 |
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Lesson
35
MRP
II/ ERP
Learning
Objectives
Discuss
benefits and requirements of MRP.
Explain
how an MRP system is useful
in Capacity Requirements
Benefits
and shortcomings of MRP
MRP
II and MRP.
MRP:
A Recap
1.
Material
Requirements Planning (MRP) is a
software focusing on production
planning and
inventory
control system used to
manage manufacturing
processes.
2.
An MRP system is intended to
simultaneously meet three
objectives:
1.
Ensure materials and products are
available for production and
delivery to customers.
2.
Maintain the lowest possible level of
inventory.
3.
Plan manufacturing activities,
delivery schedules and purchasing
activities.
MRP
Processing
1.
Gross requirements
a.
Total expected demand.
2.
Scheduled receipts
a.
Open orders scheduled to
arrive.
3.
Planned on hand
a.
Expected inventory on hand at the beginning of
each time period.
4.
Net requirements
a.
Actual amount needed in each
time period.
5.
Planned-order receipts
a.
Quantity expected to be received at the
beginning of the period.
b.
Offset by lead time.
6.
Planned-order releases
a.
Planned amount to order in each time
period.
Updating
the MRP Systems
1.
Regenerative system
a.
Updates MRP records
periodically.
2.
Net-change system
a.
Updates MPR records
continuously.
MRP
in Services
1.
Food catering service
2.
End item => catered
food
3.
Dependent demand => ingredients for
each recipe, i.e. bill of
materials
4.
Hotel renovation
5.
Activities and materials "exploded" into
component parts for cost
estimation and scheduling
6.
Benefits
of MRP
1.
Low levels of in-process
inventories
2.
Ability to track material
requirements
3.
Ability to evaluate capacity
requirements
4.
Means of allocating production
time
164

Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Requirements
of MRP
1.
Computer and necessary
software
2.
Accurate and up-to-date
3.
Master schedules
4.
Bills of materials
5.
Inventory records
6.
Integrity of data
MRP
II
1.
Expanded MRP with emphasis
placed on integration
2.
Financial planning
3.
Marketing
4.
Engineering
5.
Purchasing
6.
Manufacturing
Capacity
Planning
Capacity
requirements planning: The process of
determining short-range capacity
requirements.
Load
reports: Department or work center reports
that compare known and expected
future capacity
requirements
with projected capacity
availability.
Time
fences: Series of time
intervals during which order
changes are allowed or
restricted.
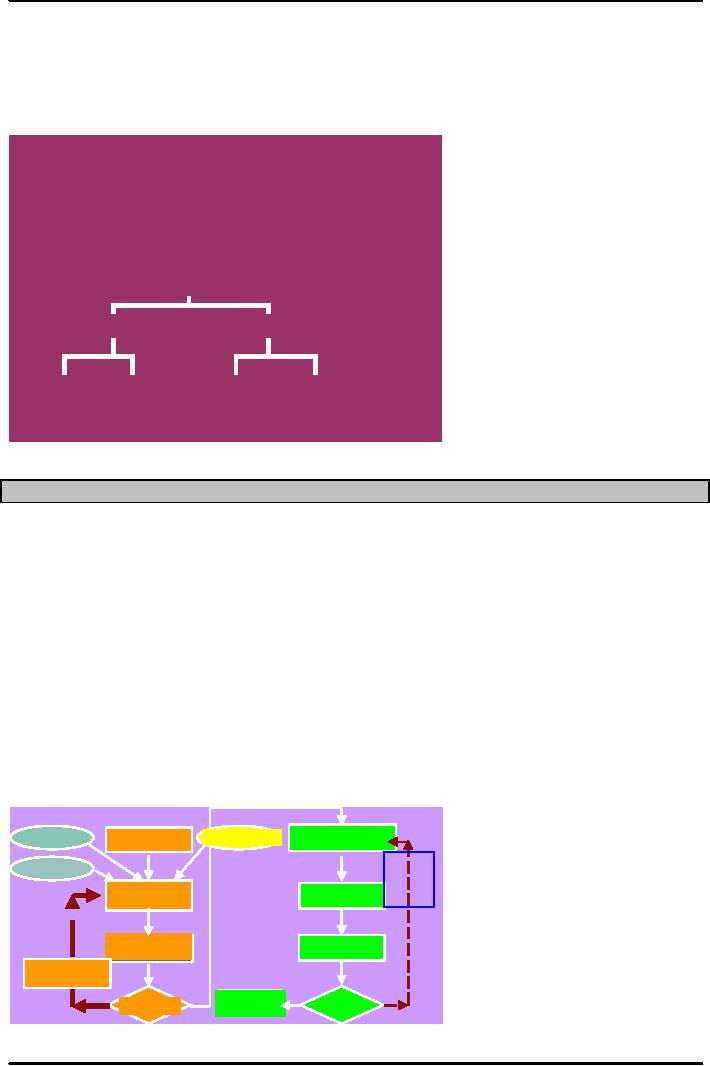
Develop
a tentative
Use
MRP to
master
production
simulate
material
schedule
requirements
Revise
tentative
Convert
material
master
production
requirements
to
schedule
resource
requirements
No
Can
Is
shop
capacity
be
No
capacity
changed
to meet
adequate?
requirements
Yes
Yes
Firm
up a portion
Change
of
the MPS
capacity
As
an operations manager we should be able
to identify the process of Capacity
Planning. Infact the
Capacity
requirements planning process determines short-range
capacity requirements. The
necessary
inputs
are:
1.
Planned order releases for
MRP
2.
The current shop
load
3.
Routing information
4.
Job times
Outputs
include load reports for
each work center.
Load
reports: Department or
work center reports that
compare known and expected future
capacity
requirements
with projected capacity
availability.
An
organization generates a Master Schedule
in terms of what is needed and
not in terms of what
is
possible
or available.
An
over view of the capacity
planning process includes the
following.
1.
The Master schedule is first
tested for feasibility and
possibly adjusted before it
becomes
permanent.
2.
The proposed schedule is processed
using MRP to ascertain the materials
requirements the
schedule
would generate.
165
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
3.
These are then translated
into capacity requirements in the form of
load reports for each
departments
or work centers.
The
initial schedule may or may
not be feasible given the
limits of production or availability
of
materials.
Also, with the aid of Time
fences ( the series of time
intervals during which order
changes are
allowed
or restricted) a feasible schedule may be
finalized.
A
listing of all raw materials, parts,
subassemblies,
and assemblies needed to
produce
one unit
P
d
T
f
I
evel X
L
X
0
B(2)
C
1
2
D(3)
E
E(2)
F(2)
MRP
II
Manufacturing
Resource Planning (MRP
II) is
defined and accepted by professionals as
a method for
the
effective planning of all
resources of a manufacturing
company.
Ideally,
it should answer operational
planning in units, financial
planning in rupees, and has
a simulation
capability
to answer "what-if" questions. and
extension of closed-loop
MRP.
This
is not exclusively a software
function, but a merger of people
skills, dedication to data
base
accuracy,
and computer resources. It is a total
company management concept for
using human resources
more
productively.
Accounting
and finance departments get accurate
costs and predict cash
flows. Operations and
Engineering
departments audit and feed in
accurate data on production
methods in detail, such
as:
1.
Bill of Materials
2.
Quality Control based
operational and functional data.
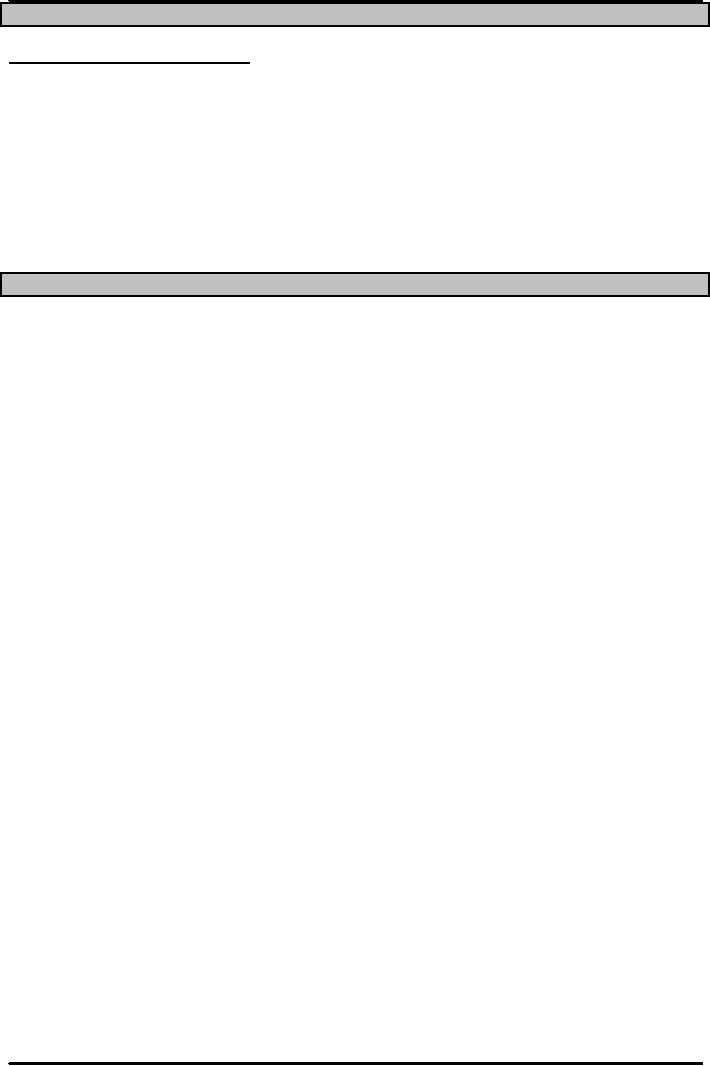
Master
Market
Manufacturin
Financ
Production
schedule
Deman
Adjust
Marketin
master
schedule
Productio
MR
n
Rough-cut
Capacit
capacity
planning
y
Adjust
production
N
Ye
Requirements
N
Ye
Problems
Problems
schedules
166
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
ERP
Enterprise
resource planning (ERP):
often called the rightful
next step in an evolution
that began with
MPR
and evolved into MRPII.
Integration of financial, manufacturing,
and human resources on a single
computer
system.
ERP
Strategy Considerations
1.
High
initial cost
2.
High
cost to maintain
3.
Future
upgrades
4.
Training
Summary
Materials
Requirements Planning (MRP) is an
information Systems used to
handle ordering of
dependent
demand items ( components of assembled
products)
The
planning process begins with
customer orders, which are
used along with any back
orders
to
develop a Master Schedule that indicates
timing and quantity of finished
goods.
The
end items are exploded using the
bill of materials; Material
Requirement Plans are
developed
show quantity and timing for
ordering or producing
components.
The
main features of MRP are the
time phasing of requirements, calculating
component
requirements
and planned order
releases.
To
be successful MRP requires a computer
program and accurate master
production schedules,
bills
of materials and inventory data.
Firms
can only implement MRP if
they have accurate
records
MRP
II links business planning,
production planning and the
MPS. ERP's are more refined
as
well
as comprehensive versions of MRP.
167
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Decision Making
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Strategy
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Service Delivery System
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Productivity
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:The Decision Process
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Demand Management
- Roadmap to the Lecture:Fundamental Types of Forecasts, Finer Classification of Forecasts
- Time Series Forecasts:Techniques for Averaging, Simple Moving Average Solution
- The formula for the moving average is:Exponential Smoothing Model, Common Nonlinear Trends
- The formula for the moving average is:Major factors in design strategy
- The formula for the moving average is:Standardization, Mass Customization
- The formula for the moving average is:DESIGN STRATEGIES
- The formula for the moving average is:Measuring Reliability, AVAILABILITY
- The formula for the moving average is:Learning Objectives, Capacity Planning
- The formula for the moving average is:Efficiency and Utilization, Evaluating Alternatives
- The formula for the moving average is:Evaluating Alternatives, Financial Analysis
- PROCESS SELECTION:Types of Operation, Intermittent Processing
- PROCESS SELECTION:Basic Layout Types, Advantages of Product Layout
- PROCESS SELECTION:Cellular Layouts, Facilities Layouts, Importance of Layout Decisions
- DESIGN OF WORK SYSTEMS:Job Design, Specialization, Methods Analysis
- LOCATION PLANNING AND ANALYSIS:MANAGING GLOBAL OPERATIONS, Regional Factors
- MANAGEMENT OF QUALITY:Dimensions of Quality, Examples of Service Quality
- SERVICE QUALITY:Moments of Truth, Perceived Service Quality, Service Gap Analysis
- TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT:Determinants of Quality, Responsibility for Quality
- TQM QUALITY:Six Sigma Team, PROCESS IMPROVEMENT
- QUALITY CONTROL & QUALITY ASSURANCE:INSPECTION, Control Chart
- ACCEPTANCE SAMPLING:CHOOSING A PLAN, CONSUMER’S AND PRODUCER’S RISK
- AGGREGATE PLANNING:Demand and Capacity Options
- AGGREGATE PLANNING:Aggregate Planning Relationships, Master Scheduling
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Objective of Inventory Control, Inventory Counting Systems
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:ABC Classification System, Cycle Counting
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Economic Production Quantity Assumptions
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Independent and Dependent Demand
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Capacity Planning, Manufacturing Resource Planning
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Organizational and Operational Strategies
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Operational Benefits, Kanban Formula
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Secondary Goals, Tiered Supplier Network
- SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT:Logistics, Distribution Requirements Planning
- SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT:Supply Chain Benefits and Drawbacks
- SCHEDULING:High-Volume Systems, Load Chart, Hungarian Method
- SEQUENCING:Assumptions to Priority Rules, Scheduling Service Operations
- PROJECT MANAGEMENT:Project Life Cycle, Work Breakdown Structure
- PROJECT MANAGEMENT:Computing Algorithm, Project Crashing, Risk Management
- Waiting Lines:Queuing Analysis, System Characteristics, Priority Model