 |
SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT:Supply Chain Benefits and Drawbacks |
| << SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT:Logistics, Distribution Requirements Planning |
| SCHEDULING:High-Volume Systems, Load Chart, Hungarian Method >> |
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Lesson
40
SUPPLY
CHAIN MANAGEMENT
Learning
Objective
In
this lecture we will focus on
certain important parameters of
Supply Chain Management. We
will
discuss
the Supply Chain Operational
Reference Metrics and Collaborative
Planning Forecasting
and
Replenishment Process, which would
help us analyze the Supply chains.
This would also
help
us
an operation manager to design effective
supply chains. We will try
to understand the concepts of
Velocity
and Bullwhip effect and how
they pose a serious
challenge to the effectiveness of the
Supply
Chain.
Supply
Chain Operational Reference (SCOR)
Metrics
Perspective
Metrics
Reliability
On-time
delivery
Order
fulfillment lead time
Fill
rate (fraction of demand met
from
stock)
Perfect
order fulfillment
Flexibility
Supply
chain response time
Upside
production flexibility
Agility
to obtain competitiveness
Expenses
Supply
chain management
costs
Warranty
cost as a percent of revenue
Value
added per employee
Assets/utilization
Total
inventory days of
supply
Cash-to-cash
cycle time
Net
asset turns
Supply
chain response time often
makes or breaks a supply
chain.
CPFR
CPFR
is an acronym derived from the
first letters of the following phrase:
Collaborative Planning,
Forecasting
and Replenishment.
1.
Focuses on information sharing among
trading partners.
2.
Forecasts can be frozen and
then converted into a
shipping plan.
3.
Eliminates typical order
processing.
CPFR
Process consists of the following
steps.
Step
1 Front-end agreement
Step
2 Joint business
plan
Steps
3-5 Sales
forecast
Steps
6-8 Order forecast
collaboration
Step
9 Order generation/delivery
execution
Creating
an Effective Supply
Chain
1.
Develop
strategic objectives and
tactics.
2.
Integrate
and coordinate activities in the internal
supply chain.
3.
Coordinate
activities with suppliers with
customers.
4.
Coordinate
planning and execution
across the supply
chain.
181
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
5.
Form strategic partnerships.
Supply
Chain Performance Drivers
1.
Quality
2.
Cost
3.
Flexibility
4.
Velocity
5.
Customer service
Velocity
1.
Inventory velocity: The rate at
which inventory (material)
goes through the supply
chain.
2.
Information velocity: The rate at
which information is communicated in a
supply chain.
Challenges
to an Effective Supply Chain
Management
1.
Barriers to integration of
organizations
2.
Getting top management on
board
3.
Dealing with
trade-offs
4.
Small businesses
5.
Variability and uncertainty
6.
Long lead times
Trade-offs
1.
Cost-customer service
a.
Disintermediation
2.
Lot-size-inventory
a.
Bullwhip effect
3.
Inventory-transportation costs
a.
Cross-docking
4.
Lead time-transportation
costs
5.
Product variety-inventory
a.
Delayed differentiation
Bullwhip
effect represents the real
life time situation that
Inventories are
progressively
larger
moving backward through the
supply chain.
Cross-docking
represents the fact that the
goods arriving at a warehouse
from a supplier are
unloaded
from the supplier's truck
and loaded onto outbound
trucks. Avoids warehouse
storage.
Delayed
differentiation relates to the Production
of standard components and
subassemblies,
which are held until
late in the process to add
differentiating features.
Disintermediation
is reducing one or more steps in a supply
chain by cutting out one
or
more
intermediaries.
Supply
Chain Issues
Strategic
Issues
Tactical
Issues
Operating
Issues
Design
of the
Inventory
policies
Quality
control
supply
chain,
Purchasing
policies
Production
planning and
partnering
Production
policies
control
Transportation
policies
Quality
policies
182
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Supply
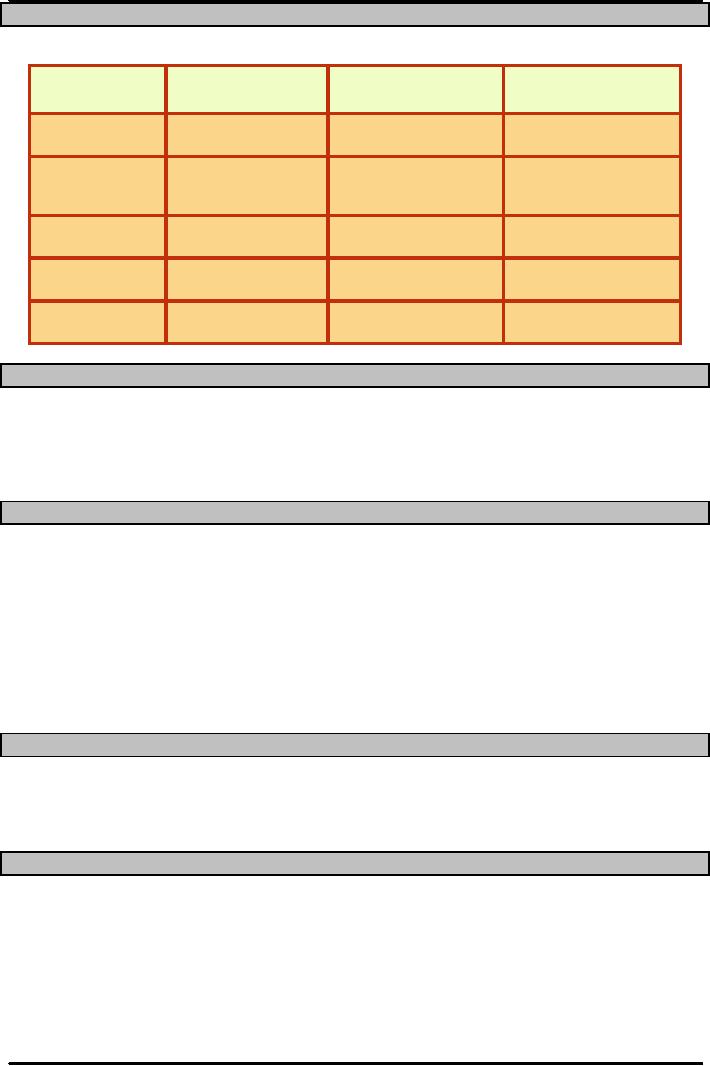
Chain Benefits and Drawbacks
Problem
Potential
Benefits
Possible
Improvement
Drawbacks
Large
Smaller,
more
Reduced
holding
Traffic
congestion
inventories
frequent
deliveries
costs
Increased
costs
Long
lead times
Delayed
Quick
response
May
not be feasible.
differentiation
May
need absorb
Disintermediation
functions
Large
number
Modular
Fewer
parts
Less
variety
of
parts
Simpler
ordering
Cost
Outsourcing
Reduced
cost, higher
Loss
of control
Quality
quality
Variability
Shorter
lead times,
Able
to match supply
Less
variety
better
forecasts
and
demand
Supplier
Partnerships
Ideas
from suppliers could lead to
improved competitiveness
1.
Reduce cost of making the
purchase
2.
Increase Revenues
3.
Enhance Performance
Critical
Issues
1.
Technology management
a.
Benefits
b.
Risks
2.
Strategic importance
a.
Quality
b.
Cost
c.
Agility
d.
Customer service
e.
Competitive advantage
Operations
Strategy
1.
SCM creates value through
changes in time, location and
quantity.
2.
SCM creates competitive advantage by
integrating and streamlining the diverse
range of
activities
that involve purchasing, internal
inventory, transfers and physical
distribution.
Summary
Supply
Chain Management dynamics allow an
Operations Manager to evolve an effective
strategy that
creates
value. Logistics and purchasing alone
can allow an operations manager to
effectively control the
flow
of information and materials with in and to and
fro from the organization.
Organizations aiming
for
SCM
implementation often fail
because of lack of training of
their employees as well as
top
managements
commitment.
183
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Decision Making
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Strategy
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Service Delivery System
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Productivity
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:The Decision Process
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Demand Management
- Roadmap to the Lecture:Fundamental Types of Forecasts, Finer Classification of Forecasts
- Time Series Forecasts:Techniques for Averaging, Simple Moving Average Solution
- The formula for the moving average is:Exponential Smoothing Model, Common Nonlinear Trends
- The formula for the moving average is:Major factors in design strategy
- The formula for the moving average is:Standardization, Mass Customization
- The formula for the moving average is:DESIGN STRATEGIES
- The formula for the moving average is:Measuring Reliability, AVAILABILITY
- The formula for the moving average is:Learning Objectives, Capacity Planning
- The formula for the moving average is:Efficiency and Utilization, Evaluating Alternatives
- The formula for the moving average is:Evaluating Alternatives, Financial Analysis
- PROCESS SELECTION:Types of Operation, Intermittent Processing
- PROCESS SELECTION:Basic Layout Types, Advantages of Product Layout
- PROCESS SELECTION:Cellular Layouts, Facilities Layouts, Importance of Layout Decisions
- DESIGN OF WORK SYSTEMS:Job Design, Specialization, Methods Analysis
- LOCATION PLANNING AND ANALYSIS:MANAGING GLOBAL OPERATIONS, Regional Factors
- MANAGEMENT OF QUALITY:Dimensions of Quality, Examples of Service Quality
- SERVICE QUALITY:Moments of Truth, Perceived Service Quality, Service Gap Analysis
- TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT:Determinants of Quality, Responsibility for Quality
- TQM QUALITY:Six Sigma Team, PROCESS IMPROVEMENT
- QUALITY CONTROL & QUALITY ASSURANCE:INSPECTION, Control Chart
- ACCEPTANCE SAMPLING:CHOOSING A PLAN, CONSUMER’S AND PRODUCER’S RISK
- AGGREGATE PLANNING:Demand and Capacity Options
- AGGREGATE PLANNING:Aggregate Planning Relationships, Master Scheduling
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Objective of Inventory Control, Inventory Counting Systems
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:ABC Classification System, Cycle Counting
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Economic Production Quantity Assumptions
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Independent and Dependent Demand
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Capacity Planning, Manufacturing Resource Planning
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Organizational and Operational Strategies
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Operational Benefits, Kanban Formula
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Secondary Goals, Tiered Supplier Network
- SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT:Logistics, Distribution Requirements Planning
- SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT:Supply Chain Benefits and Drawbacks
- SCHEDULING:High-Volume Systems, Load Chart, Hungarian Method
- SEQUENCING:Assumptions to Priority Rules, Scheduling Service Operations
- PROJECT MANAGEMENT:Project Life Cycle, Work Breakdown Structure
- PROJECT MANAGEMENT:Computing Algorithm, Project Crashing, Risk Management
- Waiting Lines:Queuing Analysis, System Characteristics, Priority Model