 |
Introduction:Model Solution, Implementation of Results |
| << Introduction:OR APPROACH TO PROBLEM SOLVING, Observation |
| Introduction:USES OF OPERATIONS RESEARCH, Marketing, Personnel >> |
Operations
Research (MTH601)
7
An OR
model is an abstract representation of an
existing problem situation. It can be
in
the
form of a graph or chart,
but mostly, an OR model consists of a
set of mathematical
relationship.
In OR terminology, these are
called objective function and
constraints.
Model
Solution
Once
models are constructed, they
are solved using the OR
techniques, presented in
the
next
section. Actually it is difficult to
separate model construction and
solution in most
cases,
since
OR technique usually applies to a
specific type of model.
Thus, the model type
and
solution
method are both part of
the OR technique.
Implementation
of Results
The
results of an OR technique are
information which helps in
making a decision.
The
beauty
of OR process lies in obtaining,
the results which are
implement able or we call it a
feasible
whole exercise will go waste.
OR
is an On-going Process
Once
the five steps described
above are completed, it does
not necessarily mean that
OR
process
is completed. The model
results and the decisions based on
the results provide
feedback
to
the original model. The
original OR model can be modified to test
different conditions and
decisions
that might occur in the
future. The results may
indicate that a different
problem exists
that
had not been thought of
previously, thus the
original model is altered or
reconstructed. As
such,
the OR process is continuous
rather than simply
consisting of one solution to one
problem.
7
Operations
Research (MTH601)
8
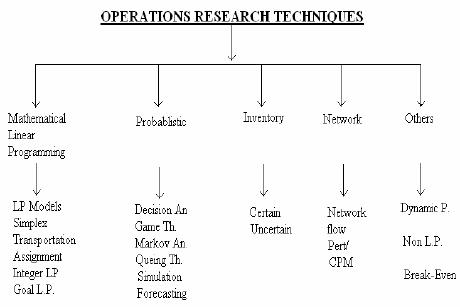
Operations
Research Techniques:
Two
of the five steps of OR
process, model construction and
solution, encompass
the
actual
use of OR techniques. These techniques
can be loosely classified into
five categories.
1)
Linear
mathematical programming technique
consist of first, identifying
problem as
being
solvable by linear programming;
second formulation of unturned
problem and then
finding
the
solution by using established
mathematical techniques. It derives
its name from the fact
that
the
functional relationship in the
mathematical model are
linear and the solution
techniques
consists
of a predetermined mathematical steps
i.e. program.
2)
Probabilistic
techniques covers those problem in
which all parameters are
not known with
certainty.
The solution results are
assumed to be known with
uncertainty, with probability
that
other
solution might exist.
3)
Inventory
techniques are specifically
designed for the analysis of
inventory problem
frequently
encountered by the business
firms. This particular
business function is singled
out for
attention,
since it typically represents a
significant area of cost for
almost every business.
This
category
is divided into probabilistic and
deterministic techniques.
8
Operations
Research (MTH601)
9
4)
Network
techniques consist of models
that are represented by diagrams
rather than
strictly
mathematical relationship i.e.
pictorial representation of the
system under
consideration.
These
models can represent either probabilistic
or deterministic systems.
5)
Other
techniques consist of all
the remaining techniques,
which do not come under
the
four
heads mentioned above. For
example, Dynamic programming
employs a different
modeling
and
solution logic than linear
programming. In non-linear programming
either the objective
function
or the constraints or both can be
non-linear functions, which
would require
altogether
different
solution technique.
USES
OF OPERATIONS RESEARCH
9
Table of Contents:
- Introduction:OR APPROACH TO PROBLEM SOLVING, Observation
- Introduction:Model Solution, Implementation of Results
- Introduction:USES OF OPERATIONS RESEARCH, Marketing, Personnel
- PERT / CPM:CONCEPT OF NETWORK, RULES FOR CONSTRUCTION OF NETWORK
- PERT / CPM:DUMMY ACTIVITIES, TO FIND THE CRITICAL PATH
- PERT / CPM:ALGORITHM FOR CRITICAL PATH, Free Slack
- PERT / CPM:Expected length of a critical path, Expected time and Critical path
- PERT / CPM:Expected time and Critical path
- PERT / CPM:RESOURCE SCHEDULING IN NETWORK
- PERT / CPM:Exercises
- Inventory Control:INVENTORY COSTS, INVENTORY MODELS (E.O.Q. MODELS)
- Inventory Control:Purchasing model with shortages
- Inventory Control:Manufacturing model with no shortages
- Inventory Control:Manufacturing model with shortages
- Inventory Control:ORDER QUANTITY WITH PRICE-BREAK
- Inventory Control:SOME DEFINITIONS, Computation of Safety Stock
- Linear Programming:Formulation of the Linear Programming Problem
- Linear Programming:Formulation of the Linear Programming Problem, Decision Variables
- Linear Programming:Model Constraints, Ingredients Mixing
- Linear Programming:VITAMIN CONTRIBUTION, Decision Variables
- Linear Programming:LINEAR PROGRAMMING PROBLEM
- Linear Programming:LIMITATIONS OF LINEAR PROGRAMMING
- Linear Programming:SOLUTION TO LINEAR PROGRAMMING PROBLEMS
- Linear Programming:SIMPLEX METHOD, Simplex Procedure
- Linear Programming:PRESENTATION IN TABULAR FORM - (SIMPLEX TABLE)
- Linear Programming:ARTIFICIAL VARIABLE TECHNIQUE
- Linear Programming:The Two Phase Method, First Iteration
- Linear Programming:VARIANTS OF THE SIMPLEX METHOD
- Linear Programming:Tie for the Leaving Basic Variable (Degeneracy)
- Linear Programming:Multiple or Alternative optimal Solutions
- Transportation Problems:TRANSPORTATION MODEL, Distribution centers
- Transportation Problems:FINDING AN INITIAL BASIC FEASIBLE SOLUTION
- Transportation Problems:MOVING TOWARDS OPTIMALITY
- Transportation Problems:DEGENERACY, Destination
- Transportation Problems:REVIEW QUESTIONS
- Assignment Problems:MATHEMATICAL FORMULATION OF THE PROBLEM
- Assignment Problems:SOLUTION OF AN ASSIGNMENT PROBLEM
- Queuing Theory:DEFINITION OF TERMS IN QUEUEING MODEL
- Queuing Theory:SINGLE-CHANNEL INFINITE-POPULATION MODEL
- Replacement Models:REPLACEMENT OF ITEMS WITH GRADUAL DETERIORATION
- Replacement Models:ITEMS DETERIORATING WITH TIME VALUE OF MONEY
- Dynamic Programming:FEATURES CHARECTERIZING DYNAMIC PROGRAMMING PROBLEMS
- Dynamic Programming:Analysis of the Result, One Stage Problem
- Miscellaneous:SEQUENCING, PROCESSING n JOBS THROUGH TWO MACHINES
- Miscellaneous:METHODS OF INTEGER PROGRAMMING SOLUTION