 |
Applications of Basic Mathematics Part 1:BASIC ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS |
| << SERIES:SUMMATION NOTATION, COMPUTING SUMMATIONS: |
| Applications of Basic Mathematics Part 4:PERCENTAGE CHANGE >> |

MTH001
Elementary Mathematics
LECTURE #
15
Applications of
Basic Mathematics
Part
1
OBJECTIVES
The
objectives of the lecture
are to learn about:
�
Different
course modules
�
Basic
Arithmetic Operations
�
Starting
Microsoft (MS) Excel
�
Using MS
Excel to carry out
arithmetic operations
BASIC
ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS
Five
arithmetic operations provide
the foundation for all
mathematical operations.
These
are:
�
Addition
�
Subtraction
�
Multiplication
�
Division
�
Exponents
Example-
Addition
12
+ 5 = 17
Example-
Subtraction
12
- 5 = 7
Example-
Multiplication
12
x 5 = 60
Example-
Exponent
(4)^2
= 16
(4)^1/2
= 2
(4)^-1/2
= 1/(4)^1/2 = � = 0.5
MICROSOFT
EXCEL IN BUSINESS MATHEMATICS &
STATISTICS
Microsoft
Corporation's Spreadsheet software
Excel
is widely
used in business
mathematics
and statistical applications.
The latest version of this
software is
EXCEL
2002 XP. This
course is based on wide
applications of EXCEL
2002. It is
recommended
that you install EXCEL
2002 XP software on
your computer. If
your
computer has Windows
2000 and
EXCEL
2000 even
that version of
EXCEL
can be used as the
applications we intend to learn
can be done using
the
earlier
version of EXCEL. Those of
you who are still
working with Windows
98
and
have EXCEL 97 installed are
encouraged to migrate to newer
version of
EXCEL
software.
Page
92
MTH001
Elementary Mathematics
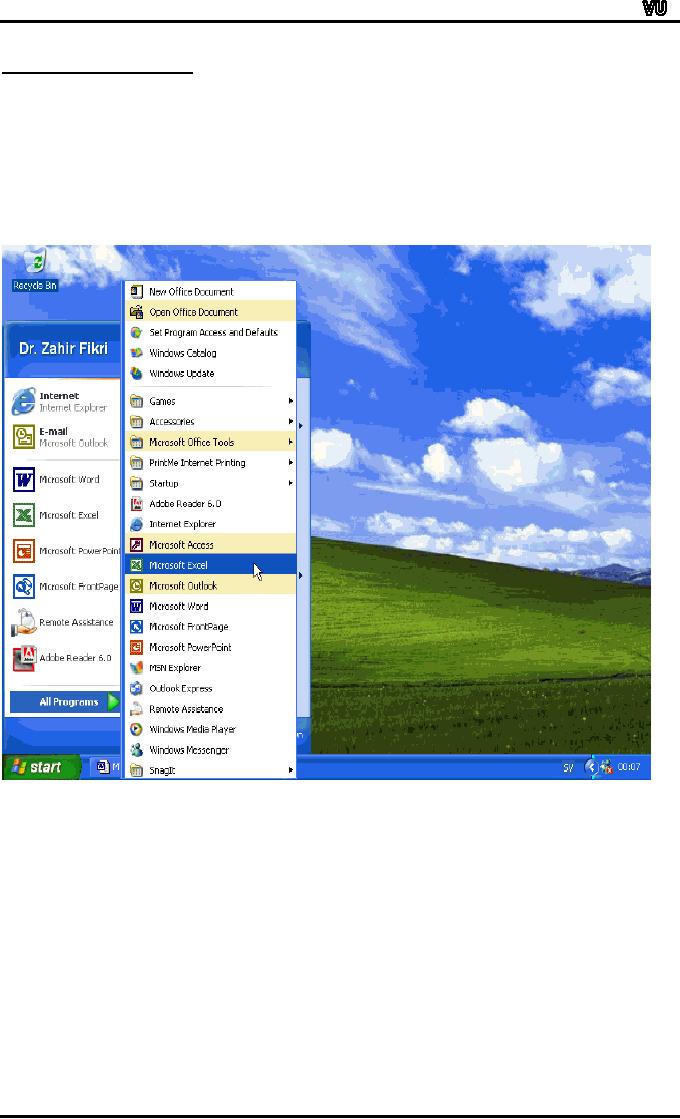
Starting
EXCEL 2000 XP
EXCEL
2000 XP can be started by
going through the following
steps:
Click
Start
on your
computer
Click
All
Programs
Click
Microsoft
Excel
The
following slides show the
operations:
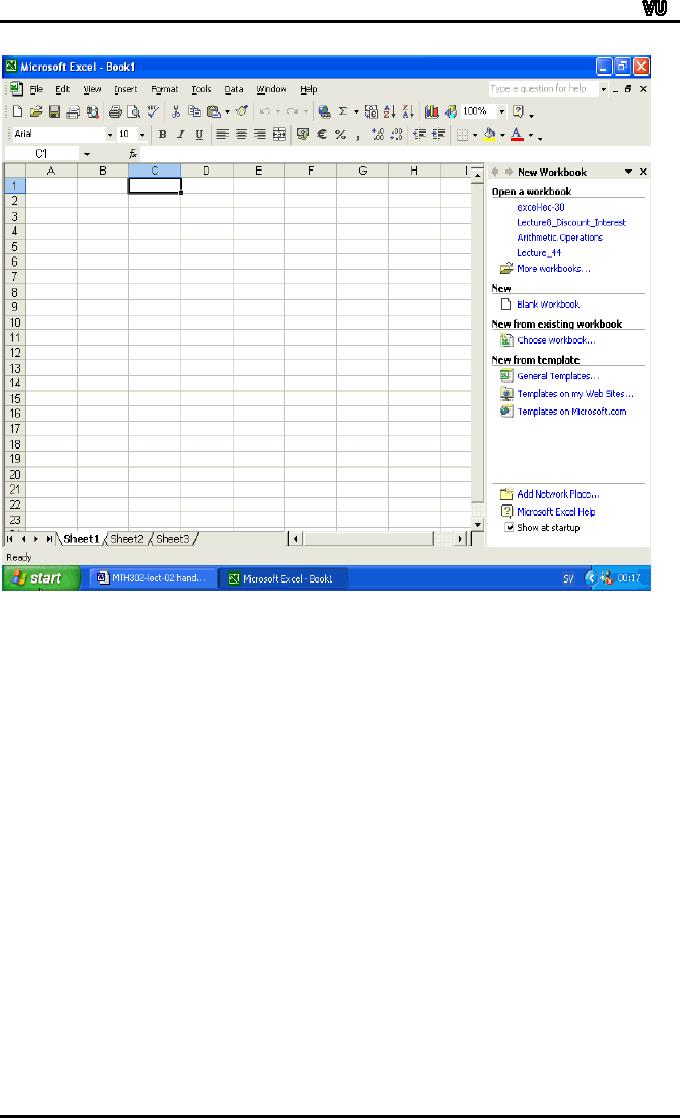
The
EXCEL window opens and a
blank worksheet becomes
available as shown
below:
Page
93
MTH001
Elementary Mathematics
The
slide shows a Workbook by
the name book1 with
three sheets: Sheet1,
Sheet2
and Sheet3. The Excel
Window has Column numbers
starting from A
and
row numbers starting from 1.
the intersection of a row
and column is called
a
Cell.
The first cell is A1 which
is the intersection of column A
and row 1. All
cells
in
a Sheet are referenced by a
combination of Column name
and row number.
Example
1: B15
means cell in column B and
row 15.
Example
2: A cell in
row 12 and column C has
reference C12.
A
Range
defines
all cells starting from
the leftmost corner where
the range starts
to
the rightmost corner in the
last row. The Range is
specified by the starting
cell,
a
colon and the ending
cell.
Example
3: A
Range
which
starts from A1 and ends at
D15 is
referenced
by A1:D15 and has all
the cells in columns A to D up to
and including
row
15.
A
value can be entered into a
cell by clicking that cell.
The mouse pointer
which
is
a rectangle moves to the
selected cell. Simply enter
the value followed by
the
Enter
key.
The mouse pointer moves to
the cell below.
If
you make a mistake while
entering the value select
the cell again (by
clicking
it).
Enter the new value.
The old value is replaced by
the new value.
Page
94

MTH001
Elementary Mathematics
If
only one or more digits
are to be changed then
select the cell. Then
double
click
the mouse. The blinking
cursor appears. Either move
the arrow key to
move
to
the digit to be changed or
move the cursor to the
desired position. Enter
the
new
value and delete the
undesired value by using the
Del
key.
I
suggest that you learn
the basic operations of
entering, deleting and
changing
data
in a worksheet.
About
calculation operators in
Excel
In
Excel there are four
different types of
operators:
Arithmetic
operators
Comparison
operators
Text
concatenation operator
Reference
operators
The
following descriptions are
reproduced from Excel's Help
file for your
ready
reference.
In the present lecture you
are directly concerned with
arithmetic
operators.
However, it is important to learn
that the comparison
operators are
used
where calculations are made
on the basis of comparisons.
The text
concatenation
operator is used to combine
two text strings. The
reference
operators
include ":" and "," or ; as
the case maybe. We shall
learn the use of
these
operators in different worksheets. You
should look through the
Excel Help
file
to see examples of these
functions. Selected material
from Excel Help
File
relating
to arithmetic operations is given in in a
separate file.
The
Excel arithmetic operators
are as follows:
Addition.
Symbol: +
(Example:
=5+4 Result: 9)
Subtraction.
Symbol: -
(Example:
=5-4 Result: 1)
Multiplication.
Symbol: *
(Example:
=5*4 Result: 20)
Division.
Symbol: /
(Example:
=12/4 Result: 3)
Percent.
Symbol: %
(Example:
=20% Result: 0.2)
Exponentiation:
^
(Example:
=5^2 Result: 25)
Excel
Formulas for
Addition
All
calculations in Excel are
made through formulas which
are written in cells
where
result is required.
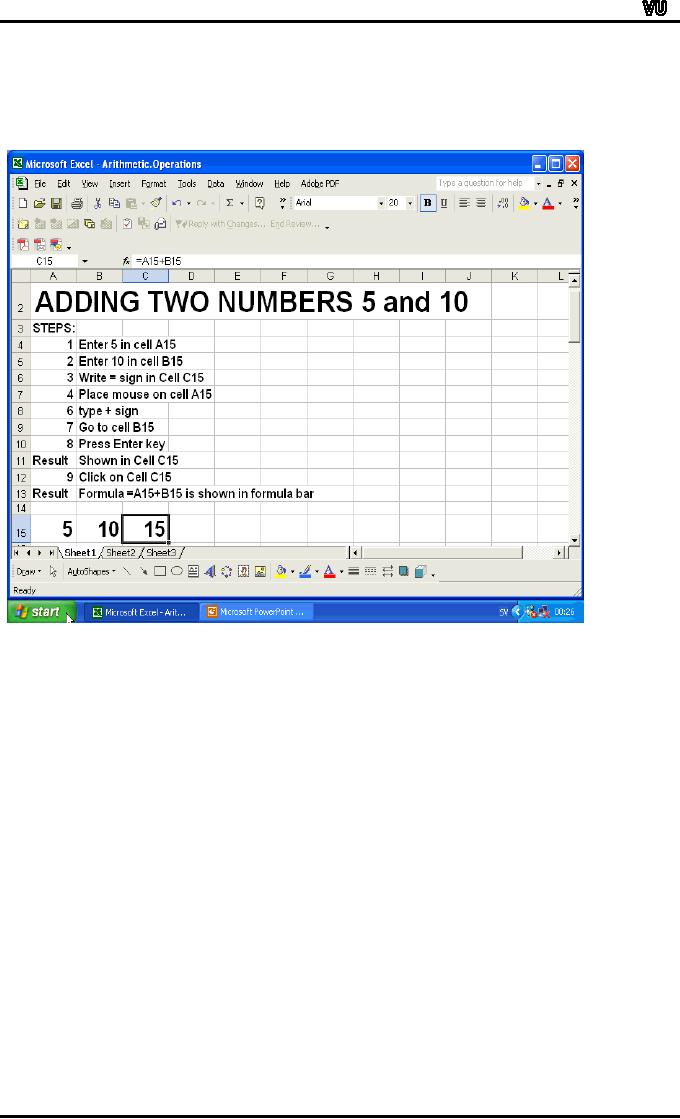
Let
us do addition of two numbers 5
and 10.
We
wish to calculate the
addition of two numbers 10
and 5. Let us see how
we
can
add these two numbers in
Excel.
1.
Open
a blank worksheet.
2.
Click
on a cell where you would
like to enter the number
10. Say cell
A15.
3.
Enter
10 in cell A15.
4.
Click
cell where you would
like to enter the number 5.
Say cell B15.
5.
Click
cell where you would
like to get the sum of 10
and 5. Say cell
C15.
6.
Start
the formula. Write equal
sign = in cell C15.
7.
After
=, write "(" (left bracket)
in cell C15.
8.
Move
mouse and left click on
value 10 which is in cell
A15. In cell C15,
the
cell reference A15 is
written.
9.
Write
"+" after "A15" in cell
C15.
10.
Move
mouse and left click on
value 5 which is in cell
B15. In cell C15,
the
cell
reference B15 is
written.
11.
Write
") " (right bracket) in cell
C15.
12.
Press
Enter key
The
answer 15 is shown in cell
C15.
Page
95
MTH001
Elementary Mathematics
If
you click on cell C15,
the formula "=A15+B15" is
displayed the formula bar
to
the
right of fx in the
Toolbar.
The
main steps along with
the entries are shown in
the slide below.
The
worksheet
MTH302-lec-02 contains the
actual entries.
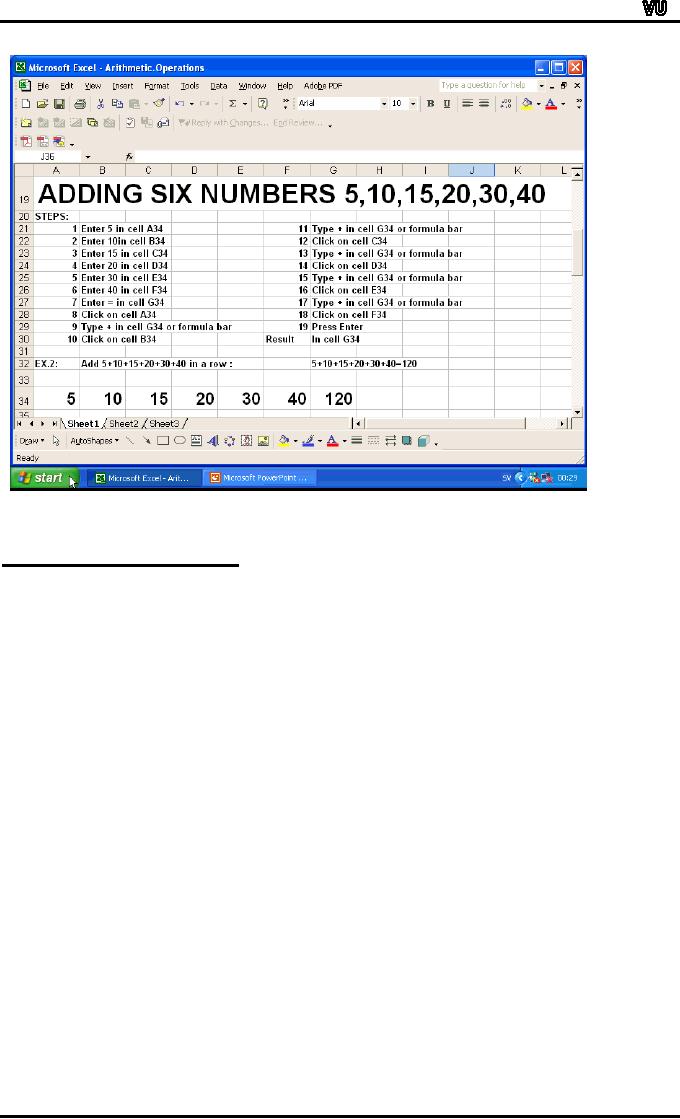
The
next slide shows addition of
6 numbers 5, 10, 15, 20, 30
and 40. The
entries
were
made in row 34. The
values were entered as
follows:
Cell
A34: 5
Cell
B34: 10
Cell
C34: 15
Cell
D34: 20
Cell
E34: 30
Cell
F34: 40
The
formula was written in cell
G34. The formula
was:
=5+10+15+20+30+40
The
answer was 120.
You
can use an Excel function
SUM along with the cell
range A34:F34 to
calculate
the sum of the above
numbers. The formula in such
a case will be:
=SUM(A34:F34)
You
enter "=" followed by SUM,
followed by "(". Click on
the cell with
value
5(reference:
A34). Drag the mouse to
cell with value
40(reference: F34) and
drop
the
mouse. Enter ")" and
then press the Enter
key.
Page
96
MTH001
Elementary Mathematics
In
the above two examples
you learnt how formulas
for addition are written
in
Excel.
Excel
Formula for
Subtraction
Excel
formulas for subtraction are
similar to those of addition
but with the
minus
sign.
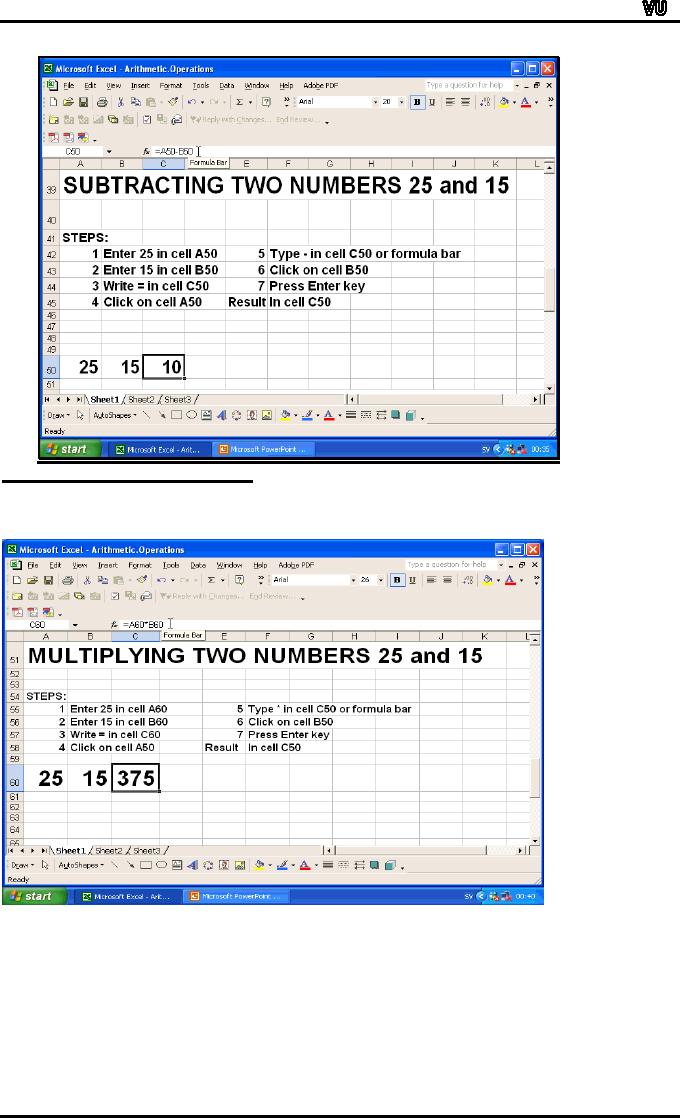
Let
us go through the steps for
subtracting 15 from 25.
Enter values in row 50
as
follows:
Cell
A50: 25
Cell
B50: 15
Write
the formula in cell C50 as
follows:
=A50-B50
To
write this formula, click
cell C50, where you
want the result. Enter
"=". Click
on
cell with value 25
(reference:A50). Enter "-"(minus
sign). Click on cell
with
value
15 (reference B50). Press
enter key.
If
you enter 15 first and 25
later, then the question
will be to find result
of
subtraction
15-25.
Page
97
MTH001
Elementary Mathematics
Excel
Formula for
Multiplication
Excel
formula for multiplication is
also similar to the formula
for addition.
Only
the sign of multiplication
will be used. The Excel
multiplication operator is *.
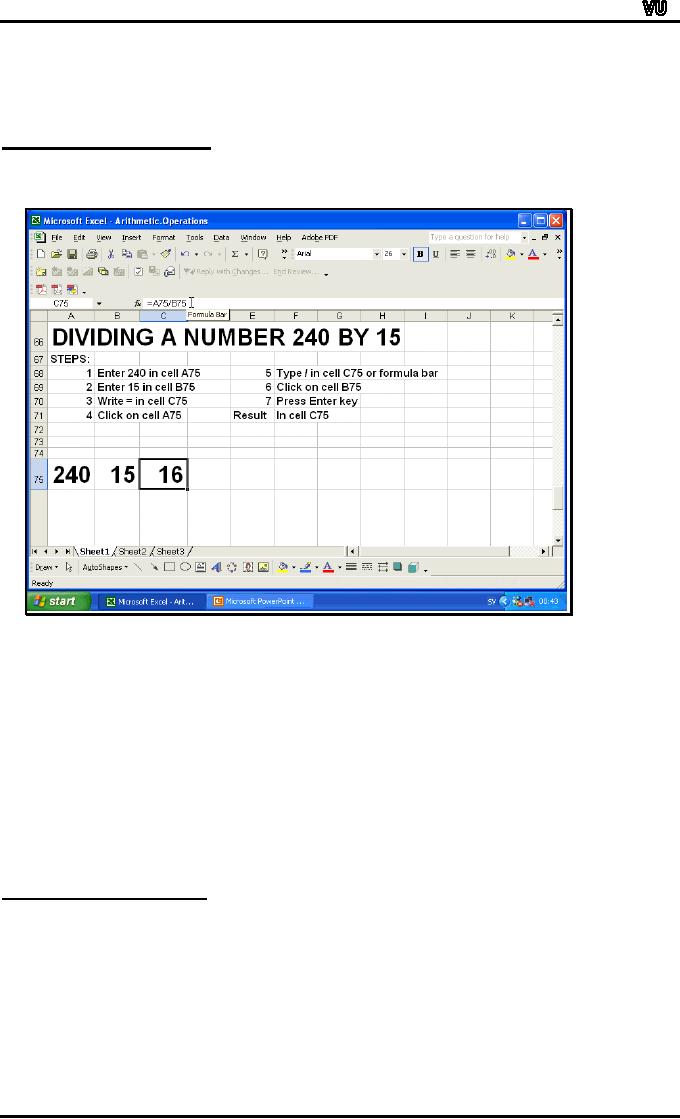
Let
us look at the multiplication of
two numbers 25 and 15.
The entries will be
made
in row 60. Enter values as
under:
Cell
A50: 25
Cell
B50: 15
The
formula for multiplication
is:
=A50*B50
Page
98
MTH001
Elementary Mathematics
Click
on cell C50 to write the
formula in that cell. Enter
"=". Click on cell
with
number 25 (reference: A50).
Enter "*". Click on cell
with number 15
(reference:
B50). Press Enter key.
The answer is 375 in cell
C50.
Excel
Formula for
Division
The
formula for division is
similar to that of multiplication
with the
difference
that the division sign
"/" will be used.
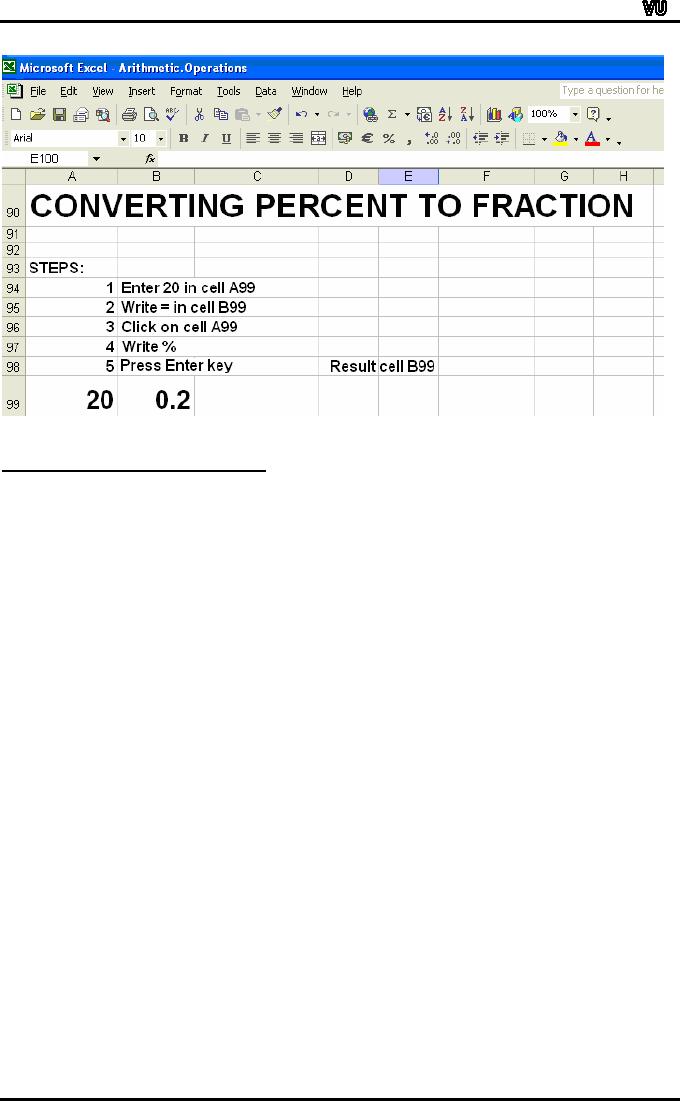
Let
us divide 240 by 15using
Excel formula for division.
Let us enter
numbers
in row 75 as follows:
Cell
A75: 240
Cell
B75: 15
The
formula for division will be
written in cell C75 as
under:
=A75/B75
The
steps are as follows: Click
the cell A75. Enter
240 in cell A75.
Click
cell
B75. Enter 15. Click
cell C75. Enter "=".
Click on cell with value
240
(reference:
A75). Enter "/". Click
cell with number 15
(reference: B75).
Press
enter
key. The answer 16 will be
displayed in cell
C75.
Excel
Formula for
Percent
The
formula for converting
percent to fraction uses the
symbol %. To convert
20%
to fraction the formula is as
under:
=20%
If
you enter 20 in cell A99,
you can write formula
for conversion to fraction
by
doing
the following:
Enter
2o in cell A99. In cell B99
enter "=". Click on cell
A99. Enter"%". Press
Enter
key. The answer 0.2 is
given in cell B99.
Page
99
MTH001
Elementary Mathematics
Excel
Formula for
Exponentiation
The
symbol for exponentiation is ^.
The formula for calculating
exponents is
similar
to multiplication with the
difference that the carat
symbol ^ will be
used.
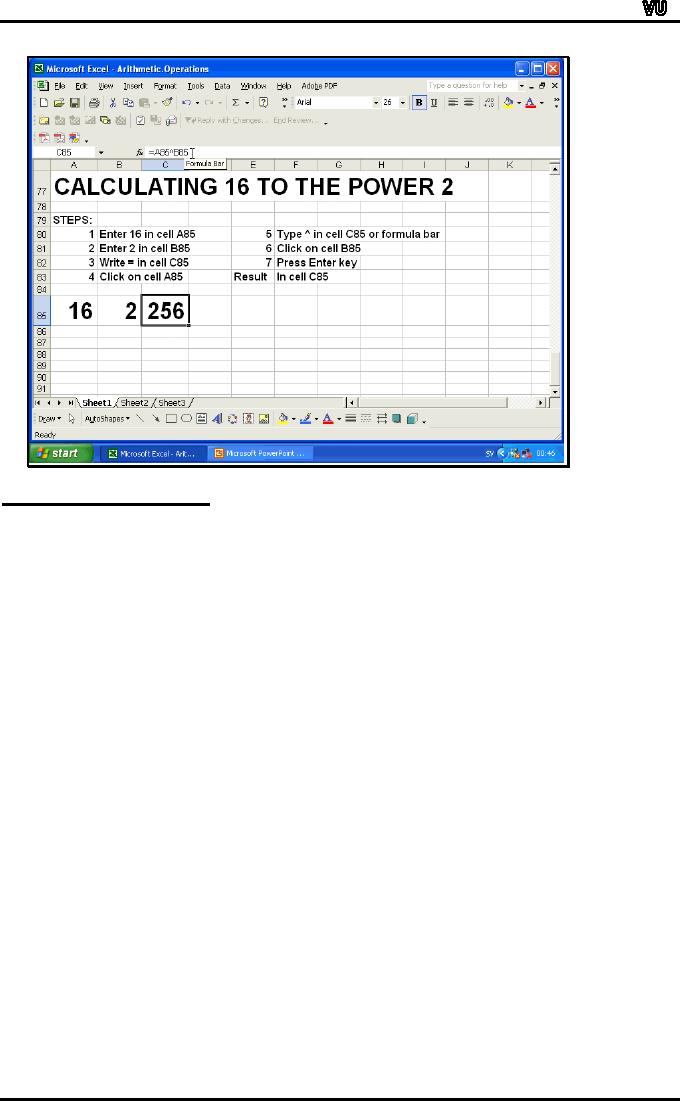
Let
us calculate 16 raised to the
power 2 by Excel formula for
exponentiation.
The
values will be entered in
row 85.
The
steps are:
Select
Cell A85. Enter 16 in this
cell.
Select
cell B85 Enter 2 in this
cell.
Select
cell C85.
Enter"=".
Select
cell with value 16
(reference:A85).
Enter
"^".
Select
number 2 (reference:
B85)
Press
Enter key.
The
result 256 is displayed in
cell C85.
Page
100
MTH001
Elementary Mathematics
Recommended
Homework
Download
worksheet MTH302-lec-02.xls from
the course web
site.
Change
values to see change in
results.
Set
up new worksheets for each
Excel operator with
different values.
Set
up worksheets with combinations of
operations.
Page
101
Table of Contents:
- Recommended Books:Set of Integers, SYMBOLIC REPRESENTATION
- Truth Tables for:DE MORGAN’S LAWS, TAUTOLOGY
- APPLYING LAWS OF LOGIC:TRANSLATING ENGLISH SENTENCES TO SYMBOLS
- BICONDITIONAL:LOGICAL EQUIVALENCE INVOLVING BICONDITIONAL
- BICONDITIONAL:ARGUMENT, VALID AND INVALID ARGUMENT
- BICONDITIONAL:TABULAR FORM, SUBSET, EQUAL SETS
- BICONDITIONAL:UNION, VENN DIAGRAM FOR UNION
- ORDERED PAIR:BINARY RELATION, BINARY RELATION
- REFLEXIVE RELATION:SYMMETRIC RELATION, TRANSITIVE RELATION
- REFLEXIVE RELATION:IRREFLEXIVE RELATION, ANTISYMMETRIC RELATION
- RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS:FUNCTIONS AND NONFUNCTIONS
- INJECTIVE FUNCTION or ONE-TO-ONE FUNCTION:FUNCTION NOT ONTO
- SEQUENCE:ARITHMETIC SEQUENCE, GEOMETRIC SEQUENCE:
- SERIES:SUMMATION NOTATION, COMPUTING SUMMATIONS:
- Applications of Basic Mathematics Part 1:BASIC ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS
- Applications of Basic Mathematics Part 4:PERCENTAGE CHANGE
- Applications of Basic Mathematics Part 5:DECREASE IN RATE
- Applications of Basic Mathematics:NOTATIONS, ACCUMULATED VALUE
- Matrix and its dimension Types of matrix:TYPICAL APPLICATIONS
- MATRICES:Matrix Representation, ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION OF MATRICES
- RATIO AND PROPORTION MERCHANDISING:Punch recipe, PROPORTION
- WHAT IS STATISTICS?:CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SCIENCE OF STATISTICS
- WHAT IS STATISTICS?:COMPONENT BAR CHAR, MULTIPLE BAR CHART
- WHAT IS STATISTICS?:DESIRABLE PROPERTIES OF THE MODE, THE ARITHMETIC MEAN
- Median in Case of a Frequency Distribution of a Continuous Variable
- GEOMETRIC MEAN:HARMONIC MEAN, MID-QUARTILE RANGE
- GEOMETRIC MEAN:Number of Pupils, QUARTILE DEVIATION:
- GEOMETRIC MEAN:MEAN DEVIATION FOR GROUPED DATA
- COUNTING RULES:RULE OF PERMUTATION, RULE OF COMBINATION
- Definitions of Probability:MUTUALLY EXCLUSIVE EVENTS, Venn Diagram
- THE RELATIVE FREQUENCY DEFINITION OF PROBABILITY:ADDITION LAW
- THE RELATIVE FREQUENCY DEFINITION OF PROBABILITY:INDEPENDENT EVENTS