 |
HISTORY OF QUALITY MANAGEMENT PARADIGMS |
| << WTO, SHIFTING FOCUS OF CORPORATE CULTURE AND ORGANIZATIONAL MODEL OF MANAGEMENT |
| DEFINING QUALITY, QUALITY MANAGEMENT AND LINKS WITH PROFITABILITY >> |
Total
Quality Management
MGT510
VU
Lesson
# 10
HISTORY
OF QUALITY MANAGEMENT
PARADIGMS
The
Evolution of Quality Approaches
The
shift to Total Quality
Management may be revolutionary
for many managers because
the tenets of
the
new paradigm are so
radically different from
past managerial practices. It
will require both a
thought
revolution
and a behavioral revolution. Approaches
to quality have evolved through a
series of gradual
refinements
over the last century. The
shift seems dramatic and
revolutionary to many
managers
because
they have not kept up with
the evolving approaches over the
years. However, they have
not
defined
their managerial roles in terms of the
latest advancements or they feel
skeptical about its
success.
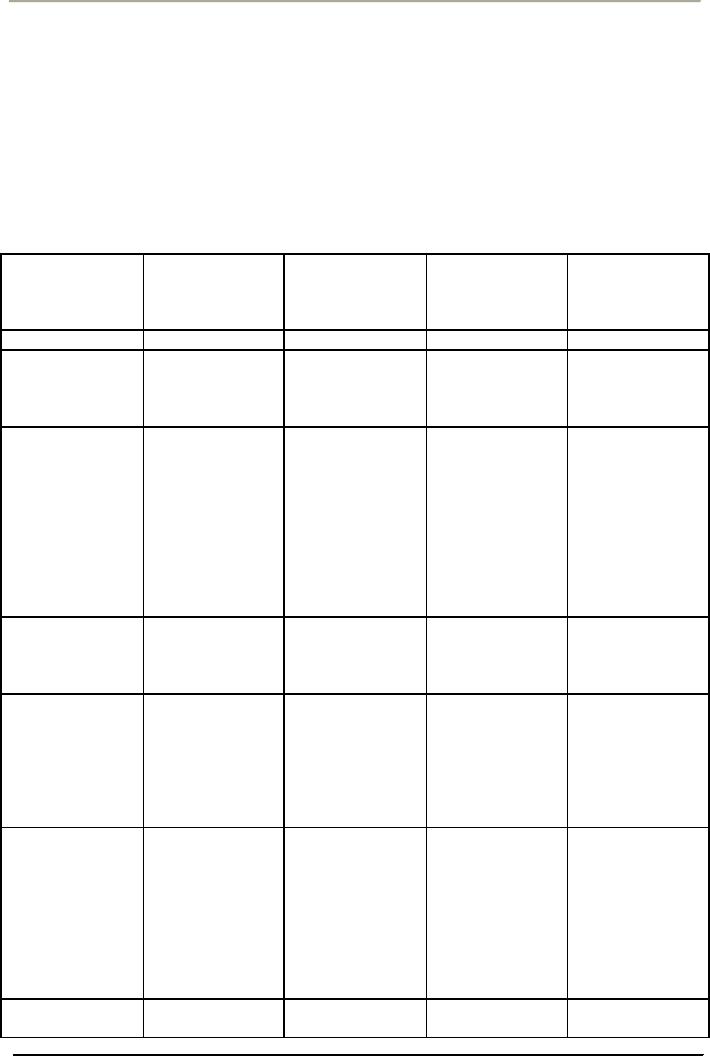
The
Four Major Quality
Eras
Identifying
Inspection
Statistical
Quality
Strategic
Total
Characteristics
(1800s)
Quality
Control
Assurance
Quality
Date
of inception
(1930s)
(1950s)
Management
(1980s)
Primary
concern
Detection
Control
Coordination
Strategic
impact
A
competitive
View
of quality
A
problem to be
A
problem to be
A
problem to be
opportunity
solved
solved
solved,
but one
that
is attacked
proactively
The
market and
Emphasis
Product
Product
uniformity The entire
consumer
needs
uniformity
with
reduced
production
chain,
inspection
from
design to
market,
and the
contribution
of all
functional
groups,
especially
designers,
to
preventing
quality
failures
Methods
Gauging
and
Statistical
tools
Programs
and
Strategic
planning,
measurement
and
techniques
systems
goal-setting,
and
mobilizing
the
organization
Role
of quality
Inspection,
Troubleshooting
Quality
Goal-setting,
professionals
sorting,
counting,
and
the application measurement,
education
and
and
grading
of
statistical
quality
planning,
training,
methods
and
program
consultative
work
design
with
other
departments,
and
program
design
Everyone
in the
Who
has
The
inspection
The
manufacturing All department,
organization,
with
responsibility
for
department
and
engineering
although
top
top
management
quality
departments
management
is
exercising
strong
only
peripherally
leadership
involved
in
designing,
planning,
and
executing
quality
policies
Orientation
and
"Inspects
in"
"Controls
in"
"Builds
in" quality "Manages
in"
approach
quality
quality
quality
34

Total
Quality Management
MGT510
VU
Customer-Craft
OR the Inspection Era
Until
the nineteenth century, skilled
craftsmen manufactured goods in small
volume. They handcrafted
and
fit together parts to form a
unique product that was
only informally inspected. Population
growth
and
industrialization brought about
production in larger volume.
Manufacturing in the
industrialized
world
tended to follow this craftsmanship model
till the factory system,
with its emphasis on
product
inspection,
started in Great Britain in
the mid-1750s and grew into
the Industrial Revolution in the
early
1800s.
The
factory system, a product of the
Industrial Revolution in Europe,
began to divide the craftsmen's
trades
into specialized tasks. This
forced craftsmen to become
factory workers and forced
shop owners
to
become production supervisors, and marked an
initial decline in employees'
sense of empowerment
and
autonomy in the workplace.
Quality
in the factory system was
ensured through the skill of laborers
supplemented by audits and/or
inspections.
Defective products were either reworked
or scrapped.
Mass
Production and Inspection
In
the 1800s, increased specialization,
division of labor, and mass
production required more
formal
inspection.
Parts had to be interchangeable. Inspectors
examined products to detect flaws
and separate
the
good from the bad. They used
gauges to catch deviant
parts and make sure parts
fit together at final
assembly.
The gauging system made
inspections more consistent than those
conducted solely by eye,
and
gave inspection a new
respectability.
Formalizing
the Inspection Function
By
the early 1900s, gauging had become more
refined, and inspection was even more
important. It was
prominent
in Henry Ford's moving
assembly line and Frederick
W. Taylor's system of shop
floor
management.
In 1922, G.S. Radford
formally linked inspection to
quality control. For the
first time,
quality
was regarded as an independent function
and a distinct management
responsibility. Radford
defined
quality in term of conformance to "established
requirements" and emphasized inspection.
He
also
suggested some lasting
quality principles, such as
getting designers involved
early, closely
coordinating
various departments, and achieving the
quality improvement results of
increased output
and
lower costs.
Late
in the 19th century the United
States broke further from
European tradition and adopted a
new
management
approach developed by Frederick W.
Taylor. Taylor's goal was to
increase productivity
without
increasing the number of skilled craftsmen. He achieved
this by assigning factory planning
to
specialized
engineers and by using craftsmen and supervisors,
who had been displaced by the growth
of
factories,
as inspectors and managers
who executed the engineers' plans.
Taylor's
approach led to remarkable rises in
productivity, but it had significant
drawbacks: Workers
were
once again stripped of their
dwindling power, and the new
emphasis on productivity had a
negative
effect on quality.
To
remedy the quality decline, factory
managers created inspection
departments to keep defective
products
from reaching customers. If
defective product did reach
the customer, it was more common
for
upper
managers to ask the inspector,
"Why did we let this get
out?" than to ask the
production manager,
"Why
did we make it this way to
begin with?"
Through
the 1920s, however, quality
control was most often
limited to inspection and
focused on
activities
such as counting, grading,
and rework, which is
antithetical to Total Quality
Management's
emphasis
on prevention to avoid defects.
Inspection departments and quality
professionals were not
35

Total
Quality Management
MGT510
VU
required
to troubleshoot, to understand and address the
causes of poor quality,
until the 1930s, with the
creation
of statistical quality
control.
In
the early 20th century, manufacturers
began to include quality
processes in quality practices.
After
the
United States entered World
War II, quality became a
critical component of the war effort:
Bullets
manufactured
in one place, for example, had to work
consistently in rifles made in
another. The armed
forces
initially inspected virtually every
unit of product; then to
simplify and speed up this
process
without
compromising safety, the military
began to use sampling techniques
for inspection, aided by
the
publication
of military-specification standards and
training courses in Walter
Shewhart's statistical
process
control techniques.
The
Statistical Quality Control
Era
In
1931, Walter A. Shewhart gave quality a
scientific footing with the
publication of his book
Economic
Control
of Quality of Manufactured Product. Shewhart
was one of a group of people at
Bell
Laboratories
investigating problems of quality. The
statistical quality control approach
that Shewhart
advocated
is based on his views of
quality. Statistical quality
control requires that numbers
derived from
measures
of processes or products be analyzed
according to a theory of variation
that links outcomes
to
uses.
Shewhart's
Views of Quality
Shewhart
offered a pragmatic concept of
quality: "The measure of
quality is a quantity which
may take
on
different numerical values. In other
words, the measure of quality, no mater
what the definition of
quality
may be, is a variable".
Shewhart's emphasis on measurement in
his definition of
quality
obviously
relates to his prescriptions
for statistical quality
control, which requires
numbers.
Shewhart
recognized that industrial processes
yield data. For example, a
process in which metal is
cut
into
sheets yields certain
measurements, such as each
sheet's length, height and
weight. Shewhart
determined
this data could be analyzed
using statistical techniques to see
whether a process is stable
and
in
control, or if it is being affected by
special causes that should be
fixed. In doing so, Shewhart
laid the
foundation
for control charts, a
modern-day quality
tool.
Shewhart's
concepts are referred to as
statistical quality control (SQC).
They differ from
product
orientation
in that they make quality
relevant not only for the
finished product but also
for the process
that
created it.
The
Quality Assurance Era
During
the quality assurance era, the
concept of quality in the United
States evolved from a
narrow,
manufacturing-based
discipline to one with implications
for management throughout a
firm. Statistics
and
manufacturing control remained important,
but coordination with other
areas, such as design,
engineering,
planning, and service activities,
also became important to
quality. While quality
remained
focused
on defect prevention, the quality
assurance era brought a more
proactive approach and
some
new
tools.
The
quality assurance era
significantly expanded the involvement of
all other functions through
total
quality
control, and inspired managers to
pursue perfection actively.
However, the approaches to
achieving
quality remained largely defensive.
Controlling quality still
meant acting on defects.
Quality
was
something that could hurt a
company if ignored, rather than a
positive characteristic necessary
in
obtaining
competitive advantage. This view
started to change in the 1970s
and 1980s, when
managers
started
to recognize the strategic importance of
quality.
36

Total
Quality Management
MGT510
VU
Total
Quality Control and Customer
Driven Quality
The
beginning of the 20th century marked the
inclusion of "processes" in quality
practices. A "process"
is
defined as a group of activities
that takes an input, adds
value to it and provides an
output, such as
when
a chef transforms a pile of ingredients
into a meal.
In
1956, Armand Feigenbaum extended this
principle by suggesting that high-quality
products are more
likely
to be produced through total quality
control than when
manufacturing works in
isolation:
The
underlying principle of this
total quality view. . . . is
that, to provide genuine
effectiveness,
control
must start with the design of the
product and end only when
the product has been
placed
in
the hands of a customer who
remains satisfied .. . . the first
principle to recognize is that
quality
is everybody's job.
The
birth of total quality in the
United States came as a
direct response to the quality
revolution in Japan
following
World War II. The Japanese
welcomed the input of Americans
Joseph M. Juran and W.
Edwards
Deming and rather than concentrating on
inspection, focused on improving
all organizational
processes
through the people who used
them.
Feigenbaum's
message reinforced Juran's
emphasis on managerial responsibility. To
make total quality
control
work, many companies
developed matrices or relationship
charts. These charts list
functions
(departments
or groups) across the top and required
activities down the side, and
shows responsibility
relationships
in each cell. The considerable
overlap among functions means
that cross-functional
teams
are
needed to ensure required
communication and collaboration, for
example, in assessing
the
"manufacturability"
of a design and debugging new
manufacturing techniques through pilot
runs.
Both
Juran and Feignebaum acknowledged that
statistical methods and manufacturing
control were still
important.
However, they also felt
total quality control would
require new management
skills to deal
with
areas such as new product
development and vendor selection.
Managers also would be
required to
engage
in activities such as quality
planning and coordinating
cross-functional teamwork. Despite
the
emphasis
on teamwork, Feigenbaum's TQC
suggests that more than half
of the primary responsibilities
for
quality belong to the quality
control department, another practice that is
antithetical to modern Total
Quality
Management.
W
Edwards Deming, a statistician with the
U.S. Department of Agriculture and
Census Bureau, became
a
proponent of Shewhart's SQC
methods and later became a leader of the
quality movement in both
Japan
and the United States.
The
Strategic Quality Management
Era
The
present quality era, Strategic
Quality Management, incorporates elements
of each of the preceding
eras,
particularly the contributions of Shewhart,
Deming, Juran, and Feigenbaum. So many
elements of
previous
eras are incorporated into
Strategic Quality Management that the
last two decades may at
first
appear
to be just a repackaging of old
ideas. There are, however,
dramatic differences from
earlier eras.
For
the first time, top managers
began to view quality
positively as a competitive advantage, and
to
address
it in their strategic planning processes,
which are focused on
customer value.
Because
quality started to attract the attention
of top managers, it impacted management
throughout the
organization.
Quality was not just
for the inspectors or people in the
quality assurance department to
worry
about. This era marks the
emergence of a new paradigm
for management. A number of
developments
were brought together and reconfigured
into a new approach to management in
all
departments
and specialties.
A
variety of external forces
brought quality to the attention of
top managers. They began to
see a link
between
losses of profitability and poor
quality. The forces that
brought this connection to
their
37

Total
Quality Management
MGT510
VU
attention
included a rising tide of
multimillion-dollar product liability
suits for defective products
and
constant
pressures from the government on several
fronts, including closer
policing of defects,
product
recalls.
Perhaps the most salient
external force was the
growing market share incursions
from foreign
competitors,
particularly the Japanese, in such
diverse industries as semiconductors,
automobiles,
machine
tools, radial tires, and
consumer electronics.
Producing
products with superior quality,
lower cost, and more reliable
delivery, Japanese firms
gained
market
shares and achieved immense
profitability. The onslaught of
these events in the mid-1970s
and
1980s
seemed rather sudden,
However, Japanese firm had
been building their
industrial capabilities
for
decades,
developing and refining approaches to
quality grounded in the principles
taught to them by
Americans
after World War II. Manager
and theorists have been captivated by
"Japanese management"
over
the last two decades. Indeed, the
Strategic Quality Management era
borrows a number of it
elements
from the developments that quality
took place in Japan at the same
time as the quality
assurance
era in the United
States.
Total
Quality Management
Just
as the definition of quality has
been a source of confusion, so
has the definition of Total
Quality
Management.
There is no consensus on what constitutes
TQM. Almost every
organization defines it
differently
or calls it something other than
TQM.
In
the United States, Total
Quality Management is often
used to refer to the management
approaches
being
developed in the current era of Strategic
Quality Management while the
new paradigm is
emerging.
Ideally, managers in the Strategic
Quality Management era regard
total Quality
management
as
something more than a "program," and
take it beyond all the
deficiencies mentioned
earlier.
In
this context, the word
"Total" conveys the idea that
all employees, throughout every
function and
level
of an organization, pursue quality.
The word "quality" suggests
excellence in every aspect of the
organization.
"Management" refers to the pursuit of
quality results through a
quality management
process.
This begins with strategic management
processes and extends through
product design,
manufacturing,
marketing, finance, and so on. It
encompasses, yet goes
beyond, all of the
earlier
definitions
of quality by puling them together
into a never-ending process of
improvement.
Accordingly,
TQM is as much about the quality
process as it is about quality
results or quality products.
It
began with people,
particularly managers.
38
Table of Contents:
- OVERVIEW OF QUALITY MANAGEMENT:PROFESSIONAL MANAGERIAL ERA (1950)
- TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT AND TOTAL ORGANIZATION EXCELLENCE:Measurement
- INTEGRATING PEOPLE AND PERFORMANCE THROUGH QUALITY MANAGEMENT
- FUNDAMENTALS OF TOTAL QUALITY AND RATERS VIEW:The Concept of Quality
- TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT AND GLOBAL COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE:Customer Focus
- TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT AND PLANNING FOR QUALITY AT OFFICE
- LEADERS IN QUALITY REVOLUTION AND DEFINING FOR QUALITY:User-Based
- TAGUCHI LOSS FUNCTION AND QUALITY MANAGEMENT
- WTO, SHIFTING FOCUS OF CORPORATE CULTURE AND ORGANIZATIONAL MODEL OF MANAGEMENT
- HISTORY OF QUALITY MANAGEMENT PARADIGMS
- DEFINING QUALITY, QUALITY MANAGEMENT AND LINKS WITH PROFITABILITY
- LEARNING ABOUT QUALITY AND APPROACHES FROM QUALITY PHILOSOPHIES
- TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT THEORIES EDWARD DEMING’S SYSTEM OF PROFOUND KNOWLEDGE
- DEMING’S PHILOSOPHY AND 14 POINTS FOR MANAGEMENT:The cost of quality
- DEMING CYCLE AND QUALITY TRILOGY:Juran’s Three Basic Steps to Progress
- JURAN AND CROSBY ON QUALITY AND QUALITY IS FREE:Quality Planning
- CROSBY’S CONCEPT OF COST OF QUALITY:Cost of Quality Attitude
- COSTS OF QUALITY AND RETURN ON QUALITY:Total Quality Costs
- OVERVIEW OF TOTAL QUALITY APPROACHES:The Future of Quality Management
- BUSINESS EXCELLENCE MODELS:Excellence in all functions
- DESIGNING ORGANIZATIONS FOR QUALITY:Customer focus, Leadership
- DEVELOPING ISO QMS FOR CERTIFICATION:Process approach
- ISO 9001(2000) QMS MANAGEMENT RESPONSIBILITY:Issues to be Considered
- ISO 9001(2000) QMS (CLAUSE # 6) RESOURCES MANAGEMENT:Training and Awareness
- ISO 9001(2000) (CLAUSE # 7) PRODUCT REALIZATION AND CUSTOMER RELATED PROCESSES
- ISO 9001(2000) QMS (CLAUSE # 7) CONTROL OF PRODUCTION AND SERVICES
- ISO 9001(2000) QMS (CLAUSE # 8) MEASUREMENT, ANALYSIS, AND IMPROVEMENT
- QUALITY IN SOFTWARE SECTOR AND MATURITY LEVELS:Structure of CMM
- INSTALLING AN ISO -9001 QM SYSTEM:Implementation, Audit and Registration
- CREATING BUSINESS EXCELLENCE:Elements of a Total Quality Culture
- CREATING QUALITY AT STRATEGIC, TACTICAL AND OPERATIONAL LEVEL
- BIG Q AND SMALL q LEADERSHIP FOR QUALITY:The roles of a Quality Leader
- STRATEGIC PLANNING FOR QUALITY AND ADVANCED QUALITY MANAGEMENT TOOLS
- HOSHIN KANRI AND STRATEGIC POLICY DEPLOYMENT:Senior Management
- QUALITY FUNCTION DEPLOYMENT (QFD) AND OTHER TOOLS FOR IMPLEMENTATION
- BASIC SQC IMPROVEMENT TOOLS:TOTAL QUALITY TOOLS DEFINED
- HOW QUALITY IS IMPLEMENTED? A DIALOGUE WITH A QUALITY MANAGER!
- CAUSE AND EFFECT DIAGRAM AND OTHER TOOLS OF QUALITY:Control Charts
- STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL (SPC) FOR CONTINUAL QUALITY IMPROVEMENT
- STATISTICAL PROCESS CONTROL….CONTD:Control Charts
- BUILDING QUALITY THROUGH SPC:Types of Data, Defining Process Capability
- AN INTERVIEW SESSION WITH OFFICERS OF A CMMI LEVEL 5 QUALITY IT PAKISTANI COMPANY
- TEAMWORK CULTURE FOR TQM:Steering Committees, Natural Work Teams
- UNDERSTANDING EMPOWERMENT FOR TQ AND CUSTOMER-SUPPLIER RELATIONSHIP
- CSR, INNOVATION, KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT AND INTRODUCING LEARNING ORGANIZATION