 |
SME
Management (MGT-601)
VU
Lesson
25
Working
capital management or current asset
management is one of the most
important aspects of
overall
financial
management in an enterprise. It is
basically concerned with the
management of current assets
and
current
liabilities and inter relationship
between them.
MEANING
OF WORKING CAPITAL
Working
capital is the amount of funds needed by an
enterprise to finance its day to
day operation. It is the
part
of capital employed in short-term
operation such as raw
materials, semi finished
products, sundry
debtors.
Because
of its variable nature, the working
capital is also referred to as circulating
capital. It may be
pointed
out
that the total working
capital is composed of two
parts.
1)
Regular Capital
2)
Variable Capital
Regular
Working capital is required for
permanent investment in any business
for holing certain
minimum
quantity
of raw material, finished
product or cash. Such investment is
irreducible minimum and
remains
permanently
sunk into business.
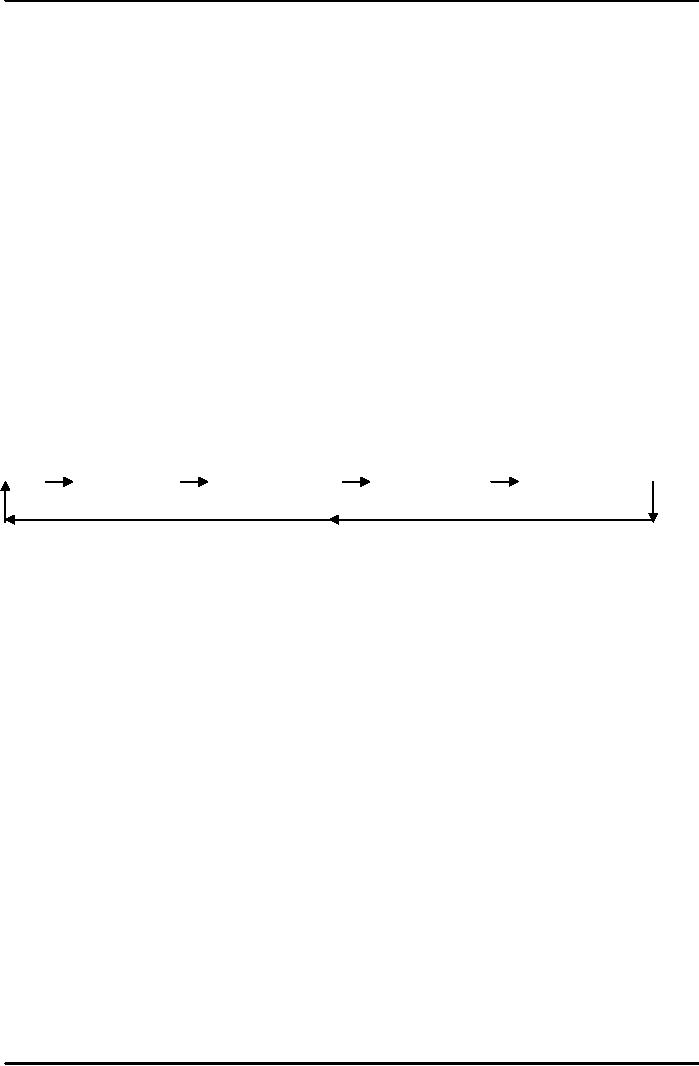
The
remaining portion of working capital is
variable. The variable portion
first gets tied up into
raw
materials
which are then converted
into finished goods. On the
sale of goods it gets converted
into account
receivables
or cash and circle is then
completed. It is depicted in following
figure.
Cash
Raw
Material
Stock
in Process
Finished
Goods
Bills
Receivable
Working
Capital Cycle
"Different
Senses of "Working
Capital"
The
term working capital is usually
used in two different senses
namely.
1)
Gross Working
Capital
2)
Net Working
Capital
Gross
Working Capital
It
represents total value of current
assets. In other words, it is the
sum total of net working
capital and
current
liabilities. It is a quantities concept showing the
total amount available for
financing the current
assets.
It cannot reveal the true position of the
company. For instance, every
increase in borrowings will
increase
the gross working capital
but net working capital will
remain the same.
Net
Working Capital
It
represents excess of current assets
over current liabilities. Current assets include
cash, debtors, stock,
and
bills
receivable, Current liabilities include
bills payable, accounts
payable, expenses payable. It
indicates the
liquidity
position of an enterprise i.e. the
soundness or otherwise of the current financial
position.
The
ratio of 2:1 between current
assets and current liabilities is
considered sound. The
concept of net
working
capital is quantitative concept
indicating firm's capacity to
meet operating expenses and
current
liabilities.
Net working capital is
increased only when there is an
increase in current assets
without
corresponding
increase in current liabilities.
Net
Working Capital = Current
assets Current
liabilities.
72

SME
Management (MGT-601)
VU
Significance
of Working Capital
�
Conversion of
cash into inventory.
�
Conversion of
inventory into
receivable.
�
Conversion of
receivable into cash.
These
events constitute operating cycle of
business. If all these
events could happen simultaneously,
there
would
not arise any need
for working capital. Since
cash inflows and cash
outflows do not match,
an
organization
need necessary cash and
liquidity to be able to meet
its obligations. Thus adequate
capital is
required
for smooth operation of any
business concern.
Sound
working capital management
results in maximization of productivity
and Profits. It requires
the
maintenance
of proper balance between
working and fixed capital,
so as to maintain both profitability
and
solvency.
Proper management synchronizes cash
receipts and cash
outlays.
For
small concerns, efficient
working capital management is
still more essential to
ensure purchase of inputs
at
competitive prices and
timely payment to factors of
production. It may be noted
that shorter the gap
between
spending of money on production of
goods and the recovery of
money through rapid
sales
turnover,
the better shall be the quality of
working capital
management.
Factors
Affecting Working Capital
Requirements
In
case of a small enterprise, the
various factors affecting its
working capital
requirements.
Size
of Business.
Size
of unit and the volume of
business.
Nature
of Process.
Nature
of production process i.e.
lengthier the duration of production,
higher shall be the working
capital
needs
and vice-versa.
Proportion
of Raw Materials and Total
Cost.
Proportion
of raw material to total
cost must be decided.
Terms
of Sale & Purchase.
Terms
of sale and purchase e.g.
sales are on cash terms,
lesser working capital will
be sufficient.
Turnover
of Inventories.
If
inventories are large and
their turnover is slow, larger
working capital would be
needed.
Labour
Vs. Capital
Intensive.
Labour
vs. capital intensive, the former
requiring higher amounts of working
capital.
Cash
Requirements.
Cash
requirements will have direct
impact on working capital
quantum.
Banking
Facilities.
Availability
of goods and dependable
banking facilities reduces working
capital needed.
Seasonal
Requirements.
Seasonal
requirements may push up the amount of
working capital
needed.
Contingencies.
If
the demand and prices for
small concerns products are
subject to wide fluctuation, contingency
provision
will
have to be made for
arranging higher amounts of working
capital.
73

SME
Management (MGT-601)
VU
Determination
of Working Capital
Needs
Working
capital requirements of a small
enterprise vary from unit to
unit and in accordance with
the
difference
on the nature of the enterprise. Broadly
speaking, working capital should be
adequate to meet
operating
expenses like raw materials,
labour, factory and other
overheads etc. Operating
expenses can be
ascertained
from the final accounts of the
firm. But the working
capital requirements needs
not be equal to
the
level of expenses. Operating cycle is of primary
significance in every
case.
Working
Capital Requirement Formula =
Operating
Exp in Previous Year
Number
of operating Cycles in Year
Ingredients
of Working Capital Management in
Small Enterprise
Budget
the Material
Requirements.
Budget
the material requirements and
devising a proper system of
control.
Production
Goes on Uninterrupted.
Ensure
that production goes on
uninterrupted so that there id
minimum blockage of working
capital in the
production
process.
Realize
Cash Fast.
Expeditious
dispatch the finished goods to
realize cash fast.
Follow
the Bills.
Follow
the bills for early realization of
cash.
Identify
Surplus Cash.
In
the field of cash management,
clearly identify the quantum of really
surplus cash which could be
utilized
to
meet financial obligations.
Working
Capital Sources.
Ensure
proper management of working
capital sources so that
there is no costly fund
rising. There must be
a
judicious blending of different resources
so that sufficient funds are
raised at the cheapest
cost.
74
Table of Contents:
- THE HISTORY:Cottage Industry, CONCEPT OF SMALL BUSINESS
- THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SMALL AND BIG BUSINESS:The SME’S in Pakistan
- THE ROLE OF ENTREPRENEURSHIPS IN SMEs:Focus and Perseverance Guide the Entrepreneur
- THE ROLE OF ENTREPRENEURSHIPS IN SMEs:Kinds of Entrepreneurs
- SMALL ENTREPRENEURS IN PAKISTAN:National Approaches
- THE DEVELOPMENT OF SMES IN PAKISTAN:The Industrial History of Pakistan
- GOVERNMENT’S EFFORT TOWARDS SME DEVELOPMENT:Financing Programs
- THIS LECTURE DEFINES THE ROLE OF NGOS AND SMEDA:Mission Statement
- ISSUES AND POLICY DEVELOPMENT FOR SME:Monitoring Developments
- ISSUES IN SME DEVELOPMENT:Business Environment, Taxation Issues
- LABOR ISSUES:Delivery of Assistance and Access to Resources, Finance
- HUMAN RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT:Market and Industry Information, Monitoring Developments
- MARKET AND INDUSTRY INFORMATION:Measuring Our Success, Gender Development
- LONG TERM ISSUES:Law and Order, Intellectual Property Rights, Infrastructure
- THE START UP PROCESS OF A SMALL ENTERPRISE:Steps in Innovative Process
- TECHNICAL FEASIBILITY:Market Feasibility, Market Testing
- FINANCIAL FEASIBILITY:Financial resources and other costs, Cash Flow Analysis
- ASSESSMENT OF PERSONAL REQUIREMENTS AND ORGANIZATIONAL CAPABILITIES:Analysis of Competition
- Post Operative Problems of a New Enterprise:Environmental Causes
- HOW TO APPROACH LENDERS:Bank’s Lending Criteria, Specific Purpose, Be Well Prepared
- WHAT A BANK NEEDS TO KNOW ABOUT YOU:General Credentials, Financial Situation
- COMMERCIAL INFORMATION:Checklist for Feasibility Study, The Market
- GUARANTEES OR COLLATERAL YOU CAN OFFER:Typical Collateral
- Aspects of Financial Management:WINNING THE CASH FLOW WAR, The Realization Concept
- MEANING OF WORKING CAPITAL:Gross Working Capital, Net Working Capital
- RECRUITMENT, SELECTION AND TRAINING:Job Description, Job Specification
- SELECTION AND HIRING THE RIGHT CANDIDATE:Application Blank, Orientation
- TRAINGING AND DEVELOPMENT:Knowledge, Methods of Training
- CONDITIONS THAT STIMULATE LEARNING:Limitations of Performance Appraisal, Discipline
- QUALITY CONTROL:Two Aspects of Quality, Manufactured Quality
- QUALITY CONTROL:International Quality Standards, MARKETING
- MARKETING:Marketing Function, MARKETING PROCESS - STEPS
- MARKETING:Controllable Variable, Marketing Uncontrollable, Marketing Mix
- MARKETING:Demerits of Product Mix, Development of new product, SMEDA
- ROLE OF TECHNOLOGY:Training programmes, Publications
- ROLE OF TECHNOLOGY:Measure to Undertake for Promoting Framework.
- EXPORT POTENTIAL OF SME IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES I:Commonly Seen Assistance Programme
- EXPORT POTENTIAL OF SME IN DEVELOPING Countries. II:At the national level
- WORLD TRADE ORGANIZATION (WTO):WTO Agreements: Salient Features
- WTO MINISTERIAL CONFERENCES:PAKISTAN AND WTO
- WORLD TRADE ORGANIZATION (WTO) PAKISTAN & WTO. II:International Treaties
- WORLD TRADE ORGANIZATION (WTO) PAKISTAN & WTO. III:Agriculture
- WORLD TRADE ORGANIZATION (WTO):PAKISTAN & WTO. III
- WORLD TRADE ORGANIZATION (WTO):CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
- SUMMARY & CONCLUSIONS:Financing Tool, Financing Tool