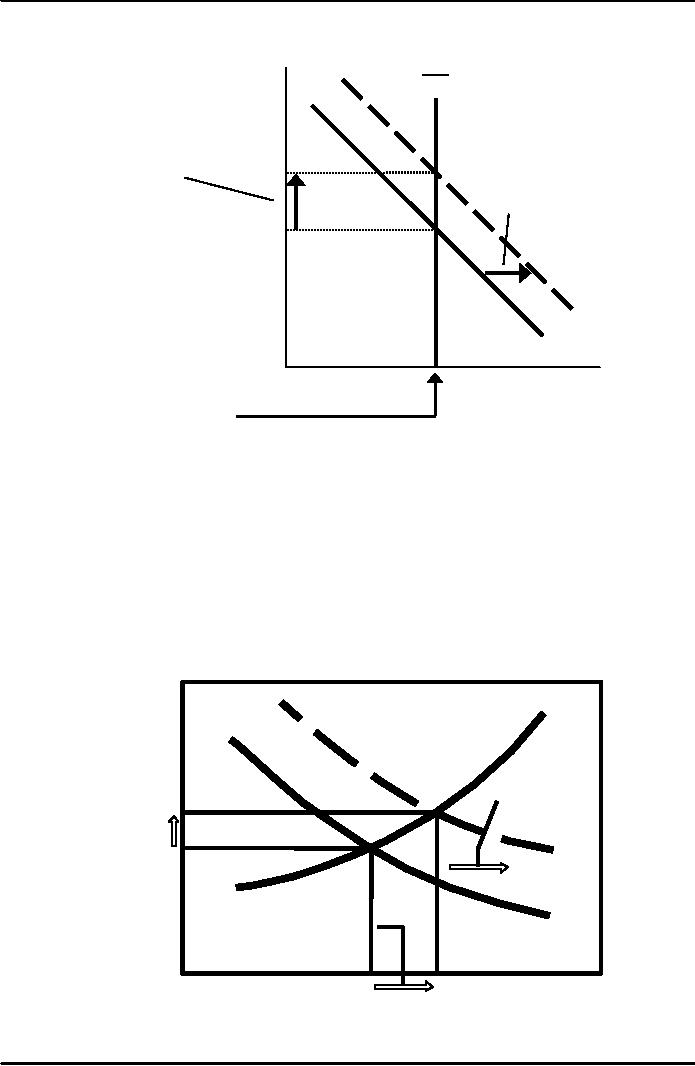
An
increase in investment
demand
r
S
An
increase
...raises
the
in
desired
interest
rate.
r2
investment...
r1
But
the equilibrium level
of
investment
cannot increase
I2
because
the supply of
I1
loanable
funds
is fixed.
S,
I
Saving
and the interest
rate
�
Why might
saving depend on r?
�
How would
the results of an increase in
investment demand be
different?
Would r
rise as much?
Would the
equilibrium value of I
change?
Rise
in investment demand when
saving depends on interest
rate
Real
interest
r
rate,
S
(r)
1.
An increase
in
desired
B
2.
.
. .
raises
investment
the
interest
A
rate
I2
3.
.
.
and raises
I1
equilibrium
investment
and
saving.
Investment,
Saving,
I,
S
33
Macroeconomics
ECO 403
VU
The
classical theory of
inflation
�
Inflation
Causes
Effects
Social
costs
�
"Classical" --
assumes prices are flexible
& markets clear.
�
Applies to the
long run.
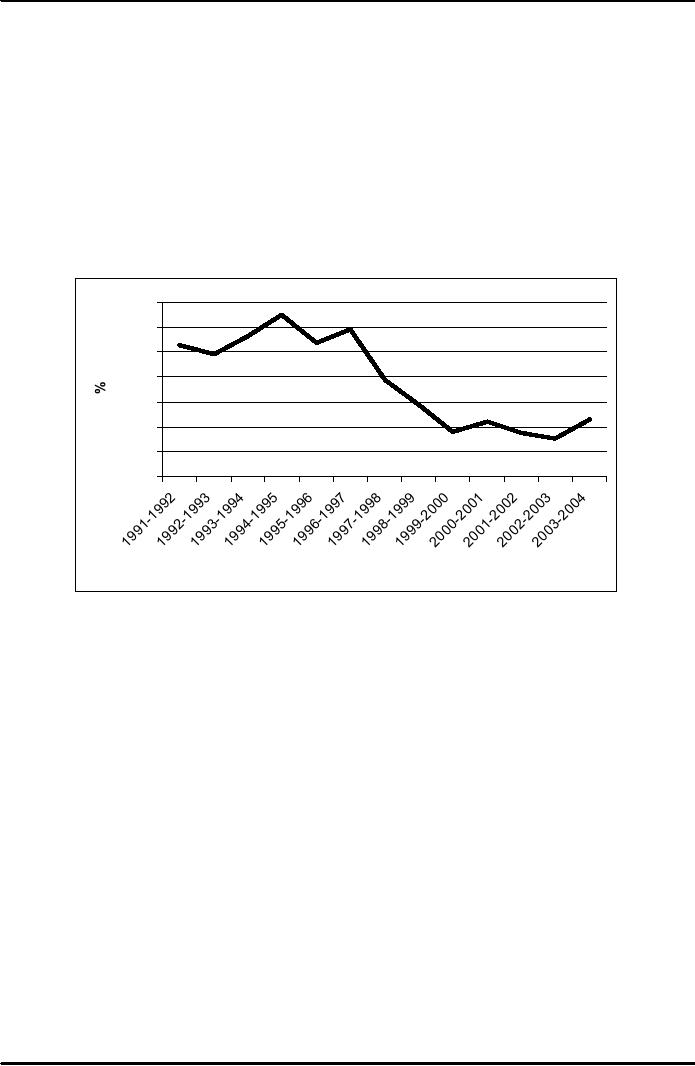
Inflation
Rate in Pakistan
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
Years
The
connection between money and
prices
�
Inflation
rate = the percentage
increase
in
the average level of
prices.
�
Price
= amount of money required
to
buy
a good.
�
Because
prices are defined in terms
of money, we need to consider
the nature of
money,
the supply of money, and
how it is controlled.
MONEY:
definition
Money
is the stock of assets that
can be readily used to make
transactions.
Money:
functions
1.
Medium of exchange
we
use it to buy stuff
2.
Unit of account
the
common unit by which
everyone measures prices and
values
3.
Store of value
transfers
purchasing power from the
present to the future
34

Macroeconomics
ECO 403
VU
The
ease with which money is
converted into other
things-- goods and
services-- is sometimes
called
money's liquidity.
Money:
Types
1.
Fiat money
�
has
no intrinsic value
�
example:
the paper currency we
use
2.
Commodity money
�
has
intrinsic value
�
examples:
gold coins,
Which
of these is money?
a.
Currency
b.
Checks
c.
Deposits
in checking accounts (called
demand deposits)
d.
Credit
cards
e.
Certificates
of deposit (called time
deposits)
The
money supply & monetary
policy
�
The
money supply is the quantity
of money available in the
economy.
�
Monetary
policy is the control over
the money supply.
The
Central Bank
�
Monetary
policy is conducted by a country's
central bank.
�
In
Pakistan, the central bank
is called State Bank of
Pakistan (SBP).
To
expand the Money
Supply:
�
The
State Bank buys Treasury
Bills and
pays for them with
new money.
To
reduce the Money
Supply:
�
The
State Bank sells Treasury
Bills and
receives the existing
dollars and then
destroys
them.
State
Bank controls the money
supply in three ways.
�Open
Market Operations (buying
and selling Treasury
bills).
�Δ
Reserve
requirements.
�
Δ
Discount
rate which
commercial banks pay to
borrow from the
State
Bank.
35

Macroeconomics
ECO 403
VU
The
Quantity Theory of
Money
�
A
simple theory linking the
inflation rate to the growth
rate of the money
supply.
�
Begins
with a concept called
"velocity"...
Velocity
�
Basic
concept: the rate at which
money circulates
�
Definition:
the number of times the
average rupee bill changes
hands in a given time
period
�
Example:
�
Rs50
billion in transactions
�
Money
supply = Rs10 billion
�
The
average rupee is used in
five transactions
�
So,
velocity = 5
�
This
suggests the following
definition:
V=T/M
where
V
= velocity
T
= value of all
transactions
M
= money supply
Velocity
�
Use
nominal GDP as a proxy for
total transactions.
Then,
V
= (P x
Y) /
M
The
Quantity Equation
�
The
quantity equation
M
�V
= P �Y
follows
from the preceding
definition of velocity.
It is an
identity:
it
holds by definition of the
variables.
36
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION:COURSE DESCRIPTION, TEN PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS
- PRINCIPLE OF MACROECONOMICS:People Face Tradeoffs
- IMPORTANCE OF MACROECONOMICS:Interest rates and rental payments
- THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS:Rules for computing GDP
- THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS (Continued…):Components of Expenditures
- THE DATA OF MACROECONOMICS (Continued…):How to construct the CPI
- NATIONAL INCOME: WHERE IT COMES FROM AND WHERE IT GOES
- NATIONAL INCOME: WHERE IT COMES FROM AND WHERE IT GOES (Continued…)
- NATIONAL INCOME: WHERE IT COMES FROM AND WHERE IT GOES (Continued…)
- NATIONAL INCOME: WHERE IT COMES FROM AND WHERE IT GOES (Continued…)
- MONEY AND INFLATION:The Quantity Equation, Inflation and interest rates
- MONEY AND INFLATION (Continued…):Money demand and the nominal interest rate
- MONEY AND INFLATION (Continued…):Costs of expected inflation:
- MONEY AND INFLATION (Continued…):The Classical Dichotomy
- OPEN ECONOMY:Three experiments, The nominal exchange rate
- OPEN ECONOMY (Continued…):The Determinants of the Nominal Exchange Rate
- OPEN ECONOMY (Continued…):A first model of the natural rate
- ISSUES IN UNEMPLOYMENT:Public Policy and Job Search
- ECONOMIC GROWTH:THE SOLOW MODEL, Saving and investment
- ECONOMIC GROWTH (Continued…):The Steady State
- ECONOMIC GROWTH (Continued…):The Golden Rule Capital Stock
- ECONOMIC GROWTH (Continued…):The Golden Rule, Policies to promote growth
- ECONOMIC GROWTH (Continued…):Possible problems with industrial policy
- AGGREGATE DEMAND AND AGGREGATE SUPPLY:When prices are sticky
- AGGREGATE DEMAND AND AGGREGATE SUPPLY (Continued…):
- AGGREGATE DEMAND AND AGGREGATE SUPPLY (Continued…):
- AGGREGATE DEMAND AND AGGREGATE SUPPLY (Continued…)
- AGGREGATE DEMAND AND AGGREGATE SUPPLY (Continued…)
- AGGREGATE DEMAND AND AGGREGATE SUPPLY (Continued…)
- AGGREGATE DEMAND IN THE OPEN ECONOMY:Lessons about fiscal policy
- AGGREGATE DEMAND IN THE OPEN ECONOMY(Continued…):Fixed exchange rates
- AGGREGATE DEMAND IN THE OPEN ECONOMY (Continued…):Why income might not rise
- AGGREGATE SUPPLY:The sticky-price model
- AGGREGATE SUPPLY (Continued…):Deriving the Phillips Curve from SRAS
- GOVERNMENT DEBT:Permanent Debt, Floating Debt, Unfunded Debts
- GOVERNMENT DEBT (Continued…):Starting with too little capital,
- CONSUMPTION:Secular Stagnation and Simon Kuznets
- CONSUMPTION (Continued…):Consumer Preferences, Constraints on Borrowings
- CONSUMPTION (Continued…):The Life-cycle Consumption Function
- INVESTMENT:The Rental Price of Capital, The Cost of Capital
- INVESTMENT (Continued…):The Determinants of Investment
- INVESTMENT (Continued…):Financing Constraints, Residential Investment
- INVESTMENT (Continued…):Inventories and the Real Interest Rate
- MONEY:Money Supply, Fractional Reserve Banking,
- MONEY (Continued…):Three Instruments of Money Supply, Money Demand