 |
DEMAND, SUPPLY AND EQUILIBRIUM (CONTINUED……..) |
| << DEMAND, SUPPLY AND EQUILIBRIUM:Goods Market and Factors Market |
| DEMAND, SUPPLY AND EQUILIBRIUM (CONTINUED……..):Equilibrium >> |
Introduction
to Economics ECO401
VU
Lesson
2.2
DEMAND,
SUPPLY AND EQUILIBRIUM
(CONTINUED........)
Supply:
Supply
is the quantity of a good
sellers wish to sell at each
conceivable price.
The
law of supply states that
the quantity supplied will
go up as the price goes up
and vice
versa.
A
supply schedule is a table
which shows various
combinations of quantity supplied
and price.
A
supply function is an equational
representation of supply as a function of
all its determinants.
A
supply curve obtains when
price is plotted against
quantity supplied.
Problems
of identification arise when we
can not determine that
the change in the
equilibrium
quantities
is either caused by a change in
demanded or by changes in both
demand and
supply.
Determinants
of supply are:
�
Costs of
production
�
Profitability
of alternative products (substitutes in
supply)
�
Profitability
of goods in joint
supply
�
Nature
and other random
shocks
�
Aims of
producers
�
Expectations
of producers
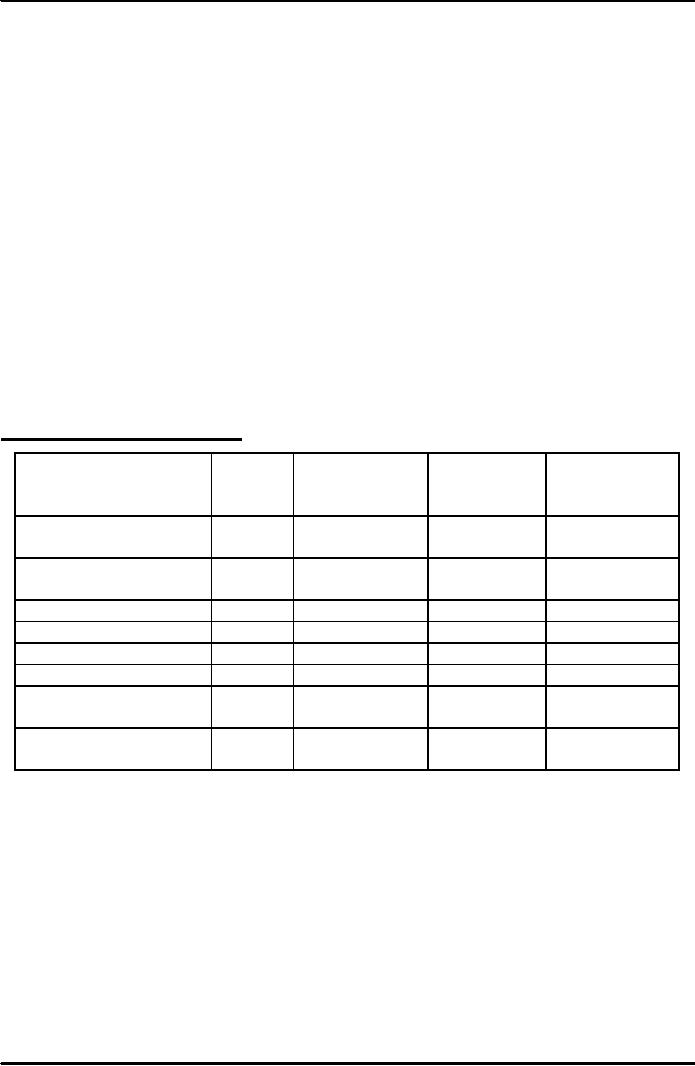
Factors
Shifting Supply Curve:
Factors
Changing
Effect
Direction
of
Effect
on
Effect
on
Supply
on
Shift
in Supply
Equilibrium
Equilibrium
Supply
Curve
Price
Quantity
Increase
in resource
Decrease
Leftward
Increase
Decrease
price
Decrease
in resource
Increase
Rightward
Decrease
Increase
price
Improved
technology
Increase
Rightward
Decrease
Increase
Decline
in technology
Decrease
Leftward
Increase
Decrease
Expect
a price increase
Decrease
Leftward
Increase
Decrease
Expect
a price decrease
Increase
Rightward
Decrease
Increase
Increase
in number of
Increase
Rightward
Decrease
Increase
suppliers
Decrease
in number of
Decrease
Leftward
Increase
Decrease
suppliers
10
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS:Economic Systems
- INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS (CONTINUED………):Opportunity Cost
- DEMAND, SUPPLY AND EQUILIBRIUM:Goods Market and Factors Market
- DEMAND, SUPPLY AND EQUILIBRIUM (CONTINUED……..)
- DEMAND, SUPPLY AND EQUILIBRIUM (CONTINUED……..):Equilibrium
- ELASTICITIES:Price Elasticity of Demand, Point Elasticity, Arc Elasticity
- ELASTICITIES (CONTINUED………….):Total revenue and Elasticity
- ELASTICITIES (CONTINUED………….):Short Run and Long Run, Incidence of Taxation
- BACKGROUND TO DEMAND/CONSUMPTION:CONSUMER BEHAVIOR
- BACKGROUND TO DEMAND/CONSUMPTION (CONTINUED…………….)
- BACKGROUND TO DEMAND/CONSUMPTION (CONTINUED…………….)The Indifference Curve Approach
- BACKGROUND TO DEMAND/CONSUMPTION (CONTINUED…………….):Normal Goods and Giffen Good
- BACKGROUND TO SUPPLY/COSTS:PRODUCTIVE THEORY
- BACKGROUND TO SUPPLY/COSTS (CONTINUED…………..):The Scale of Production
- BACKGROUND TO SUPPLY/COSTS (CONTINUED…………..):Isoquant
- BACKGROUND TO SUPPLY/COSTS (CONTINUED…………..):COSTS
- BACKGROUND TO SUPPLY/COSTS (CONTINUED…………..):REVENUES
- BACKGROUND TO SUPPLY/COSTS (CONTINUED…………..):PROFIT MAXIMISATION
- MARKET STRUCTURES:PERFECT COMPETITION, Allocative efficiency
- MARKET STRUCTURES (CONTINUED………..):MONOPOLY
- MARKET STRUCTURES (CONTINUED………..):PRICE DISCRIMINATION
- MARKET STRUCTURES (CONTINUED………..):OLIGOPOLY
- SELECTED ISSUES IN MICROECONOMICS:WELFARE ECONOMICS
- SELECTED ISSUES IN MICROECONOMICS (CONTINUED……………)
- INTRODUCTION TO MACROECONOMICS:Price Level and its Effects:
- INTRODUCTION TO MACROECONOMICS (CONTINUED………..)
- INTRODUCTION TO MACROECONOMICS (CONTINUED………..):The Monetarist School
- THE USE OF MACROECONOMIC DATA, AND THE DEFINITION AND ACCOUNTING OF NATIONAL INCOME
- THE USE OF MACROECONOMIC DATA, AND THE DEFINITION AND ACCOUNTING OF NATIONAL INCOME (CONTINUED……………..)
- MACROECONOMIC EQUILIBRIUM & VARIABLES; THE DETERMINATION OF EQUILIBRIUM INCOME
- MACROECONOMIC EQUILIBRIUM & VARIABLES; THE DETERMINATION OF EQUILIBRIUM INCOME (CONTINUED………..)
- MACROECONOMIC EQUILIBRIUM & VARIABLES; THE DETERMINATION OF EQUILIBRIUM INCOME (CONTINUED………..):The Accelerator
- THE FOUR BIG MACROECONOMIC ISSUES AND THEIR INTER-RELATIONSHIPS
- THE FOUR BIG MACROECONOMIC ISSUES AND THEIR INTER-RELATIONSHIPS (CONTINUED…….)
- THE FOUR BIG MACROECONOMIC ISSUES AND THEIR INTER-RELATIONSHIPS (CONTINUED…….):Causes of Inflation
- THE FOUR BIG MACROECONOMIC ISSUES AND THEIR INTER-RELATIONSHIPS (CONTINUED…….):BALANCE OF PAYMENTS
- THE FOUR BIG MACROECONOMIC ISSUES AND THEIR INTER-RELATIONSHIPS (CONTINUED…….):GROWTH
- THE FOUR BIG MACROECONOMIC ISSUES AND THEIR INTER-RELATIONSHIPS (CONTINUED…….):Land
- THE FOUR BIG MACROECONOMIC ISSUES AND THEIR INTER-RELATIONSHIPS (CONTINUED…….):Growth-inflation
- FISCAL POLICY AND TAXATION:Budget Deficit, Budget Surplus and Balanced Budget
- MONEY, CENTRAL BANKING AND MONETARY POLICY
- MONEY, CENTRAL BANKING AND MONETARY POLICY (CONTINUED…….)
- JOINT EQUILIBRIUM IN THE MONEY AND GOODS MARKETS: THE IS-LM FRAMEWORK
- AN INTRODUCTION TO INTERNATIONAL TRADE AND FINANCE
- PROBLEMS OF LOWER INCOME COUNTRIES:Poverty trap theories: