 |
Data Transfer Service (DTS) |
| << Web Warehousing: Issues, Time-contiguous Log Entries, Transient Cookies, SSL, session ID Ping-pong, Persistent Cookies |
| Lab Data Set: Multi -Campus University >> |
Lab
Lect-2
Lab Data
Set
In previous
lecture I gave you an overview of
the tool to be used for
the lab i.e. Data
Transformation
Services (DTS), MS SQL
Server. Now keeping in view
the real issue of
data
acquisition, we
will provide you with a
simulated data set, so as to make
you ready to start
exploring
the tool. The data is
for a multi-campus university
having campuses in four
major
cities. We
discussed the details of
such a university in Lect-6 of the
course i.e. normalization.
Each of
the campus has its
own conventions and norms regarding
storing Student information.
Multi
-Campus University
�
University
has four campuses situated
at:
� Lahore
� Karachi
� Islamabad
� Peshawar
�
University
Head Office in
Islamabad
Data warehouse
is a single source of truth. We have to put
all data from different
data sources
(campuses) at
one place in some standard
form. The task is not
trivial. Different sources of
data
have a
lot of inherent issues of ETL.
High level steps given in
the slide give just an
overview of
the
task. First of all, we have to
identify the source systems.
It is quite possible that each
campus
uses
different database systems or
same organization at different
geographical locations
uses
different
database management systems. To put
data into a single source,
after extracting from
such diverse
sources, requires powerful
tools especially designed to
fulfill the requirements
of
ETL. We
will use Microsoft SQL Server
DTS which is a user friendly
graphical tool and
makes
such a
complex task doable by some
practice. After identification of source
systems, it is
necessary to
study the issues that
must be considered before
putting all the data
together at a
single
location. Microsoft SQL Server
provides a powerful support to
perform Extract,
Transform
and
Load (ETL) data from
source systems to destination
system. Finally certain
steps are
performed to
check and improve quality of
data.
In this lab
lecture we will look into
the data for each of
the campuses in detail. This
would lead us
to identify
the core issues that
are needed to be taken care
of before extracting data from
these
diverse sources
into a single
destination.
Degree
Programs
�
At each
campus university has two
degree programs:
� BS
� MS
�
University
started its BS degree
program in year 1994 and MS
degree program in
year
2001
Our
Example University offers
undergraduate and graduate
degrees in all of its
campuses. The
undergraduate
degrees were started in year 1994
and graduate degrees were
started in year 2001.
375
Disciplines
for BS
�
Four
disciplines at BS level
� Computer
Science (CS)
� Computer
Engineering (CE)
� System
Engineering (SE)
� Telecommunication
(TC)
�
All
campuses offer these four
disciplines
The
slide is self explanatory.
Disciplines
for MS
�
Four
disciplines at MS level
� Computer
Science (MS-CS)
� Software
Project Mgmt. (MS-SPM)
� Networking
(MS-NW)
� Telecommunication
(MS-TC)
�
Lahore & Karachi
campuses offer all the
four disciplines
�
Islamabad
offers MS-CS & MS-SPM
�
Peshawar
offers MS-CS & MS-TC
The
slide is self explanatory.
The
need
�
Four
campuses of the University maintain
their students record
locally
�
No standardized
way of record
management
�
Standardized
reporting is difficult and time
consuming.
�
No centralized
repository of data
�
Head
Office wants a central data
repository for decision support
i.e. a DWH
�
We will
study the record management
at each campus
�
In this
lecture, we will collect
data from each campus
and figure out the is
sues
As mentioned
earlier, our example university
has multiple campuses and
each campus
independently
maintains its student
records without any
meaningful level of coordination.
There
is no any
standardized record management system or
agreement among t hese
campuses. Each of
376

the
campuses uses its own
student record management practices
independent of the other
campuses.
The head office of the
university now wants to
consolidate the student
records from all
of the
four campuses into a central
repository for decision support. Thus
they are planning for
a
DWH.
Students
Record Keeping & Mgmt.
�
One by
one we discuss the record
management system specific to
each campus of the
University
1.
Lahore
2.
Karachi
3.
Islamabad
4.
Peshawar
In real
life when we need to work
with heterogeneous systems
from multiple sources then
the
problems
like poor design becomes
prominent and significant. In this
student record
management
system
none of the database is
properly designed and in
some cases, there is no
database at all.
The
databases are not
normalized. Each of the
campus maintains two "tables" to
store student
information. I
have used double quotes as the
word table is not used in
its literal meaning,
especially in
the case of a single flat
text file.
Student
Table:
In each
database Student table is
used to maintain personal records of
the students. This table
has
only
one entry for each
student in each campus. A
student may have entries in
student tables of
two
campuses in the issues like
transfer cases.
Registration
Table:
Second
table is registration table that
maintains the record for
course registration. This
table
contains as
many records for each
student as many times he/she
registered any
course.
Each
campus keeps two tables
does not mean that
each campus has two
files only (one for
each
table).
Each campus maintains its
information independent of each
other. Lahore campus
maintains
two text files for
each batch i.e. entry taken
in a year. For each batch
one file contains
student
information and other file
contains registration information. For
eleven batches of BS
Lahore
campus has 22 text files.
For four batches of MS
Lahore campus contains eight
text files.
Same is
the mechanism used in
Peshawar campus to store the
data in text files. Islamabad
campus
has MS
Access d atabase with three
tables. Two of these three
tables contain student
information.
One
table for MS and the other
for BS students. The third
table contains Registration data
for
both degree
programs i.e. MS and BS.
Karachi campus manages to store
all this information in
MS Excel
sheets. Three Excel Books
are maintained. Two out of
three contains
registration
records
(one for BS and the
other for MS) and
the third one contains
student records for
both
degree
programs.
Let us
discuss "student record
management systems" at each of
the campuses.
377

Data from
Lahore Campus
�
Data at Lahore
campus is stored in Text
files
�
To store
data regarding one complete
batch 2 text files are
used:
�
Lhr_Student_batch
(Student record)
�
Lhr_Detail_batch
(Course Reg. record)
�
22 text files
for 11 BS batches
�
8 text files
for 4 MS batches
The
slide is self explanatory. Here batch is
the year the student
entry was taken i.e.
94, 95,.... 104
i.e.
year 2004.
Data from
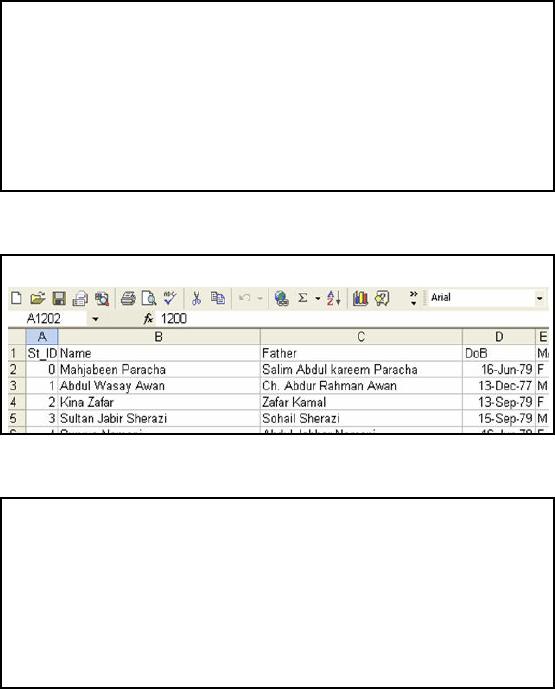
Lahore Campus: Sample
�
Flat
file student data at Lahore
campus
The
slide shows the screenshot
of a sample text file for
student records at Lahore
campus. We can
see
that the first row
contains the header and
the columns are delimited by
comma. Let's discuss
header of both
student and registration tables in
deta il.
Lahore:
Header of Student
Table
�
SID: Student
ID
� A numerical value,
starting from 0
� Starts
from 0 individually for both
degrees BS & MS
� It is unique
within a degree (BS/MS) but
not unique across the
degrees
� Combination of
SID and degree is always
unique within a campus
�
St_Name:
Student
name
�
Father_Name:
Father
name
378
The
slide is self explanatory.
Lahore:
Header of Student
Table
�
Gender:
� 0 for
Male
� 1 for
Female
�
Address:
Permanent
Address
�
[Date of
Birth]:
� 14-Apr-1980
�
[Reg
Date]: Date on
which student was
enrolled
This is
the convention used for
storing some critical data at
the Lahore campus. There is
no
guarantee
that the same convention
will be used at other campuses
too, actually in some cases
the
converse may be
true. We will identify and
work on these apparent
anomalies in the data
profiling
phase before we do the
actual transformation.
Lahore:
Header of Student
Table
�
[Reg
Status]:
� `A' if
student was enrolled as new
Admission
� `T' if
student was enrolled as
Transfer case
� [Degree
Status]:
� `C'
(complete) if student has
graduated
� `I' for
incomplete degree
� [Last
Degree]:
� F.Sc. / A
level for BS
� M.Sc. / BS
/ BE for MS
The
slide is self explanatory.
Lahore:
Header of Course Reg.
Table
�
SID:
�
Degree:
BS/MS
�
Semester:
e.g.
Fall04
�
Course:
Course
code
�
Marks:
Out of
100
�
Discipline:
CS/TC/SE/CE
The
slide shows the header
and sample values for Course
registration table at Lahore
Campus.
Lahore:
Facts About Dat a
�
Total
students = 5,200
�
Total
male students=
3,466
�
Total BS
students= 4,400
�
Number of
graduated students= 3,200
�
Number of
post graduated std.= 600
379
The
slide shows some of the
facts about Lahore campus.
These facts can be used
for data
validation in
later steps. However, this
has to be taken with a
"pinch of salt" because the
facts
before
resolving the data quality
issues will most likely be
different as compared to the
ones after
the
data has been
cleansed.
Data from
Karachi Campus
�
Data at
Karachi campus is stored in
MS-Excel books
�
Three
books are maintained
� STUDENT_KHR
(Student record)
� Reg_BS_KHR
(BS course Reg.
record)
� Reg_MS_KHR
(MS course Reg.
record)
�
STUDENT_KHR
keeps two sheets
� `BS'
for BS students
records
� `MS'
for MS students
records
The
slide is self explanatory.
Data from
Karachi Campus:
Sample
The slide
shows MS Excel screenshot of
the sample data for
Karachi campus. Let's
discuss its
header in detail
for both student and registration
tables.
Karachi:
Header of Student
Table
�
St_ID:
Student
identity
�
Name:
Student
name
�
Father:
Father
name
�
DoB:
Date of
Birth
�
M/F:
Gender
(M/F)
�
DoReg:
Date of
Registration/Enrollment
�
RStatus:
Status of
enrollment (A/T)
�
DStatus:
Status of
Degree (C/I)
�
Address:
Permanent
address
�
Qualification:
Last
degree achieved
380
The
slide is self explanatory.
Karachi:
Header of Course Reg.
Table
�
SID:
�
Courses:
Course
code
�
Score:
Out of
100
�
Sem:
e.g.
Fall04
�
Disp:
CS/TC/SE/CE
The
slide is self explanatory.
Karachi:
Facts About Data
�
Total
students = 6,000
�
Total
male students=
4,500
�
Total BS
students= 4,000
�
Number of
graduated students= 3,500
�
Number of
post graduated std.=
1,500
The slide
shows some of the facts
about Karachi campus. These
facts can be used for
data
validation in
later steps. Again we have to
look at the facts keeping in
mind that the same
may
change after
data has been
cleansed.
Data from
Islamabad Campus
�
M S-Access is
used at Islamabad
campus
�
Database
has three tables
� Isb_BS_Student
(MS Student record)
� Isb_MS_Student
(BS Student record)
� Registration
(All reg. record BS +
MS)
�
Roll number is
also used as primary key in
student table
The
slide is self explanatory.
Data from
Islamabad Campus:
Sample
381
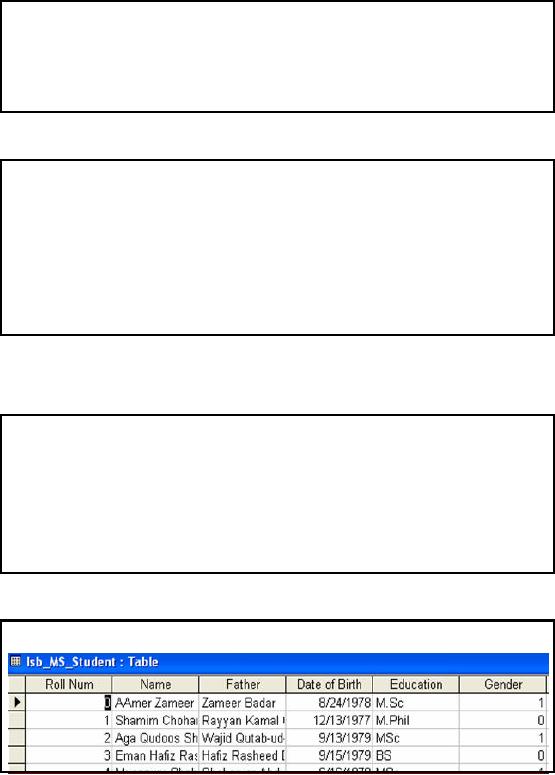
The
slide shows MS Access
screenshot of the sample
data for Islamabad campus.
Let's discuss its
header in detail
for both student and registration
tables.
Islamabad:
Header of Student
Table
�
Roll
Num: Student
identity
�
Name:
Student
name
�
Father:
Father
name
�
Reg
Date: Date of
Enrollment
�
Reg
Status: Status of
Enrollment (A/T)
�
Degree
Status: Status of
Degree (C/I)
�
Date of
Birth: Date of
Birth
�
Education:
Last
degree achieved
�
Gender:
Gender
(Male=1, Female =0)
�
Address:
Permanent
address
The
slide is self explanatory.
Islamaba d:
Header of Course Reg.
Table
�
Roll
Num:
�
Course:
Course
code
�
Marks:
Out of
100
�
Discipline:
CS/TC/SE/CE
�
Session:
e.g.
Fall04
Here we
can see that Degree (BS/MS)
is missing, whereas same
table contains records for
both.
Only way to
differentiate is through discipline attribute.
Islamabad:
Facts About Data
�
Total
students = 4,400
�
Total
male students=
3,700
�
Total BS
students= 3,200
�
Number of
graduated students= 2,500
�
Number of
post graduated std.= 900
The slide
shows some of the facts
about Islamabad campus.
These facts can be used
for data
validation in
later steps.
382
Data from
Peshawar Campus
�
Data at
Peshawar campus is stored in
Text files
�
To store
data regarding one complete
batch 2 text files are
used
� Lhr_Student_batch
(Student record)
� Lhr_Detail_batch
(Course Reg. record)
�
22 text files
for 11 BS batches
�
8 text files
for 4 MS batches
The
slide is self explanatory.
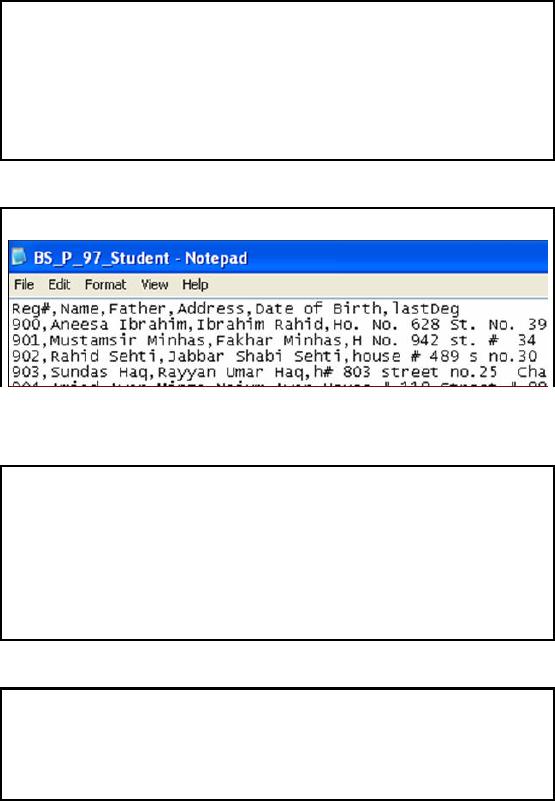
Data from
Peshawar Campus:
Sample
The slide
shows the screenshot of a
sample test file for
student records at Peshawar
campus. We
can
see that the first
row contains the header
and the columns are
delimited by comma. Let's
discuss
header of both student and registration
tables in detail.
Peshawar:
Header of Student
Table
�
Reg#: Student
identity
�
Name:
Student
name
�
Father:
Father
name
�
Address:
Permanent
address
�
Date of
Birth: Date of
Birth
�
lastDeg:
Last
degree achieved
�
Reg
Date: Date of
Enrollment
�
Reg
Status: Status of
Enrollment (A/T)
�
Degree
Status: Status of
Degree (C/I)
The
slide is self
explanatory.
Peshawar:
Header of Course Reg.
Table
�
Reg#:
�
Courses:
Course
code
�
Score:
Out of
100
�
Program:
CS/TC/SE/CE
�
Sem:
Fall/Spring
�
Year:
YYYY
e.g. 1999
383

Here we need to
identify semester session
(fall04) through combination of Sem and
Year
Lab
Exercise
�
Collect
demographics for Peshawar
campus
�
Figure out
problems in data at Peshawar
campus
�
Suggest
suitable solutions to the
problems identified above
Here is a small
exercise. You are required
to find the facts for
the Peshawar campus.
What
problems are
there in the data? And
what, in your opinion, could be
possible solutions for
those
problems.
Now by
looking at each of the
campus data individually, we
found following problems
that need
to be considered
and solved properly before
extracting the data and u
ltimately loading it into the
central
repository.
Problem-1:
Non-Standard data
sources
�
Each
campus uses data sources
independent of other
campuses
The major
problem is the inconsistent data
sources at different campuses.
The slide summarizes
the
data sources at four
campuses. We can see that
Lahore and Peshawar campuses
are using text
files
while Islamabad and Karachi
campuses are using MS Access
and MS Excel
respectively.
384
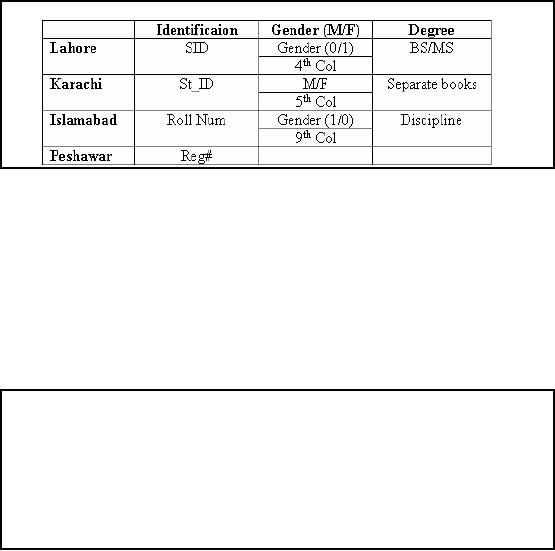
Problem-2:
Non-standard attributes
The
second problem is non standardized
attributes across campuses.
While looking at the
header
of data
from different campuses we
came to know the following
problems regarding attributes
and is
summarized in the table in
the slide.
Each of
the campuses uses different
attribute name for the
identification or primary keys
e.g.
Lahore uses
SID
while
Peshawar usesReg#
and so
on.
Different
conventions for representing
Gender across the campuses
e.g. Lahore campus uses
0/1
while
Islamabad uses 1/0 for
representing male and female
respectively.
Similarly,
there are different conventions
for representing degree attribute
across different
campuses.
Problem-3:
No Normalized database
�
None
of
the campuses uses well
designed normalized
database
�
Each
campus uses two
"tables":
� One
table to store students'
personal data
� Second
table to store course registration
data of each student
�
Each
campus uses multiple files
to store these two
tables
Actually Lahore,
Karachi and Peshawar campus
does not have databases at
all, so there is no
concept of
normalization. These campuses maintain
the data in sample shown as
follows:
Lhr_detail_94
: Is a
text file that contains
the following
details:
SID,Degree,Semester,Course,Marks,Discipline
Lhr_student_94: Is a text
file that contains the
following details:
SID,St_Name,Father_Name,Gender,Address,Date
of Birth,Last Degree _
385
Note
pad: Issues (1)
�
Use of
text files in record
management systems is least
suitable
�
We cannot
run any query on text
file
�
We cannot
validate any input to text
file
�
Comma is
used as a field separator,
any erroneous placement of
comma can spoil the
whole
record
�
There is no
technical way of locating any particular
record
Having
discussed the three major
problems, lets now look at
what are the issues
regarding the
record
management tools at individual
campuses. This slide and
the following four list the
issues
related to
Notepad.
Note
pad: Issues (2)
�
If I want to
locate the record of `Mohammad Ali
Nawaz' and I do not know his
roll
number,
what would I do?
�
At Lahore
campus, academic officer
used to do it by "Find" option of
text file
�
Is it a proper
way? Does it work
always?
� What
about `Mohamed Ali
Nawaz'?
People at
different campuses, including
the Lahore campus have developed ways
and means to
answer some
questions. But these so called
"techniques" have their own
inherent limitations. For
example, if I
want to find the information
about a student named `Mohammad
Ali Nawaz' I can
use
the find command from
the notepad, but what if there is a
slight change i the spelling? Of
n
course
the technique is not going to
work.
Note
pad: Issues (3)
�
If I want to
count total students who belong to
Multan, can I do it in note
pad?
� No
�
To achieve this
purpose, admin at Lahore used to
open the file in
Microsoft Word.
Then
use
"Replace with" functionality of
Microsoft Word to count
total occurrences of Multan.
In `Replace
With' dialog box if I enter
`Multan' is replaced with
`Multan' & use `Replace
All'
option. I can
get the total occurrences of
Multan. Interesting
Some
simple questions that can be
answered if there was a
database can not be answered,
such as
the number of
students from any particular
city. There can be number of
short -term self-
developed
ad-hoc mechanisms, but they
are not guaranteed to succeed
and have their own
inherent
limitations.
386
Note
pad: Issues (4)
�
Some improper
ways can work for
very limited cases
�
We can't
collect demographics in note
pad
� Total
number of male students
� Students
with a particular age
� Students
with a particular educational ba
ckground
� Students
with a particular CGPA
� Etc.
Some
very simple statistics can
not be collected in the
absence of a database as we have a big
text
file.
Some of the examples are
number of male students or students of
particular age. We can
get
answer to these
problems by parsing the
files, but text parsing is not
only very slow, but is
also
very
complicated. All these
complications and inefficiencies
can be reduced, and even
removed if
he had a
database in place.
MS -Excel:
Issues (1)
�
Karachi campus
uses MS-Excel sheets to maintain students
record
�
M S-Excel is
again not basically developed
for this purpose
�
However, it
works somewhat better than
note pad, as it can answer
to more questions but
once
again in an improper way
�
Both methods
adopted for notepad are
available here also but it
can work more than
that
MS Excel is
better than having a big
text file. For example
Excel supports some simple
tests and
other commands
that can help more
efficiently answer the
questions that could not be
answered
usin g a
plain text file. But, still
Excel is not the right way
to store and keep the
data for a host of
reasons,
that we discussed in Lect-6 of
the theory part.
MS -Excel :
Issues (2)
�
Now, I
can count total number of
male or female students?
�
I can
sort all columns on basis of
gender and get all
males and females
clustered
�
I can
get student-wise particular
scores
�
I can
get answers to many
questions through conditional queries
supported by MS-Excel
The
slides gives a way of
finding answer to some
questio ns, but remember
that we are dealing
with large
data sets, and for
such large sets comparison
sort which at best is O(n
log n) really
hurts.
387
MS -Excel :
Issues (3)
�
Maintenance of
records in MS-Excel is better
with respect to the data
quality concernin g
issues
�
M S-Excel
recognizes the correct data
type of columns
�
It somewhat
validates the input, i.e.
illegal input is
filtered
Some
more benefits of Excel. At
least there is a column type
i.e. not all values
are textual in
nature,
and this helps in the
context of data
validation.
MS -Access:
Issues (1)
�
M S-Access is a
proper RDBMS and can work
well for small
databases
�
At Islamabad
campus, the problem is the
poor design of database, not
the tool
�
SQL of
MS-Access is not very powerful,
like that of SQL Server, but it works
fine to
maintain
records at campus
level
Finally
Islamabad campus at least is
using the right tool
i.e. Access databases, but it works
for
small
personal databases not years of
data of a single campus and
then pooling together the d
ata
of multiple
campuses. Thus the problem is not of
the poor design (As
there is no real design) but
of the
wrong tool. The correct
choice could have been to
use MS SQL server which can
handle
larger work
loads more gracefully.
Problem
Statement
�
We have
disparate sources of
data
�
We have to
implement single source of truth i.e.
DWH, so that decision makers
can be
supported to
get detailed or summarized
university level view, irrespective of
particular
campus
�
In the
lab exercises and working we
will experience interesting
and complicated
issues
need to be
handled while moving towards
single standardized
source.
Thus, in
view of the issues and
challenges in our simulated
scenario of a multi-campus
university,
the
problem ahead can be
summarized as under.
There
are disparate and diverse
data sources and we have to
implement a DWH i.e. single
source
of truth that
can support the decision
making at the head
office.
388
Table of Contents:
- Need of Data Warehousing
- Why a DWH, Warehousing
- The Basic Concept of Data Warehousing
- Classical SDLC and DWH SDLC, CLDS, Online Transaction Processing
- Types of Data Warehouses: Financial, Telecommunication, Insurance, Human Resource
- Normalization: Anomalies, 1NF, 2NF, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
- De-Normalization: Balance between Normalization and De-Normalization
- DeNormalization Techniques: Splitting Tables, Horizontal splitting, Vertical Splitting, Pre-Joining Tables, Adding Redundant Columns, Derived Attributes
- Issues of De-Normalization: Storage, Performance, Maintenance, Ease-of-use
- Online Analytical Processing OLAP: DWH and OLAP, OLTP
- OLAP Implementations: MOLAP, ROLAP, HOLAP, DOLAP
- ROLAP: Relational Database, ROLAP cube, Issues
- Dimensional Modeling DM: ER modeling, The Paradox, ER vs. DM,
- Process of Dimensional Modeling: Four Step: Choose Business Process, Grain, Facts, Dimensions
- Issues of Dimensional Modeling: Additive vs Non-Additive facts, Classification of Aggregation Functions
- Extract Transform Load ETL: ETL Cycle, Processing, Data Extraction, Data Transformation
- Issues of ETL: Diversity in source systems and platforms
- Issues of ETL: legacy data, Web scrapping, data quality, ETL vs ELT
- ETL Detail: Data Cleansing: data scrubbing, Dirty Data, Lexical Errors, Irregularities, Integrity Constraint Violation, Duplication
- Data Duplication Elimination and BSN Method: Record linkage, Merge, purge, Entity reconciliation, List washing and data cleansing
- Introduction to Data Quality Management: Intrinsic, Realistic, Orr’s Laws of Data Quality, TQM
- DQM: Quantifying Data Quality: Free-of-error, Completeness, Consistency, Ratios
- Total DQM: TDQM in a DWH, Data Quality Management Process
- Need for Speed: Parallelism: Scalability, Terminology, Parallelization OLTP Vs DSS
- Need for Speed: Hardware Techniques: Data Parallelism Concept
- Conventional Indexing Techniques: Concept, Goals, Dense Index, Sparse Index
- Special Indexing Techniques: Inverted, Bit map, Cluster, Join indexes
- Join Techniques: Nested loop, Sort Merge, Hash based join
- Data mining (DM): Knowledge Discovery in Databases KDD
- Data Mining: CLASSIFICATION, ESTIMATION, PREDICTION, CLUSTERING,
- Data Structures, types of Data Mining, Min-Max Distance, One-way, K-Means Clustering
- DWH Lifecycle: Data-Driven, Goal-Driven, User-Driven Methodologies
- DWH Implementation: Goal Driven Approach
- DWH Implementation: Goal Driven Approach
- DWH Life Cycle: Pitfalls, Mistakes, Tips
- Course Project
- Contents of Project Reports
- Case Study: Agri-Data Warehouse
- Web Warehousing: Drawbacks of traditional web sear ches, web search, Web traffic record: Log files
- Web Warehousing: Issues, Time-contiguous Log Entries, Transient Cookies, SSL, session ID Ping-pong, Persistent Cookies
- Data Transfer Service (DTS)
- Lab Data Set: Multi -Campus University
- Extracting Data Using Wizard
- Data Profiling