 |

Strategic
Management MGT603
VU
Lesson
24
THREATS-OPPORTUNITIES-WEAKNESSES-STRENGTHS
(TOWS) MATRIX
Learning
object
After
understanding this chapter you are
able to understand TWOS
matrix and also understand
how to scan
internal
and external environment of the
organization
The
Threats-Opportunities-Weaknesses-Strengths (TOWS)
Matrix
The
Threats-Opportunities-Weaknesses-Strengths
(TOWS) is
also named as SWOT analysis.
A TWOS Analysis is
a
strategic
planning tool
used to evaluate the Threats,
Opportunities and Strengths,
Weaknesses, involved in
a
project
or
in a business
venture
or in any other situation
requiring a decision.
This
is an important tool in order to
formulate strategy. This Matrix is an
important matching tool
that
helps
managers develops four types
of strategies: SO Strategies (strength-opportunities),
WO Strategies
(weakness-
opportunities), ST Strategies
(strength-threats), and WT Strategies
(weakness-threats).The most
difficult
part of TOWS matrix is to
match internal and external
factor.
Once
the objective has been identified,
TOWS are discovered and
listed. TOWS are defined
precisely as
follows:
Strengths
are
attributes of the organization that are
helpful to the achievement of the
objective.
Weaknesses
are
attributes of the organization that are
harmful to the achievement of the
objective.
Opportunities
are
external conditions that are
helpful to the achievement of the
objective.
Threats
are
external conditions that are
harmful to the achievement of the
objective.
Strengths
and weaknesses are internal factors.
For
example, strength could be your
specialist marketing
expertise.
A weakness could be the lack of a new
product.
Opportunities
and threats are external
factors. For
example, an opportunity could be a
developing
distribution
channel such as the Internet, or
changing consumer lifestyles
that potentially increase
demand
for
a company's products. A threat could be a
new competitor in an important existing
market or a
technological
change that makes existing
products potentially
obsolete.
it
is worth pointing out that
SWOT analysis can be very
subjective - two people rarely
come-up with the
same
version of a SWOT analysis even when
given the same information about the same
business and its
environment.
Accordingly, SWOT analysis is
best used as a guide and
not a prescription. Adding
and
weighting
criteria to each factor increases the
validity of the analysis.
SO
Strategies: Every
firm desires to obtain
benefit form its resources
such benefit can only be
obtained if
utilize
its strength to take external
opportunity. Resources (Assets) an
important firm's strength to
get
opportunity
for external resources. For
example the firm enjoying a
good financial position which
is
strength
for a firm and externally
opportunity to expand business.
The strong financial position provides
an
opportunity
to expand the business. The
matched strategy is known as SO
strategy.
WO
Strategies:
WO
Strategies developed to match weakness
with opportunities of the firm. WO
strategy is very useful if
the
firm take advantage to external
resources in order to overcome the
weakness. For example the
firm is in
the
critical financial problems that is
weakness and firm is availing
merger with Multinational
Corporation.
ST
Strategies
ST
Strategies is an important strategy to
overcome external threats. This does
not mean that a
strong
organization
should always meet threats in the
external environment head-on. This
strategy is adopted by
various
colleges by opening new
branches in order to overcome
competitive thereat. These
threats also
explain
by the Porter in its competitive
model.
98
Strategic
Management MGT603
VU
WT
Strategies
Every
firm has a desire to
overcome its weakness and
reducing threats. This type of
strategy helpful when
weaknesses
are removed to overcome external
threats. It is difficult to target WT
strategy. For example
weak
distribution network creating
many problems for the firm
if it strong many external threats
can be
removed.
Steps
for developing
strategies:
There
are eight steps involved in constructing
a TOWS Matrix:
1.
Rank external opportunities
2.
Rank external threats
3.
Rank internal
strength
4.
Rank internal
weaknesses.
5.
Match internal strengths
with external opportunities and
mention the result in the SO
Strategies
cell.
6.
Match internal weaknesses
with external opportunities and
mention the result in the WO
Strategies
cell..
7.
Match internal strengths
with external threats and
mention the result in the ST Strategies
cell.
8.
Match internal weaknesses
with external threats and
mention the result in the WT strategies
cell.
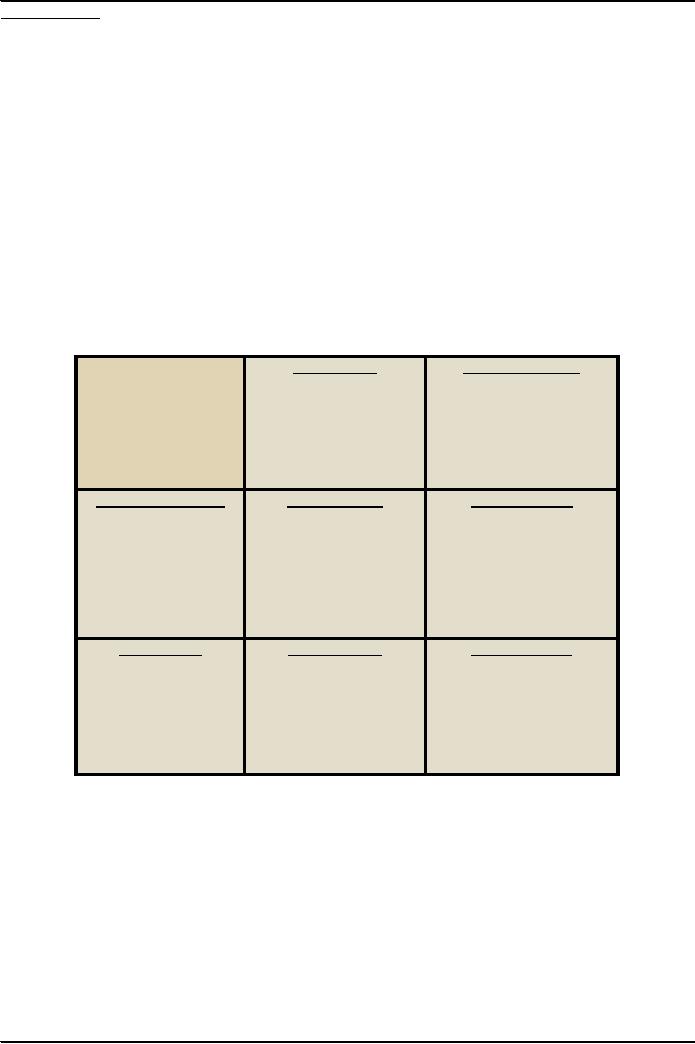
StrengthsS
Weaknesses
W
List
Weaknesses
List
Strengths
Blank
Opportunities
O
SO-Strategies
WO-Strategies
List
Opportunities
Use
strength to obtain
Overcome
weaknesses by
opportunities
taking
advantage of
opportunities
Threats
T
ST-Strategies
WT-Strategies
List
Threats
Use
strengths to avoid
Minimize
weaknesses and
threats
avoid
threats
99
Table of Contents:
- NATURE OF STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT:Interpretation, Strategy evaluation
- KEY TERMS IN STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT:Adapting to change, Mission Statements
- INTERNAL FACTORS & LONG TERM GOALS:Strategies, Annual Objectives
- BENEFITS OF STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT:Non- financial Benefits, Nature of global competition
- COMPREHENSIVE STRATEGIC MODEL:Mission statement, Narrow Mission:
- CHARACTERISTICS OF A MISSION STATEMENT:A Declaration of Attitude
- EXTERNAL ASSESSMENT:The Nature of an External Audit, Economic Forces
- KEY EXTERNAL FACTORS:Economic Forces, Trends for the 2000’s USA
- EXTERNAL ASSESSMENT (KEY EXTERNAL FACTORS):Political, Governmental, and Legal Forces
- TECHNOLOGICAL FORCES:Technology-based issues
- INDUSTRY ANALYSIS:Global challenge, The Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM)
- IFE MATRIX:The Internal Factor Evaluation (IFE) Matrix, Internal Audit
- FUNCTIONS OF MANAGEMENT:Planning, Organizing, Motivating, Staffing
- FUNCTIONS OF MANAGEMENT:Customer Analysis, Product and Service Planning, Pricing
- INTERNAL ASSESSMENT (FINANCE/ACCOUNTING):Basic Types of Financial Ratios
- ANALYTICAL TOOLS:Research and Development, The functional support role
- THE INTERNAL FACTOR EVALUATION (IFE) MATRIX:Explanation
- TYPES OF STRATEGIES:The Nature of Long-Term Objectives, Integration Strategies
- TYPES OF STRATEGIES:Horizontal Integration, Michael Porter’s Generic Strategies
- TYPES OF STRATEGIES:Intensive Strategies, Market Development, Product Development
- TYPES OF STRATEGIES:Diversification Strategies, Conglomerate Diversification
- TYPES OF STRATEGIES:Guidelines for Divestiture, Guidelines for Liquidation
- STRATEGY-FORMULATION FRAMEWORK:A Comprehensive Strategy-Formulation Framework
- THREATS-OPPORTUNITIES-WEAKNESSES-STRENGTHS (TOWS) MATRIX:WT Strategies
- THE STRATEGIC POSITION AND ACTION EVALUATION (SPACE) MATRIX
- THE STRATEGIC POSITION AND ACTION EVALUATION (SPACE) MATRIX
- BOSTON CONSULTING GROUP (BCG) MATRIX:Cash cows, Question marks
- BOSTON CONSULTING GROUP (BCG) MATRIX:Steps for the development of IE matrix
- GRAND STRATEGY MATRIX:RAPID MARKET GROWTH, SLOW MARKET GROWTH
- GRAND STRATEGY MATRIX:Preparation of matrix, Key External Factors
- THE NATURE OF STRATEGY IMPLEMENTATION:Management Perspectives, The SMART criteria
- RESOURCE ALLOCATION
- ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE:Divisional Structure, The Matrix Structure
- RESTRUCTURING:Characteristics, Results, Reengineering
- PRODUCTION/OPERATIONS CONCERNS WHEN IMPLEMENTING STRATEGIES:Philosophy
- MARKET SEGMENTATION:Demographic Segmentation, Behavioralistic Segmentation
- MARKET SEGMENTATION:Product Decisions, Distribution (Place) Decisions, Product Positioning
- FINANCE/ACCOUNTING ISSUES:DEBIT, USES OF PRO FORMA STATEMENTS
- RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT ISSUES
- STRATEGY REVIEW, EVALUATION AND CONTROL:Evaluation, The threat of new entrants
- PORTER SUPPLY CHAIN MODEL:The activities of the Value Chain, Support activities
- STRATEGY EVALUATION:Consistency, The process of evaluating Strategies
- REVIEWING BASES OF STRATEGY:Measuring Organizational Performance
- MEASURING ORGANIZATIONAL PERFORMANCE
- CHARACTERISTICS OF AN EFFECTIVE EVALUATION SYSTEM:Contingency Planning