 |
Coordinates, Graphs and Lines |
| Absolute Values >> |
Calculus
and Analytical
Geometry
MTH101
LECTUER -
1
Coordinates,
Graphs and Lines
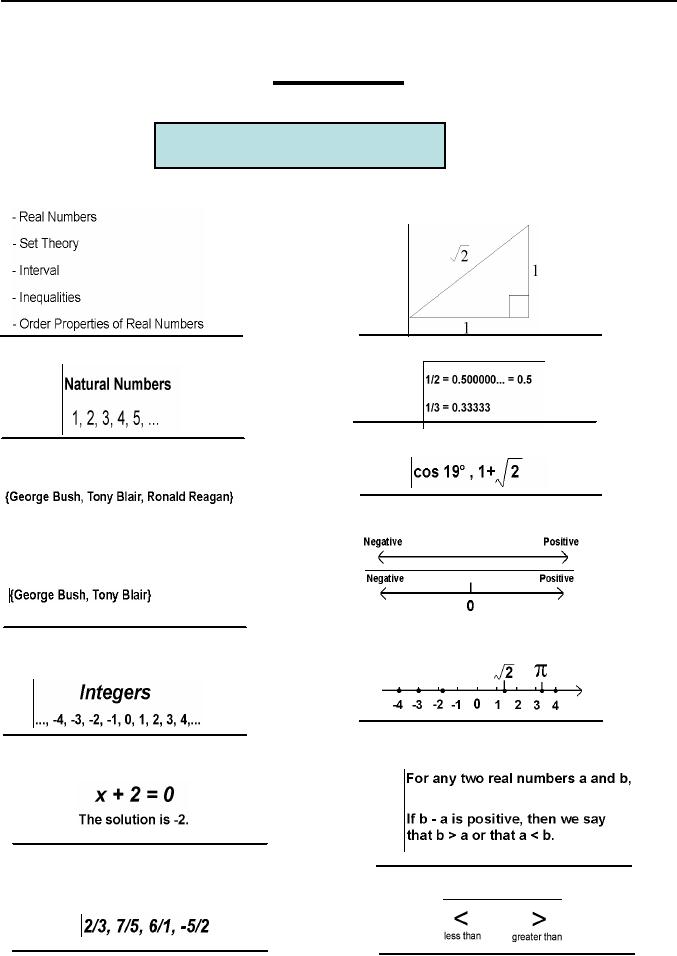
The
hypotenuse of this right
triangle can
In
this lecture we shall
be
expressed as the ratio of
integers.
discuss:
Decimal
representation of Rational
numbers
The
simplest numbers are
the
are
Some
examples of irrational numbers
are
The
collection of well defined
objects is
called
a
set . For example
Coordinate
lines
A
portion of a set B
is a subset of
A
iff
every member of B
is a
member
of
A. e.g. one
subset of above set
is
Example
Approximate
locations of some
The
natural numbers form a
subset of a
irrational
large
class of numbers called
the
numbers
Order
Example:
In this
equation
Property
The
integers in turn are a
subset of a still
larger
class
of numbers called the
rational numbers.
Here
are notations
The
examples of rational numbers
are
of
Mth101
Page
1
Calculus
and Analytical
Geometry
The
symbol
means
that a<b
With
the exception that division
by zero is
and
b<c
ruled
out, the rational numbers
are formed
The
symbol
means
that a<b
by
taking the ratios of
integers.
and
b<c
Similarly
you, the symbol
means
that a<b,b<c and
c<d
Coordinates,
Graphs and Lines
Here
are some examples of
some
When
it is inconvenient or
impossible
to list the members of a
set,
one
can use the set
builder notation:
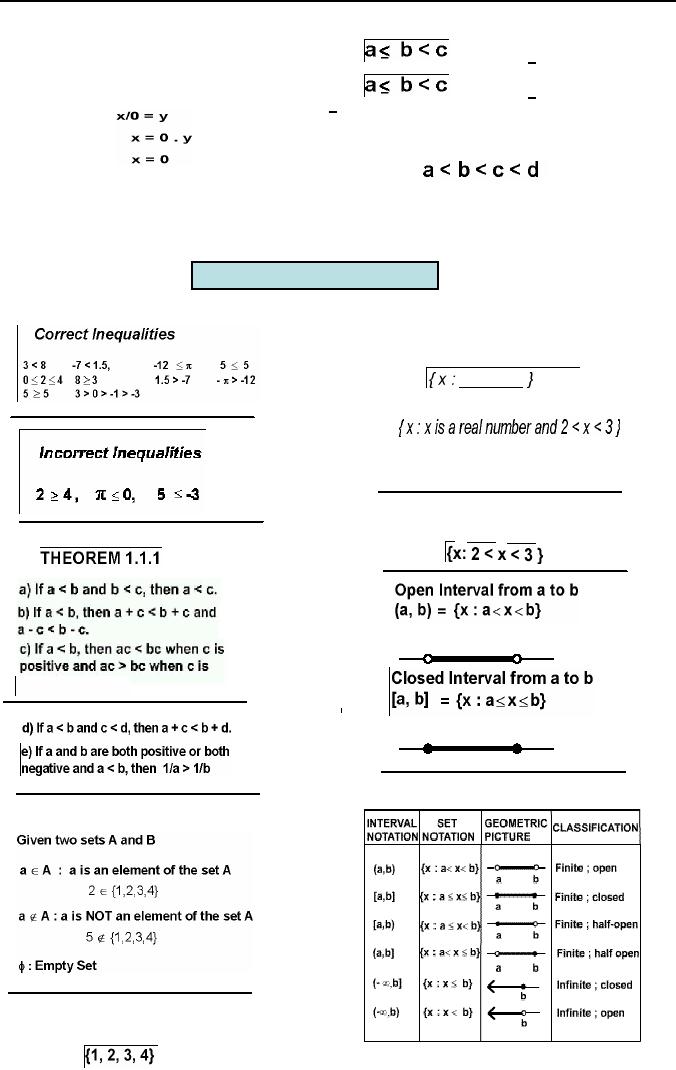
Thus
And
the
are
Is
read, "the set of all
such that x is a real
number
and 2<x<3".
The
proceeding set can be
written more
briefly
as
On
real line
a
b
negative.
On
real line
a
b
Table
1.1.3
Some
useful notations are
The
set of all positive integers
less than
5
can be written as
Mth101
Page
2
Calculus
and Analytical
Geometry
The
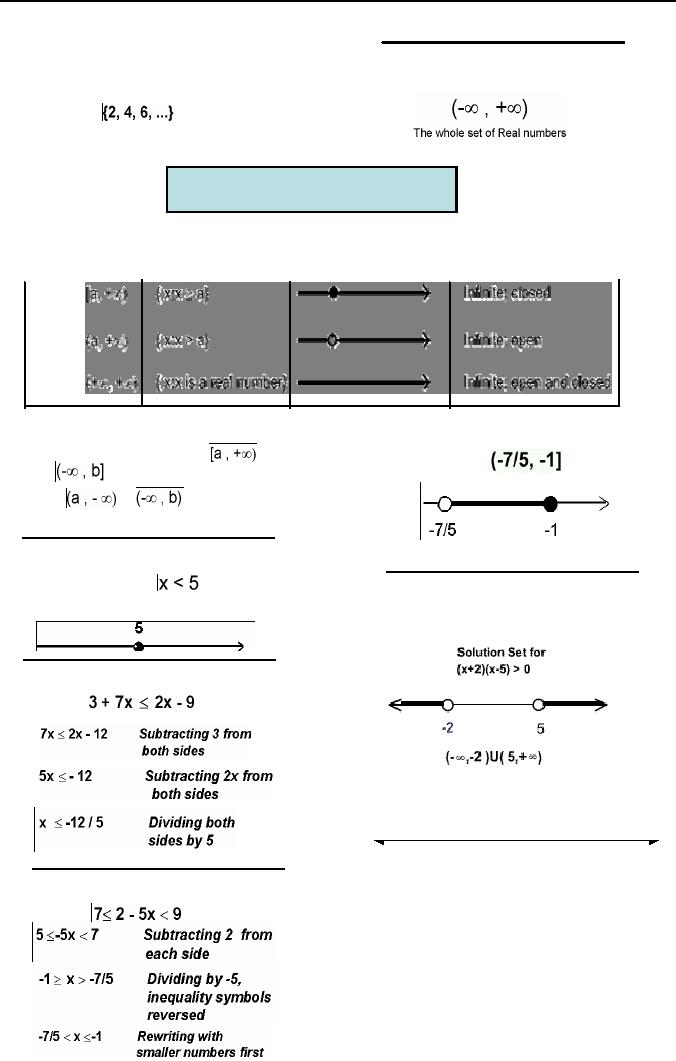
following interval has no
endpoints; it is
The
set of all positive even
integers can
regarded
to be both open and
closed.
be
written as
Coordinates,
Graphs and Lines
Interval
Set
Geometric
Picture
Classification
Table
1.1.3 (Continued)
On
real line,
is
shown as
The
infinite intervals of the
form
or
are
considered to be closed as
they
contain their endpoint and
those of the
form
or
are
considered to
be
open as they do not.
A
solution of an inequality in an
unknown
x
is a value for x that makes
the inequality
a
true statement e.g.
Means
all
Example
Values
of x less than 5 as shown in
the graph.
Similarly,
you can find
is
Example
Solve
Example
Solve
Mth101
Page
3
Table of Contents:
- Coordinates, Graphs and Lines
- Absolute Values
- Coordinate Planes and Graphs
- Line and Definition of Slope
- Distance, Circles, Quadratic Equations
- Functions and Limits
- Operations on Functions
- Graphs of Functions
- Limits (Intuitive Introduction)
- Limits and Computational Approach
- Limits: A Rigorous Approach
- Continuity
- Limit and Continuity of Trigonometric Functions
- Tangent Lines and Rates of Change
- The Derivative