 |

Project
Management MGMT627
VU
LESSON
39
PROJECT
EFFECTIVENESS THROUGH ENHANCED
PRODUCTIVITY
BROAD
CONTENTS
Competitiveness
Productivity
in the Context of PM
Definitions
of Effectiveness and Efficiency
Types
of Productivity
White
Collar Productivity
Critical
Barriers/ Problems to
Productivity
Causes
of Productivity Decline in
Organizations
Productivity
Improvement
Categories
of Productivity Factors
Soft
Factors
39.1
Competitiveness:
Competitiveness
emerged strongly in new era
of globalization describes "economic
strength"
of
any "organization" or position of
certain company" with
respect to its competitors in
market
place.
Competitiveness
is process by which one entity
strives to outperform another.
Competitiveness
in
Organization is Ability to get customers
to choose your prod or svc
over competing
alternatives
on sustainable basis.
Competitiveness
continually "sustained incorporated in
productivity" resulting in high
wages
and
living standards competitiveness -
demonstrated by "ability to meet, rest of
free
international
markets" while "expanding
real income."
39.1.1
Indicators of Competitiveness:
Macro
level competitiveness of nations
reflects standard of living of their
citizens. National
competitiveness
consolidation of micro-level performances
of company's and individual is
true
"Agents
of Economic Growth".
Figure
39.1: Competitiveness
Pyramid
296
Project
Management MGMT627
VU
Competitiveness
depends on productivity:
"Standard
of living is determined by productivity
of a nation's economy which is measured by the
value
of
goods and services (products) produced
per unit of the nation's human, capital and
natural resources".
Indicators
of competitiveness:
Productivity:
Efficiency
with which goods and
services are produced and provided and
determined by:
·
Previous
investments
·
Quality
and performance of workforce,
·
Technology
innovation
·
Quality
of plant and equipment
·
Efficiency
with which these factors of
production are
utilized
Productivity
of "local" industries is of fundamental
importance to competitiveness. It depends
on:
1.
Sophistication with "which
company's compete"
2.
Quality of "microeconomic business
environment".
When
productivity and quality considered
together competitiveness can be enhanced.
Definition of
productivity
successful project management
organization create surplus through
productive output,
productivity
is output input agreement on
consideration "quality and
time".
Productivity
= Outputs (Time /Quality)
Inputs
39.2
Productivity
in the Context of Project
Management:
39.2.1
Definition of Productivity:
1.
Ratio of output to input by
large number of professionals.
2.
ILO Definition: "Ratio between "output of
wealth produced" and "input
resources used up" in
"process
of production".
3.
Comparative tool for
managers, industrial engineers,
economists, and politicians.
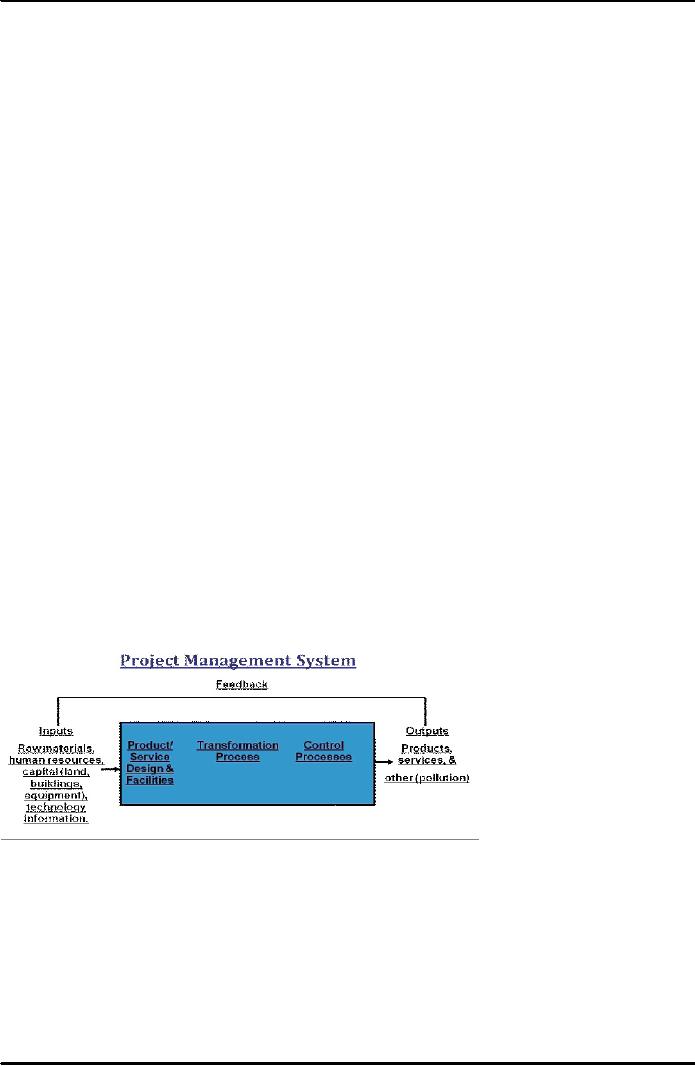
Figure
39.2: Project
Management System
297

Project
Management MGMT627
VU
39.2.2
Difference between Production and
Productivity:
Production: Concerned
with activity of "producing
goods and or
services".
Productivity:
"Efficient
utilization of resources" (input) in
"producing goods/services"
(output).
The
basic differences between production
and productivity are as
follows:
·
Production
is quantity of output produced.
·
Productivity
"ratio of output produced in input
(s) used".
·
Higher
productivity means accomplishing more
with same "amount of
resources" or achieving
higher
output In terms of volume/quality
for same input.
39.2.3
Messages
of Productivity:
Taylor's
Message of Productivity:
·
Various
pay plans based on output
for surplus increase labor
productivity not possible
work
order:
a.
Provided ample reward
b.
Adequate targets
c.
Managerial help
·
Careful
advance planning by
manager
·
Managers
to design work system for
worker to do their
best.
Fredrick
Concluded:
Low
productivity is matter of ignorance on
part of labor and management
ignorance. "Fair
day's
work"
and "fair day pay"
productivity enhancement answer to
high wages/profits.
Peter
Drucker Says:
Problem
faced in developing countries is problem
not of "underdevelopment but rather of
under
management".
Actually productivity is most
serious challenge confronting
management.
39.2.4
Perspectives
on Productivity:
Productivity
Manager's Perspective:
Use
"accounting ratios" for
management-usually interested in productivity
measures that enable
it
to
easily assess the present profitability of
company.
Productivity
Engineer's Perspective:
Seek
measures of physical assets
and other resources. For
example: Production/hour.
o
Man
hours/unit
o
Material
required/unit, material/consumption,
utilization,
o
Space
utilization
o
May
fail to relate to overall
productivity.
Productivity
Behaviorist's
Perspective:
View
productivity of people in organization in
terms of time they spend at
work versus total
time
available
a misleading measure.
298

Project
Management MGMT627
VU
Productivity
Accountant's
Perspective:
"Costing
and budgeting" approach to productivity
budget figure, rather than
optimum achievable
values,
used as standards can be a false
impression of high productivity.
Productivity
Economist's
Perspective:
Partial
measures, such as "labor
productivity" employed by economists,
total factor and
total
productivity
but again definitions do not
agree.
39.3
Definition
of Effectiveness and
Efficiency:
Productivity
implies effectiveness
and
efficiency
both
individual and organization
performance.
·
Effectiveness
is
"achievement
of objectives".
It entails promptly achieving
stated objective.
·
Efficiency
is
"achievement
of ends with least amount of
resources.
Resources to achieve
objective
weighted against what is
actually accomplished.
39.3
Types of Productivity:
1.
Partial Productivity
2.
Total Factor Productivity
3.
Total Productivity
Total
Factor Productivity:
Ratio
of "net output to sum of
associated labor and capital"
(factor) inputs net output-
total output
minus
intermediate goods and services
purchased.
Finding
of Survey in Different
Industries
o
Average,
only 4.4 hours per day used
productively
o
1.2
hours lost due to personal and other
unavoidable delays
o
hrs
are simply wasted because of
management's inability to effectively
"plan and control"
the
worker's tasks.
Productivity
Loss:
·
Percent
due to poor: "Planning and
scheduling" of work.
·
25
Percent due to: "Unclear and
untimely instructions".
·
Percent
due to: "Inability to adjust staff
size" and duties during "peak and
valley workload
periods".
·
25
Percent due to: "Poor
co-ordination" of material flow,
unavailability of needed tools,
excess
travel
time.
39.5
White-Collar
Productivity:
Productivity
of "white-collar workers" is no less
important than that of
direct labor or
manufacturing
employees.
It is usually least known,
least analyzed, and least
managed of all factors of
productivity.
White
collar employees are productive
only 50% of time. Remainder is
non-productive time and
can
be
traced to personal delays (15%) and
improper management
(35%).
Examples
of White Collar
Waste:
o
Poor
staffing
o
Inadequate
communication
o
Unproductive
meeting and telephone
conversations
299

Project
Management MGMT627
VU
Poor
scheduling
o
Slack
start and quiet times
o
Lack
of communication between function
o
Information
overload
o
39.6
Critical
Barriers/Problems to
Productivity:
o
Family-controlled
industry
o
Earning
easy money
o
Monopolistic
market, in some segments,
some high competitive
o
Erratic
inflow of orders
o
Lack
of productivity and quality
culture
o
Shortage of
funds low level
codification
o
Automation
-not encouraged
o
Low
priority of market and commercial
activities
o
Poor
after service
o
Complicated
government policy, rules and
regulations
o
Poor
infra structure support/road
transport
o
Energy
shortage
o
Poor
working conditions, light,
ventilation, safety, housekeeping
o
Non
availability of basic material
components (to be
imported)
o
Unreliable
suppliers
39.7
Causes
of Productivity Decline in
Organizations:
Inability
to measure, evaluates, and manages
productivity of white collar employees.
This
o
causes
shocking waste of
resources.
Rewards
and benefits given without
requiring equivalent in productivity
and
o
accountability
Diffused
authority and inefficiency in
complex organizations, thereby, causing
delays and
o
time
lags.
Organization
expansion lowers productivity
growth result in soaring
costs.
o
Low
motivation among rising number of
affluent workers with new
attitudes.
o
Late
Deliveries caused by schedule have
been disrupted by limited
materials.
o
Unresolved
human conflicts difficulties in teamwork,
resulting in project
inefficiencies.
o
Include
legislative intrusions antiquated laws,
resulting in constrained "management
o
options
and prerogatives".
Specialization
in work processes resulting in
monotony and Boredom.
o
Rapid
technology changes and high
costs, resulting in decline in
new opportunities and
o
innovation.
Include
demand of leisure time causing
disruption in operations.
o
Project
manager's inability to keep pace with the
latest information and knowledge.
o
39.8
Productivity Improvement
(PI):
o
How
can projects improve their
productivity?
Productivity
is composed of:
o
People
o
Operations
variables
To
improve productivity, management
needs to focus on the following two
points:
o
Productivity
does not just happen by
"trying harder". It must be
planned.
o
But
how do you plan for
productivity, and what factors
are involved?
Improvement
means
"increase ratio of output of goods and
services produced divided by input
used to
produce".
Ratio can be included by
either increase output,
reducing input or
both.
300
Project
Management MGMT627
VU
Financial
and social benefits of "productivity
improvement strategy" in project
manager should be
greater
than "implementation cost", in
long run.
Task
of project manager is to evaluate
those factors that have bearing on
productivity and take
appropriate
measures to use effectively. In
order to raise productivity
and to reduce cost, we
must
eliminate
bad features in design and
specifications that cause
excessive work
contents.
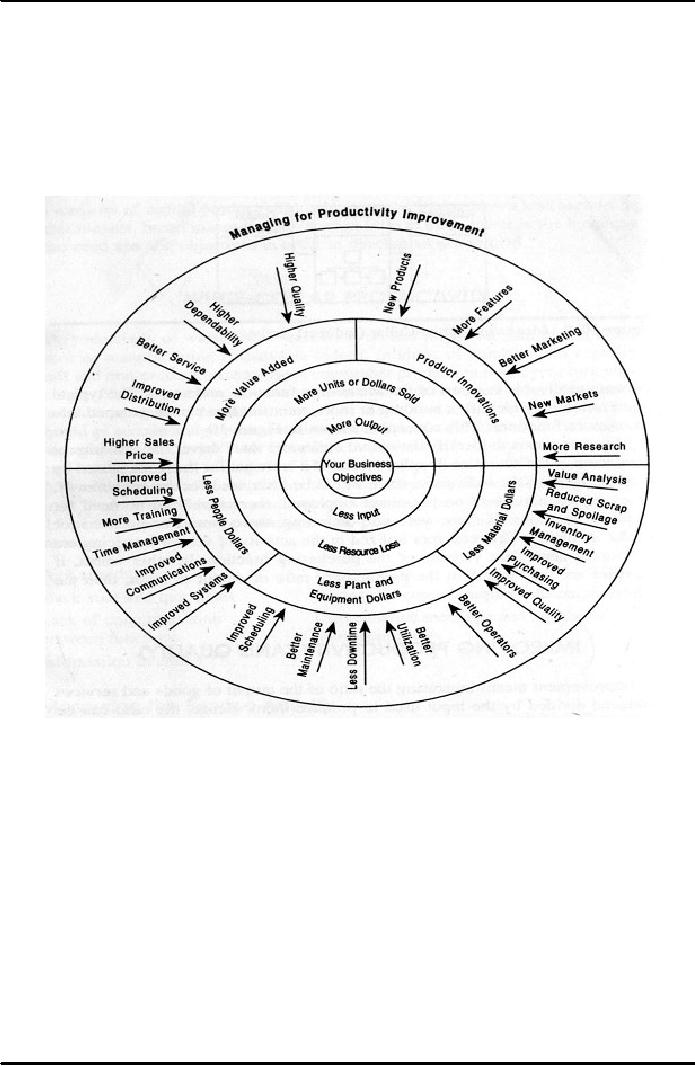
Figure
39.3: Productivity
Wheel
39.8.1
Productivity Improvement
Factors:
Productivity
improvement (PI) is not just
"doing things better", but
more importantly, it is "doing
right
things better". Inter-relationships
between labor, capital and
socio-organizational environment
are
important in a way that they
are balanced and co-ordinate into
integrated whole.
Three
Main Productivity Factor
Groups:
There
are three major productivity
factor groups:
o
Job-related
o
Resource-related
o
Environment-related
39.9
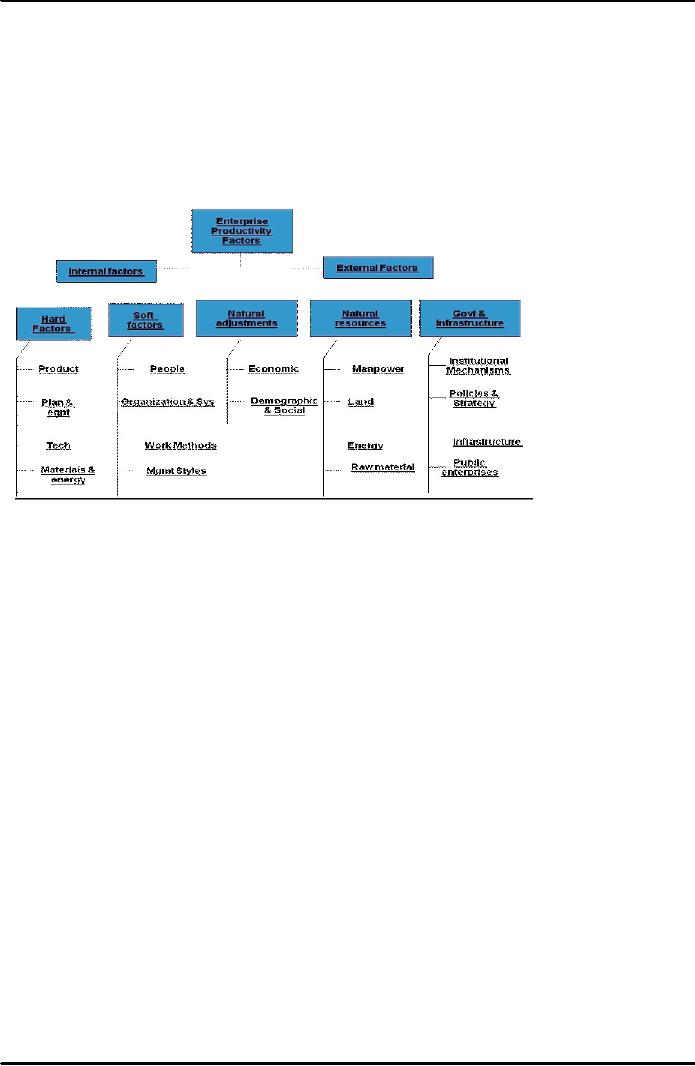
Categories
of Productivity Factors:
There
are the two following major
categories of productivity
factors:
301
Project
Management MGMT627
VU
External
(not controllable)
o
Internal
(controllable)
o
External
Factors: Beyond
control of individual enterprise.
Understanding of them can
motivate
certain
actions which migrates change
enterprise's or project behavior and
its productivity in
LR.
Internal
Factors: Within
its control first step
towards productivity improvement is to
identify
problem
areas within these factor
groups.
Figure
39.4: Integrated
Model of Project Productivity
Factors
39.10
Soft Factors:
People:
Principal
resource central factor in
productivity improvement, drives
people in organization
all
have role to play as workers, engineers,
managers, entrepreneurs, trade union
members.
Each
role has two
aspects:
o
Application
o
Effectiveness
Application:
Degree
to which people apply
themselves to their work. People
differ not only in
their
ability
but also in their will to
work.
Law
of Behavior: Motivation
decreases if it is either satisfied or
blocked from satisfaction.
Workers
may
do their jobs work order
working hard (no
motivation), but even if they
work to their full
capacity
they would not be satisfied
(motivation is blocked from
satisfaction).
Motivation
is basic to all human behavior and to
efforts in productivity improvement.
Material needs
predominant,
but does not mean
that non-financial incentives
not effective or have no place.
Project
manager see what stimulates and
maintains motivation to bring
about changes in attitude
of
managers,
engineers and workers. Develop set of
values conducive to higher
productivity.
Workers'
success in increasing productivity
by:
·
Rewards
·
Improving
recognition
·
Involvement
302

Project
Management MGMT627
VU
·
Learning
Opportunities
·
Elimination
of negative rewards
Execute
effective incentive schemes,
result significant improvement in
productivity. Wage
incentives
related
to amount of change accomplishes.
Project
manager should work to
encourage workers to apply
their creative talents by taking
special
interest
in their problems by promoting favorable
social climate.
2.
Effectiveness: Effectiveness
is extent to which application of human
effort brings desired results
in
output
and quality. It is the ability to do
productive job improved
through:
·
Training
and development
·
Job
rotation and placements,
systematic job progression
(promotion)
·
Career
planning
Key
approaches, methods and
techniques to improve labor
productivity:
·
Wages
and salaries
·
Training
and education
·
Social
security pensions and
health plans
·
Rewards
·
Incentive
plans
·
Participation
or co-determination
·
Contract
negotiations
·
Attitudes
to work, to supervision and to
change
·
Motivation
to higher productivity
·
Co-operation
·
Organization
development
·
Improved
communications
·
Suggestion
systems
·
Career
planning
·
Attendance
·
Turnover
·
Job
security
Financial
Incentives (Individual and
Group):
Individual
plan is
made to give financial
incentives on basis of individual
performance.
Types
of Individual Plan:
·
Piece
work plan
·
Standard
hour plan
·
Measured
day work plan
·
Emerson
plan
Group
plan is made to give
financial incentives on basis of
group performance.
Types
of Group Plan:
·
Scanlon
plan
·
Ruker
plan
·
Kaiser
plan
·
Tonnage
plane
·
Dollar
sales plan
303

Project
Management MGMT627
VU
·
Profit
sharing
·
Improshare
Fringe
Benefits:
Some
intangible means of rewarding and
encouraging management employee.
These are referred to
as
"fringes"
and include the following:
·
Free
Medical
·
Insurance
·
Free
Air
·
Fares
·
Entertainment
·
Company
Car
·
Telephone
·
Subsidized
education etc.
Employee
Promotion:
·
Both
financial and non-financial form of
motivation: Up gradation of employee
status is
natural
way to recognize skill knowledge,
proficiency, and efforts to
job.
Maslow's
Hierarchy of Needs.
Only
dissatisfied needs can
motivate workers to high
productivity,) physiological, safety,
security,
belongingness,
self esteem, self
actualization (realizations of one
potential)
·
Japanese
on basis of seniority
·
USA
on basis of extra ordinary
performance
·
Debatable
issue
Job
Enrichment:
Non-financial-motivation
technique that
provides
·
Variety
in assigned tasks
·
Employment
autonomy and discretion in
performing talks
·
Feed
back on performance
·
Herzberg's
two-factor theory applied
Two
Factors Theory:
"Motivators"
factors leading to job satisfaction.
Achievement recognition, nature of work
responsibility,
growth
etc. Factors leading to dissatisfaction
avoidance are Hygiene, Company's
policy, admin,
supervision,
pay status
Job
Enlargement:
·
Enlargement
of responsibilities associated with
job.
·
Enhanced
scope and responsibility. Proponents say
job get to be boring and monotonous,
causing
high
absenteeism, high turnover, and
low morale, with consequent
low productivity.
·
Volvo
Sweden. Worker could stamp
name on engine.
304

Project
Management MGMT627
VU
Job
Rotation:
Involves
rotation of workers in different
jobs for short periods of time
provide "all-rounder" in
company's
op for which - not
originally hired for:
·
Relieves
boredom by flexibility in job
assignments.
·
Not
retraining conscious -on
going basis effort to
provide opportunity to exercise
freedom in
staying
on a job for a fixed
period.
Workers
Participation and
Empowerment:
Over
coming resistance to change
through employee involvement in
planning and implementing
change,
mental
and emotional involvement in groups
encourage workers to contribute in
group goals sharing of
responsibility.
Workers
Participation Approaches:
Following
are the approaches for
workers participation in quality
culture change and empowerment:
·
Quality
control circles
·
Productivity
quality teams
·
Productivity
action teams
·
Productivity
circles
·
Productivity
maintenance group
·
Employee
participation group
Skill
Enhancement:
Formalized
techniques to increase skills needed to
perform job. Skill training
needed for employee
when
employee's
attitude is positive but his
abilities are low.
·
In
information age there is a great need
for skill at all
levels.
Management
by Objectives (MBO):
Managerial
motivation techniques, aids motivation on
all participation by having
superior and
subordinate
managers
jointly identify common goals, carefully
define them. Together monitor
progress towards
achieving
results to both employer and
employee.
·
In
setting up goals care must be
taken.
·
Set
simplistic goals.
·
Set
goals without adequate
resources.
·
Not
set harsh goals that cause
resentment.
·
If
properly administered, MBO can
create joint goals and can
help in team building.
·
MBO
goals provide fairness to both
employee and employer.
Working
Condition Improvement Quality of
Work Life (QWL):
It
is often emphasized but
rarely applied technique
that involves detailed audit
of working conditions
designing
improved conditions of working
installing and maintaining improvements
in working
conditions.
Designing
Improved Factors:
They
include:
·
Temperature,
light and humidity
·
Noise
·
Colors
of surroundings
·
Extent
of handling hazardous material,
parts or product
·
Extent
of manual handling of heavy items
305

Project
Management MGMT627
VU
Training:
·
Seeks
to achieve improved human productivity by increasing
ability levels of
workforce
·
Seeks
to meet demands of growth and
change
·
Training
may actually decrease total
productivity initially
·
Some
type of training
·
On the
job targets
·
Apprenticeship
·
Internship
·
Outside
course
·
Visitation
training
Role
Perception:
·
Refer
to manner in which individual defines
his or her job
·
Type
of effort employee believes is
essential for effective job
performance.
·
If
workers see high or low
productivity as path to attainment of one
or more of their personal
goals
in work situation, they will
tend to be high or low
processors.
Quality
of Supervision:
·
Concerned
with work of creating and
maintaining environments in which
people can accomplish
goals
efficiently and effectively.
·
In
order to improve supervision
quality itself, supervisors must be
trained in
o
Interpersonal
skills
o
Human
management
o
Group
dynamic
o
Other
behavioral tools
Recognition:
Management
shows acknowledgement of employee's
outstanding performance in terms of
improved
productivity,
ideas, or any act of good
workmanship. They
include:
·
Pay
raise
·
Bonus
·
Awards
·
Certificate
of appreciation
·
Special
highlights in company newsletter
·
Special
parking provision
·
Engraving
on plaque in cafeteria
Punishment:
·
Punishment
contingency attempt to decrease
likelihood of particular behavior
occurring by
making
punishment contingency on
behavior.
·
Common
punishment contingencies used in work
organizations include:
o
Disciplinary
layoffs
o
Transfer
to undesirable jobs
o
Withholding
salary increases
Quality
Circles: Group
of employees who voluntarily cooperative
to solve problems related to
production,
quality, work environment, maintenance
scheduling, or anything that affects
these
areas.
Productivity
and Quality
Teams:
Small
groups of people doing similar
tasks meet regularly to
select, investigate, and solve
problems
related
to workplace, products, and services.
Effective means of improving
employee morale,
quality,
306

Project
Management MGMT627
VU
and
productivity in organizations. Team
spirit, positive thinking, and
philosophy of achieving
excellence
are three important characteristics of
productivity and quality
teams.
Zero
Defects:
Zero
defects program attempts to
improve quality by changing
workers attitudes. Their
theme, "do it
right
first time" stresses error
free performance. It relies on workers to
identify error prone
situations
with
assumption that people best prepared to
eliminate errors are those
who create them.
Time
Management:
·
Powerful
technique, particularly for
white collar, supervisory and
management personnel
·
Time
management involves minimization of
wasteful elements of person's
administrative work.
·
Interruptions
by drop-in visitors (without
appointment)
·
Attending
lengthy and unnecessary meetings
that accomplish very
little
·
Inability
to say "no" for some
tasks
·
Procrastination
and lack of decisiveness
·
Inability
to delegate work
·
Taking
on much more than can be
handled
·
Lack
of responsibility and authority to do
certain jobs
·
Delayed,
inaccurate or inadequate information
·
Taking
orders from too many
people
·
Handling
too many "crisis"
situations
·
Lack
of organization of tasks by priority or
target dates
·
Lack
of determination to complete tasks
assigned
·
Lack
of organization on and around
desk
·
Unnecessary
socialization
·
Poor
filling system
·
Making
unnecessary trips to people,
departments, copy machines
etc.
·
Excessive
conversation time
·
Too
many rescheduling of meeting, personal
engagements etc.
To
minimize these "time-wasters",
time management applies
simple, common-sensible but very
effective
programming
rules to very item of work,
one of which is: "never
handle same paper twice".
Time
management
always improves human productivity. It is
too often ignored,
particular by management
people
who preach productivity to
their subordinates.
Flex
Time:
·
Employees
are given freedom in
determining their hours of
work
·
Core
time (hours when all employees
must be at work)
·
Flexible
time (hours when employees can
vary their time of arrival
and departure)
Compressed
Work Week:
·
Working
for same number of hours but
for fewer days
week
·
Hours
·
08 hours 05
days
·
10 hours 04
days
Harmonization:
Integration
of interest of stockholders, board of directors,
management at all levels and
all employees in
consistent
manner both within and
outside physical boundaries of
organization.
307
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO PROJECT MANAGEMENT:Broad Contents, Functions of Management
- CONCEPTS, DEFINITIONS AND NATURE OF PROJECTS:Why Projects are initiated?, Project Participants
- CONCEPTS OF PROJECT MANAGEMENT:THE PROJECT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM, Managerial Skills
- PROJECT MANAGEMENT METHODOLOGIES AND ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURES:Systems, Programs, and Projects
- PROJECT LIFE CYCLES:Conceptual Phase, Implementation Phase, Engineering Project
- THE PROJECT MANAGER:Team Building Skills, Conflict Resolution Skills, Organizing
- THE PROJECT MANAGER (CONTD.):Project Champions, Project Authority Breakdown
- PROJECT CONCEPTION AND PROJECT FEASIBILITY:Feasibility Analysis
- PROJECT FEASIBILITY (CONTD.):Scope of Feasibility Analysis, Project Impacts
- PROJECT FEASIBILITY (CONTD.):Operations and Production, Sales and Marketing
- PROJECT SELECTION:Modeling, The Operating Necessity, The Competitive Necessity
- PROJECT SELECTION (CONTD.):Payback Period, Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
- PROJECT PROPOSAL:Preparation for Future Proposal, Proposal Effort
- PROJECT PROPOSAL (CONTD.):Background on the Opportunity, Costs, Resources Required
- PROJECT PLANNING:Planning of Execution, Operations, Installation and Use
- PROJECT PLANNING (CONTD.):Outside Clients, Quality Control Planning
- PROJECT PLANNING (CONTD.):Elements of a Project Plan, Potential Problems
- PROJECT PLANNING (CONTD.):Sorting Out Project, Project Mission, Categories of Planning
- PROJECT PLANNING (CONTD.):Identifying Strategic Project Variables, Competitive Resources
- PROJECT PLANNING (CONTD.):Responsibilities of Key Players, Line manager will define
- PROJECT PLANNING (CONTD.):The Statement of Work (Sow)
- WORK BREAKDOWN STRUCTURE:Characteristics of Work Package
- WORK BREAKDOWN STRUCTURE:Why Do Plans Fail?
- SCHEDULES AND CHARTS:Master Production Scheduling, Program Plan
- TOTAL PROJECT PLANNING:Management Control, Project Fast-Tracking
- PROJECT SCOPE MANAGEMENT:Why is Scope Important?, Scope Management Plan
- PROJECT SCOPE MANAGEMENT:Project Scope Definition, Scope Change Control
- NETWORK SCHEDULING TECHNIQUES:Historical Evolution of Networks, Dummy Activities
- NETWORK SCHEDULING TECHNIQUES:Slack Time Calculation, Network Re-planning
- NETWORK SCHEDULING TECHNIQUES:Total PERT/CPM Planning, PERT/CPM Problem Areas
- PRICING AND ESTIMATION:GLOBAL PRICING STRATEGIES, TYPES OF ESTIMATES
- PRICING AND ESTIMATION (CONTD.):LABOR DISTRIBUTIONS, OVERHEAD RATES
- PRICING AND ESTIMATION (CONTD.):MATERIALS/SUPPORT COSTS, PRICING OUT THE WORK
- QUALITY IN PROJECT MANAGEMENT:Value-Based Perspective, Customer-Driven Quality
- QUALITY IN PROJECT MANAGEMENT (CONTD.):Total Quality Management
- PRINCIPLES OF TOTAL QUALITY:EMPOWERMENT, COST OF QUALITY
- CUSTOMER FOCUSED PROJECT MANAGEMENT:Threshold Attributes
- QUALITY IMPROVEMENT TOOLS:Data Tables, Identify the problem, Random method
- PROJECT EFFECTIVENESS THROUGH ENHANCED PRODUCTIVITY:Messages of Productivity, Productivity Improvement
- COST MANAGEMENT AND CONTROL IN PROJECTS:Project benefits, Understanding Control
- COST MANAGEMENT AND CONTROL IN PROJECTS:Variance, Depreciation
- PROJECT MANAGEMENT THROUGH LEADERSHIP:The Tasks of Leadership, The Job of a Leader
- COMMUNICATION IN THE PROJECT MANAGEMENT:Cost of Correspondence, CHANNEL
- PROJECT RISK MANAGEMENT:Components of Risk, Categories of Risk, Risk Planning
- PROJECT PROCUREMENT, CONTRACT MANAGEMENT, AND ETHICS IN PROJECT MANAGEMENT:Procurement Cycles