 |
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Lesson
04
Distinctive
Competencies
The
special attributes or abilities that
give an organization a competitive
edge.
7.
Price
8.
Quality
9.
Time
10.
Flexibility
11.
Service
12.
Location
A.
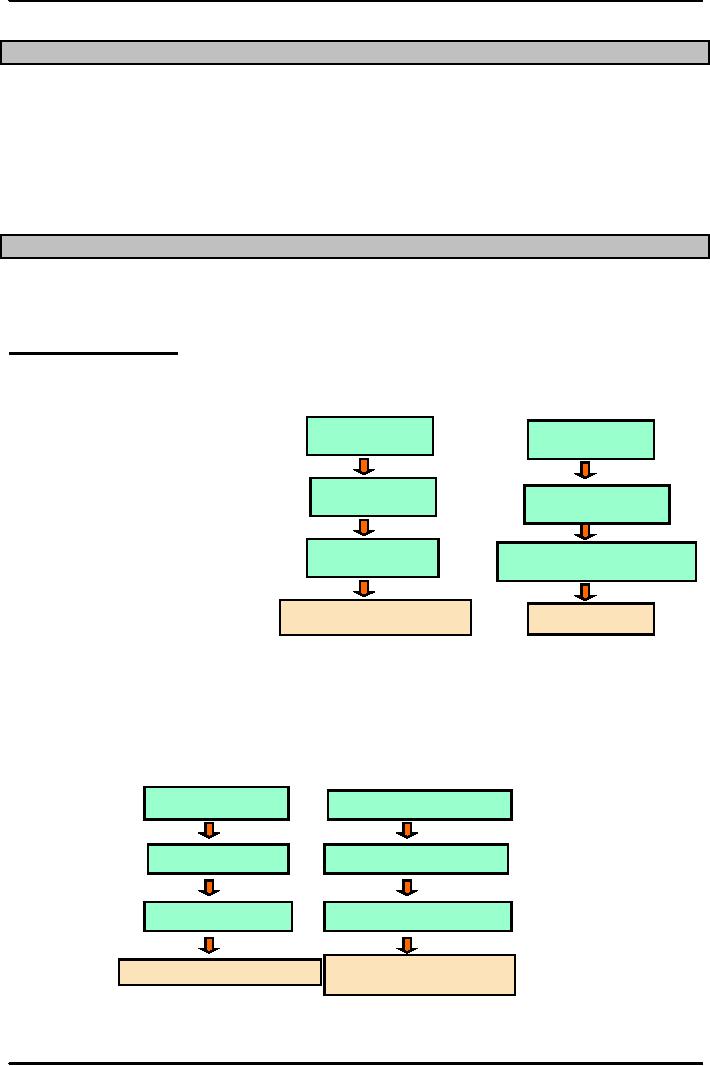
Operations Strategy
�Operations
strategy The approach, consistent
with organization strategy that is
used to guide the
operations
function. We first study strategy design
process with example for
manufacturing and
Services.
Strategy
Design Process
Strategy
Process
Example
Customer
Needs
More
Product
Corporate
Strategy
Increase
Organization
Size
Operations
Strategy
Increase
Production Capacity
Decisions
on Processes
Build
New Factory
and
Infrastructure
Strategy
Design Process for Services
Strategy
Map
Desired
Results
ancial
Perspective
Improve
Shareholder Value
Customer
Perspective
Customer
Value Proposition
Internal
Perspective
Build-Increase-Achieve
Learning
and Growth
Perspective
A
Motivated and
Prepared
Workforce
14
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Relationship
between Operations and Organizational
Strategy
�Organizational
strategy is
an
over all big picture
for the whole
organization.
Longer
in time horizon
Less
detailed and broader in scope.
�Operational
Strategy is
Narrower
in scope and in more detail
Prepared
by middle management.
Should
be in line with the Organization
strategy
�Operational
Strategy if
Designed
and implemented successfully can make an
organization more successful.
Organizations
started focusing on operational
strategies in early 1990s
before that
organizations
focused on financial and marketing
strategies.
Operational
strategies mostly function on
two dimensions of quality
management and
service/manufacturing
strategy.
An
operations Manager should avoid
SUBOPTIMIZATION meaning his
operational strategy for the
department
and divisions goals should not harm the
overall Organizational strategy. He
should opt for
systems
approach or a big picture approach or
strictly base his operations strategy on
Organizational
strategy.
Operations
Strategy for Service
Organizations
Service
Organizations in Pakistan function with a
very detailed and elaborative Operations
Strategy. It
is
important to identify the Strategy
Design Process and able to recognize the
concepts associated
with
Strategy
Formulation. Service Organizations are no
exceptions and work diligently to
identify, nurture
and
protect their distinctive
competencies. Service Organizations are
busy carrying out
detailed
environmental
scanning and also periodically
carryout SWOT
Analysis.
As
operations manager of a service based
organization, one should be able to
understand the
importance
of both Order qualifiers and
Order winners. Order
qualifiers
are
those significant characteristics
that service customers perceive as
minimum standards of
acceptability
to be considered as a potential purchase
while order winners
are
the characteristics of an organization's
services that cause it to be
perceived as better than
the
competitors
services. A bank offering 10 percent
return on customers' holdings would be an
order
qualifier
but if the same service has an
additional characteristic of some added
feature like
availability
of
interest free loans for purchase of
car or building of homes,
then the banks service becomes
order
winner.
Steps
in Developing a Manufacturing/Service
Strategy
1.
Segment the market according to the
product/Service group ( A person
interested in buying a sedan
car
would rarely show interest in buying an
SUV car, the market segmentation should
be just and
judicious)
2.
Identify product/Service requirements,
demand patterns, and profit margins of
each group ( Your
Market
research department should be able to
capture these with the help of MIS
systems)
3.
Determine order qualifiers
and winners for each
group ( Order Qualifiers
would meet customer
requirements
and Order Winners would
satisfy customers)
4.
Convert order winners into
specific performance requirements ( Continuous
improvement always
helps
and it is what the Japanese
has perfected through
KAIZEN)
15

Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Key
External Factors
1.
Economic
conditions should include
both Micro and Macro
Economics.
2.
Political
conditions require the organization to
carryout PEST analysis.
3.
Legal
environment relates to government
regulations for investor
protection.
4.
Technology
.Gap Analysis focusing
market leaders in the respective
field.
5.
Competition
so as to expect no free lunches or no
monopolies.
6.
Markets
are always free markets
till proven otherwise
Key
Internal Factors
1.
Human Resources include
Trained, skilled and qualified
employees.
2.
Facilities and equipment are a
good source for motivation,
and obtaining competitive
advantage
over
your competitors.
3.
Financial resources. A higher
Free cash flow makes a
company outperform its
competitors.
4.
Customers include repeat
customers, as well as customer
relationship Management.
5.
Products and services relates to
how does the organization values
itself whether it
provides
products
or services that add
value)
6.
Technology .Legacy Systems or
Technology that is competitive and
has the potential to
gain
competitive
advantage.
7.
Suppliers .Companies have taken care of
the supplier issue by making
use of effective
Supply
Chain
Management Strategies or use vertical or
horizontal integration techniques.
Strategic
Service Vision
Service
Concept includes
Service
Levels refer to the important
elements of the service to be provided,
usually stated in
terms
of results produced for
customers.
Perception
corresponds to the elements perceived by
the target market segment, by the
market
in
general, by employees, & by others. How do
customers perceive the service
concept.
Delivery
focuses on the efforts in terms of
the manner in which the service is
designed,
delivered,
marketed.
Strategic
Service
Vision
Operating
Strategy
Focus
Area includes important
elements of the strategy: operations,
financing, marketing,
organization,
human resources, control. Also the
central service area along
with the location of
investments
( human resource or Technology).
Central
Operations to control quality and
costs, improve measures,
incentives, rewards. The
expected
results should be evaluated in
terms of, quality of service,
cost profile,
productivity,
morale/loyalty
of servers.
Service
Delivery System
The
important features of the service
delivery system include role
of people, technology,
equipment,
layout,
procedures
The
capacity it has to provide at peak
levels
The
extent to which it should
help to insure quality standards,
differentiate the service from
competition,
provide barriers to entry by
competitors.
Relatively
Low (as compared to
manufacturing) Overall Entry
Barriers
Economies
of Scale Limited (not always
but most of the time)
High
Transportation Costs
Erratic
Sales Fluctuations
16
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
No
Power Dealing with Buyers or
Suppliers
Product
Substitutions for Service
High
Customer Loyalty
Exit
Barriers
Competitive
Service Strategies (Overall
Cost Leadership)
Seeking
Out Low-cost
Customers
Standardizing
a Custom Service
Reducing
the Personal Element in Service Delivery
(promote self-service)
Reducing
Network Costs (hub and
spoke)
Taking
Service Operations Off-line
Competitive
Service Strategies (Differentiation)
Making
the Intangible Tangible
(memorable)
Customizing
the Standard Product
Reducing
Perceived Risk
Giving
Attention to Personnel
Training
Controlling
Quality
Note:
Differentiation in service means being
unique in brand image, technology
use, features, or
reputation
for customer service.
Customer
Criteria for Selecting an
online Banking Service Provider in
Pakistan
We
can apply our concepts of
service to an online banking service
provider in Pakistan. We
investigate
the
service being provided by the bank by
checking for availability, convenience,
dependability,
personalization,
price, quality, reputation, safety
and speed. This should
help us understand the strength
of
service industry in a competitive
environment especially in our
country of Pakistan.
CHARACTERISTIC
REMARKS
Availability
24
hour ATM or online financial
transaction
Convenience
Site
location from any
internet equipped
computer
in and out of Pakistan
Dependability
On-time
performance and correct information
Personalization
Know
customer's name and ID
Price
The
fee a customer pays for
online service
Quality
Reflected
in service.
Reputation
Word-of-mouth
and audited and examined by
neutral
bodies.
Safety
Customers
online data is safe and
inaccessible
to
others and hackers
Speed
Avoid
excessive waiting in website loading
and
data
available online.
Online
banking service providers are
often checked for:
Anti-competitiveness
i.e. whether are not
allowing other online
banking service providers to
enter
the market by constructing barriers to
entry
Fairness
indicates the concept of Yield
management. Meaning whether the
bank is actually
providing
the same return as it had promised to the
customer
Invasion
of Privacy. Calling people
through telephones or visiting offices
thus making use of
Micro-marketing
concepts, which often makes
the patron and customer feel
that his privacy
has
been
compromised.
17
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Data
Security. Banks make it a point
that the financial records of the
customers are not
accessed
by
unauthorized personnel.
Reliability.
Banks always strive that
their service is reliable and considered
safe and usable by
its
customers. Most online
banking service providers allow
its customers to access
their account
statement,
free of cost.
Service
Purchase Decision
In
order to understand further we evaluate
the service organizations in terms of
Purchase Decision.
Service
Qualifier: To be
taken seriously a certain
level must be attained on the
competitive
dimension,
as defined by other market
players. Examples are cleanliness for a
fast food
restaurant
or safe aircraft for an
airline.
Service
Winner: The
competitive dimension used to make the
final choice among competitors.
Example
is price of airline ticket or
bus fare.
Service
Loser:
Failure to deliver at or above the expected
level for a competitive
dimension.
Examples
are failure to repair auto
(dependability), rude treatment (personalization) or
late
delivery
of package (speed).
Using
Information to Categorize Customers ( For
Call Centers in Pakistan)
Coding
grades customers on how
profitable their business
is.
Routing
is used by call centers to place
customers in different queues
based on customer
code.
Targeting
allows choice customers to have fees
waived and get other hidden
discounts.
Sharing
data about your transaction
history with other firms is
a source of revenue.
Quality
and Time Strategies
�Quality-based
strategies
Focuses
on maintaining or improving the quality
of an organization's products or
services
Quality
at the source
�Time-based
strategies
Focuses
on reduction of time needed to accomplish
tasks
Time
Based Strategies: Organizations have registered
reduction in time by employing
the
following
"6" time based strategies.
There are 6 time based
strategies namely:-
1.
Planning Time The time
required to react to a competitive
threat, or to adopt
new
technologies,
or to approve changes to an existing
facility
2.
Products/Service Design Time The
time needed to develop or
market new or redesigned products
or
services
3.
Processing Time The time
required to produce goods or services,
includes repairing
equipment,
quality
training, inventory
etc
4.
Changeover Time is the time needed to
change from producing one
type of product or service to
another.
New model, new insurance
/health service.
5.
Delivery Time is the time
needed to fill
orders.
6.
Response Time for complaints
is the required to improve the model or
service features according to
customer
inputs and improving employee
working conditions.
18
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Decision Making
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Strategy
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Service Delivery System
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Productivity
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:The Decision Process
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Demand Management
- Roadmap to the Lecture:Fundamental Types of Forecasts, Finer Classification of Forecasts
- Time Series Forecasts:Techniques for Averaging, Simple Moving Average Solution
- The formula for the moving average is:Exponential Smoothing Model, Common Nonlinear Trends
- The formula for the moving average is:Major factors in design strategy
- The formula for the moving average is:Standardization, Mass Customization
- The formula for the moving average is:DESIGN STRATEGIES
- The formula for the moving average is:Measuring Reliability, AVAILABILITY
- The formula for the moving average is:Learning Objectives, Capacity Planning
- The formula for the moving average is:Efficiency and Utilization, Evaluating Alternatives
- The formula for the moving average is:Evaluating Alternatives, Financial Analysis
- PROCESS SELECTION:Types of Operation, Intermittent Processing
- PROCESS SELECTION:Basic Layout Types, Advantages of Product Layout
- PROCESS SELECTION:Cellular Layouts, Facilities Layouts, Importance of Layout Decisions
- DESIGN OF WORK SYSTEMS:Job Design, Specialization, Methods Analysis
- LOCATION PLANNING AND ANALYSIS:MANAGING GLOBAL OPERATIONS, Regional Factors
- MANAGEMENT OF QUALITY:Dimensions of Quality, Examples of Service Quality
- SERVICE QUALITY:Moments of Truth, Perceived Service Quality, Service Gap Analysis
- TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT:Determinants of Quality, Responsibility for Quality
- TQM QUALITY:Six Sigma Team, PROCESS IMPROVEMENT
- QUALITY CONTROL & QUALITY ASSURANCE:INSPECTION, Control Chart
- ACCEPTANCE SAMPLING:CHOOSING A PLAN, CONSUMER’S AND PRODUCER’S RISK
- AGGREGATE PLANNING:Demand and Capacity Options
- AGGREGATE PLANNING:Aggregate Planning Relationships, Master Scheduling
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Objective of Inventory Control, Inventory Counting Systems
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:ABC Classification System, Cycle Counting
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Economic Production Quantity Assumptions
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Independent and Dependent Demand
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Capacity Planning, Manufacturing Resource Planning
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Organizational and Operational Strategies
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Operational Benefits, Kanban Formula
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Secondary Goals, Tiered Supplier Network
- SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT:Logistics, Distribution Requirements Planning
- SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT:Supply Chain Benefits and Drawbacks
- SCHEDULING:High-Volume Systems, Load Chart, Hungarian Method
- SEQUENCING:Assumptions to Priority Rules, Scheduling Service Operations
- PROJECT MANAGEMENT:Project Life Cycle, Work Breakdown Structure
- PROJECT MANAGEMENT:Computing Algorithm, Project Crashing, Risk Management
- Waiting Lines:Queuing Analysis, System Characteristics, Priority Model