 |
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Lesson
03
Meanings
of Competitiveness, Strategy and
Productivity
We
are already familiar with
these three terms, for the
sake of easy reference, let us
revisit their
definitions
1.
Competitiveness
refers to an
aggressive willingness to
compete
2.
Strategy is an elaborate
and systematic plan of action
with defined resources
and
3.
Productivity
refers to the
ratio of the quantity and quality of
units produced to the labor per
unit
of time or simply ratio of
output to input
How
Organization
Compete
against
each
other
Businesses
since the beginning of time have
competed against each other. On the
basis of competition,
various
types of market exist for
nearly all lines of products and
services. We already know
that
absolute
monopoly and perfect competition
type of markets are not
that pervasive, yet
businesses try to
avoid
perfect competition and strive to go
for absolute monopoly so they
can enjoy no competition
and
exploit
the customer sentiments for
buying. We can identify the
following common and widespread
ways
in which organizations can
compete against other
organizations.
1.
Price: In our day to day
routine observations, we often see
that a lower price would
attract more
customers
provided the product or service fulfils
its intended use. Lower
price helps an
organization
to increase its customer
base.
2.
Quality is an important dimension by
which superior raw materials as
well as high Skillman
ship
would ensure that product
manufactured or service developed is offered to the
customer
with
something extra. That something extra is
nothing else but Quality.
Quality is always
offered
free of cost, we will
discuss this when we study
in details Quality Management
and
Total
Quality Management.
3.
Product Differentiation refers to special features
that make the product or service
look more
suitable
to the customers like an automobile
manufacturer decides to provide GPS
system to
selected
customer at an additional price
etc.
4.
Flexibility is the ability to respond to
changes. It may refer to
changes in target sales,
product
feature
like adding GPS device to
all automobiles
5.
Time refers to the period required to
provide a product or service to a
customer from the
moment
the order is booked to the delivery,
also time required to
rectify a shortcoming or
mistake
A.
Competitiveness
Competitiveness
is how effectively an organization
meets the needs and requirements of
customers
relative
to other (Competitors) organizations
that offer similar goods or
services
The
key to successfully competing against the
organizations competitors or rivals is to
answer these two
questions
diligently
I.
What do the Customers
Want?
II.
How can our business
deliver the required Value to the
customers?
The
first question begets a
natural and logical answer
which is that the customers
want Value. Similarly
the
second question also asks
for a logical answer which
is the way organizations would
deliver value to
the
customer as per the understanding of the
organization. If an organization can
understand that Value
is
always the tradeoff between performance and
cost then it can adopt
various means to provide
value to
the
customer.
9
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
Mathematically
speaking value equals the performance
(of the product or service) divided by
cost.
Most
organizations have different measurement
rules attached in measurement of quality,
speed and
flexibility.
Value=
Performance/Cost= (Quality +Speed+
Flexibility)/Cost_______ Eq. 1
The
equation above also captures the
product differentiation concept, which in
reality is an important
dimension
of quality. The concept of
quality would be covered at a later
stage, towards the middle of the
semester.
We
can also say that, the
customer is measuring performance with the
help of Quality, Speed
and
Flexibility
for the price or cost he is
willing to pay.
The
point worth noting is that
in most of the cases the three factors of performance
would not be
weighed
equally in some cases,
quality would be more important
than speed or flexibility
etc. We can
thus
make use of an important
concept of assigning weights so the
equation changes to
Value=
(w1 x Quality + w2 x Speed+ w3 X
Flexibility) / Cost_______Eq.2
Where
w1, w2 and w 3 are different
weights and if they all have
same value then equation 2
reduces to
equation
1 again. IN other words, equation 2 is
not only generic but more
reflective of performance
measurement
of an organization.
Different
organizations assign different
means to obtain the value of
these weights by developing
in-
house
or a consultant derived Performance Measurement Model
(PMM). This can be used to
obtain an
overall
performance score by measuring the success of a
manufacturing company in its
operational
activities.
The developed PMM measures a
company's level of performance in
critical dimensions and
combines
these performance scores to obtain a
ranking score. A set of
critical dimensions and their
sub-
components
is fully defined, and performance
scorecards are developed to
guide the assignment of
performance
scores. Performance scores are
assigned according to the level of
intensity of a
manufacturing
company's investments, practices, actions or
infrastructures in the critical dimensions.
How
Organizations can gain Competitive
Advantage
As
Students of Organization Management, we
can look at value in terms
of the three important
functions
of any organization to see
how organizations can gain
competitive advantage
1.
Marketing
2.
Finance
3.
Operations
A.
Businesses Gain Competitive Advantage by
using Market based
strategies
1.
Identifying consumer wants
and needs
2.
Pricing
3.
Advertising and promotion
B.
Businesses Gain Competitive Advantage by
using Finance based
strategies
1.
Identifying
sources of funds and applications of
funds.
2.
Capital
and Financial Investments.
3.
Financial
Leverage ( Debt to Equity)
and
4.
Capital
structure.
10

Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
C.
Businesses Gain Competitive Advantage by
using Operations based
strategies
1.
Product and service design. The design is not
only the starting point but
allows certain
features
to
be added which makes your
product or service favorable to the
customer.
2.
Cost or Cost Leadership,
offers the product or service at an
economical price
3.
Location refers to the Convenient
point of sales, it can be a
petrol pump (services) with
an
attached
convenience store
4.
Quality should always match
the price and service.
5.
Quick response aka Also
known as Agility and an organization on
this basis is often known
as
Agile
Organization)
6.
Flexibility. Flexibility change the
car model from sedan to
coupe based on your
marketing
divisions
inputs.
7.
Inventory management. Maintain safety
stocks and critical
spares.
8.
Supply chain management.
Develop and sustain an active and strong
chain between suppliers
and
end customers.
9.
Service .After sales service, owning the
customers issue as your own,
a concept which has
failed
PK in its quest for foreign
market penetration.
Throughout
the semester our aim would
be to identify and understand different
types of strategies
which
have been exploited to the fullest by
various organizations and adopted
religiously as their
actual
Operational strategies companies.
This has helped these
organizations to gain
competitive
advantage
over their counterparts.
Common
Reasons why Organizations
Fail
We
can identify certain
familiar reasons why
Organizations fail to achieve a
competitive advantage and
end
up loosing out to their competitors.
These reasons are universal
in nature and find the same
footing
in
Pakistan as well as any other place in
the world.
1.
Too much emphasis on short-term
financial performance. Quite often,
cost cutting, profit
maximizing
at the cost of social responsibility or
employee motivation is a failed
strategy
pursued
by organizations, which just
hastens their status to
oblivion.
2.
Failing to take advantage of strengths
and opportunities. This is in reality
failing to hold on
to
proven successful strategies or
core competencies. Sometimes a
change in leadership
leads
to change in strategy, where just
for the sake of glory and
high profits,
organizations
forget
their core competence and
opt for strategies and
tactic which cause their
downfall.
3.
Failing to recognize competitive threats.
This reason is the exact opposite of
failure to make
use
of the organizations strengths. Quite
often organizations decide to pursue
status quo and
ends
up bringing no new product or service or
even no innovation in its existing
product or
service
line leading to lack of
customer satisfaction, decline in
profits and finally
being
declared
a failure.
4.
Neglecting operations strategy. This is
definitely the most important
reason of failure;
organizations
often end up employing non
productive techniques which lead to
inconsistent
and
failed operations. Absence of an Operations Strategy
leads to
5.
Too much emphasis in product
and service design and not enough on
improvement.
Differentiation
in terms of service and product, American
companies in 1980s did that
they
never
introduced incremental refinements rather
went for big changes and
thus lost to
Japanese
competitors.
6.
Neglecting investments in capital and human
resources. A total disregard to use the
best
resource.
Capital and human resources in the long
run make or break an
organization.
7.
Failing to establish good internal
communications. Matrix organizations or
hierarchy or
such
a strong structure that often the structure
does not allow
communication.
11
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
8.
Failing
to consider customer wants and needs.
This is actually indicative of
an
organizations
lack of marketing research
skills. This also shows
that there is no respect to
Customer
Relationship Management Concept and
certainly no respect to the
customer.
Mission/Strategy/Tactics
Most
of the organizations tend to answer the
question that how does
mission, strategies and tactics
relate
to
their decision making and
attaining distinctive competencies?
Organizations over the years
have
mastered
the art and technique of developing a
vision and a mission statement, which
helps them to
come
with functional strategies and
practical tactics by which
they can make judicious
decisions and
attain
distinctive competencies
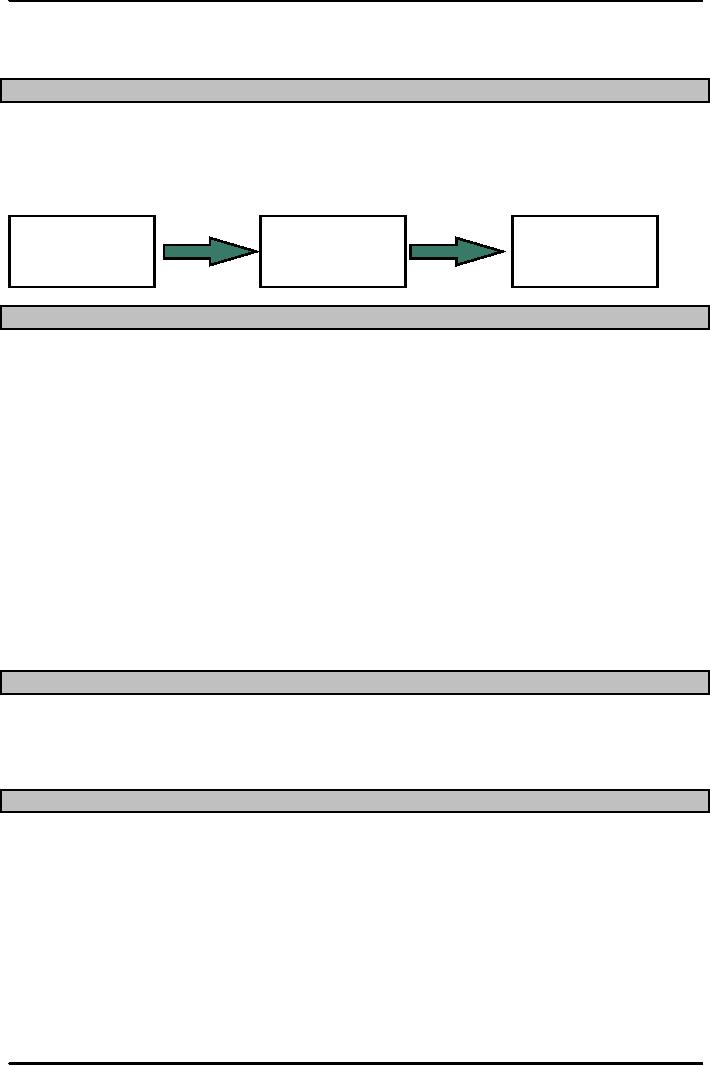
Mission
Strategy
Tactics
2.
Strategy
1.
Strategies are Plans for
achieving organizational goals
Mission
is the reason for existence for an
organization
Mission
Statement answers the question
"What business are we
in?"
Goals
provide detail and scope of
mission
Tactics
are the methods and actions
taken to accomplish strategies
2.
Concept of Strategy for a Pakistani
Automobile manufacturer
Strategies
are plans for achieving
organizational goals
Mission
is to provide BEST AUTOMOBILES to
individuals as well as
BUSINESS
organizations
of Pakistan
Mission
Statement is to give you
safe wheels to move
around"
Goals
are to provide utility, and
heavy equipment
mobiles.
Tactics
consist of employing TQM methods to
accomplish strategies
Planning
and Decision
Making
Planning
and decision making concepts
make use of setting a mission, goal,
strategy and achieving the
end
result through some
effective and practical tactic. In
hierarchical order the organization
first makes
or
develops a mission and employ tactics by
developing operational
procedures.
Strategy
Example
You
are a business student at Virtual
University of Pakistan. You
would like to have a career
in
business,
have a good job, and
earn enough income to live
comfortably
12
Production
and Operations Management
MGT613
VU
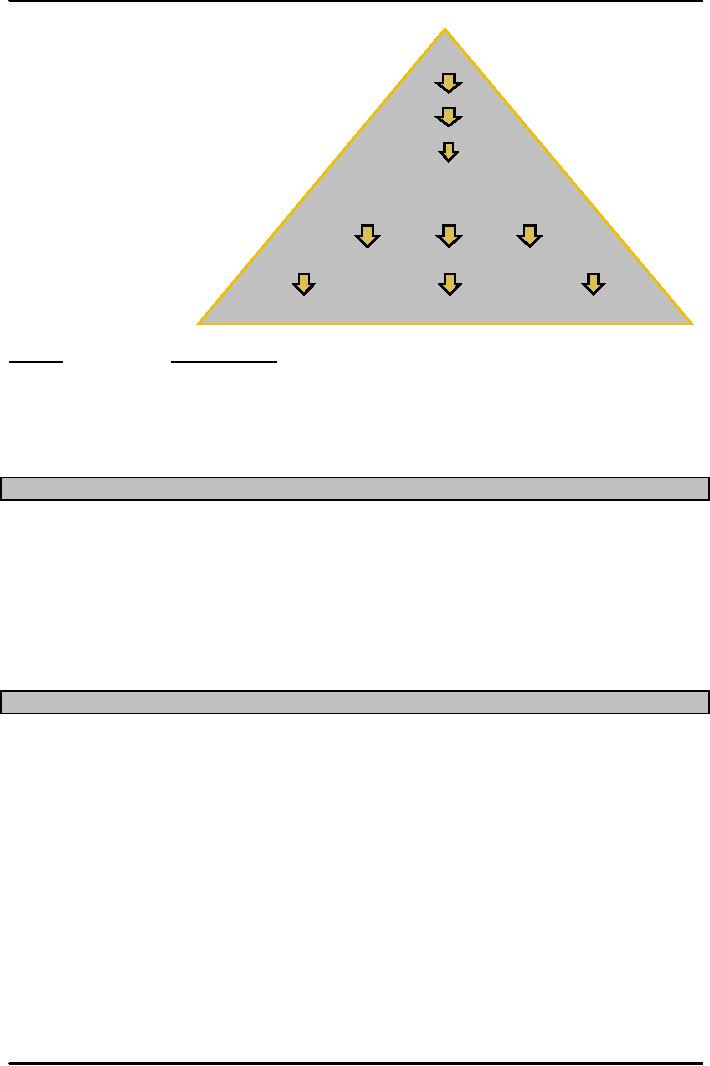
Mission
Goals
Organizational
Strategies
Functional
Goals
Finance
Operations
Marketing
Strategies
Strategies
Strategies
Tactics
Tactics
Tactics
Operating
Operating
Operating
procedures
procedures
procedures
Mission:
Live
a good life
�Goal:
Successful
career, good income
�Strategy:
Obtain
a Business Degree from VU.
�Tactics:
Select
a business field of your interest and
high market value
�Operations:
Register,
buy books, take
courses
study,
graduate, apply & get job
Examples
of Strategies
1.
Low
cost ( Cost Leadership/Economical
)
2.
Scale-based
strategies ( Critical
Value)
3.
Specialization
( Specific characteristics)
4.
Flexible
operations ( To change production design of products
on the same infrastructure)
5.
High
quality ( exceeds customer requirements
and satisfactions)
6.
Service
( meets minimum standard
specifications)
Distinctive
Competencies
The
special attributes or abilities that
give an organization a competitive
edge.
1.
Price
2.
Quality
3.
Time
4.
Flexibility
5.
Service
6.
Location
13
Table of Contents:
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Decision Making
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Strategy
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Service Delivery System
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Productivity
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:The Decision Process
- INTRODUCTION TO PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT:Demand Management
- Roadmap to the Lecture:Fundamental Types of Forecasts, Finer Classification of Forecasts
- Time Series Forecasts:Techniques for Averaging, Simple Moving Average Solution
- The formula for the moving average is:Exponential Smoothing Model, Common Nonlinear Trends
- The formula for the moving average is:Major factors in design strategy
- The formula for the moving average is:Standardization, Mass Customization
- The formula for the moving average is:DESIGN STRATEGIES
- The formula for the moving average is:Measuring Reliability, AVAILABILITY
- The formula for the moving average is:Learning Objectives, Capacity Planning
- The formula for the moving average is:Efficiency and Utilization, Evaluating Alternatives
- The formula for the moving average is:Evaluating Alternatives, Financial Analysis
- PROCESS SELECTION:Types of Operation, Intermittent Processing
- PROCESS SELECTION:Basic Layout Types, Advantages of Product Layout
- PROCESS SELECTION:Cellular Layouts, Facilities Layouts, Importance of Layout Decisions
- DESIGN OF WORK SYSTEMS:Job Design, Specialization, Methods Analysis
- LOCATION PLANNING AND ANALYSIS:MANAGING GLOBAL OPERATIONS, Regional Factors
- MANAGEMENT OF QUALITY:Dimensions of Quality, Examples of Service Quality
- SERVICE QUALITY:Moments of Truth, Perceived Service Quality, Service Gap Analysis
- TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT:Determinants of Quality, Responsibility for Quality
- TQM QUALITY:Six Sigma Team, PROCESS IMPROVEMENT
- QUALITY CONTROL & QUALITY ASSURANCE:INSPECTION, Control Chart
- ACCEPTANCE SAMPLING:CHOOSING A PLAN, CONSUMER’S AND PRODUCER’S RISK
- AGGREGATE PLANNING:Demand and Capacity Options
- AGGREGATE PLANNING:Aggregate Planning Relationships, Master Scheduling
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Objective of Inventory Control, Inventory Counting Systems
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:ABC Classification System, Cycle Counting
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Economic Production Quantity Assumptions
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Independent and Dependent Demand
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT:Capacity Planning, Manufacturing Resource Planning
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Organizational and Operational Strategies
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Operational Benefits, Kanban Formula
- JUST IN TIME PRODUCTION SYSTEMS:Secondary Goals, Tiered Supplier Network
- SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT:Logistics, Distribution Requirements Planning
- SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT:Supply Chain Benefits and Drawbacks
- SCHEDULING:High-Volume Systems, Load Chart, Hungarian Method
- SEQUENCING:Assumptions to Priority Rules, Scheduling Service Operations
- PROJECT MANAGEMENT:Project Life Cycle, Work Breakdown Structure
- PROJECT MANAGEMENT:Computing Algorithm, Project Crashing, Risk Management
- Waiting Lines:Queuing Analysis, System Characteristics, Priority Model