 |
SME
Management (MGT-601)
VU
Lesson
17
Dealing
with the financial feasibility, flow
sheets, short term and long term
loans, cash flow analysis
and
financial
cost.
FINANCIAL
FEASIBILITY
It
covers the following:
Determination
of total financial
requirements
It
can be done by preparing a financial statement in the
following way:
Financial
Requirement Statement:
Initial
Expense
Period
1
Period
2
Expense
in product development
-------
-------
Legal
expense
-------
-------
Product
testing expenditure
-------
-------
Marketing
and technical
feasibility
-------
-------
Expenditure
Miscellaneous
expense
-------
-------
Fixed
investments
-------
-------
Building
-------
-------
Equipment
and machinery
-------
-------
Patents
-------
-------
Other
equipments
-------
-------
Operational
expenditure
-------
-------
Material
-------
-------
Wages
-------
-------
Sales
promotion, distribution
-------
-------
Rent,
interest, insurance,
taxes
-------
-------
Contingency
-------
-------
TOTAL
In
making the above estimation, provision
must be made for cost
escalation that is inevitable
due to price
changes.
Besides, appropriate sales forecasts
should also be made to have a
clear picture of expenditure. The
projection
could be weekly or monthly.
Financial
resources and other
costs
Financial
resources could be categorized on the
basis of periodicity
into:
Short
term resources: (those
payable in a year). Trade credit
supplies, short term loans
from
backs
or other lending institutions,
sales of account receivable
etc. belong to this
category.
Term
Loans: Intermediate
term loans are those
available for one to three
(sometimes five)
years.
It includes terms loans from
banks, lease finance,
financial assistance
from
institutions
etc.
Long-term
loans are
those from banks, equity
capital and investments of
earnings.
While
considering different sources, it is
better to consider specific costs as
well as advantages
and
disadvantages of each. It would be
appropriate to compute weighted average
cost of funds
as
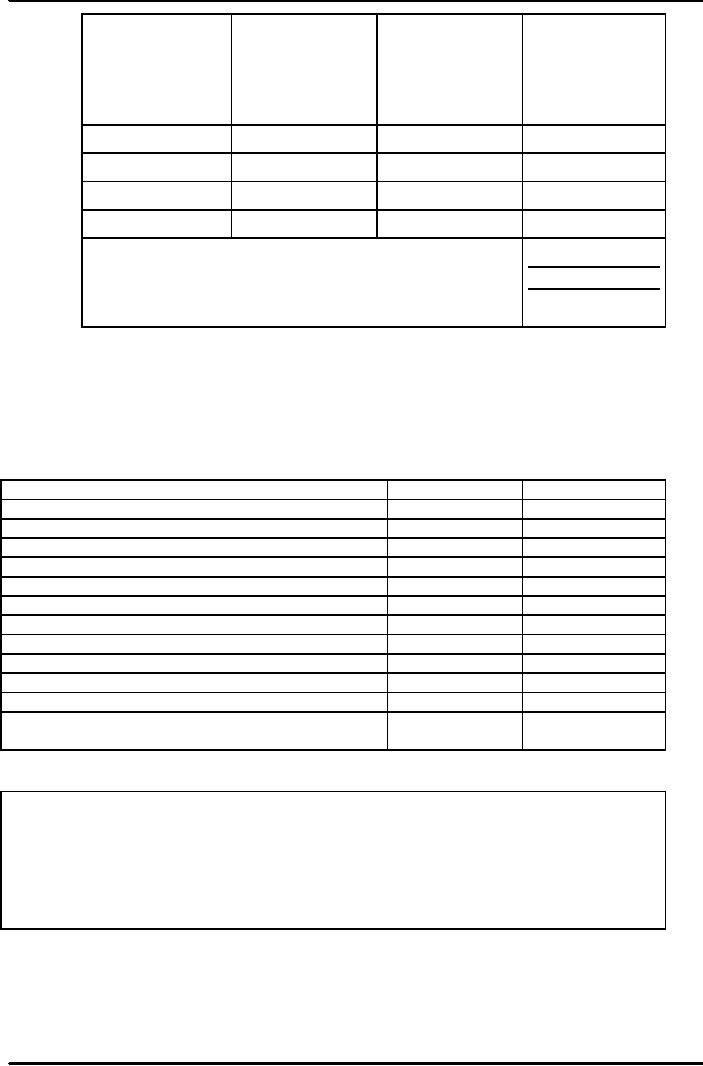
illustrated below:
50
SME
Management (MGT-601)
VU
4
1
2
3
Weighted
Cost
Method
of finance
Proportion
Cost
(Assumed)
[2X3]
(Assumed)
Short
term debt
20
7%
1.40
Intermediate
dept
10
8%
0.80
Long
term debt
20
9%
1.80
Equity
20
10%
5.00
Weighted
Average Cost of
Capital
9.00
On
the basis of average cost of
capital, it is possible to ascertain
whether there is positive
net
present value when anticipated cash
flow are discounted at
average rate of cost of
capital.
C)
Cash Flow
Analysis
If
the projected sales associated financial
requirements and available financial
resources are known,
the
anticipated
cash flow can easily be
determined.
Cash
Flow (projected)
Cash
flow and financial
transactions
Period
1
Period
2
1)
Cash flow
Initial
expense
Fixed
investment
Operating
expense
Total
cash outflow
2)
Cash inflow
Cash
sales
Account
receivables
Total
operating inflow
3)
Net cash flow
(2-1)
4)
Desired minimum cash
balance
5)
Total amount of funds
required
[3
(if negative +
4)]
Source
of funds
Short
term:
Net
trade credit
Commercial
loans
�
Intermediate
loans
�
Long
term loans
�
Equity
Total
Financing
Anticipated
return on investment
Financial
feasibility is adjudged on the basis of
satisfactory yield on investment. It can
be calculated by
relating
the average earnings expected
over a given period to either the total
amount of investment or
51

SME
Management (MGT-601)
VU
net
worth of organization (Return on equity). Both
are compared with potential
yield from alternative
investment
opportunities to ascertain the
acceptability or otherwise of a new
venture.
Key
Terms
Feasibility
study
a
detailed study about judging
the future of a commercial
project/product
52
Table of Contents:
- THE HISTORY:Cottage Industry, CONCEPT OF SMALL BUSINESS
- THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SMALL AND BIG BUSINESS:The SME’S in Pakistan
- THE ROLE OF ENTREPRENEURSHIPS IN SMEs:Focus and Perseverance Guide the Entrepreneur
- THE ROLE OF ENTREPRENEURSHIPS IN SMEs:Kinds of Entrepreneurs
- SMALL ENTREPRENEURS IN PAKISTAN:National Approaches
- THE DEVELOPMENT OF SMES IN PAKISTAN:The Industrial History of Pakistan
- GOVERNMENT’S EFFORT TOWARDS SME DEVELOPMENT:Financing Programs
- THIS LECTURE DEFINES THE ROLE OF NGOS AND SMEDA:Mission Statement
- ISSUES AND POLICY DEVELOPMENT FOR SME:Monitoring Developments
- ISSUES IN SME DEVELOPMENT:Business Environment, Taxation Issues
- LABOR ISSUES:Delivery of Assistance and Access to Resources, Finance
- HUMAN RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT:Market and Industry Information, Monitoring Developments
- MARKET AND INDUSTRY INFORMATION:Measuring Our Success, Gender Development
- LONG TERM ISSUES:Law and Order, Intellectual Property Rights, Infrastructure
- THE START UP PROCESS OF A SMALL ENTERPRISE:Steps in Innovative Process
- TECHNICAL FEASIBILITY:Market Feasibility, Market Testing
- FINANCIAL FEASIBILITY:Financial resources and other costs, Cash Flow Analysis
- ASSESSMENT OF PERSONAL REQUIREMENTS AND ORGANIZATIONAL CAPABILITIES:Analysis of Competition
- Post Operative Problems of a New Enterprise:Environmental Causes
- HOW TO APPROACH LENDERS:Bank’s Lending Criteria, Specific Purpose, Be Well Prepared
- WHAT A BANK NEEDS TO KNOW ABOUT YOU:General Credentials, Financial Situation
- COMMERCIAL INFORMATION:Checklist for Feasibility Study, The Market
- GUARANTEES OR COLLATERAL YOU CAN OFFER:Typical Collateral
- Aspects of Financial Management:WINNING THE CASH FLOW WAR, The Realization Concept
- MEANING OF WORKING CAPITAL:Gross Working Capital, Net Working Capital
- RECRUITMENT, SELECTION AND TRAINING:Job Description, Job Specification
- SELECTION AND HIRING THE RIGHT CANDIDATE:Application Blank, Orientation
- TRAINGING AND DEVELOPMENT:Knowledge, Methods of Training
- CONDITIONS THAT STIMULATE LEARNING:Limitations of Performance Appraisal, Discipline
- QUALITY CONTROL:Two Aspects of Quality, Manufactured Quality
- QUALITY CONTROL:International Quality Standards, MARKETING
- MARKETING:Marketing Function, MARKETING PROCESS - STEPS
- MARKETING:Controllable Variable, Marketing Uncontrollable, Marketing Mix
- MARKETING:Demerits of Product Mix, Development of new product, SMEDA
- ROLE OF TECHNOLOGY:Training programmes, Publications
- ROLE OF TECHNOLOGY:Measure to Undertake for Promoting Framework.
- EXPORT POTENTIAL OF SME IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES I:Commonly Seen Assistance Programme
- EXPORT POTENTIAL OF SME IN DEVELOPING Countries. II:At the national level
- WORLD TRADE ORGANIZATION (WTO):WTO Agreements: Salient Features
- WTO MINISTERIAL CONFERENCES:PAKISTAN AND WTO
- WORLD TRADE ORGANIZATION (WTO) PAKISTAN & WTO. II:International Treaties
- WORLD TRADE ORGANIZATION (WTO) PAKISTAN & WTO. III:Agriculture
- WORLD TRADE ORGANIZATION (WTO):PAKISTAN & WTO. III
- WORLD TRADE ORGANIZATION (WTO):CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
- SUMMARY & CONCLUSIONS:Financing Tool, Financing Tool