 |
Strategic
Management MGT603
VU
Lesson
28
BOSTON
CONSULTING GROUP (BCG)
MATRIX
Learning
objective
After
understanding this chapter you are
able to understand BCG and
IE matrices and also
understand
how
to prepare these matrices
for any organization and what
its practical implementation in
various
organizations.
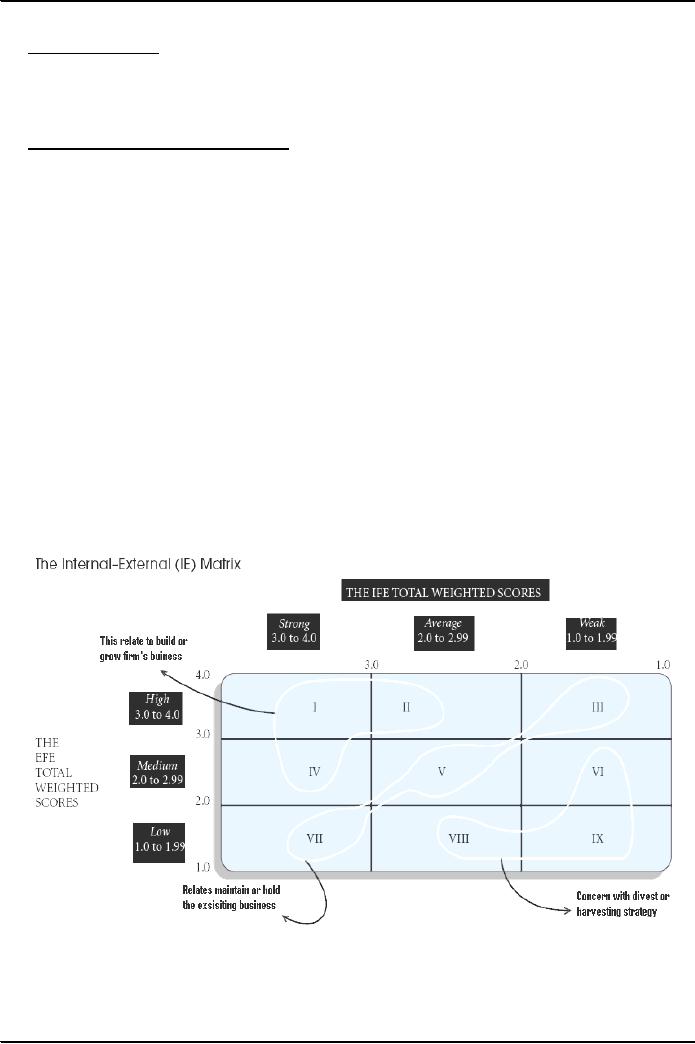
The
Internal-External (IE)
Matrix
This
is also an important matrix of
matching stage of strategy
formulation. This matrix already
explains
earlier.
It relate to internal (IFE)
and external factor evaluation (EFE).
The findings form internal
and
external
position and weighted score
plot on it. It contains nine
cells. Its characteristics is a s
follow
�
Positions
an organization's various divisions in a nine-cell
display.
�
Similar
to BCG Matrix except the IE
Matrix:
o
Requires
more information about the
divisions
o
Strategic
implications of each matrix are
different
�
Based
on two key dimensions
o
The
IFE total weighted scores on the
x-axis
o
The
EFE total weighted scores on the
y-axis
�
Divided
into three major
regions
o
Grow
and build Cells I, II, or
IV
o
Hold
and maintain Cells III, V, or
VII
o
Harvest or
divest Cells VI, VIII, or IX
105

Strategic
Management MGT603
VU
Steps
for the development of IE
matrix
1.
Based on two key dimensions
IFE and EFE.
2.
Plot IFE total weighted
scores on the x-axis
and the EFE total weighted
scores on the y
axis
3.
On the x-axis
of the IE Matrix, an IFE total
weighted score of 1.0 to
1.99 represents a
weak
internal
position; a score of 2.0 to
2.99 is considered average;
and a score of 3.0 to 4.0 is
strong.
4.
On the y-axis,
an EFE total weighted score of
1.0 to 1.99 is considered
low; a score of 2.0 to 2.99
is
medium;
and a score of 3.0 to 4.0 is
high.
5.
IE Matrix divided into three
major regions.
Grow
and build Cells I, II, or
IV
Hold
and maintain Cells III, V, or
VII
Harvest
or divest Cells VI, VIII, or
IX
106
Table of Contents:
- NATURE OF STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT:Interpretation, Strategy evaluation
- KEY TERMS IN STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT:Adapting to change, Mission Statements
- INTERNAL FACTORS & LONG TERM GOALS:Strategies, Annual Objectives
- BENEFITS OF STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT:Non- financial Benefits, Nature of global competition
- COMPREHENSIVE STRATEGIC MODEL:Mission statement, Narrow Mission:
- CHARACTERISTICS OF A MISSION STATEMENT:A Declaration of Attitude
- EXTERNAL ASSESSMENT:The Nature of an External Audit, Economic Forces
- KEY EXTERNAL FACTORS:Economic Forces, Trends for the 2000’s USA
- EXTERNAL ASSESSMENT (KEY EXTERNAL FACTORS):Political, Governmental, and Legal Forces
- TECHNOLOGICAL FORCES:Technology-based issues
- INDUSTRY ANALYSIS:Global challenge, The Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM)
- IFE MATRIX:The Internal Factor Evaluation (IFE) Matrix, Internal Audit
- FUNCTIONS OF MANAGEMENT:Planning, Organizing, Motivating, Staffing
- FUNCTIONS OF MANAGEMENT:Customer Analysis, Product and Service Planning, Pricing
- INTERNAL ASSESSMENT (FINANCE/ACCOUNTING):Basic Types of Financial Ratios
- ANALYTICAL TOOLS:Research and Development, The functional support role
- THE INTERNAL FACTOR EVALUATION (IFE) MATRIX:Explanation
- TYPES OF STRATEGIES:The Nature of Long-Term Objectives, Integration Strategies
- TYPES OF STRATEGIES:Horizontal Integration, Michael Porter’s Generic Strategies
- TYPES OF STRATEGIES:Intensive Strategies, Market Development, Product Development
- TYPES OF STRATEGIES:Diversification Strategies, Conglomerate Diversification
- TYPES OF STRATEGIES:Guidelines for Divestiture, Guidelines for Liquidation
- STRATEGY-FORMULATION FRAMEWORK:A Comprehensive Strategy-Formulation Framework
- THREATS-OPPORTUNITIES-WEAKNESSES-STRENGTHS (TOWS) MATRIX:WT Strategies
- THE STRATEGIC POSITION AND ACTION EVALUATION (SPACE) MATRIX
- THE STRATEGIC POSITION AND ACTION EVALUATION (SPACE) MATRIX
- BOSTON CONSULTING GROUP (BCG) MATRIX:Cash cows, Question marks
- BOSTON CONSULTING GROUP (BCG) MATRIX:Steps for the development of IE matrix
- GRAND STRATEGY MATRIX:RAPID MARKET GROWTH, SLOW MARKET GROWTH
- GRAND STRATEGY MATRIX:Preparation of matrix, Key External Factors
- THE NATURE OF STRATEGY IMPLEMENTATION:Management Perspectives, The SMART criteria
- RESOURCE ALLOCATION
- ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE:Divisional Structure, The Matrix Structure
- RESTRUCTURING:Characteristics, Results, Reengineering
- PRODUCTION/OPERATIONS CONCERNS WHEN IMPLEMENTING STRATEGIES:Philosophy
- MARKET SEGMENTATION:Demographic Segmentation, Behavioralistic Segmentation
- MARKET SEGMENTATION:Product Decisions, Distribution (Place) Decisions, Product Positioning
- FINANCE/ACCOUNTING ISSUES:DEBIT, USES OF PRO FORMA STATEMENTS
- RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT ISSUES
- STRATEGY REVIEW, EVALUATION AND CONTROL:Evaluation, The threat of new entrants
- PORTER SUPPLY CHAIN MODEL:The activities of the Value Chain, Support activities
- STRATEGY EVALUATION:Consistency, The process of evaluating Strategies
- REVIEWING BASES OF STRATEGY:Measuring Organizational Performance
- MEASURING ORGANIZATIONAL PERFORMANCE
- CHARACTERISTICS OF AN EFFECTIVE EVALUATION SYSTEM:Contingency Planning